ANA 110 (Salmeron)-University of Kentucky--Exam 2
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
Functions of Blood
-transports nutrients and waste
- regulates body fluids
- protects the body via clotting and the immune system
Components of blood
- plasma (55%)
- Leukocytes and platelets (1%) (Buffycoat)
- Red blood cells (44%)
Blood plasma
extracellular matrix of blood that mainly contains water and proteins
What are formed elements of the blood?
- leukocytes (WBC)
- erythrocytes (RDC)
- Platelets--cell membrane fragments
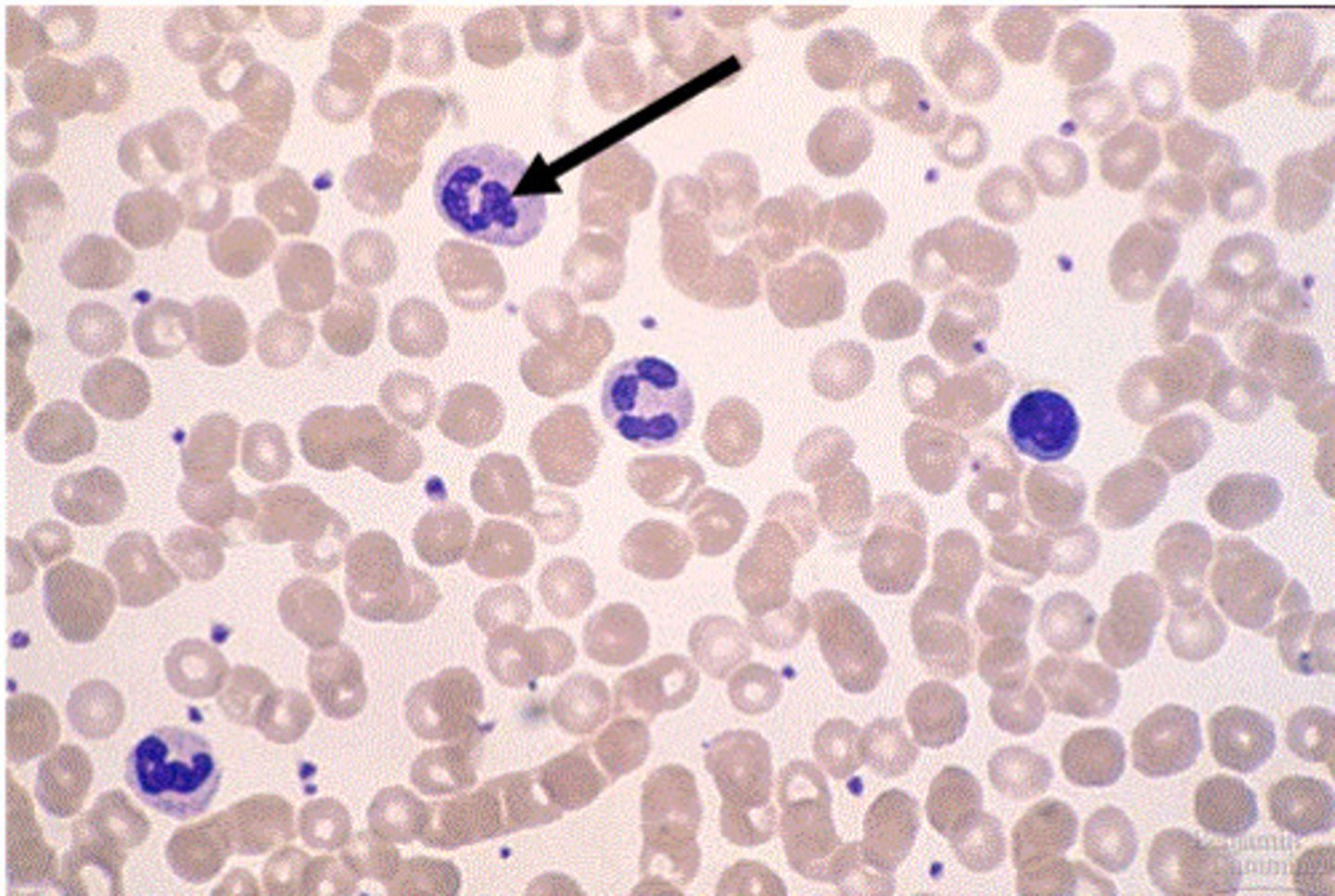
White blood cells anatomy
Red blood cells anatomy
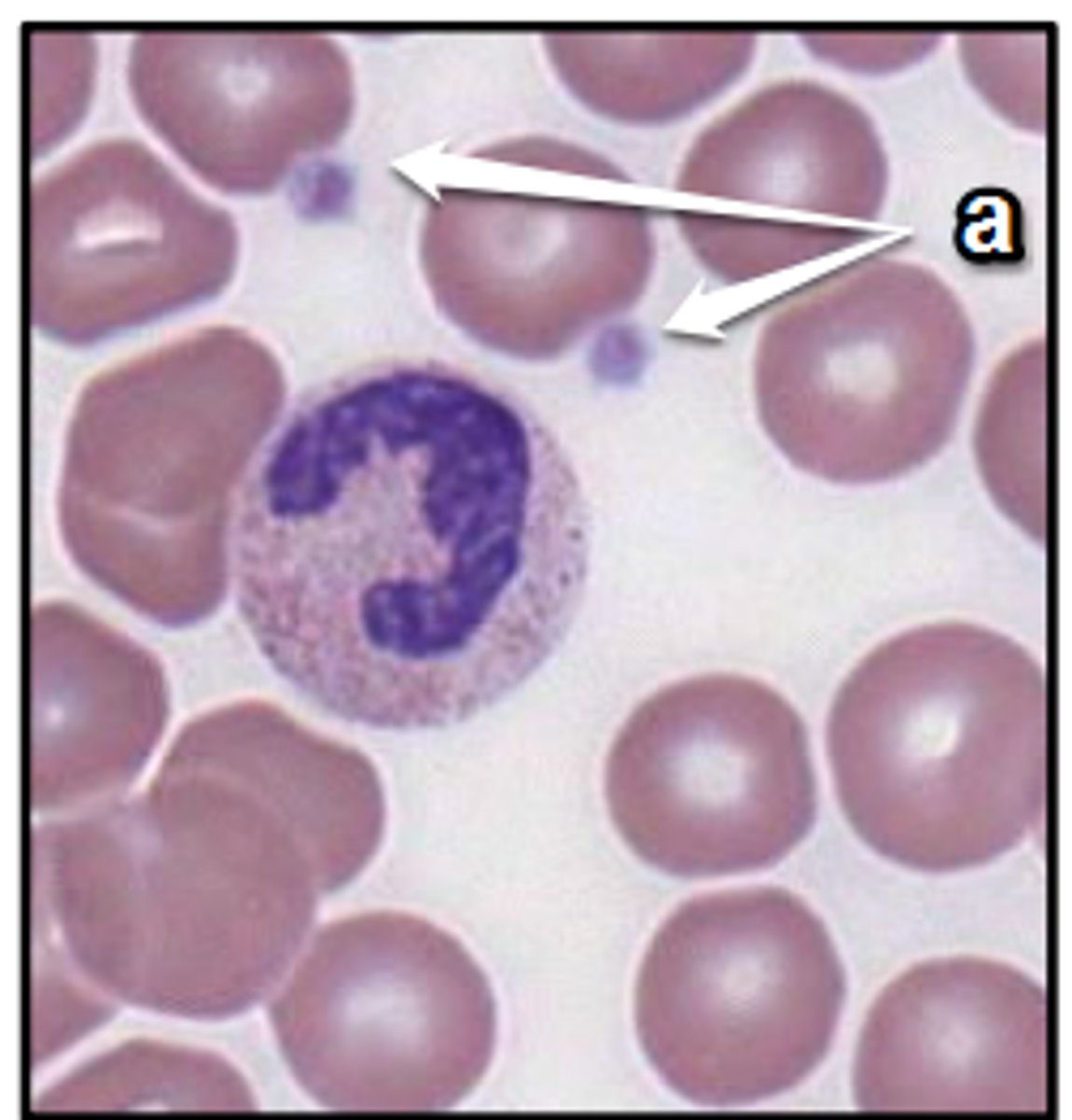
Platelets anatomy
What is normal blood pH?
7.35-7.45
- tightly regulated because it is very critical for life (ex: enzymes)
Average Adult Blood Volume for men and women
Men: 5-6 liters
Women: 4-5 liters
Major function of red blood cells
transport oxygen
________ lack nuclei and other major organelles
red blood cells
Red blood cells are almost entirely _________
hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
key protein for O2 and CO2 transport
What gives RBCs their red color?
hemoglobin
Hemoglobin has 4 _____ groups, which each contain _____
heme, iron
Cells of the immune system
leukocytes
Leukocytes have a _____, but lack _______
nucleus, hemoglobin
types of leukocytes
granulocytes ("grainy") and agranulocytes (not "grainy")
