Chapter 10- Bony Thorax (Sternum and Ribs)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
name the 2 major functions of the bony thorax
1. expansion and contraction for respiration
2. protection of respiratory organs and vital structures within the mediastinum
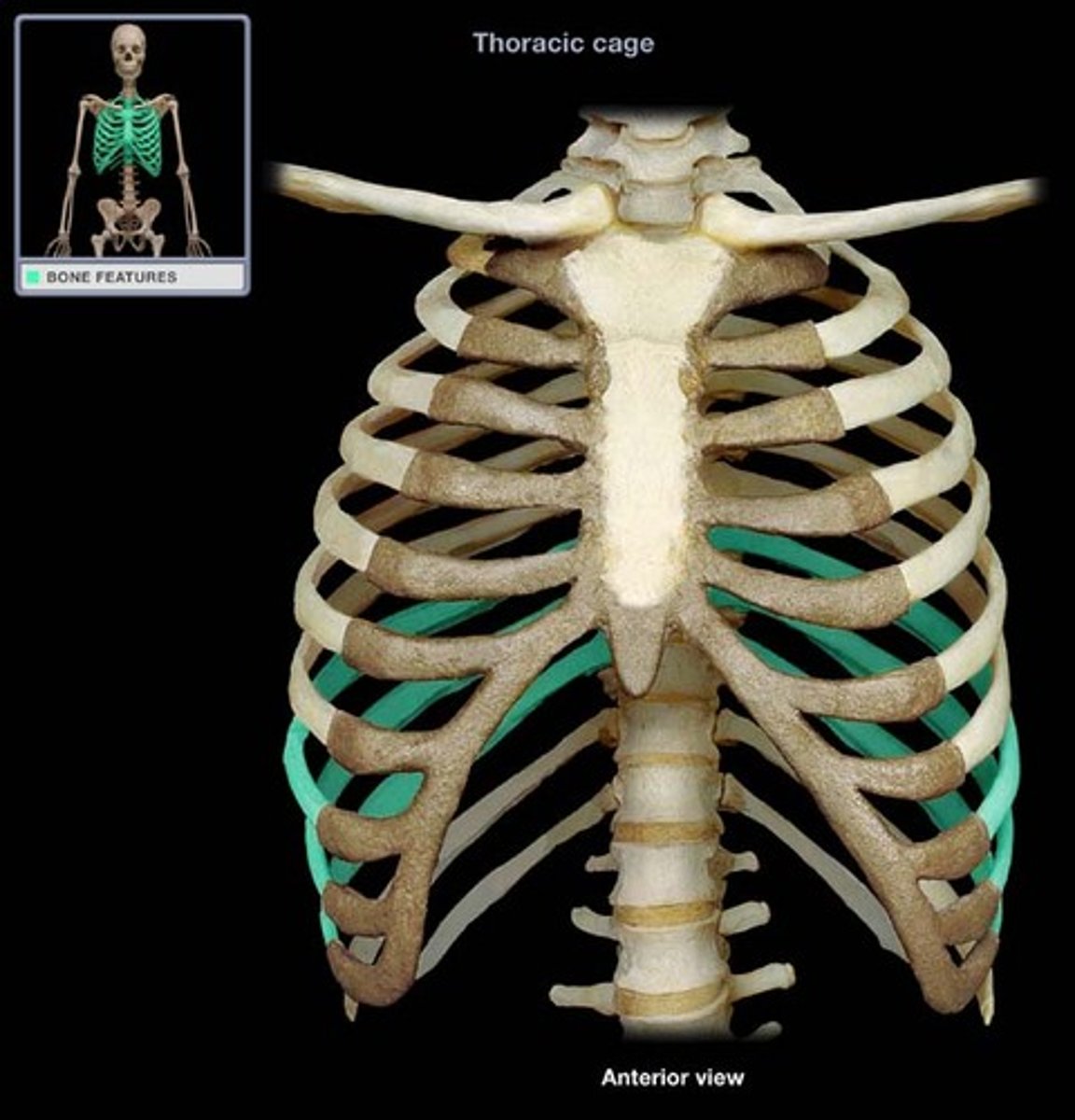
the bony thorax consists of the ____________ anteriorly, the ____________ ____________ posteriorly and the _____ pairs of ribs
sternum, thoracic vertebra, 12 pairs of ribs
the widest and most superior portion of the sternum is the _______________
manubrium
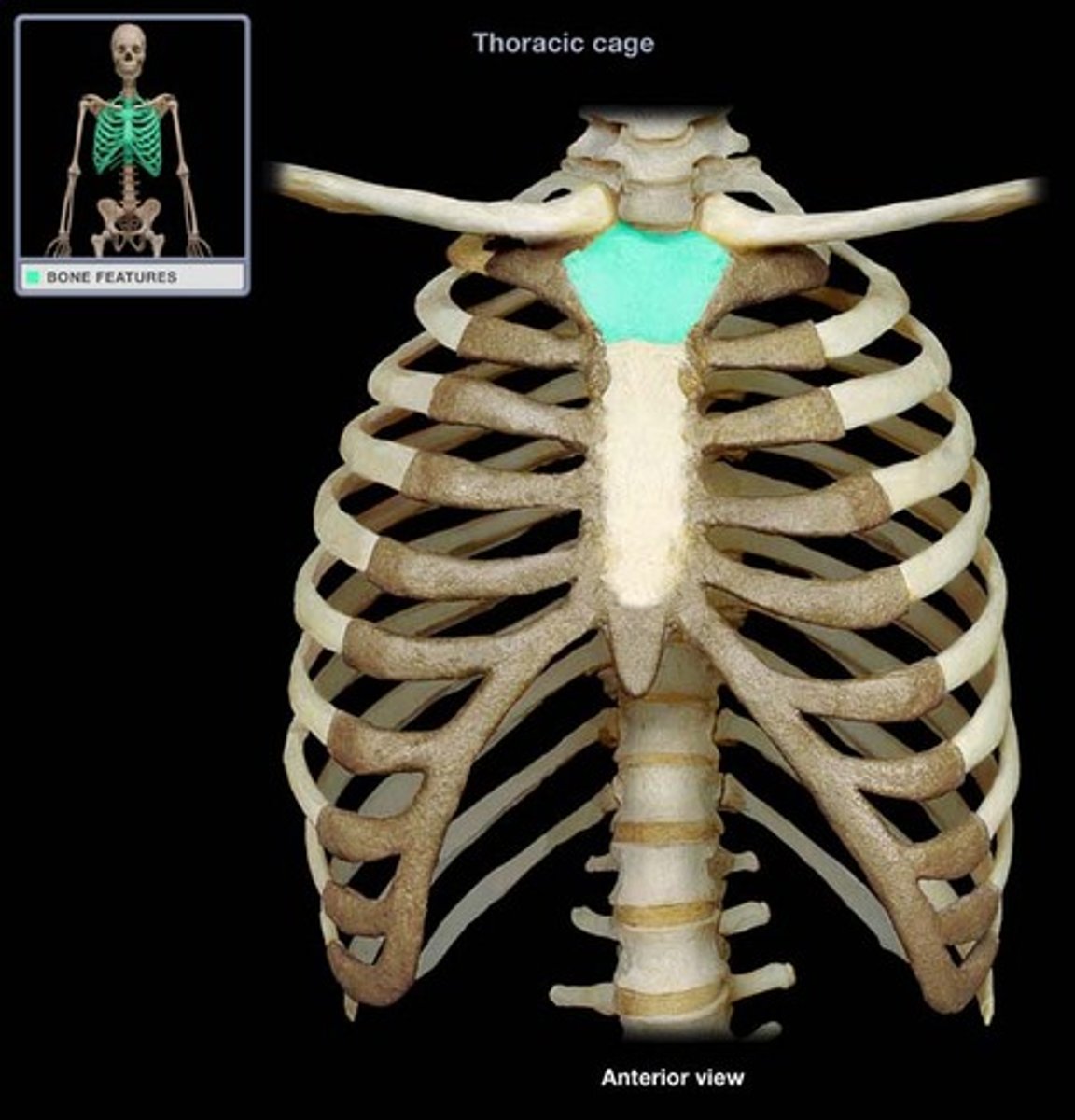
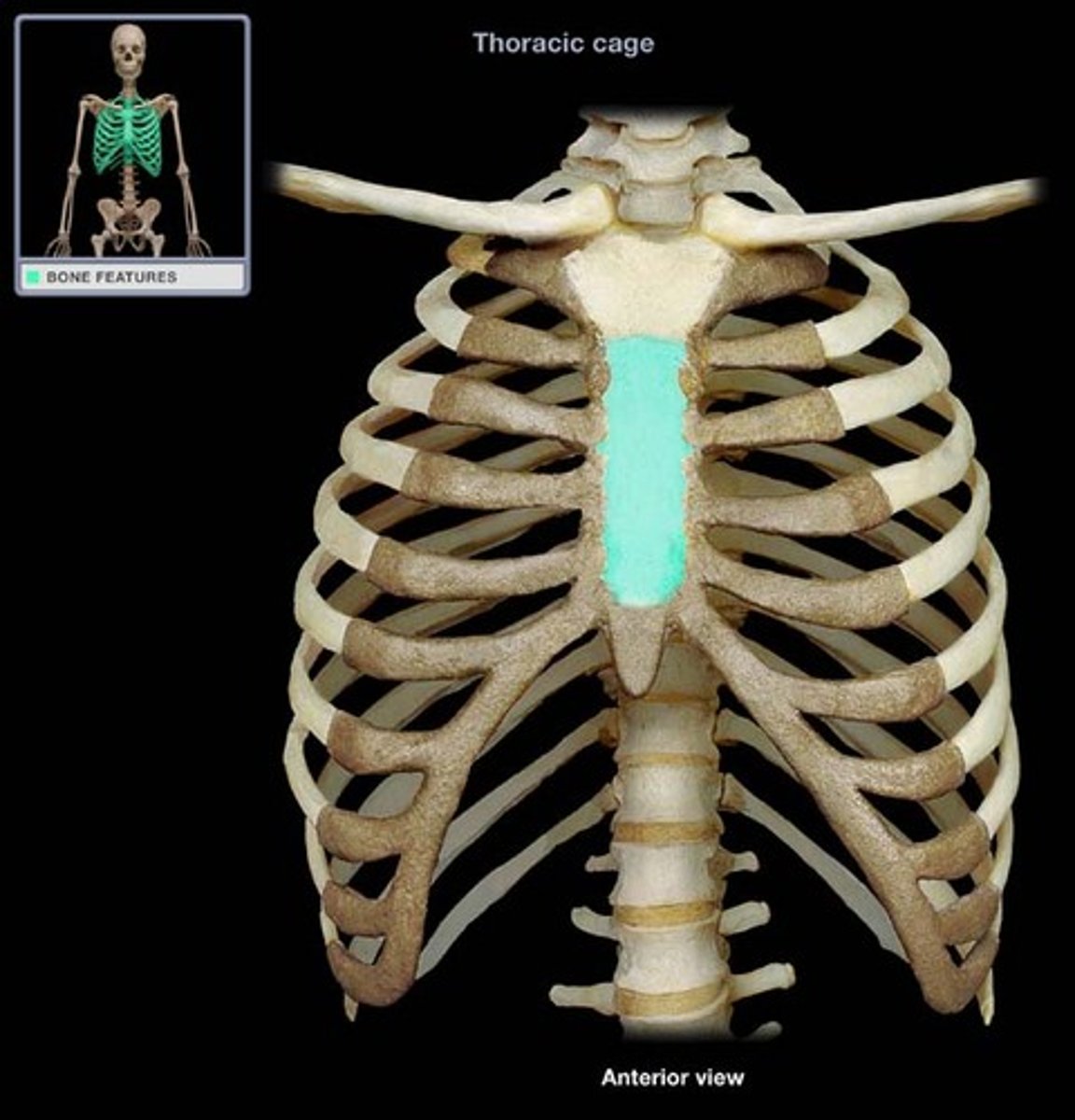
