Geography ✿ Distinctive landscapes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Landscape
an area of land with both physical features and human features
Where are upland areas usually found?
north and west of the UK
Where are lowland areas usually found?
south and west of the UK
Where are glaciated areas usually found?
north-west of the UK
state 4 characteristics of upland areas
formed of harder rocks (slate, granite, limestone)
climate is usually cool and wet
thin soils due to harsh climate
land used for farming and tourism
state 4 characteristics of lowland areas
formed of softer rocks (chalk, clay, sandstone)
climate is warm and dry
fertile soils
land used for industries and farming
state 4 characteristics of glaciated areas
ice causes erosion of the landscape causing valleys
ice also melts which deposits material
mountainous areas
steep slopes
weathering
break down or dissolving of rocks
erosion
transportation of rocks or minerals
biological weathering
the breakdown of rock caused by the movement of animals and plants
chemical weathering
the breakdown of rock by changing it’s chemical composition
mechanical weathering
process of physical changes such as wind, temperature and waves which breakdown rock
3 upper course landforms
v shaped valley
waterfalls
gorges
3 middle course landforms
wide valleys
meanders
ox-bow lakes
3 lower course landforms
ox-bow lakes
flood plains
levees
flood plain
flat land next to a river, material is deposited here when a river is flooded
hard engineering
using artificial structures to control nature
soft engineering
working with natural coastal processes

solution (erosion)
dissolved carbon dioxide making waters acidic, the acid reacts with rocks
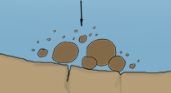
abrasion
when rocks scrape against the seabed, removing small pieces

attrition
rocks smashing into each other, breaking them into smaller fragments
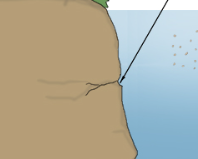
hydraulic action
the force of water crashing into headlands/ river banks
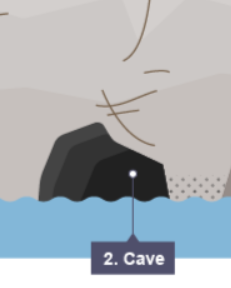
how are caves formed?
waves crash into the headlands, forming cracks by hydraulic action
repeated erosion causes the cracks to open, forming a cave
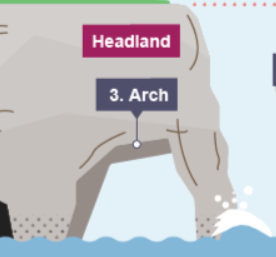
how are arcs formed?
a cave becomes larger and eventually breaks through the headland
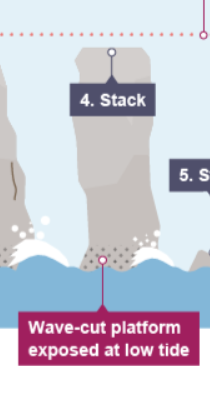
how are stacks formed?
the base of an arch becomes wider through further erosion, the roof becomes too heavy and collapses
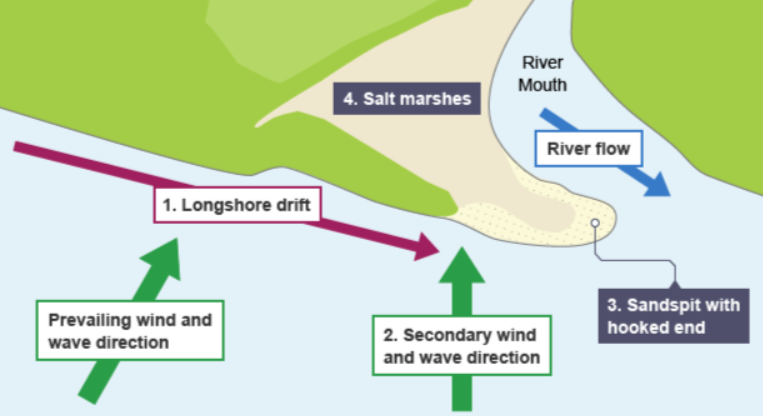
how are spits formed?
sediment is carried by longshore drift
a change in wind direction causes a hooked end
![<p>How are <strong>v shaped valleys</strong> formed? [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2148da03-44ca-4131-b722-e2de63c3eaca.jpg)
How are v shaped valleys formed? [3]
a river that flows through a mountain is eroded vertically
overtime this deepens the river bed, creating a deep v shape valley
mass movement and weathering on valley sides causes lose material to fall which the river carries down stream, deepening its shape
how is a river levee formed? [3]
a river is flooded and spreads out on the floodplain
as water overflows, heavy sediment is deposited closest to banks
this repeats overtime which creates build up of sediment, creating raised embankments
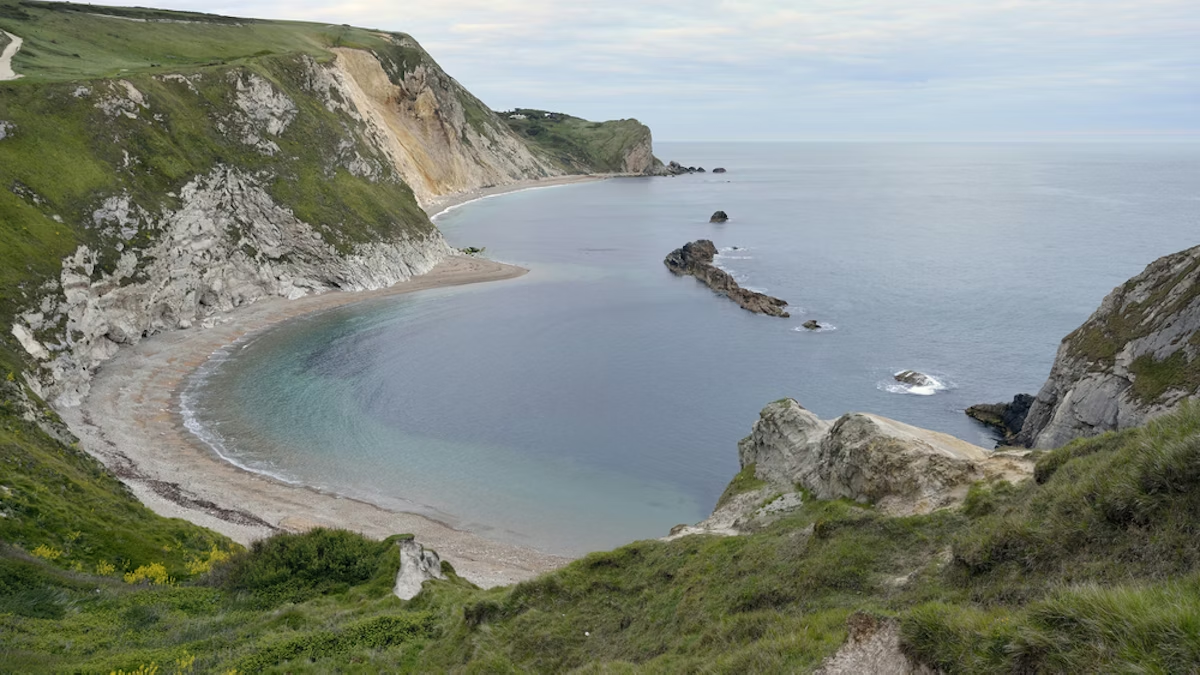