Types of granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
Neutrophils
- granulocyte
- most common WBC
- attack infection
- first responder
Eosinophils
- granulocyte
- parasite response
- deals with asthma and eczema
Basophils
- granulocyte
- allergic resposne
- release histamine and heparin
types of agranulocytes
lymphocytes and monocytes
Lymphocytes
- agranulocytes
- attack cancer cells and virus-infected cells
- immune memory
- coordination
Monocytes
- agranulocytes
- become macrophages
- eat infection and debris
Platelet
- cell fragments released from megakaryocyte
- plug holes in blood vessels
Where are platelets found?
buffy coat
Erythrocytes carry ____ in and ______ out
O2, CO2
RBC's have a _______ lifespan
short (120 days)
Where are new blood cells produced?
red bone marrow
Where is most red bone marrow found in adults?
axial skeleton
Hematopoiesis
formation of blood cells
What is hematopoiesis mainly controlled by
the hormone erythropoietin (EPO)
Hemopoietic stem cells form ________ cells which mature into blood cells
immature precursor
osteogenic cells form _______
osteoblasts
hemopeotic cells form______
osteoclasts
hematopoiesis =
hemopoiesis
What is required for hematopoiesis to occur?
- hemoglobin raw materials (iron, globin, heme)
- vitamins that support cell division (folate, Vitamin B12)
- erythropoietin (EPO)
What happens when a RBC reaches the end of its life?