the middle and longest portion of the sternum is the __________, which projects anteriorly and inferiorly
body
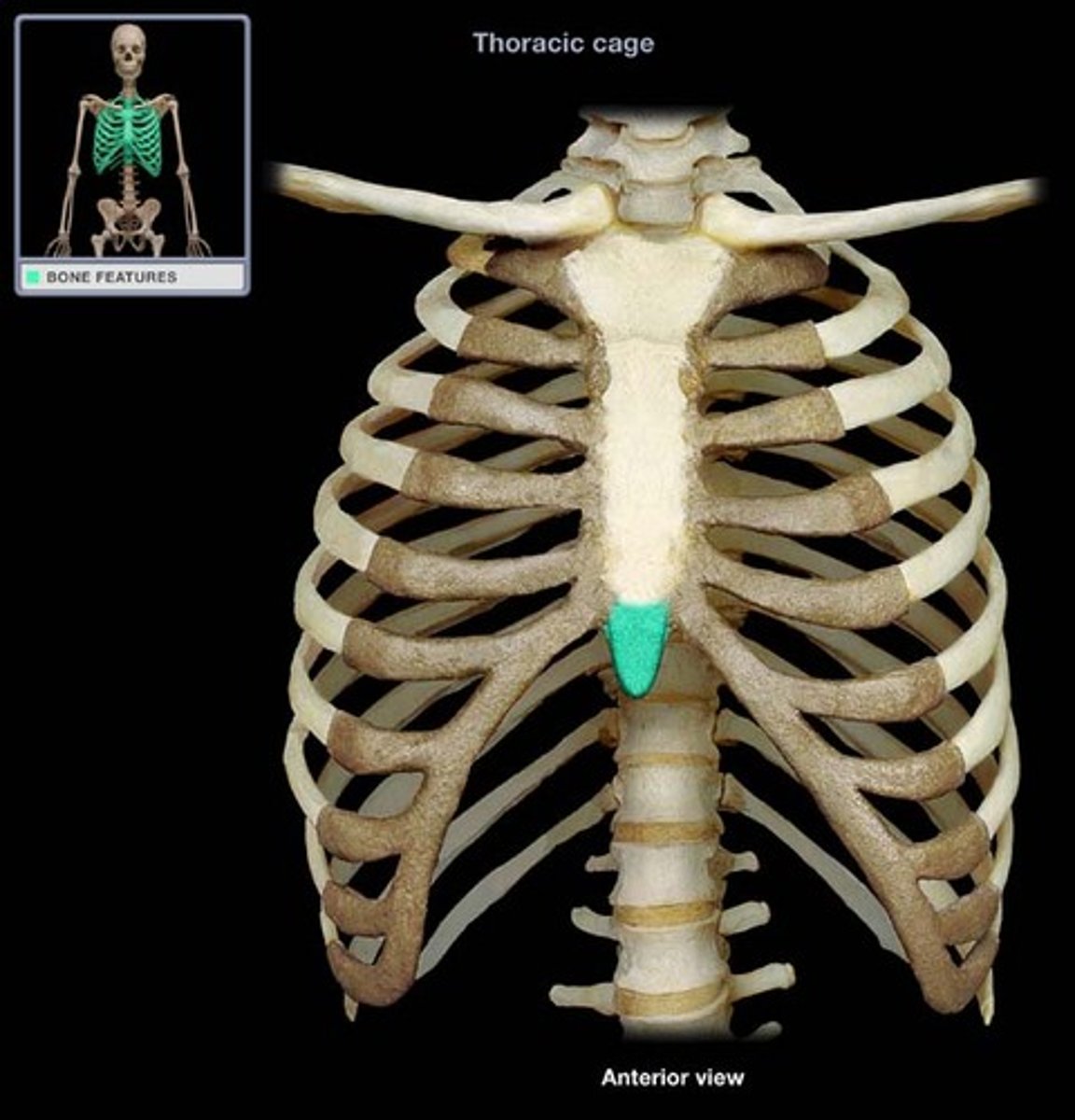
the most inferior portion of the sternum is the _____________, which is composed of cartilage during youth and doesn't completely ossify until about 40 years old
xiphoid
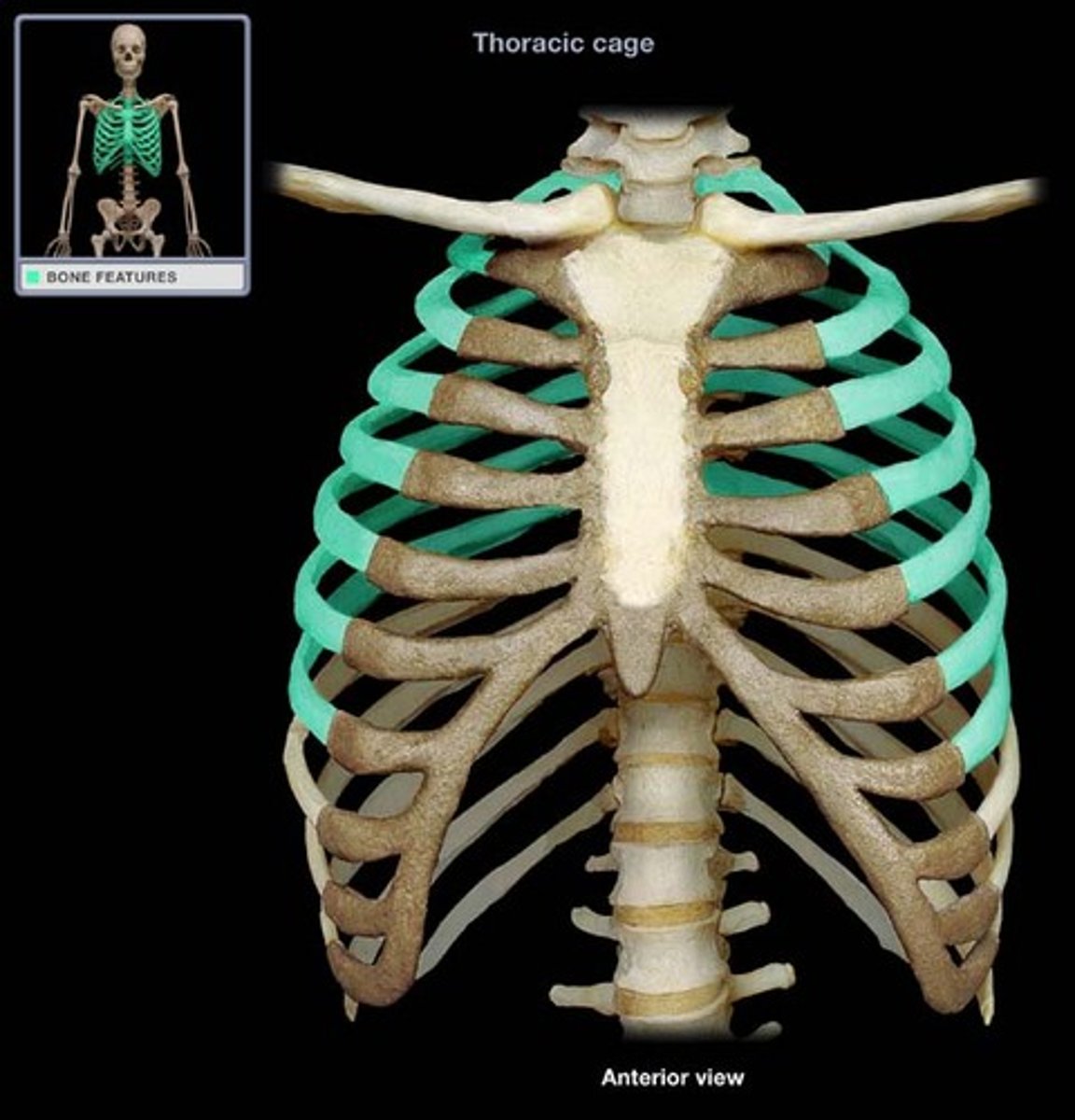
which ribs are true ribs, meaning they connect directly to the sternum with a short piece of costocartilage?
rib pairs 1-7
which ribs are false ribs, meaning they have costal cartilage that joins with the cartilage of rib 7, then to the sternum?
