Lecture 26: Gowth Hormone and IGF-1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
________ produces Growth Hormone (GH) in anterior Pituitary
somatotrophs
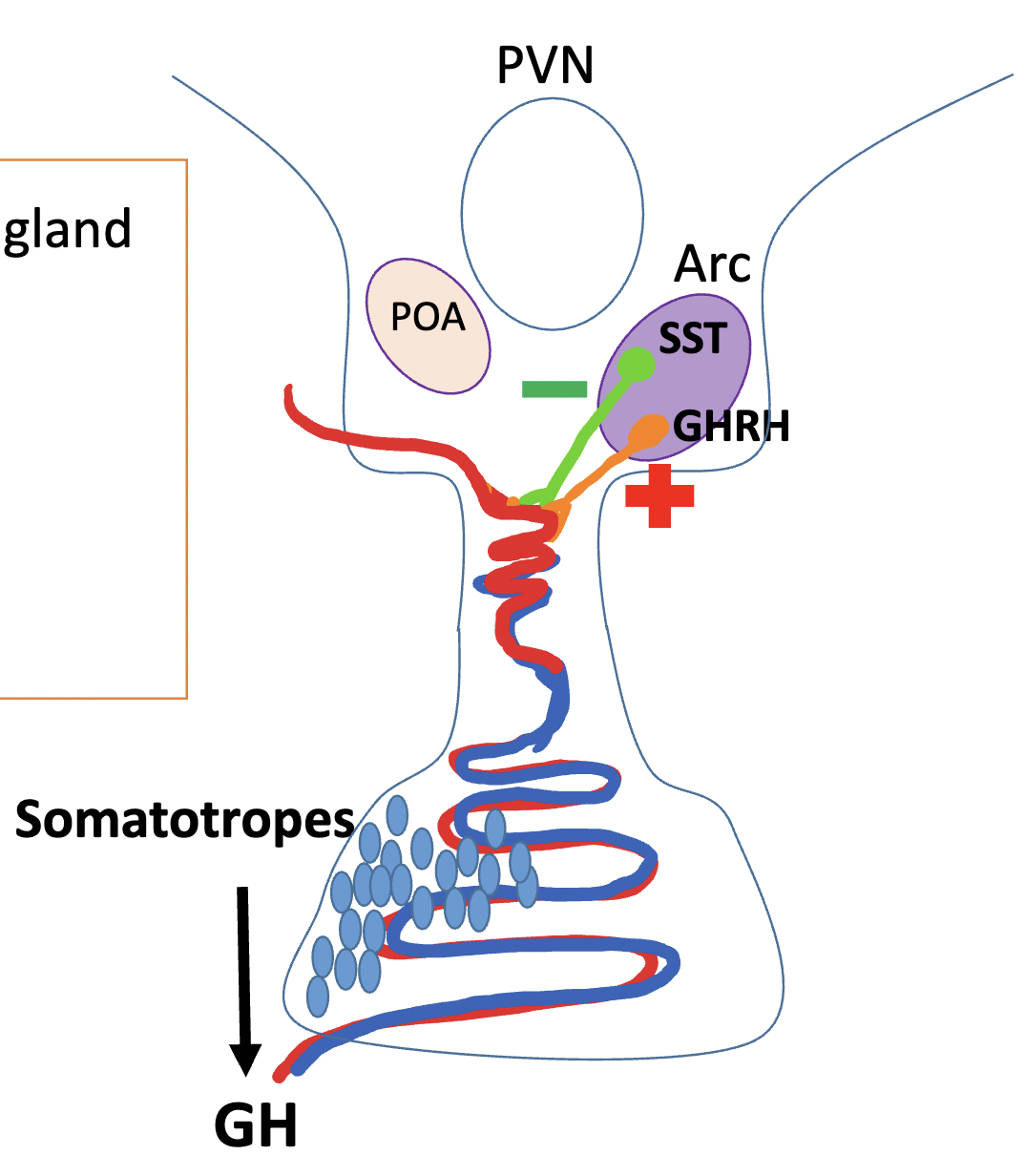
t/f: GH is released in a pulsatile secretion pattern
true
t/f: GHRH regulates SYNTHESIS and SECRETION of GH
YESS true
t/f: Somatostatin regulates SECRETION of GH
Yes true, only secretion and NOT SYNTHESIS
t/f: Somatostatin regulates SYNTHESIS and SECRETION of GH
FALSEE!!! Somatostatin only regulates secretion!!!
what 3 signals regulate GH release?
