BIO FINAL (part 1)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Potential and kinetic energy
potential- energy an object possesses
kinetic- energy of motion
1st Law of Thermodynamics
the total amount of energy in the universe is constant it can’t be created or destroyed
Endergonic and Exergonic reactions - meanings and examples
exergonic- releases energy (cellular respiration - from food)
endergonic- requires input of energy (photosynthesis - from sun)
Metabolism
is made up of all endergonic and exergonic chemical reactions
ATP, ADP
ATP- immediate source of energy
ADP- is left after ATP is used as a fuel and loses one phosphate
What are enzymes?
proteins that function as biological catalysts
Enzymes - substrate, active site
enzymes have target molecules called substrates (where it wants to catalyze)
active site where substrate attaches TO enzyme to be broken down
Be able to explain how metabolism is regulated (Feedback inhibition)
if a reaction has made ENOUGH of a product the products can act as an inhibitor to STOP the enzyme from making more
Competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors
competitive- compete for enzyme site BLOCK substrate
non-competitive- change shape of enzyme active site no longer FITS substrate
Know the equation for cellular respiration. What are the reactants and products?
C6 H12 O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP (energy)
3 stages of cellular respiration in order
glycolysis
citric acid cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
What happens during each stage?
glycolysis- glucose to pyruvate
citric acid cycle - (IN MITOCHONDRIA) breaks down pyruvate, CO2 relseased, electrons carried to next stage
oxidative phosphorylation- (INNER mitochondria) electrons through transport chain release energy, water formed
Electron carriers
NADH and FADH2
Which organelle is involved in cellular respiration?
mitochondrion
Glycolysis
glucose to pyruvate
Compare fermentation and cellular respiration. Which produces more ATP?
Cellular respiration
Lactic acid fermentation vs alcohol fermentation
LAF- lactate and 2 ATP our muscles can do it and can be used to make dairy
AF- ethanol, CO2, and 2 ATP, yeasts do AF to make alc
What is photosynthesis?
Know the equation for photosynthesis
sunlight energy + CO2 + H2O → glucose + O2
Autotrophs, heterotrophs
autotrophs - plants create own food through photosynthesis
heterotrophs - animals obtain food through other organisms
Stomata, mesophyll, thylakoids, grana
stomata- tiny pores in leaf let CO2 in and out
mesophyll- green tissue in interior of leaf have chloroplasts
thylakoids- disks inside chloroplasts
grana- stack of thylakoids
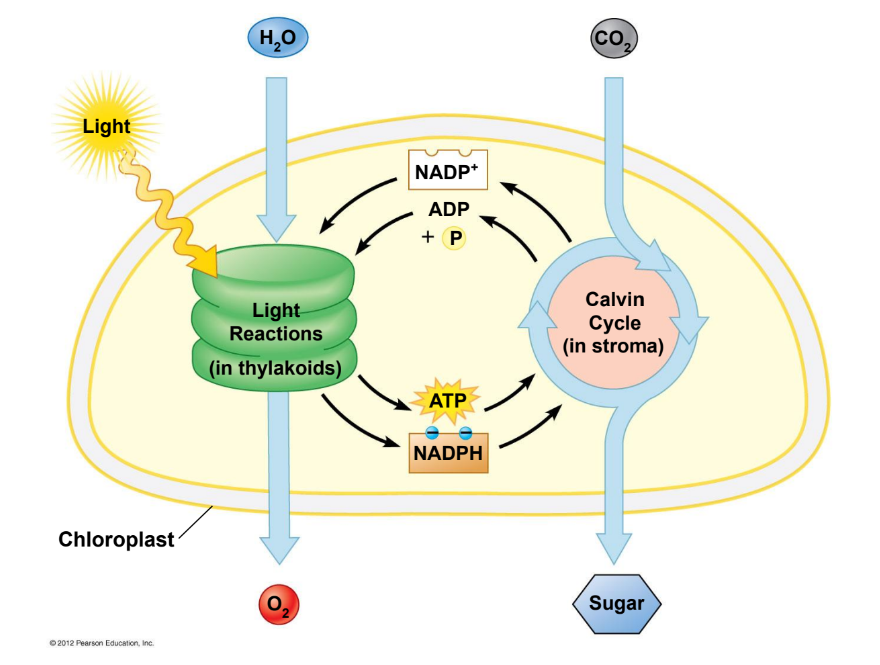
During photosynthesis - where do light reactions occur? Where does the Calvin cycle occur?
light reaction- thylakoid membrane
Calvin cycle- stroma (fluid in chloroplasts)
What is carbon fixation?
incorporation of CO2 into organic compounds
Chlorophyll and which colors of light are reflected?
Chlorophyll a- reflects green
Chlorophyll b- reflects yellow-green
carotenoids- reflect yellow and orange
Plant cells perform…
photosynthesis AND cellular respiration
What causes global warming?
increased level of green house gasses
Be able to label the Stages of Photosynthesis figure
Neanderthals relationship to modern humans
closest relative, interbred with modern humans
What is natural selection?
process where organisms with certain traits more likely to survive and reproduce
What is the process of natural selection?
genetic variation, overproduction of offspring, differential survival and reproduction
Homologous structures, examples
features in different species w similar structure
Vestigial structures, examples
structures that served important functions in an organisms ancestors but now of little importance
Evidence for evolution - be able to complete the table on the evolution worksheet
Innate vs adaptive immune response
innate- available when born
adaptive- built over time
First line of defense, examples
BARRIERS skin, mucus, tears, saliva, etc.
Second line of defense, examples
white blood cells, fever, inflammation, etc.
Cells of the innate immune response: types of leukocytes
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, dendritic cells, mast cells, natural killer cells
Cytokines
cell signaling molecules
Second line of defense, examples
white blood cells, non specific responses (vasodilation , fever, inflammation)
Pyrogens
chemicals that cause fever
Third line of defense
adaptive immune response (specific)
Antigen, antibody
antigen- protein on surface of cell or virus trigger immune response
antibody- defensive protein specialized for specific antigens
MHC proteins
major histocompatibility complex proteins recognized as “self” cells by immune system
Lymphocytes - B calls and T cells, what do they each do?
b cells- produce antibodies
t-cells - directly attack foreign cells
Immune memory
activate when exposed to antigen
Passive vs. Active immunization, examples
passive- antibodies to someone who is or has been sick from someone who has immunity
active - vaccination inject someone with dead or weakened pathogen
Types of vaccines
live attenuated- weakened version of virus
inactivated/killed - killed virus
subunit vaccine- parts of virus like proteins not actual virus
viral vector- harmless virus to give viral DNA
nucleic acid- mRNA that codes for virus given so body produces protein and antibodies
Herd immunity
large part of population is immune to specific disease through vaccination
Be able to briefly describe the 3 lines of defense against pathogens
1st barriers (skin, mucus, saliva, tears)
2nd non specific (white blood cells, fever, etc.)
3rd specific (antigens and antibodies recognize self and non self, b cells, t cells)