rib pairs 8-12
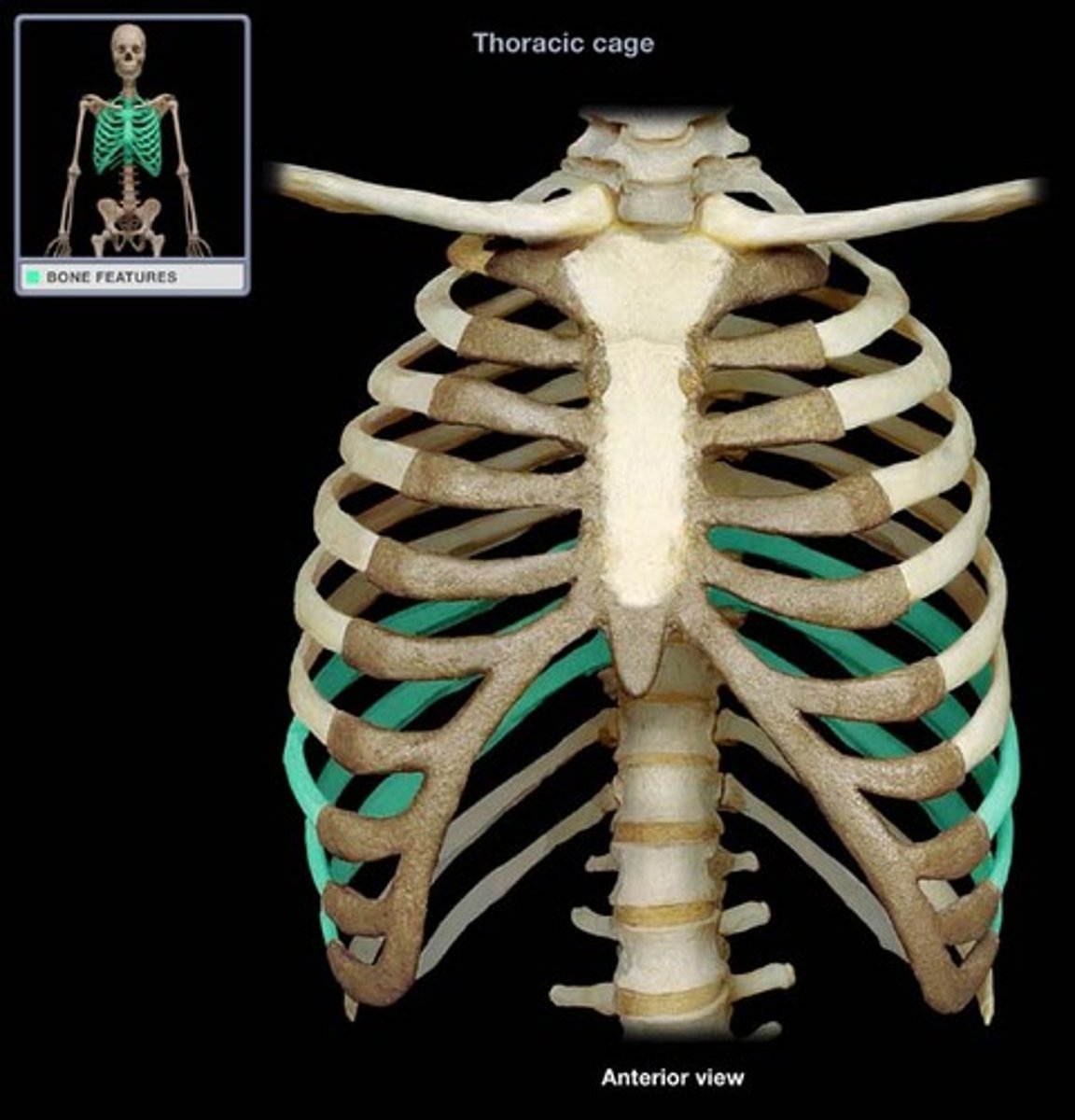
which ribs are floating ribs, meaning they do not have costal cartilage and therefore do not connect to the sternum?
rib pairs 11 and 12
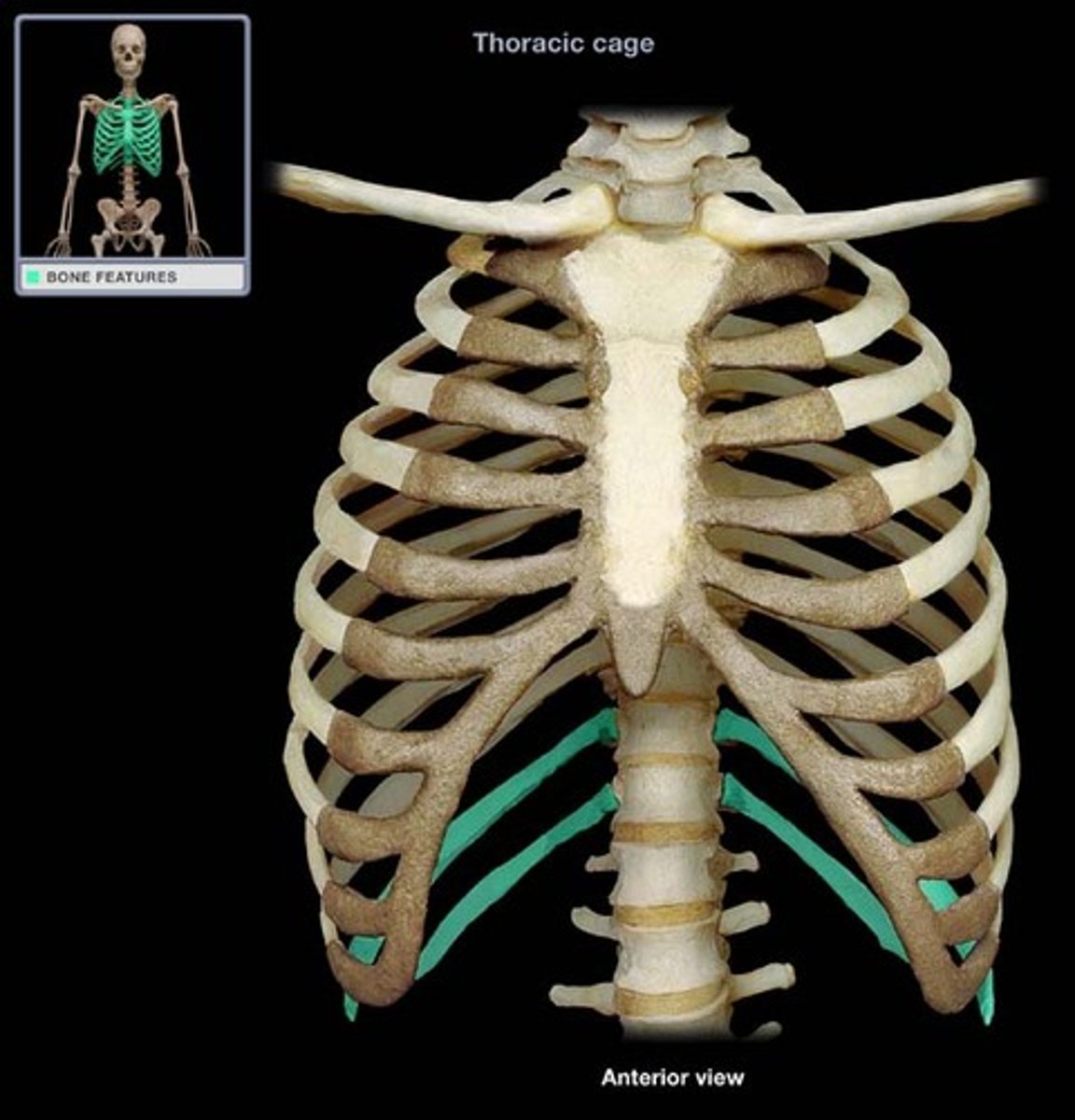
each rib has a ______________ end, which articulates with the thoracic vertebrae, and an _______________ end, which articulates with the costal cartilage
posterior/vertebral, anterior/sternal
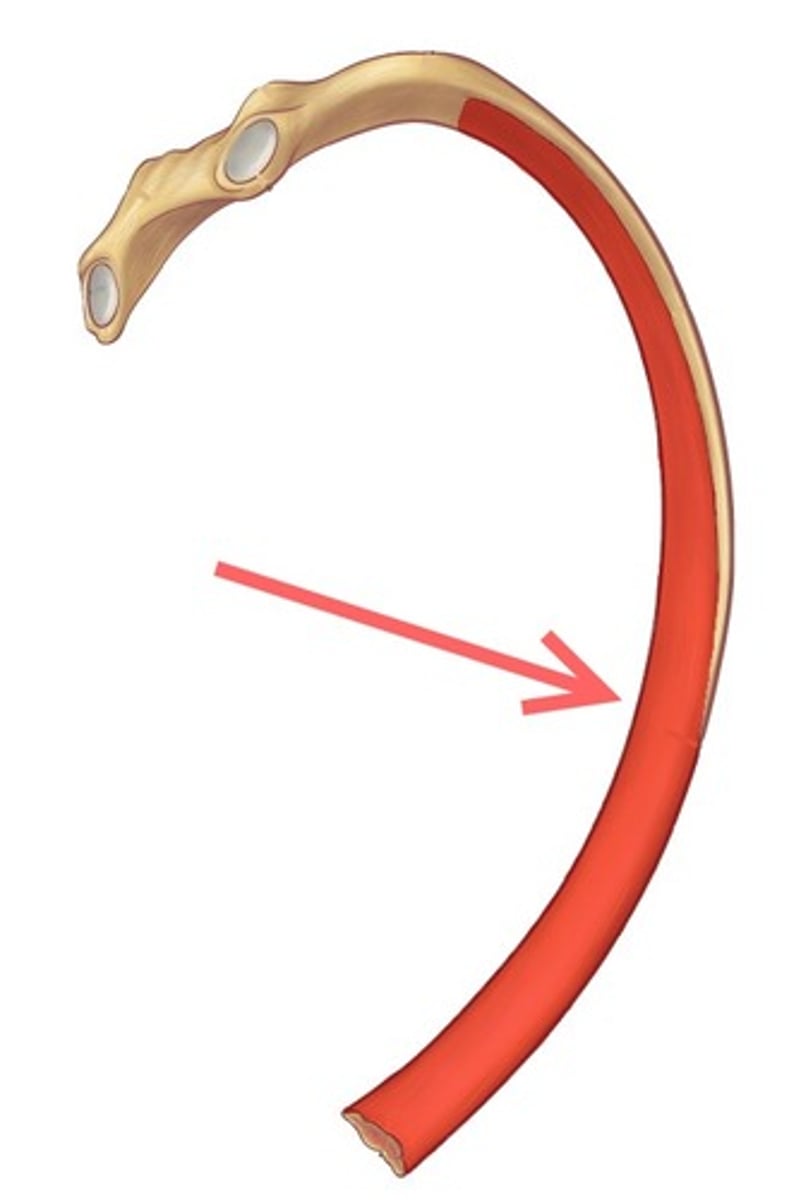
the area between the two ends of the rib is known as the __________
shaft/body