- old or damaged RBCs are destroyed in spleen or liver
- hemoglobin is broken down and recycled
How is iron from heme recycled?
transported by transferrin to red bone marrow
How is heme recycled?
broken down to bilirubin
How are cell fragments phagocytized?
monocytes
Life cycle of WBC
most live only a few days
- during infection, some live only for a few hours
- some can live for months or years
WBC count will __________ when they are "called to action"
increase
What to WBCs do to get to tissues where they are needed?
exit the bloodstream
Hemostasis
stoppage of bleeding
Three mechanisms of hemostasis
vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, coagulation
Vascular spasm
- INVOLUNTARY
- smooth muscle in wall of damaged vessel contracts immediately to reduce blood loss
platelet plug formation
- platelets stick to damaged tissue
- other platelets are activated to sustain vascular spasm
- platelet plug is formed by oncoming platelets
Coagulation (blood clotting)
- positive feedback
- thrombin and fibrin in action
Thrombin
enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin during coagulation
Fibrin
final product that forms majority of a blood clot
Fibrinolysis
Breakdown and removal of a clot and fibrin
anticoagulant
prevents blood clotting
Endogenous anticoagulant
heparin from basophils
Pharmaceutical anticoagulants
warfarin--blocks vitamin K recycling
What is blood type?
set of glycoproteins and antigens displayed on the surface of their RBCs
Two major typing systems for blood types
ABO and Rh
Type A blood
A antigens, B antibodies
Type B blood has
B antigens, A antibodies
Type AB blood
A and B antigens, no antibodies
Type O blood
no antigens, A and B antibodies
universal donor
Type O
universal receiver
AB
Type A can donate to
Type A and Type AB
Type B can donate to
B, AB
Type AB can donate to
AB
Type O can donate to
A, B, AB, O
Rh+
has antigen
Rh-
no antigen
Rh is especially important to understand what?
pregnancy screening
Respiratory system
