MAE Consonant Allophones
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Suprasegmental Features:
Refer to aspects of speech that extend beyond or “above” the segment level. (Syllables, stress, tone, intonation, rhythm)
Sonority
A phonological feature related to acoustic energy.
Phonemes that are more sonorous typically…
Are louder, have more airflow and have more vocal fold vibration.
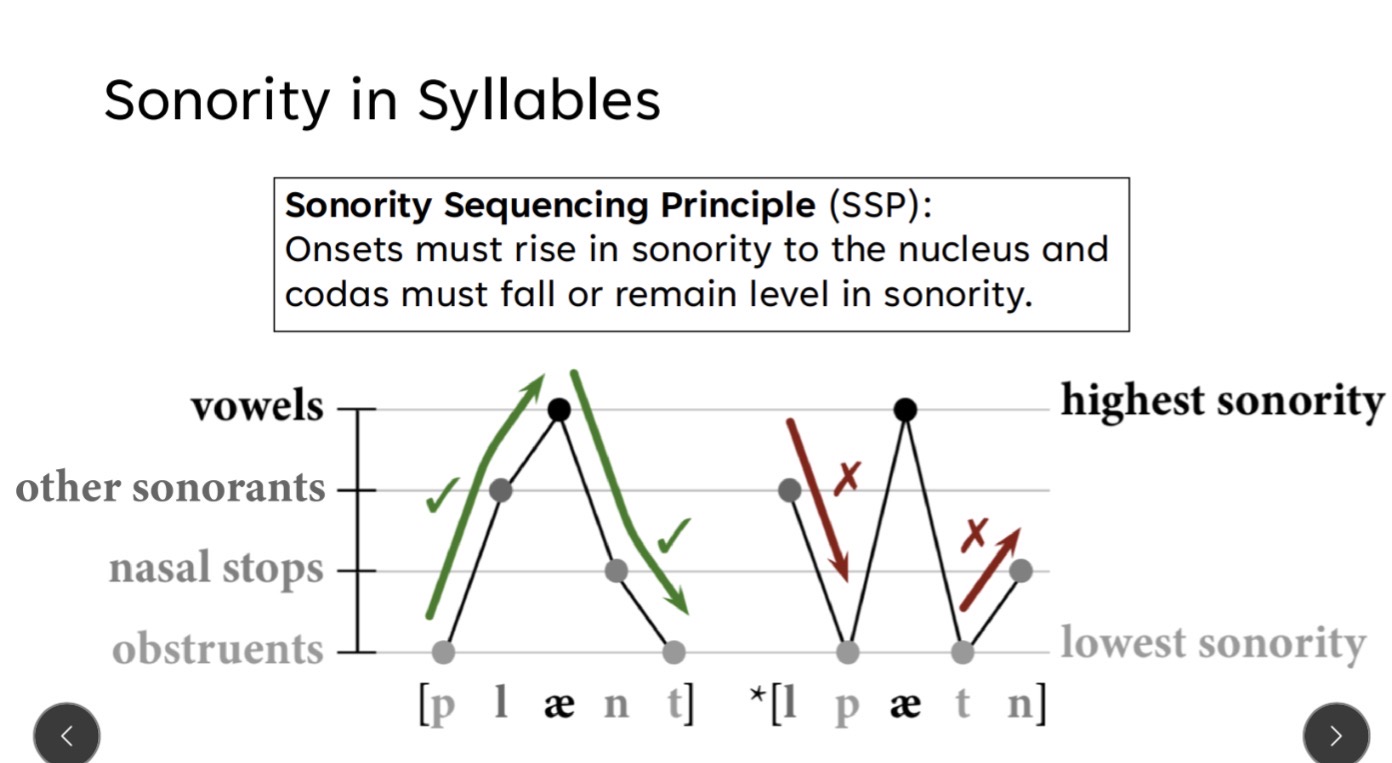
Sonority Sequencing Principle (SSP)
Onsets must rise in sonority to the nucleus and codas must fall or remain level in sonority.
Stress
Is a lexical characteristic that occurs at three levels:
Primary: most prominent stress in a word.
