LS 7C Midterm 1
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
signaling cell
the source of the signaling molecule
signaling molecule
the carrier of information transmitted when the signaling molecule binds to a receptor; also referred to as a ligand
receptor protein
the molecule on the responding cell that binds to the signaling molecule.
responding cell
the cell that receives information from the signaling molecule
receptor activation
the "turning on" of a receptor, which often occurs when a signaling molecule binds to a receptor on a responding cell
signal transduction
the process in which an extracellular molecule acts as a signal to activate a receptor, which transmits information through the cytoplasm
response
a change in cellular behavior, such as activation of enzymes or genes, following a signal
termination
in protein translation, the time at which the addition of amino acids stops and the completed polypeptide chain is released from the ribosome. In cell communication, the stopping of a signal
endocrine signaling
signaling by molecules that travel through the bloodstream
paracrine signaling
signaling by a molecule that travels a short distance to the nearest neighboring cell to bind its receptor and deliver its message
growth factoring
any one of a group of small, soluble molecules, usually the signal in paracrine signaling, that affect cell growth, cell division, and changes in gene expression
autocrine signaling
signaling between different parts of a cell; the signaling cell and the responding cell are one and the same
ligand
alternative term for a signaling molecule that binds with a receptor, usually a protein
ligand-binding site
the specific location on the receptor protein where a signaling molecule binds
G protein-coupled receptor
a receptor that couples to G proteins, which bind to the guanine nucleotides GTP and GDP
G protein
a protein that binds to the guanine nucleotides GTP and GDP
receptor kinase
a receptor that is an enzyme that adds a phosphate group to another molecule
phosphatase
an enzyme that removes a phosphate group from another molecule
ion channels
cell-surface receptors that open and close, thereby altering the flow of ions across the plasma membrane
second messenger
an intermediate cytosolic signaling molecule that transmits signals from a receptor to a target within the cell; (first messengers transmit signals from outside the cell to a receptor)
binding affinity
the tightness of the binding between the receptor and the signaling molecule
tissue
a collection of cells that work together to perform a specialized function
organ
two or more tissues that combine and function together
cytoskeleton
in eukaryotes, an internal protein scaffold that helps cells to maintain their shape and serves as a network of tracks for the movement of substances within cells
cell junction