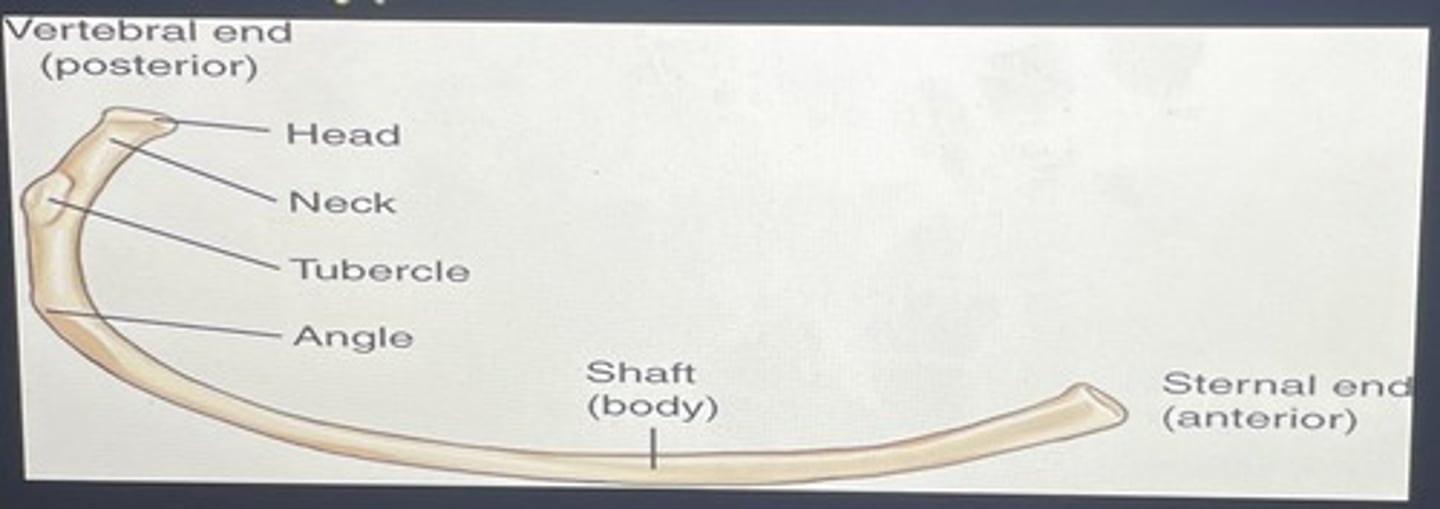
the vertebral end of a rib consists of a ________, which articulates with 1-2 thoracic vertebral bodies, and a flattened _________
head, neck
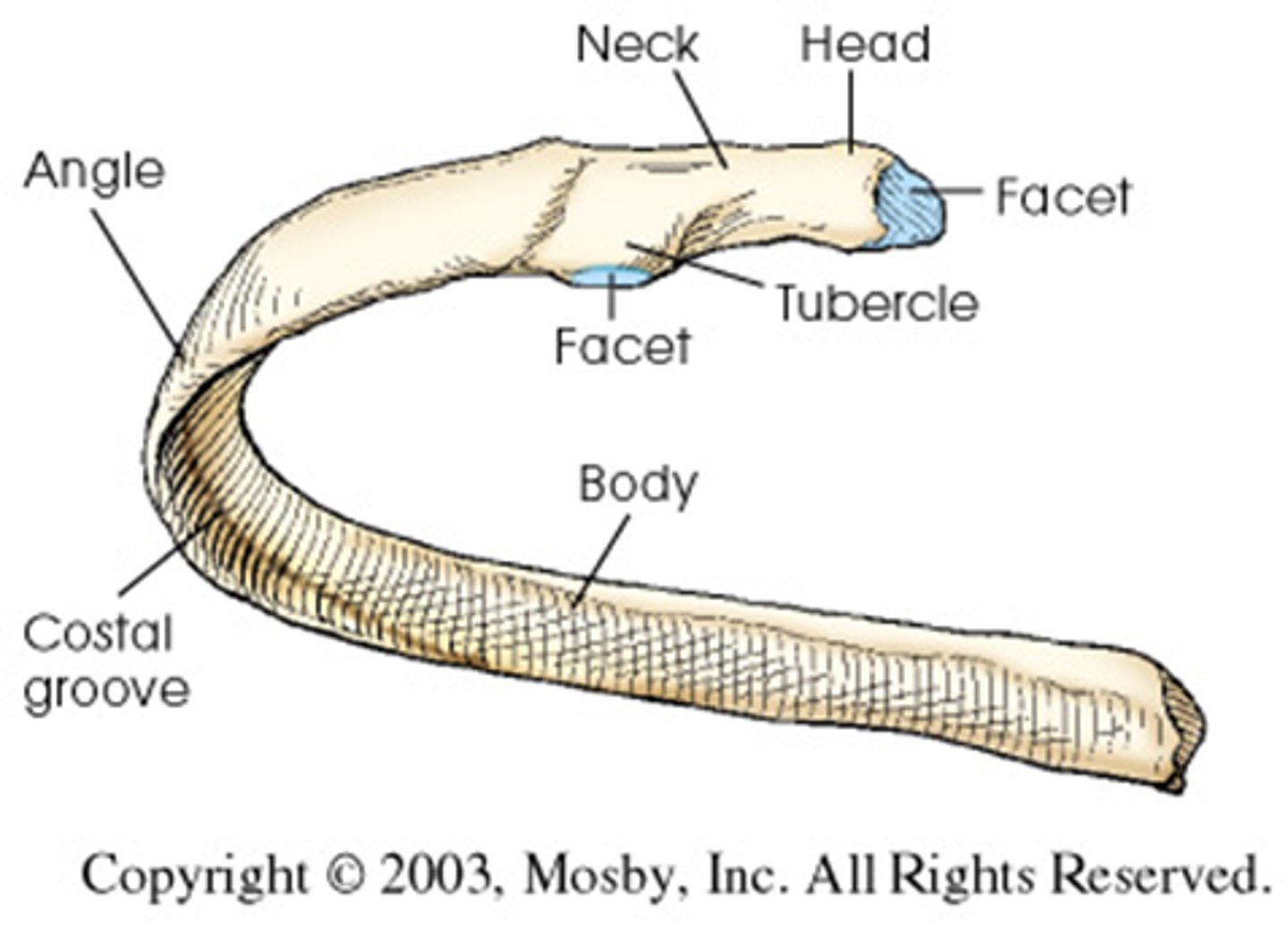
lateral to the neck of the vertebral end of the rib is an elevated ______________, which articulates with the transverse process of the vertebra allowing for attachment of a ligament
tubercle
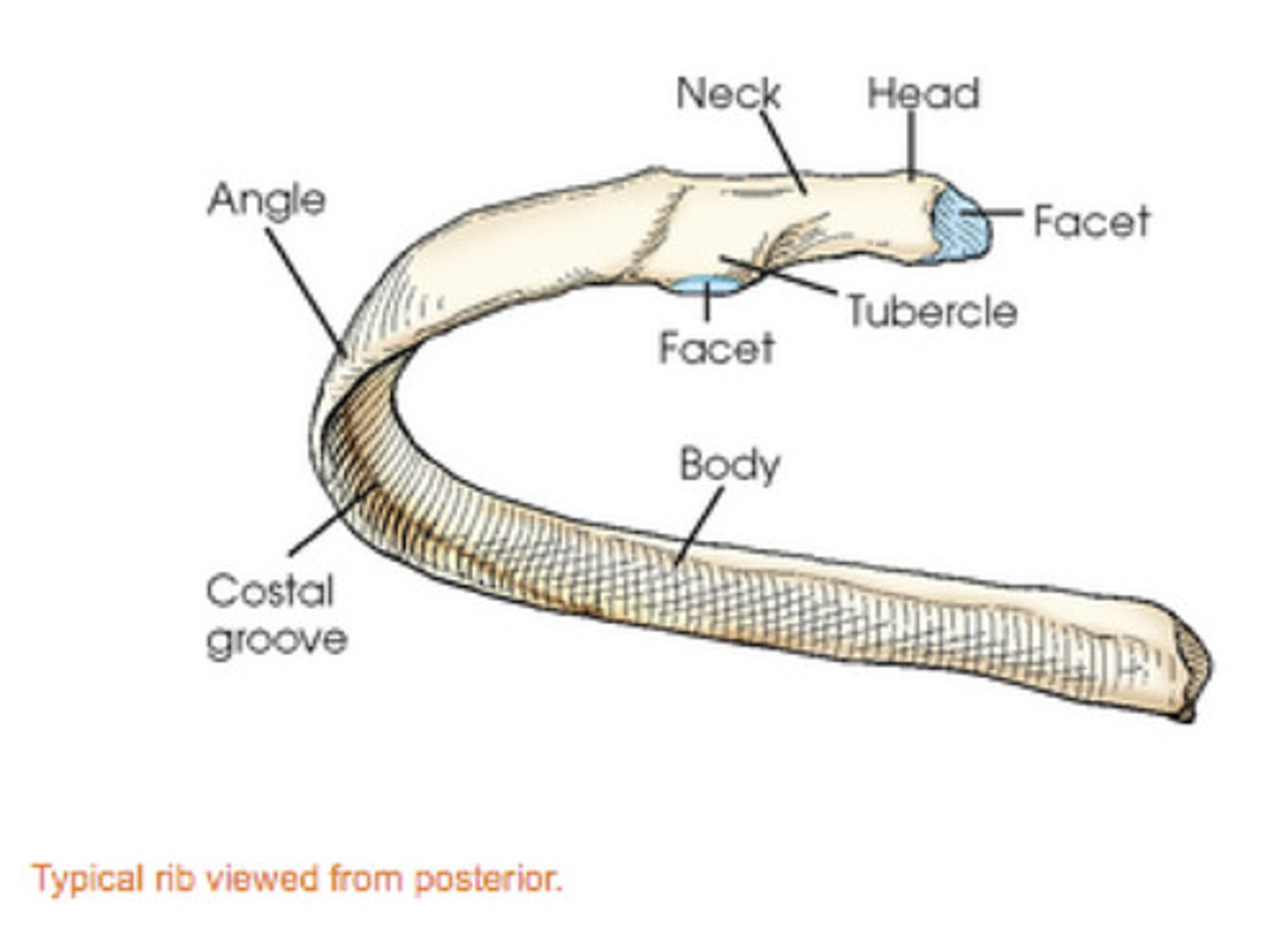
along the inferior internal margin of each rib is the _________ _________, which protects an artery, a vein, and a nerve