Secondary: less prominent but noticeable.
Unstressed
Tone
Not a contrastive feature in English.
Intonation
A feature at the phrase or sentence level.
Falling: statements, commands
Rising: yes/no questions
Mixed: lists, choice questions
Contrastive
Rhythm
The timing of speech. Is highly variable. English is often desceribed as “stress-Timed”
Acoustic Correlates of Stress:
Intensity (loudness)
Duration (length)
Frequency (pitch)
Minimal Pair
Two separate/distinct words that differ by only one phoneme.
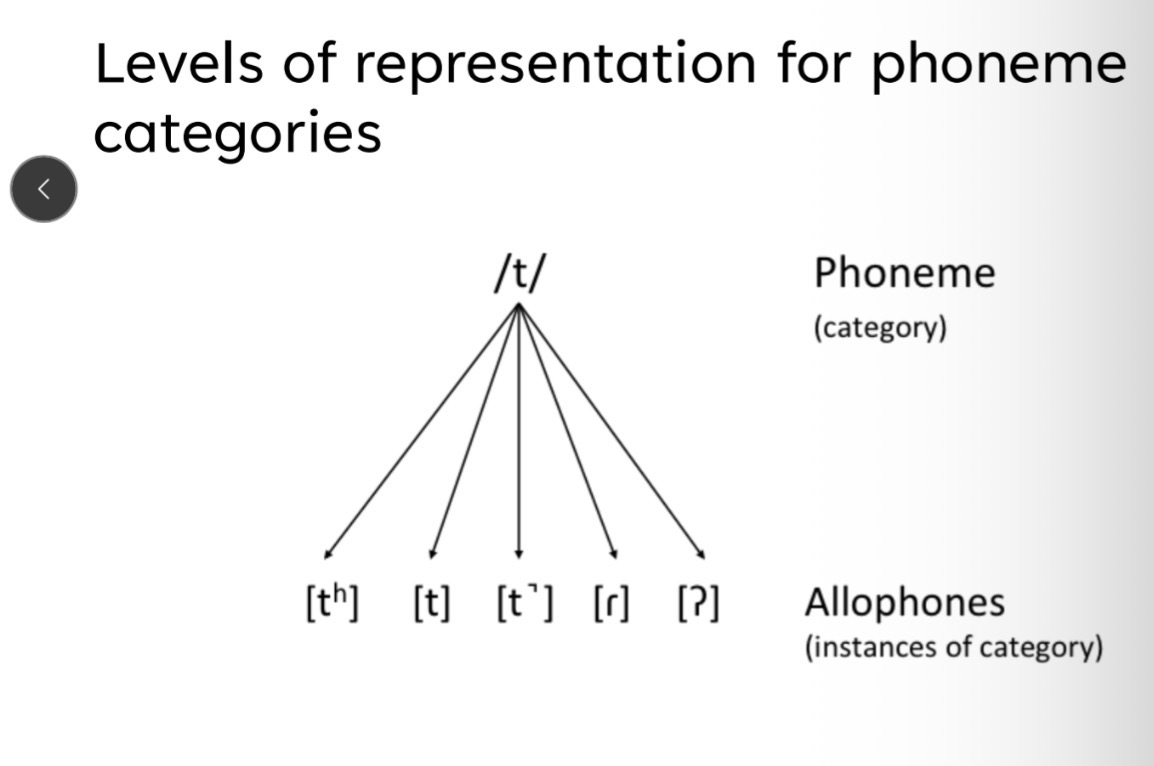
Allophones
Levels of representation for phoneme categories.
Dialects of a language have unique…
Characteristics spanning all domains (phonetics, phonology, morphosyntax, vocabulary and pragmatics)
Dialect features can be:
Phonological, morphosyntactic or lexical
Accent
The phonetics and phonology of a dialect.
Idiolect
Personal dialect of an individual speaker. Vocal tract and laryngeal physiology result in unique aspects of voice quality, resonance and pitch.
A phoneme is really just…
A family or category of sounds. Broad transcription identifies the phoneme “categories”. Narrow transcription differentiates between examples of the category.