a complex of proteins in the plasma membrane where a cell makes contact with another cell or the extracellular matrix; allows tissues to be held together so that they can function as a unit; physically connect one cell to another and anchor cells to the cellular matrix
extracellular matrix
a meshwork of proteins and polysaccharides outside the cell; the main constituent of connective tissue; important for strong, properly shaped tissues and organs
epidermis
the outer layer of skin which serves as a water-resistant, protective barrier; composed of multicellular layers of skin cells (epithelial tissue)
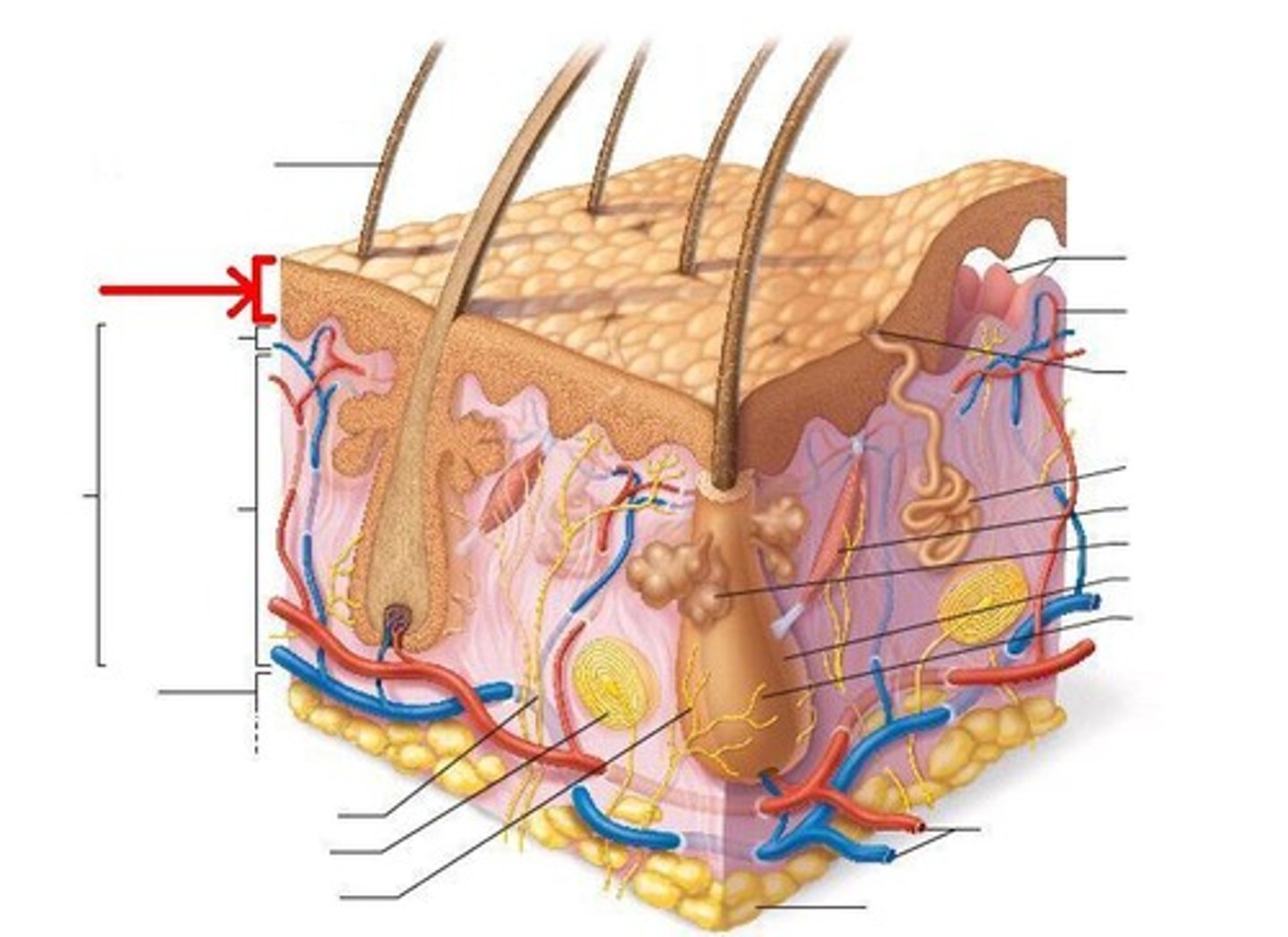
dermis
the layer of skin beneath the epidermis, consisting of connective tissue, hair follicles, blood and lymphatic vessels, and glands; it supports the epidermis both physically and by supplying it with nutrients and provides a cushion surrounding the body
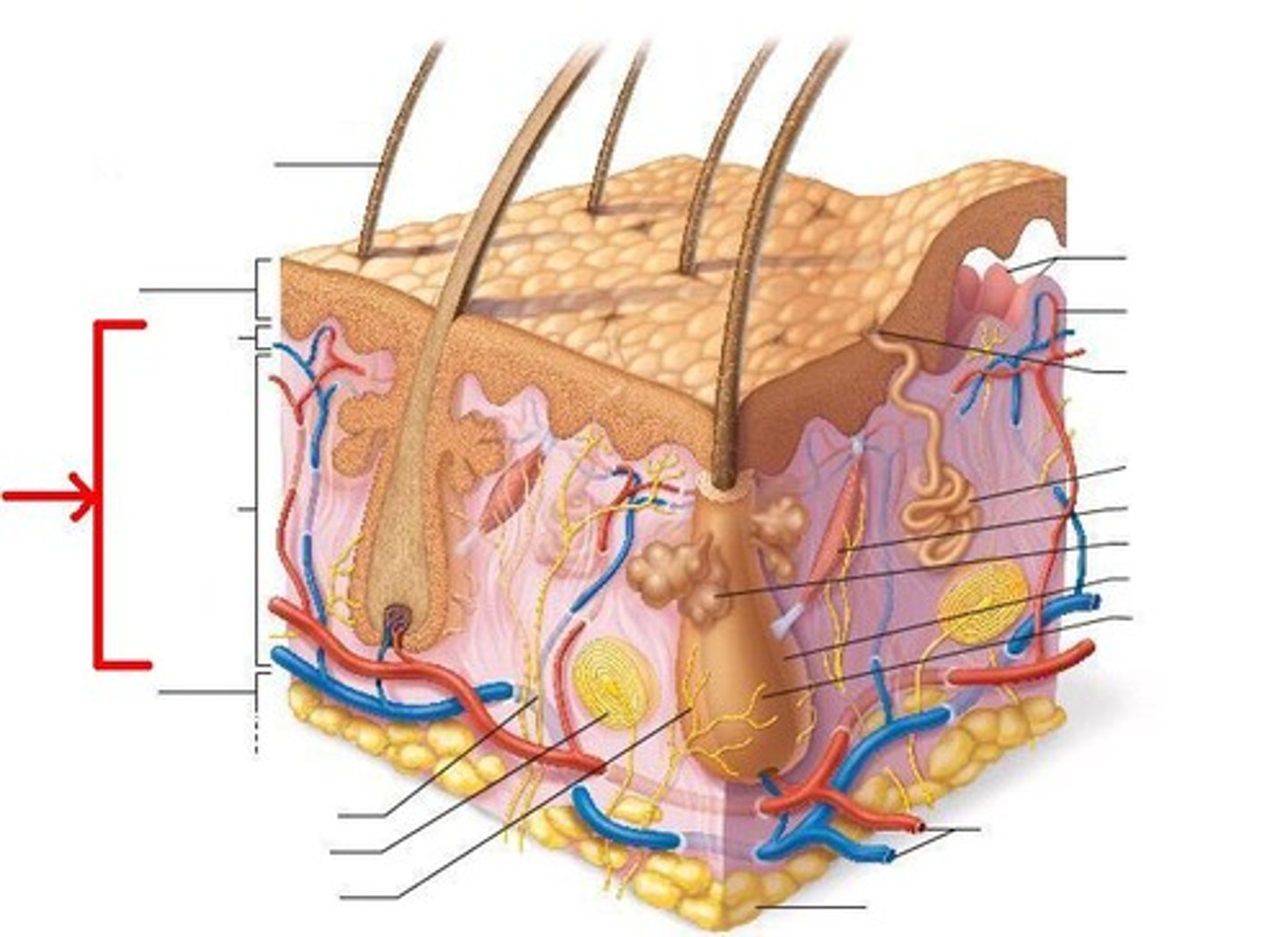
basal lamina
a specialized form of extracellular matrix that underlies and supports all epithelial tissues
microtubule
a hollow, tubelike polymer of tubulin dimers that helps make up the cytoskeleton
microfilament
a helical polymer of actin monomers, present in various locations in the cytoplasm, that helps make up the cytoskeleton
intermediate filament
only in animal cells; a polymer of proteins, which vary according to cell type, that combine to form strong, cable-like filaments that provide animal cells with mechanical strength
tubulin
dimers (composed of an α tubulin and a β tubulin) that assemble into microfilaments; one α tubulin and one β tubulin combine to make a tubulin dimer and the tubulin dimers are assembled to form the microtubule
centrosome
a compact structure that is the microtubule organizing center for animal cells
actin
a protein subunit that makes up microfilaments; used by both striated and smooth muscles to contract and generate force; microfilaments are polymers of these monomers arranged to form a helix
dynamic instability
cycles of shrinkage and growth in microtubules
motor protein
any of various proteins that are involved in intracellular transport or cause muscle contraction by moving the actin microfilaments inside muscle cells
kinesin
a motor protein, similar in structure to myosin, that transports cargo toward the plus end of microtubules
dynein
a motor protein that carries cargo away from the plasma membrane toward the minus ends of microtubules
cilium
a hairlike organelle that propels the movement of cells or of substances within cells or out of the body; shorter than a flagellum
flagellum
an organelle that propels the movement of cells or of substances within cells; longer than a cilium
myosin
a motor protein found in cells that carries cargo to the plus ends of microfilaments and is also used by both striated and smooth muscles to contract and generate force; muscle contraction depends on the interaction of this with microfilaments, and is powered by ATP