how are headlands and bays formed?
erosion occurs at more harder rocks which erodes slower than the softer rock
as the soft rock is eroded away quicker it creates a bay leaving the harder rock sticking out into the sea as headlands
describe the 2 types of waves
constructive and destructive
deposition
when material is being carried by the water (in rivers or seas) and dropped off
describe the 2 types of mass movement
slumps → material shifts with a rotation
slides → material shifts in a line
mass movement
the shifting of rocks and loose material down a slope
traction
rocks are pushed along the river seabed by force of the water
saltation
rocks being bounced along the seabed
suspension
rocks like silt and clay are carried along by water
solution (transportation)
soluble material dissolved in the water are carried along
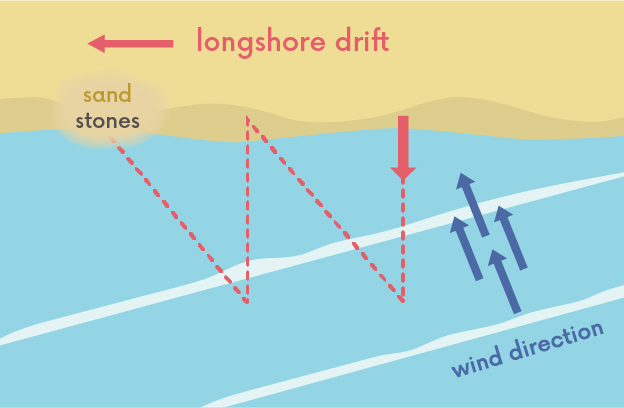
what happens during longshore drift?
waves hit the coast at an angle
swash carries sediment up the beach at an angle
backwash carries sediment down the beach at right angles
which creates a zig-zag movement of sediment along the beach
Explain why the south and east of England lack glaciated landscapes
there are warmer latitudes, so the ice would melt
Suggest two reasons for variations in the of a river
erosion such as attrition
upper course or lower course
How are ox-bow lakes formed? [3]
erosion in a meander causes outside bends to move closer by hydraulic action
the river breaks through and the river flows along the shortest route while depositing material
deposition then cuts off the meander over time
How are meanders formed? [3]
the river flows fastest on the outside bend, causing erosion by hydraulic action
the river flows slowest on the inside bend so material is deposited there
over time, erosion and deposition bend the river even more
How are gorges formed? [4]
the soft rock is eroded quicker than the hard rock which creates a gap
the hard rock is undercut, abrasion and hydraulic action erode to create a plunge pool
over time this gets bigger, and the hard rock collapses
this repeats and the waterfall retreats upstream, leaving a gorge
natural landscape
an area of land which has more physical features
built landscape
an area of land which has more human features
give 3 characteristics of constructive waves
low waves
deposits more material and erode
powerful swash which carries sediment but weak backwash that causes deposition
give 3 characteristics of destructive waves
steep waves
erodes coastlines
weak swash but powerful backwash which erodes sediment