costal groove
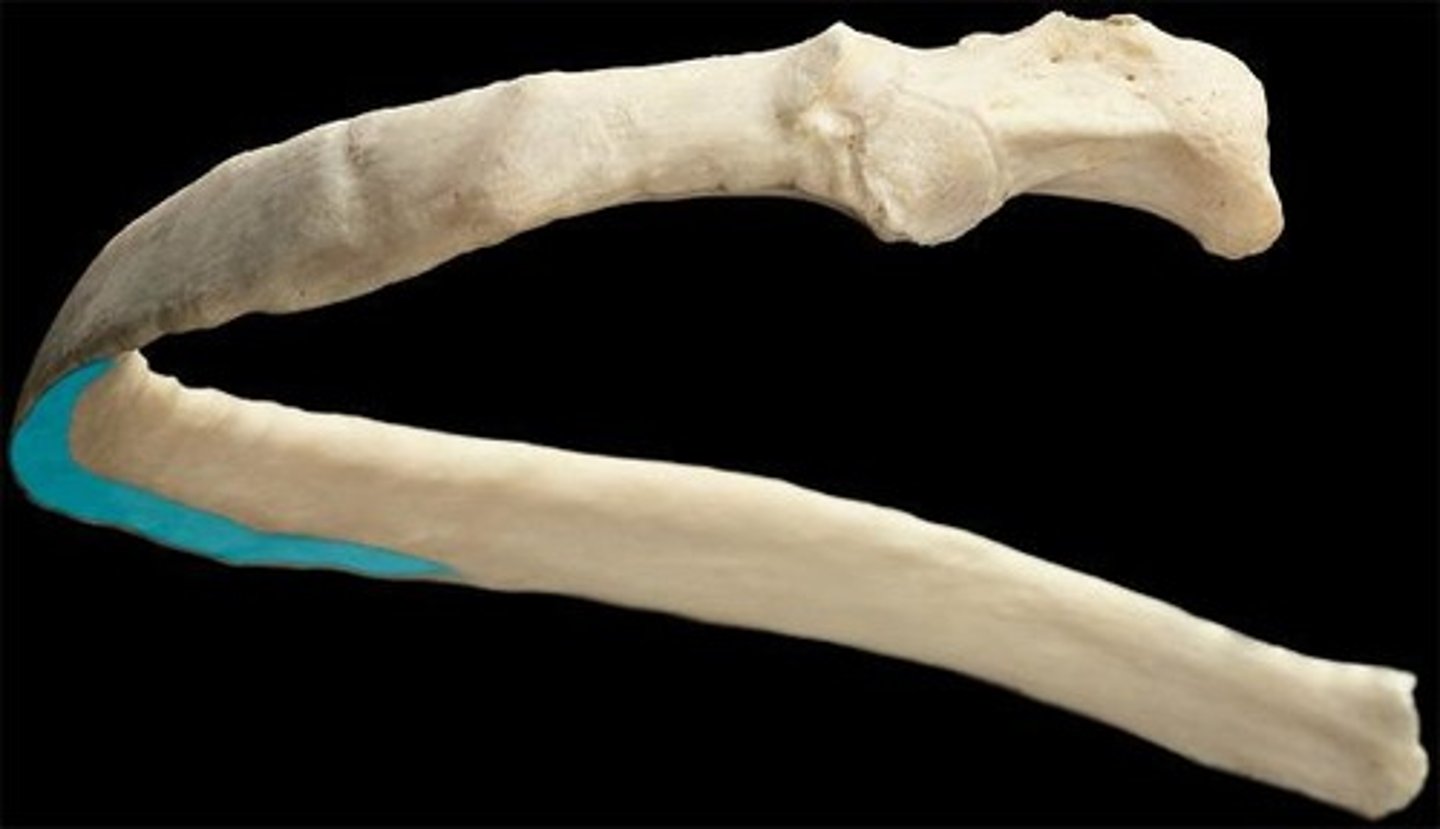
which end of the rib is more superior?
the posterior/vertebral end
where is the bony thorax the widest?
around the 8th/9th ribs
the _____ pair of ribs have the sharpest curvature at the angle
1st
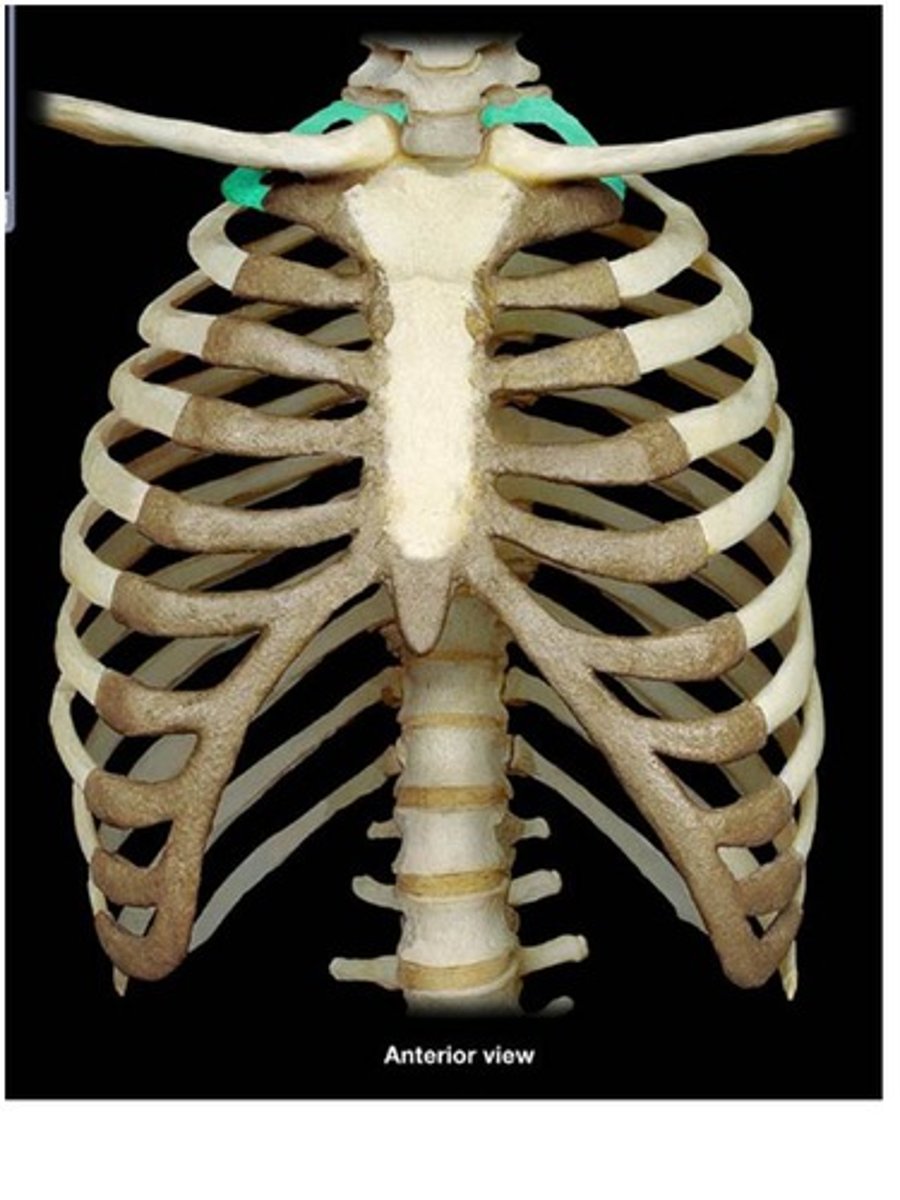
the superior border of the manubrium has a slightly notched area between the 2 clavicles called the ___________ __________
jugular notch
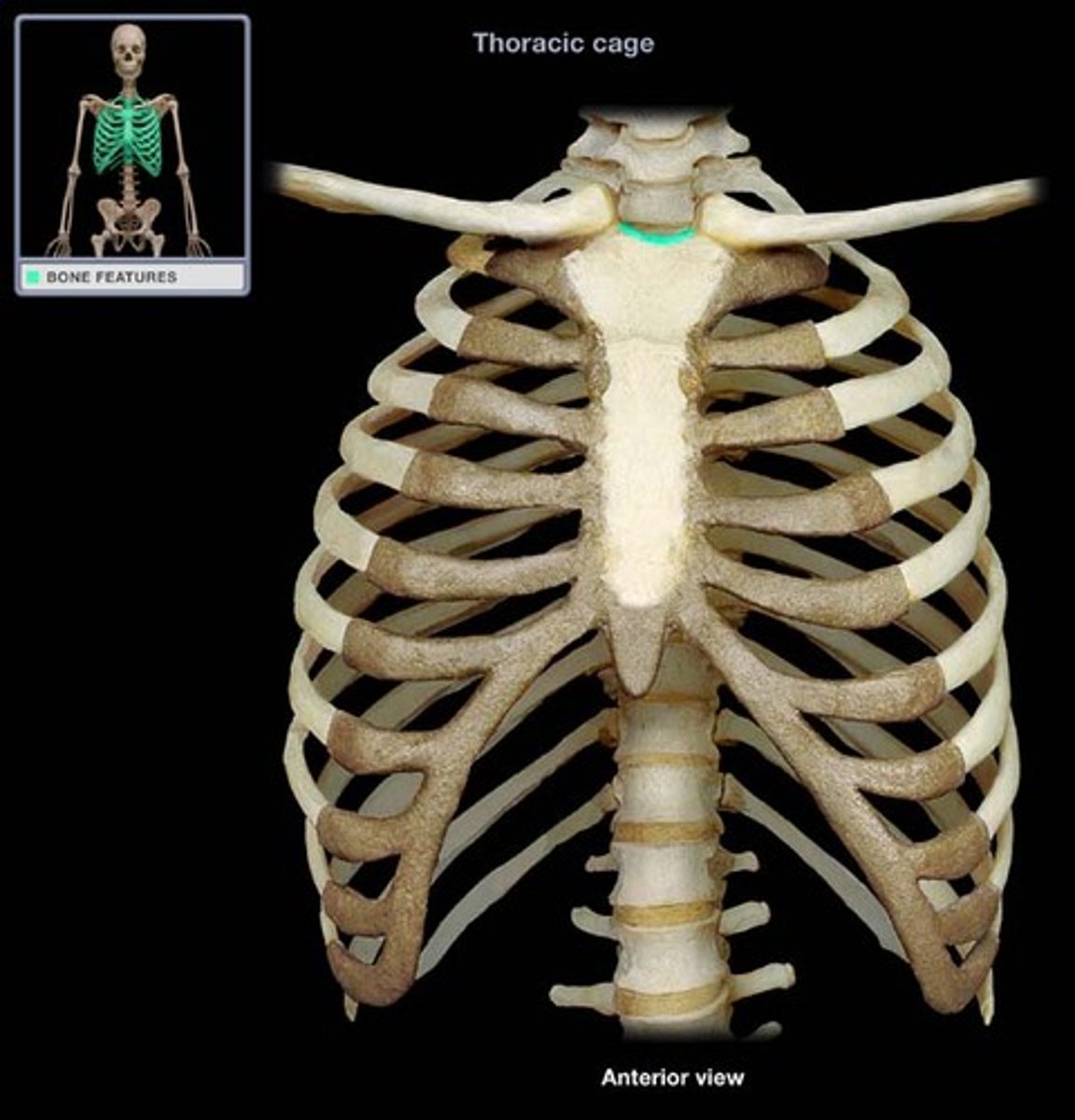
the jugular notch corresponds to what level?