acts with the cardiovascular system to bring oxygen into the body and remove carbon dioxide from the body
function of respiratory system
- gas exchange
- regulate blood pH
- produces vocal sounds
Paired thoracic cavity organs
lungs
visceral pleura
covers the lungs
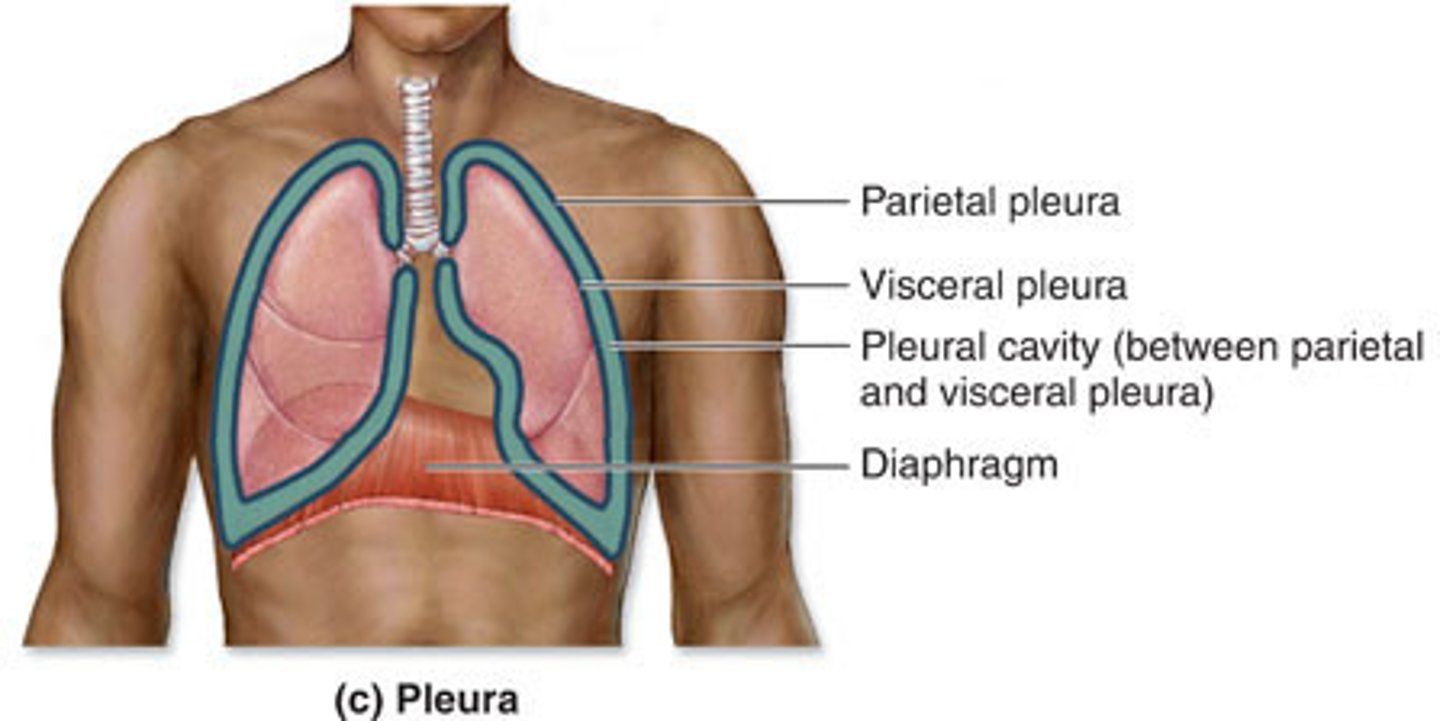
Parietal pleura
lines the thoracic cavity
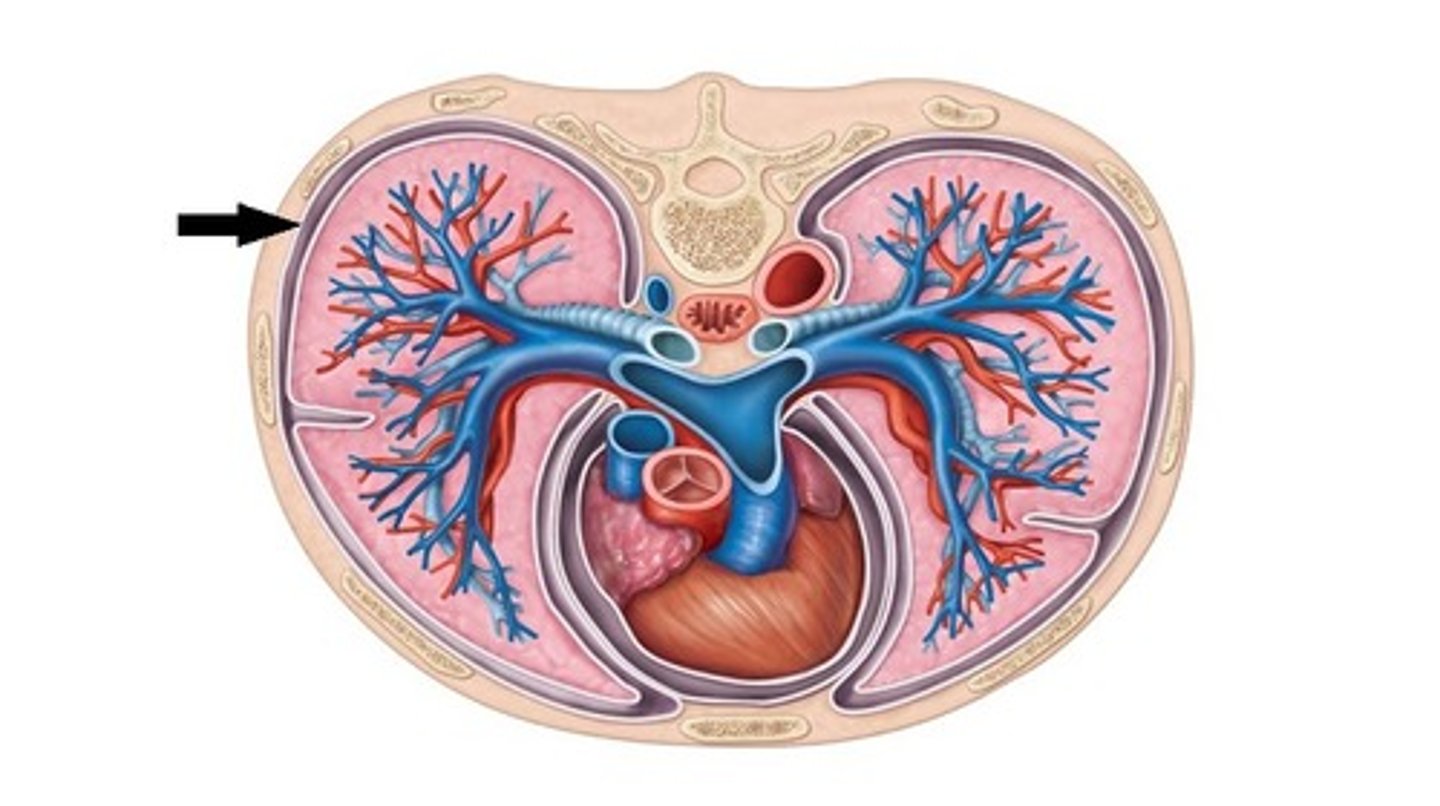
Pleaural cavity is filled with ________
serous fluid
Structural formation of respiratory system
- upper respiratory
- lower respiratory
Upper respiratory
nose and pharynx
Lower respiratory
larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
Functional structures of respiratory system
- conducting zone
- respiratory zone