One (1) way that variations can be address is when the original phoneme is…
Replaced with a different phoneme.
Ex. Add voicing to /s/ = [z]
The second (2) way that variations can be addressed is when the original phoneme can be modified with…
A diacritic symbol
Ex. Add voicing to /s/ = [s̬]
Some variations can only be expressed with diacritics such as
Nasalization of a vowel
Ex. [i] = [ĩ]
Transcription Practice: “spooky”
Broad: /ˈspu.ki/
Narrow: [ˈspuː.kʰiː]
Nasals are:
Consonants that have the velopharyngeal port open and the oral cavity occluded. Airflow is blocked out of the oral cavity and flows freely through and out of the nasal cavity.
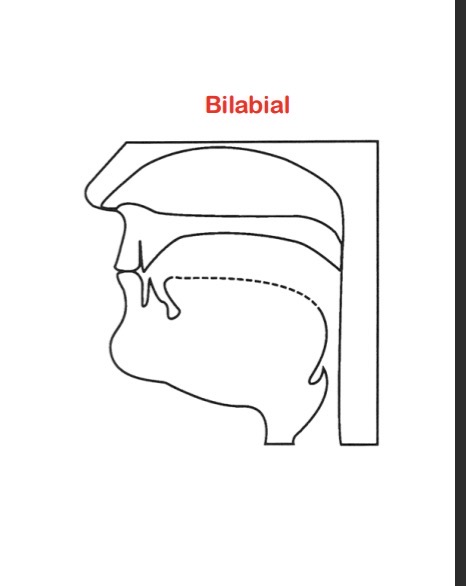
/m/ → Bilabial Nazalisation
occlusion at the lips
Tongue neutral
Ex: mood, dime
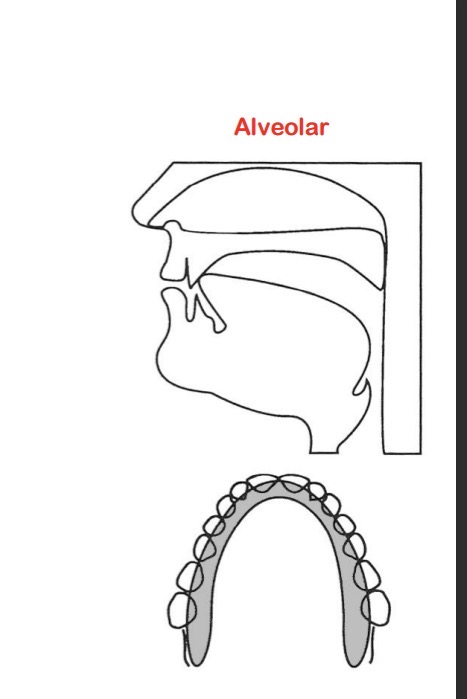
/n/ - alveolar nazalisation
occlusion is at alveolar ridge (tongue blade)
Sides of the tongue are against upper teeth
Ex: nook, fine, knot
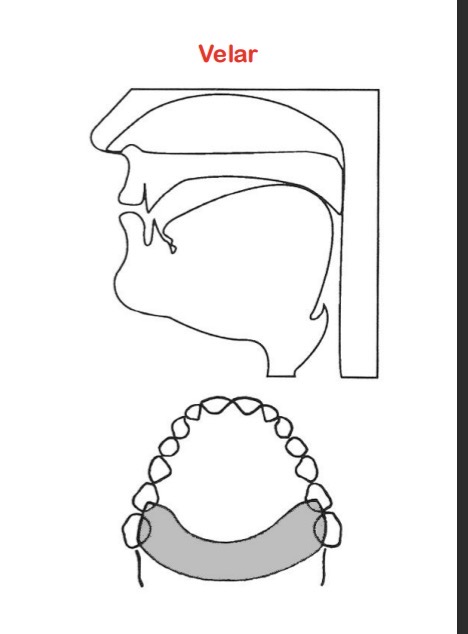
/ŋ/ - Velar Nasalization
Occlusion is at the soft palate (velum)
“Ng” sound
Cannot occur in onset (phonotactic constraint)
Ex: sing, angle