T2-T3
the inferior end of the manubrium joins the body of the sternum to form a palpable anterior prominence, the ___________ ___________
sternal angle
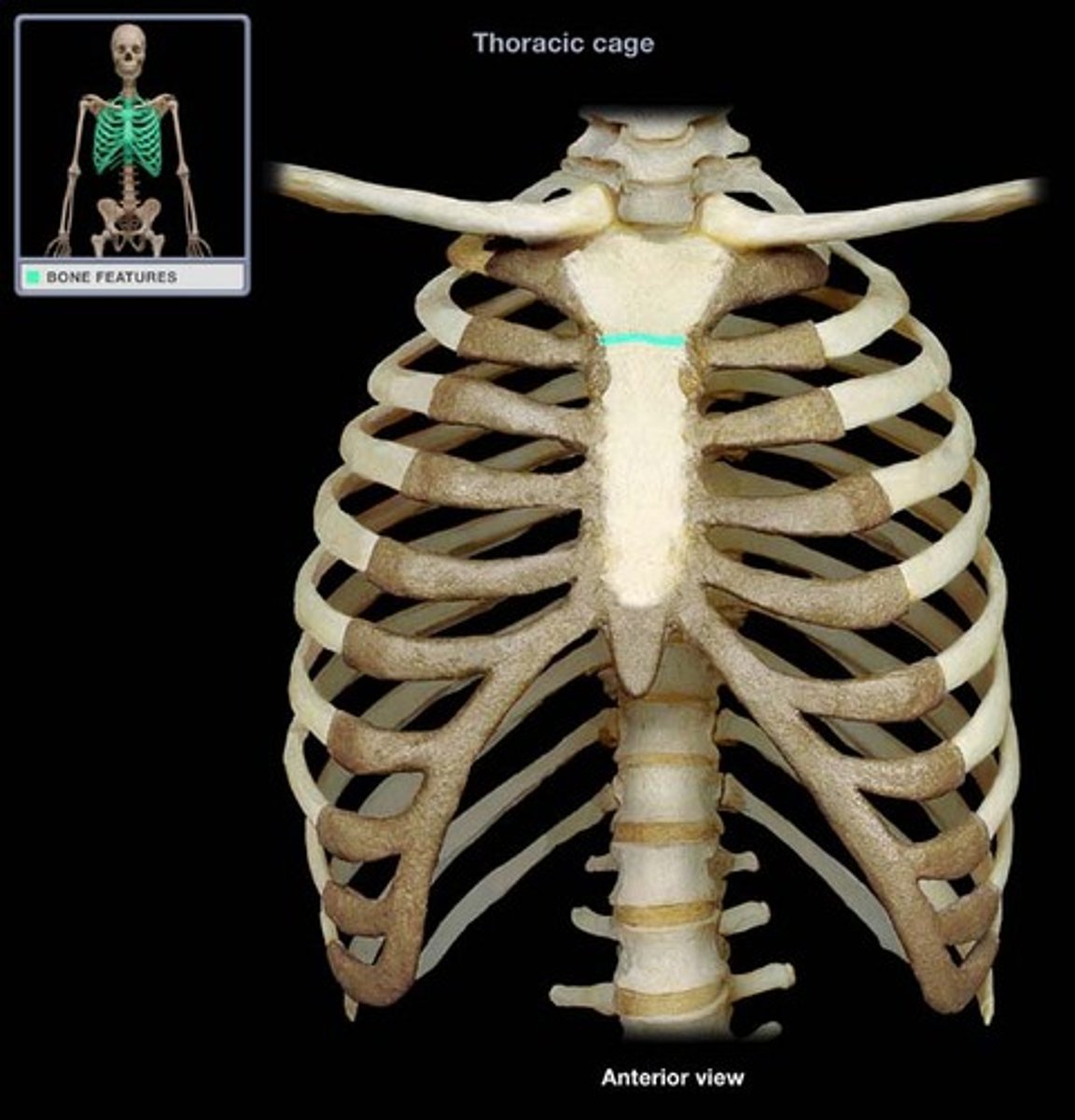
the sternal angle corresponds to what level?
T4-T5
what is the only bony connection between each shoulder girdle and the bony thorax?
the sternoclavicular (SC) joints
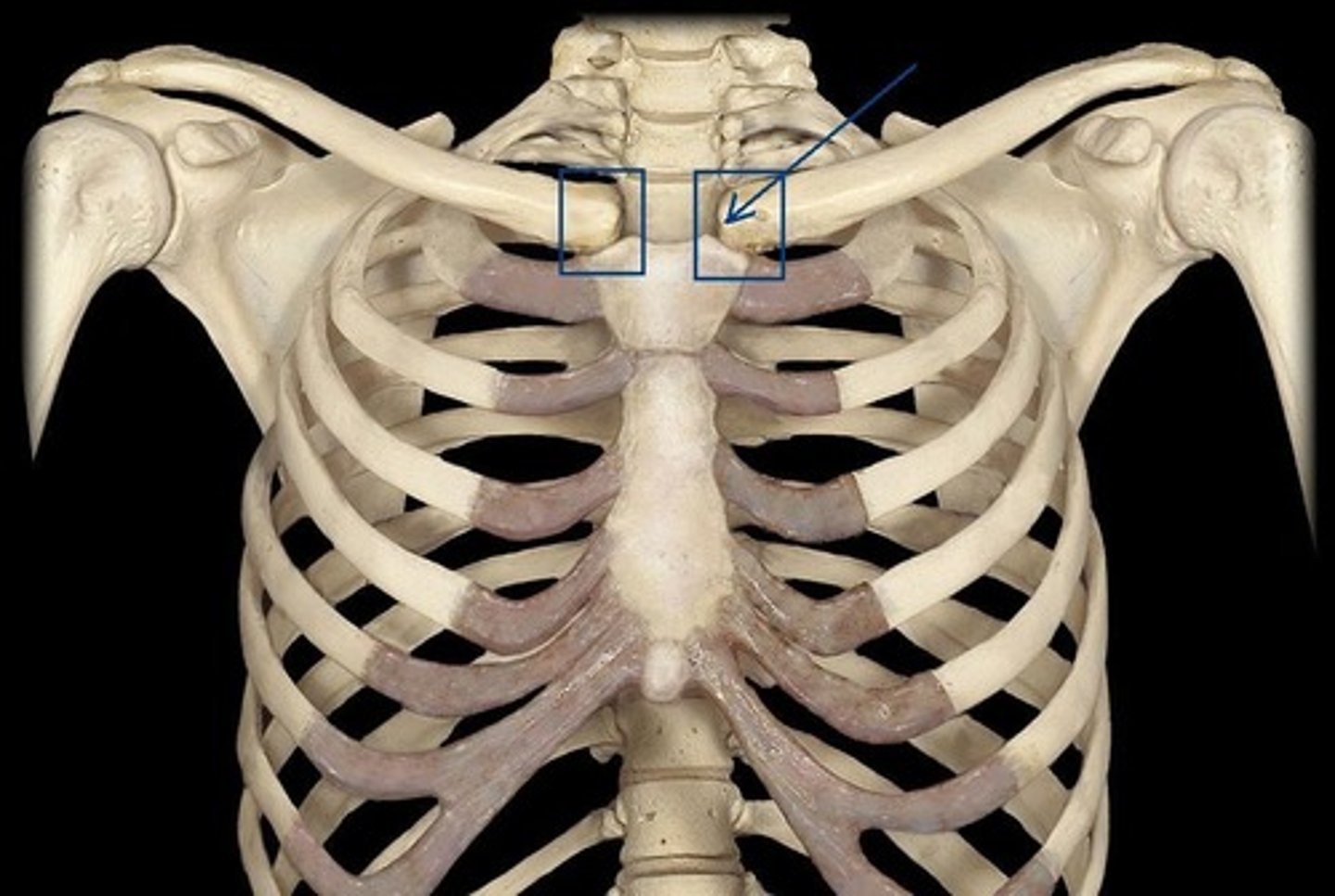
the sternum has ___ pairs of facets/depressions located laterally along the manubrium and body to accept the costal cartilage
7
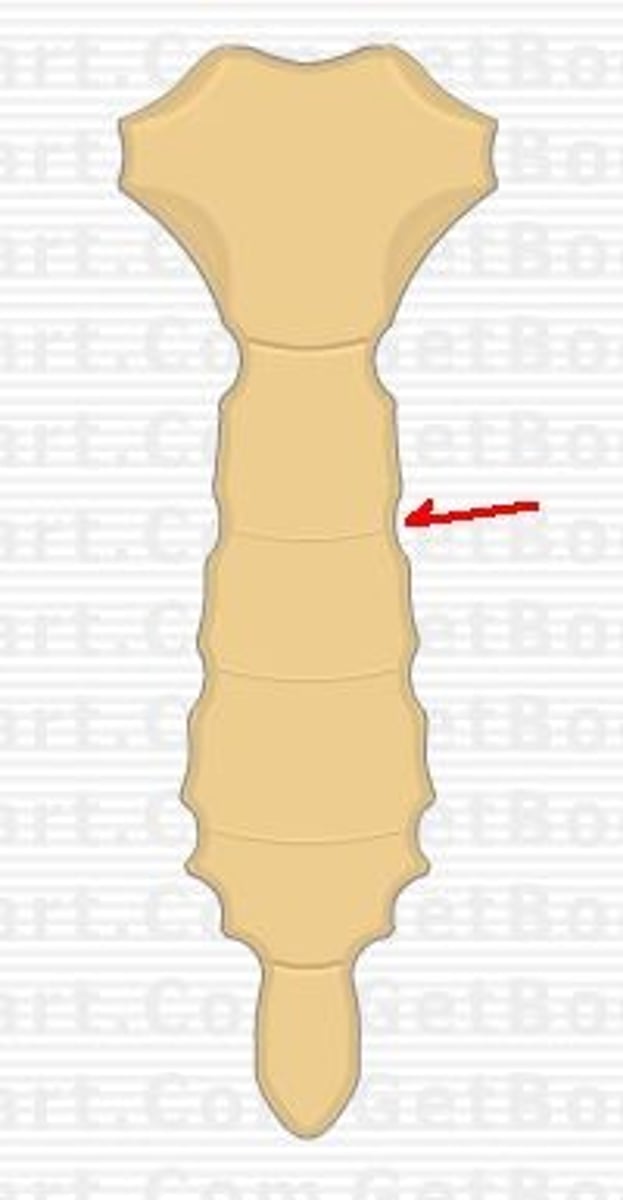
the second costal cartilage connects to the sternum at the level of the __________ _________
sternal angle

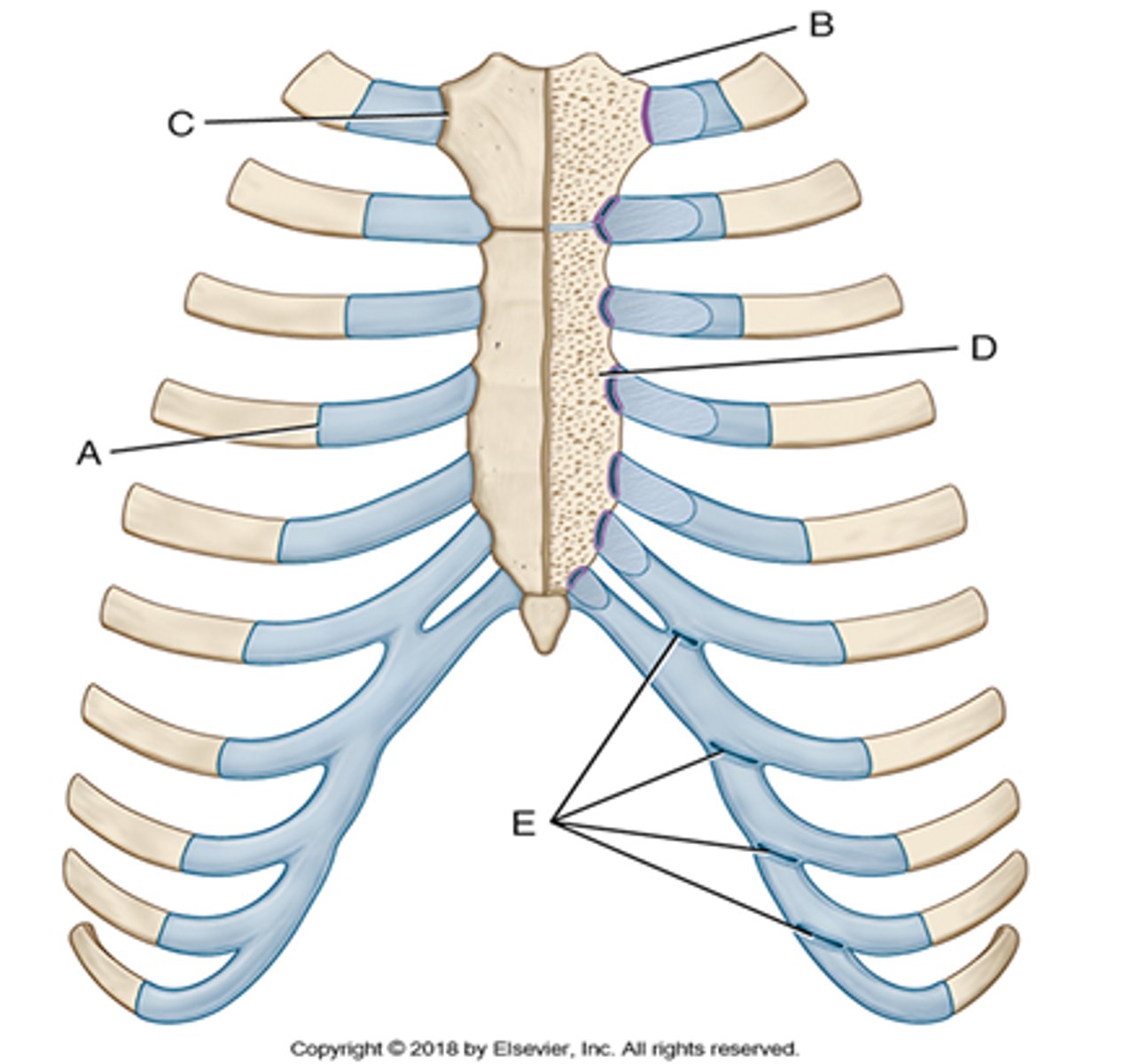
a costochondral union occurs between the ___________ _____________ and the ___________ end of a rib
costal cartilage, sternal end (labeled A)
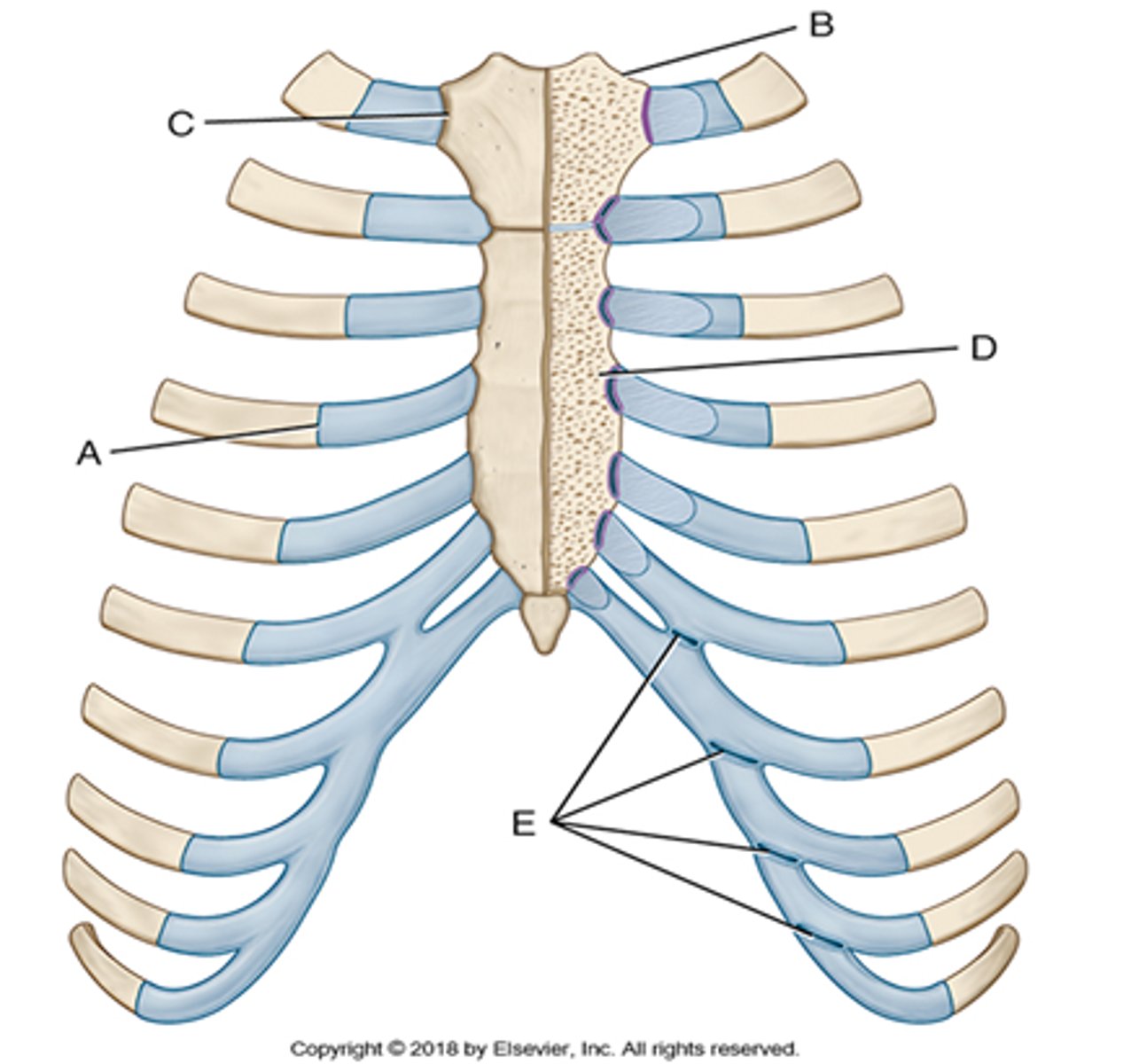
a sternoclavicular joint occurs between a ____________ and the _______________ of the sternum
clavicle, manubrium (labeled B)
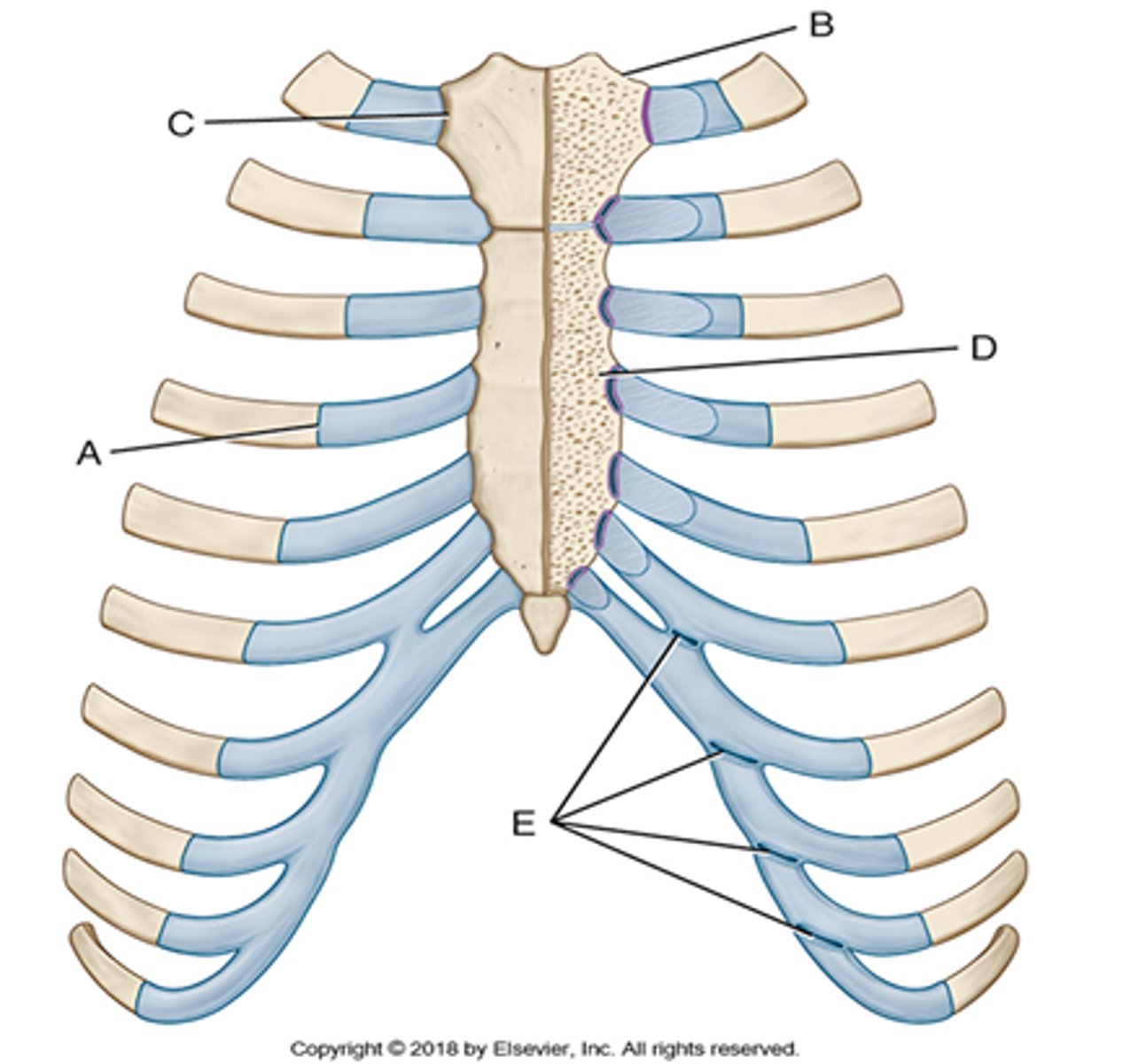
the sternocostal joints of the 2nd-7th ribs occur between _________ __________ and the ____________
costal cartilage, sternum (labeled D)
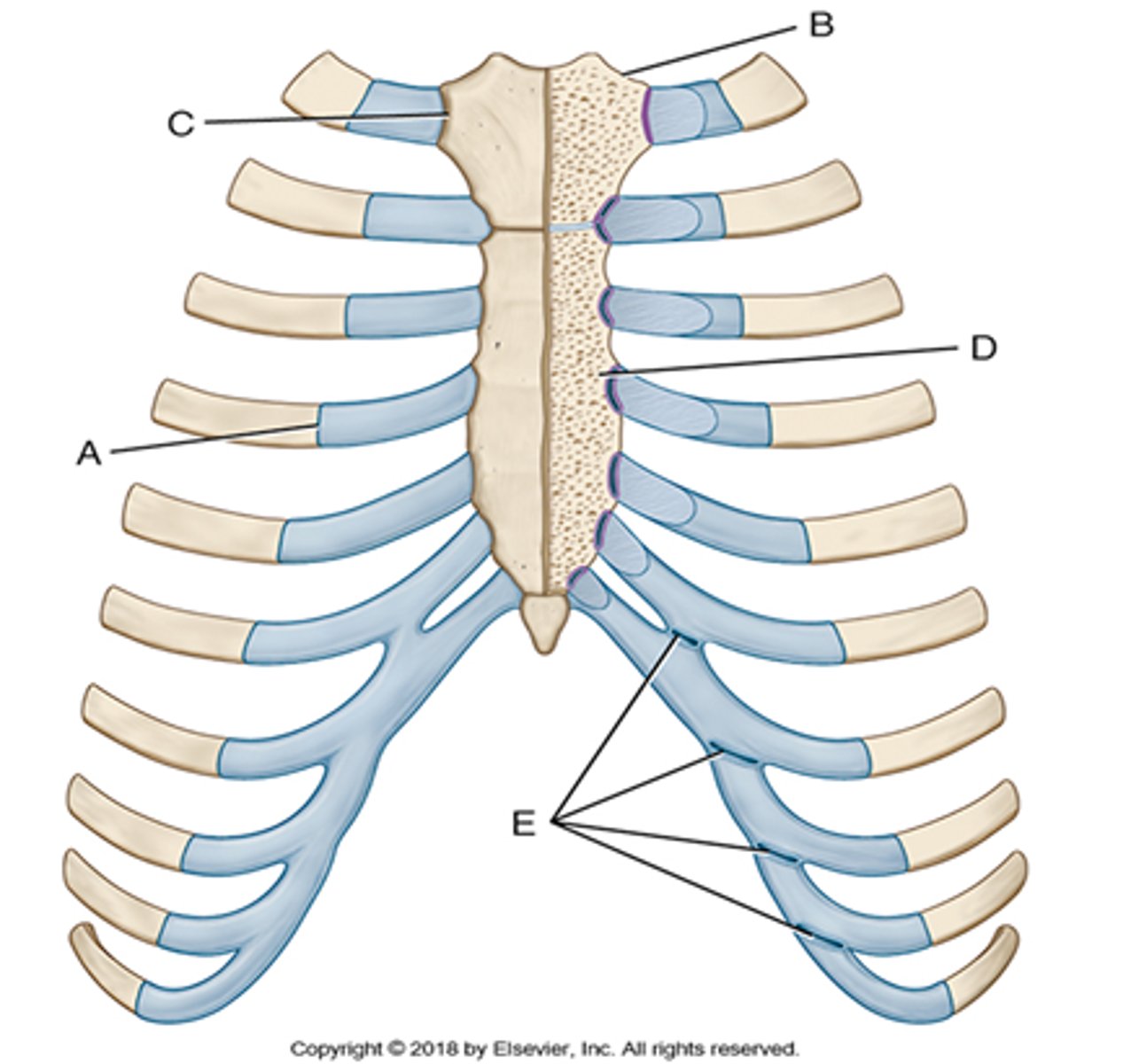
the interchondral (endochondral) joints occur between the __________ ___________ of the anterior 6-9th ribs
costal cartilages (labeled E)
RAO Sternum