Conducting zone
filter, warm, and moisten air and conduct it into the lungs
Respiratory zone
site of gas exchange (alveolar sacs)
Alveolar sacs
clusters of alveoli that allow for rapid gas exchange
floor of nasal cavity
hard and soft palate
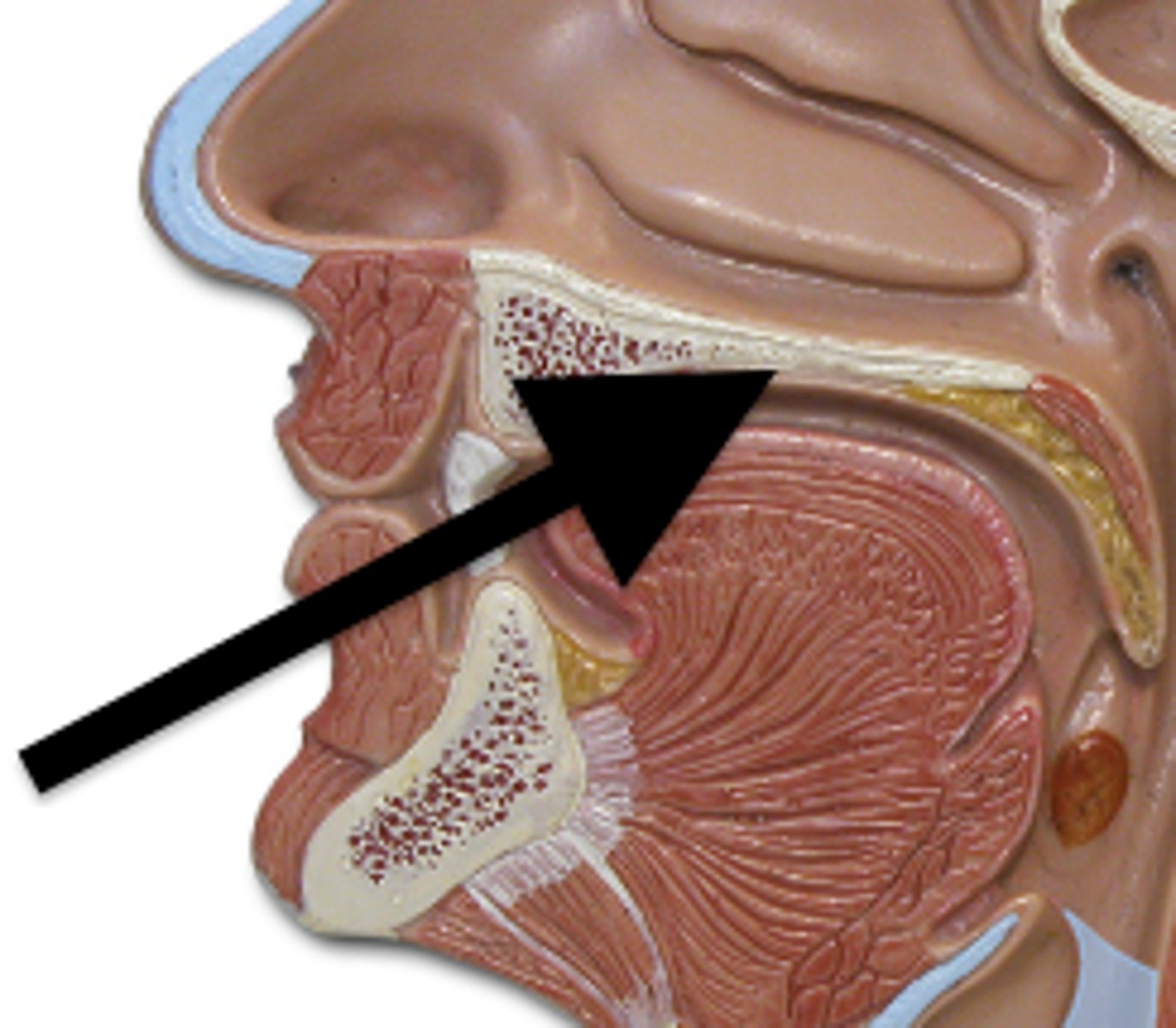
roof of nasal cavity
ethmoid and sphenoid bones
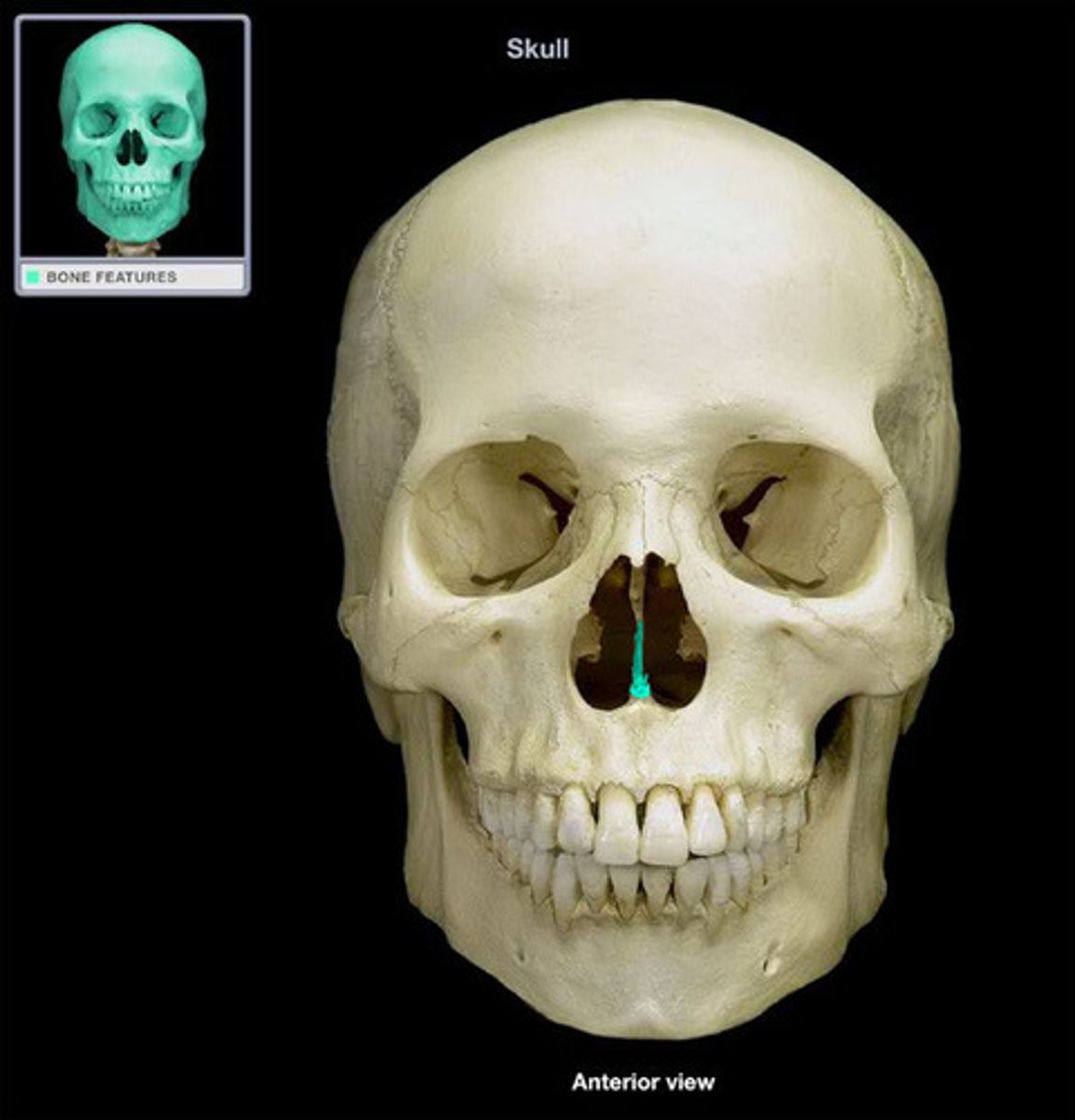
Midline of nasal cavity:
vomer and septal cartilage
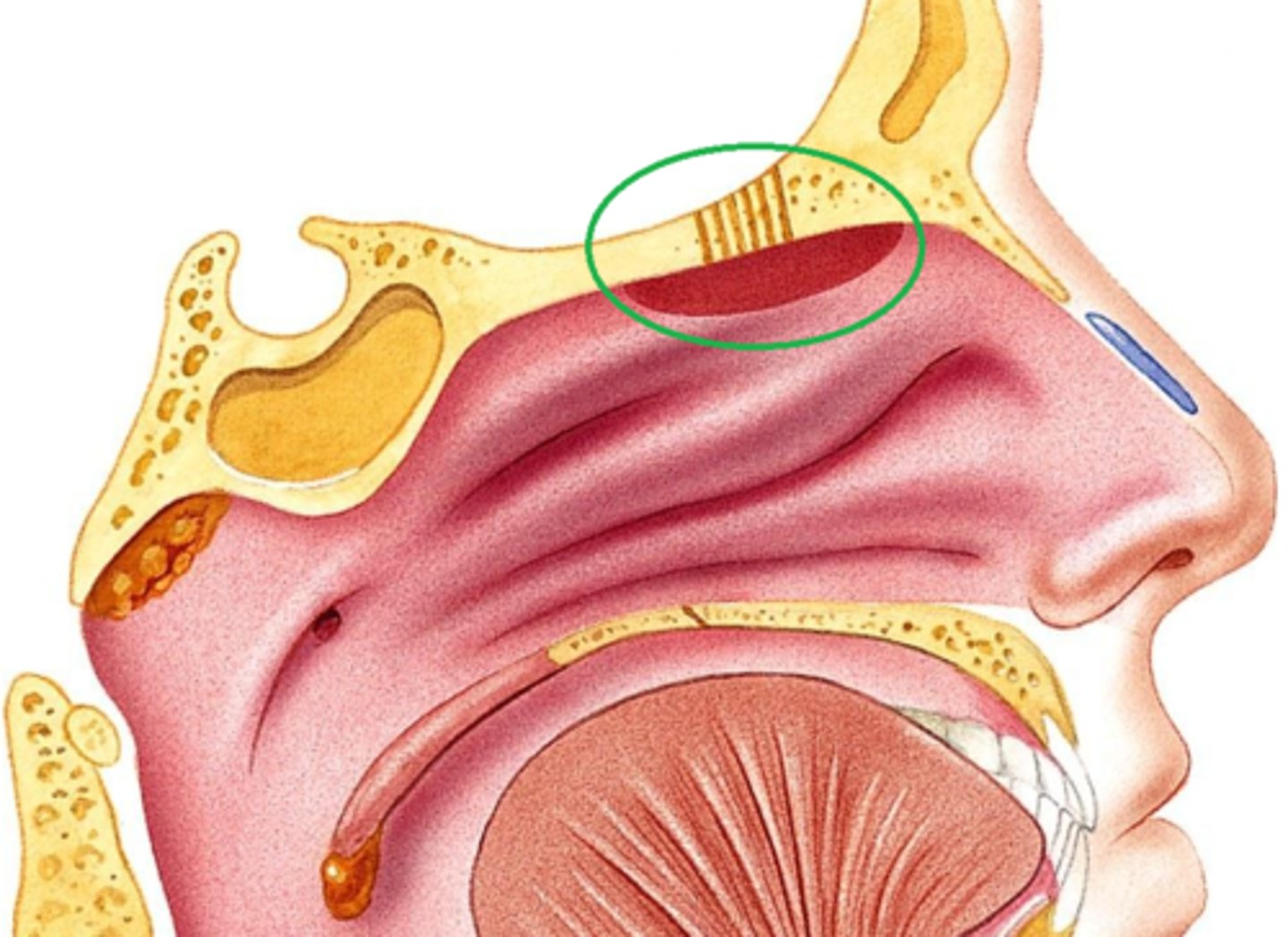
cilia in nasal cavity
push mucus to back of throat to be swallowed and digested
Conchae
lobes in nasal cavity that provide produce a quart of fluid a day to protect from pathogens
Pharynx (throat)