cell adhesion molecule
a cell-surface protein that attaches cells to one another and to the extracellular matrix
cadherins
transmembrane proteins; a calcium-dependent adherence protein, important in the adhesion of cells to other cells; there are many different types of these but they may only bind with ones of the same type; bind to both intermediate filaments and microfilaments
integrin
a transmembrane protein, present on the surface of virtually every animal cell, that enables cells to adhere to the extracellular matrix; their cytoplasmic domain is linked to microfilaments or intermediate filaments; also act as receptors that communicate information about the extracellular matrix to the interior of the cell
adherens junction
a beltlike junctional complex composed of cadherins that attaches a band of actin to the plasma membrane
desmosome
a buttonlike point of adhesion that holds the plasma membranes of adjacent cells together; cell junctions that allow cells to adhere to one another
hemidesmosome
a type of desmosome in which integrins are the prominent cell adhesion molecules; integrins are the prominent cell adhesion molecules in these
tight junctions
establish a seal between cells so that the only way a substance can travel from one side of a sheet of epithelial cells to the other is by moving through the cells by means of one of the cellular transport mechanisms
gap junction
a type of connection between the plasma membranes of adjacent animal cells that permits materials to pass directly from the cytoplasm of one cell to the cytoplasm of another; a complex of integral membrane proteins called connexins arranged in a ring
plasmodesmata
connections between the plasma membranes of adjacent plant cells that permit molecules to pass directly from the cytoplasm of one cell to the cytoplasm of another; the plasma membranes of the two connected cells are actually continuous
molting
periodic shedding, as of an exoskeleton
metamorphosis
the process in some animals in which the body changes dramatically at key stages in development
neurosecretory cell
a neuron in the hypothalamus that secretes hormones into the bloodstream
pituitary gland
A gland beneath the brain that produces a number of hormones, including growth hormone
peptide hormone
hydrophilic hormone, a hormone that is a short chain of linked amino acids
amine hormone
hydrophilic hormone, a hormone that is derived from a single aromatic amino acid, such as tyrosine
steroid hormone
hydrophobic hormone; a hormone that is derived from cholesterol; sex hormones are these type of hormones
releasing factor
a peptide hormone that signals to the anterior pituitary gland through blood vessels, leading to a much larger release of associated hormones from that organ
anterior pituitary gland