Technical Factors
SID: 40"
Field Size: 10 x 12, portrait
Grid: Yes
kVp: 75-85
Positioning
-Patient erect in a 15-20 degree RAO
-CR to mid-sternum, 1" left of midline
Respiration
-Suspended on expiration
NOTES: begin with patient AP, light field ~2 inches above the jugular notch, then turn patient into RAO
Lateral Sternum
Technical Factors
SID: 72"
Field Size: 10 x 12, portrait
Grid: Yes
kVp: 75-85
Positioning
-Patient erect in a true lateral, hands clasped behind back to draw shoulders down, chest puffed out
-Place top of IR 1.5" above the jugular notch
-CR to mid-sternum, midway between jugular notch and xiphoid process
-Turn collimator to align long axis of sternum to CR
Respiration
-Suspended on expiration
AP Ribs Above Diaphragm
Technical Factors
SID: 40"
Field Size: 14x17 portrait (unilateral), 14x17 landscape (bilateral)
Grid: Yes
kVp: 75-85
Positioning- Unilateral
-Patient erect in AP projection
-Align the side of thorax of interest to midline of bucky
-Raise chin slightly, arm of side of interest out of the way
-CR 3-4" below jugular notch, midway between MSP and lateral margin of thorax
Positioning- Bilateral
-Patient erect in AP projection
-Raise chin slightly, arms away from sides
-Rotate shoulders anteriorly
-CR 3-4" below jugular notch to MSP
Respiration
-Suspended on deep inspiration
AP Ribs Below Diaphragm
Technical Factors
SID: 40"