performs the swallowing action that passes food from the mouth into the esophagus
Pharyngeal regions
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
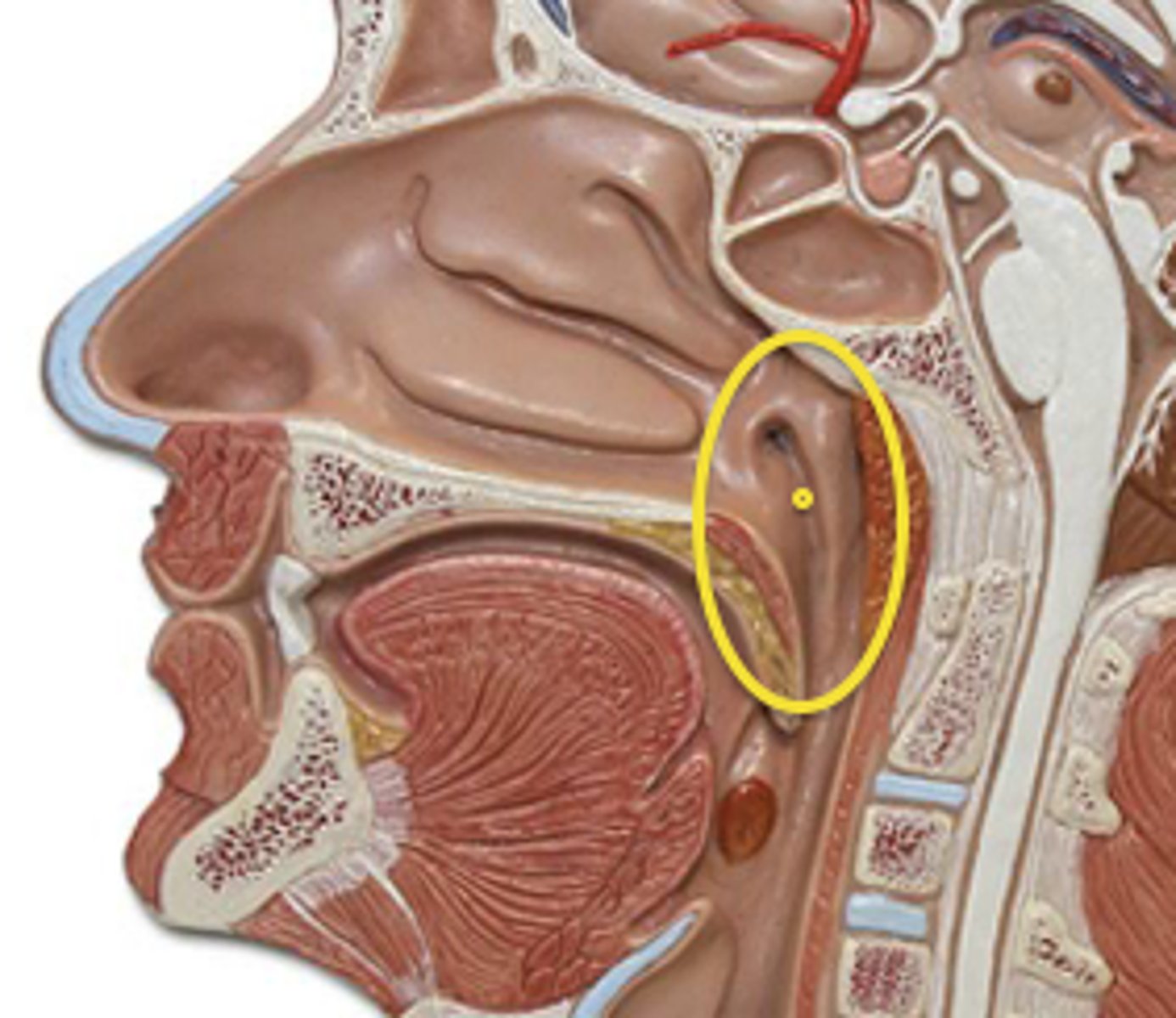
nasopharynx
mostly air
oropharynx
air and food passageway
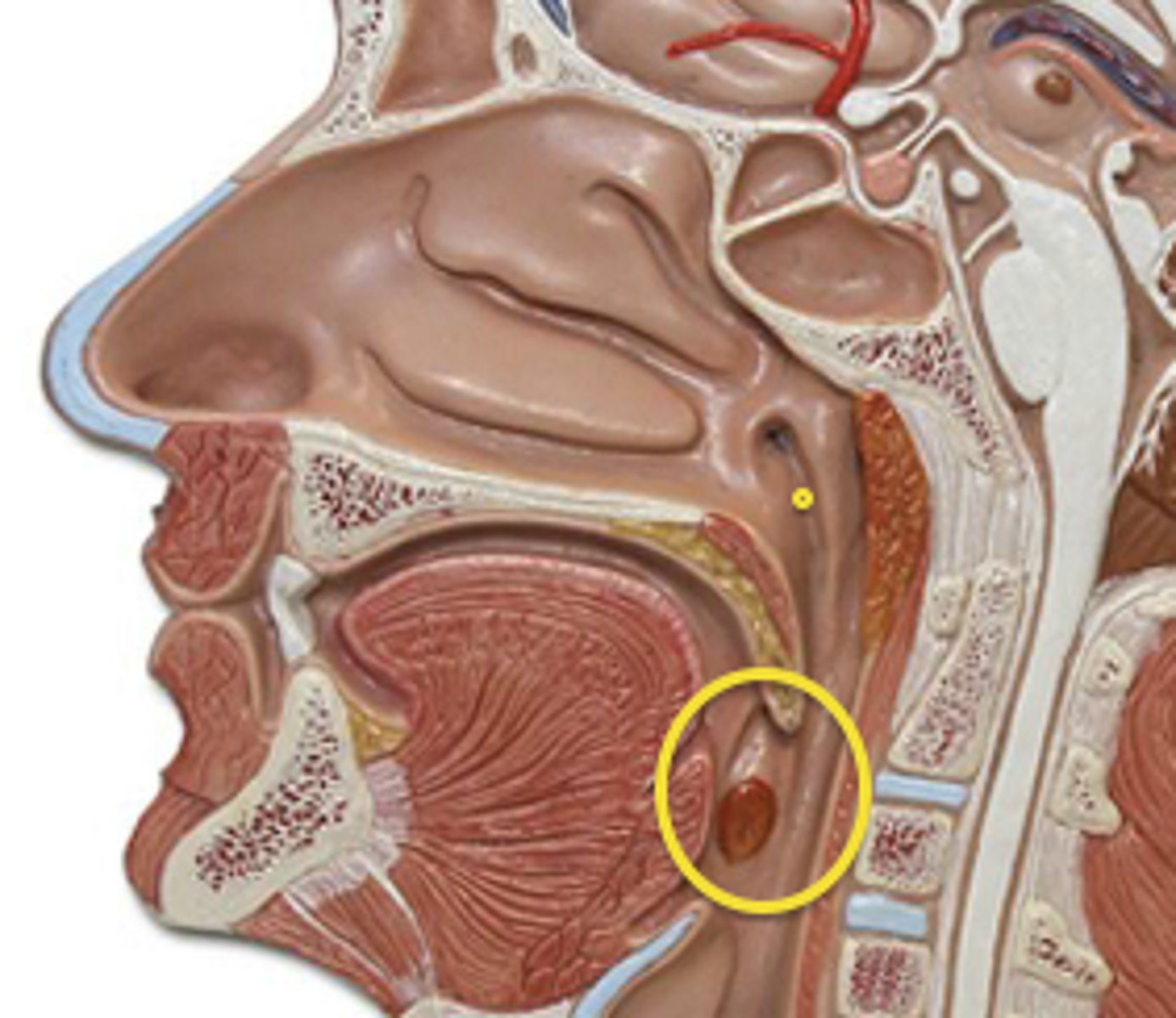
laryngopharynx
air and food pasage
Larynx
- voice box
- passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea
- contains vocal cords
Larynx anatomy
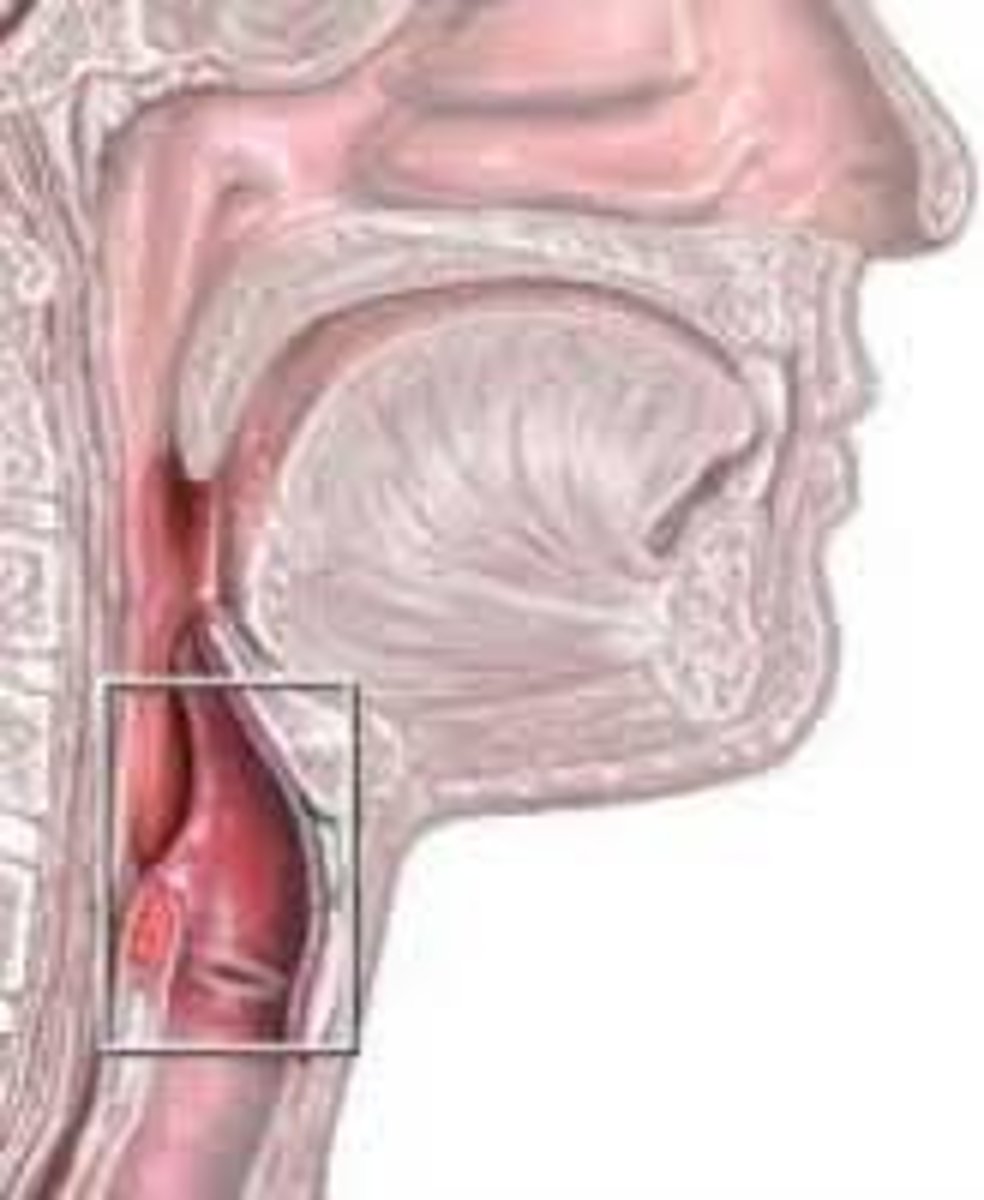
What are the two regions of the larynx?
epiglottis and glottis
Epiglottis
covers larynx during swallowing
Glottis
space between the vocal folds
Ventricular folds
hold breath, do not produce sound