the region of the pituitary gland that forms from epithelial cells that develop and push up from the roof of the mouth; it receives hormones from the hypothalamus that stimulate it to release hormones in turn
posterior pituitary gland
the region of the pituitary gland that develops from neural tissue at the base of the brain and into which neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus extend that secrete releasing factors
tropic hormone
a hormone that controls the release of other hormones
oxytocin
a posterior pituitary gland hormone that causes uterine contraction during labor and stimulates the release of milk during breastfeeding
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
a posterior pituitary gland hormone that acts on the kidneys and controls the water permeability of the collecting ducts, thus regulating the concentration of urine that an animal excretes; also known as vasopressin
thyroid gland
a gland located in the front of the neck that leads to the release of two peptide hormones, thyroxine and triiodothyorine
adrenal glands
paired glands located adjacent to the kidneys that secrete cortisol in times of stress
parathyroid gland
a gland adjacent to the thyroid gland that secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH), which, with calcitonin, regulates the actions of bone cells
pineal gland
a gland located in the thalamic region of the brain that responds to autonomic nervous system input by secreting melatonin, which controls wakefulness
adrenal medulla
the inner part of the adrenal gland, which is stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system
acclimatization
an adaptive change in body function to a new environment
paracrine function
chemical compounds that act locally; ex. growth factors and histamines
autocrine function
chemical compounds that act on the secreting cell itself; the chemical signals may stimulate or inhibit their own secretion
pheromone
a water- or airborne chemical compound released by animals into the environment that signals and influences the behavior of other members of their species
external fertilization
fertilization that takes place outside the body of the female; in aquatic organisms, for example, eggs and sperm are released into the water
internal fertilization
fertilization that takes place inside the body of the female
r-strategist
a species that produces large numbers of offspring but provides few resources for their support
k-strategist
a species that produces relatively few young but invests considerable resources into their support
yolk
a substance in the eggs of animals with external fertilization that provides all the nutrients that the developing embryo needs until it hatches
amnion
in the amniotic egg, a membrane surrounding a fluid-filled cavity that allows the embryo to develop in a watery environment
allantois