Field Size: 14x14 (unilateral), 14x17 (bilateral)
Grid: Yes
kVp: 75-85
Positioning- Unilateral
-Patient erect in AP projection
-Align the side of thorax of interest to midline of bucky
-Arm of side of interest out of the way
-CR midway between xiphoid process and lower rib margin, midway between MSP and lateral margin of thorax
Positioning- Bilateral
-Patient erect in AP projection
-Arms away from sides
-CR midway between xiphoid process and lower rib margin at MSP
Respiration
-Suspended on deep inspiration
NOTES: bottom of light field at iliac crest
AP Oblique Axillary Ribs (RPO/LPO)
Technical Factors
SID: 40"
Field Size: 14x17
Grid: Yes
kVp: 75-85
Positioning
-Patient erect in AP projection, rotated into 45 degree posterior oblique w/ affected side closest to IR
-Arms out of the way
-Align thorax to midline of IR
-CR to T7
Respiration
-Suspended on inspiration
NOTES: LPO shows right side angles and left side elongated
RPO shows left side angles and right side elongated
PA Oblique Axillary Ribs (RAO/LAO)
Technical Factors
SID: 40"
Field Size: 14x17
Grid: Yes
kVp: 75-85
Positioning
-Patient erect in PA projection, rotated into 45 degree anterior oblique w/ affected side away from IR
-Arms out of the way
-Align thorax to midline of IR
-CR to T7
Respiration
-Suspended on inspiration
NOTES: RAO shows right side angles and left side elongated
LAO shows left side angles and right side elongated