in the amniotic egg, a membrane that encloses a space where metabolic wastes collect
chorion
in the amniotic egg, a membrane that surrounds the entire embryo along with its yolk and allantoic sac
extraembryonic membrane
in the amniotic egg, one of several sheets of cells that extend out from the developing embryo and form the yolk sac, amnion, allantois, and chorion
oviparity
internal fertilization egg birth; animals that lay eggs; used by most insects, fish, amphibians, and reptiles, as well as all birds; very little, if any, embryonic development inside the mother, and all the nutrients for the developing embryo come from the yolk
ovoviviparity
giving birth to live young, with nutritional support of the embryo from the yolk; embryos develop inside eggs that are retained inside the mother until they hatch
viviparity
giving birth to live young, with nutritional support of the embryo from the mother
placenta
in placental mammals, an organ formed by the fusion of the chorion and allantois that allows the embryo to obtain nutrients directly from the mother
gonads
in mammals, the part of the reproductive system where haploid gametes are produced; male gonads are testes, where sperm are produced; female gonads are ovaries, where eggs are produced
acrosome
an organelle that surrounds the head of the sperm containing enzymes that enable sperm to transverse the outer coating of the egg
scrotum
a sac outside the abdominal cavity of the male that holds the testes
seminiferous tubules
a series of tubes in the testes where sperm are produced
epididymis
an organ that lies above the testes where sperm become motile and are stored prior to ejaculation
vas deferens
a long, muscular tube from the scrotum, through the abdominal cavity, along the bladder, and connecting with the ejaculatory duct
ejaculatory duct
the duct through which sperm travel from the vas deferens to the urethra
urethra
a tube from the bladder that in males carries semen as well as urine from the body
prostate gland
an exocrine gland that produces a thin, slightly alkaline fluid that helps maintain sperm motility and counteracts the acidity of the female reproductive tract
seminal vesicles
two glands at the junction of the vas deferens and the prostate gland that secrete a protein- and sugar-rich fluid that makes up most of the semen and provides energy for sperm motility
bulbourethral glands
glands below the prostate gland that produce a clear fluid that lubricates the urethra for passage of the sperm
oocyte
the unfertilized egg cell produced by the mother; the developing female gamete
fallopian tube (oviduct)
a tube from each ovary, through one of which a released oocyte passes.
uterus
a hollow organ within the reproductive tract of female mammals with thick, muscular walls that is adapted to support the developing embryo if fertilization occurs and to deliver the baby during birth