Gonadal Sterioids, Thyroid Hormones, Cortisol
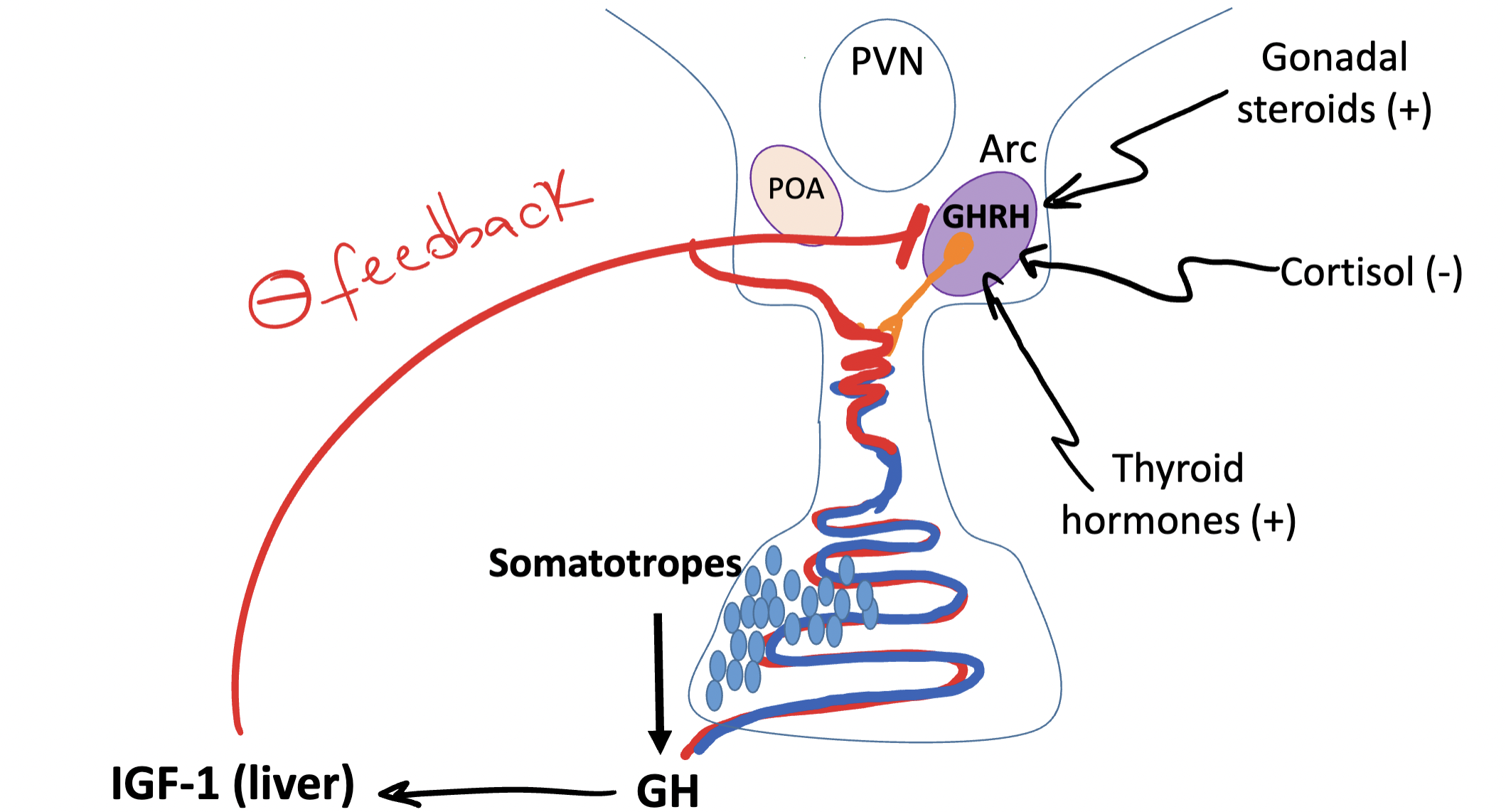
Once GH is released by Somatotropes, it releases ______ in the liver
IGF-1 (which makes a negative feedback to ARC when there is too much production )
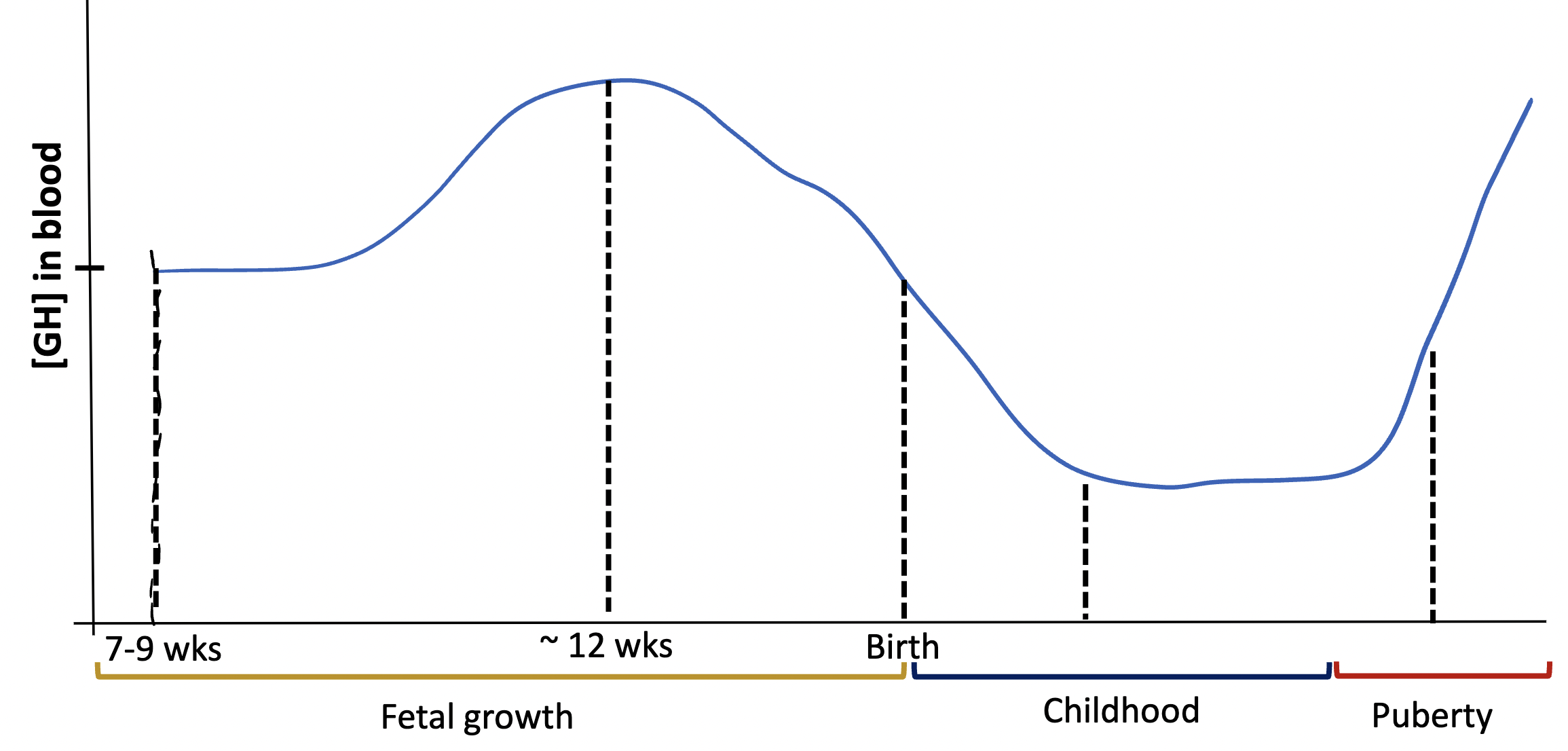
in this graph, why is there a sudden increase during puberty?
sex hormones (gonadal steroids) and Thyroid Hormones are stimulating growth
Thyroid Hormone, such as T3, has significant effect on:
a. postnatal growth and bone maturation
b. growth hormone for reproduction
c. inhibits growth hormone
a. postnatal growth and bone maturation.
thyroid hormone, T3, stimulates bone growth by stimulating….
Hyprtrophic Chondrocyte differentiation
t/f: thyroid hormone, T3, stimulates bone mineralization and angiogenesis
yes true, this means its making new blood vessels and creating more circulation in bone for nutrition and oxygen
Sex Hormones (Gonadal Hormones), has significant effect on:
a. postnatal growth and bone maturation
b. growth hormone for reproduction
c. inhibits growth hormone
b. growth hormone for reproduction. this is why its called a puberty hormones
the Gonadal Hormone, androgen, stimulates GH from _________ accelerating growth during puberty
somatotrophs
the Gonadal Hormone, estrogen, stimulates closure of ____________ which stops growth
epiphyseal plate…. therefore when women reach menopause, more estrogen will occur blocking growth of bones and may cause issues related to bones
Cortisol, (glucocorticoids), has significant effect on:
a. postnatal growth and bone maturation
b. growth hormone for reproduction
c. inhibition of growth hormone
c. inhibition of growth hormone. it blocks Gh from somatotropes via inhibirion of hypothalamus
cortisol blocks GH from __________ via inhibition of hypothalamus and stimulation of __________ that inhibits/impairs growth hormone (GH)
somatotropes, somatostatin
what are the loactions that do the action of cortisol inhibition
Hypothalamic, pituitary, and peripheral
what type of receptor do growth hormones (GH) use
cytokine receptor (similar to tyrosine kinase receptor)
what happens in the cytokine receptor once GH binds?
Jak-Stat-Dimer process:
once Gh binds, Jaks cross phosphorylate eachother on tyrosine, once these Jaks are activates they will phosorylate the tyrosine receptors, now that the tyrosine receptor is activated it will attract Stat 1 and Stat2 molecules, once they are phosphorylates, they will leave and make a dimer which then are transported to the nucleus to start transcription
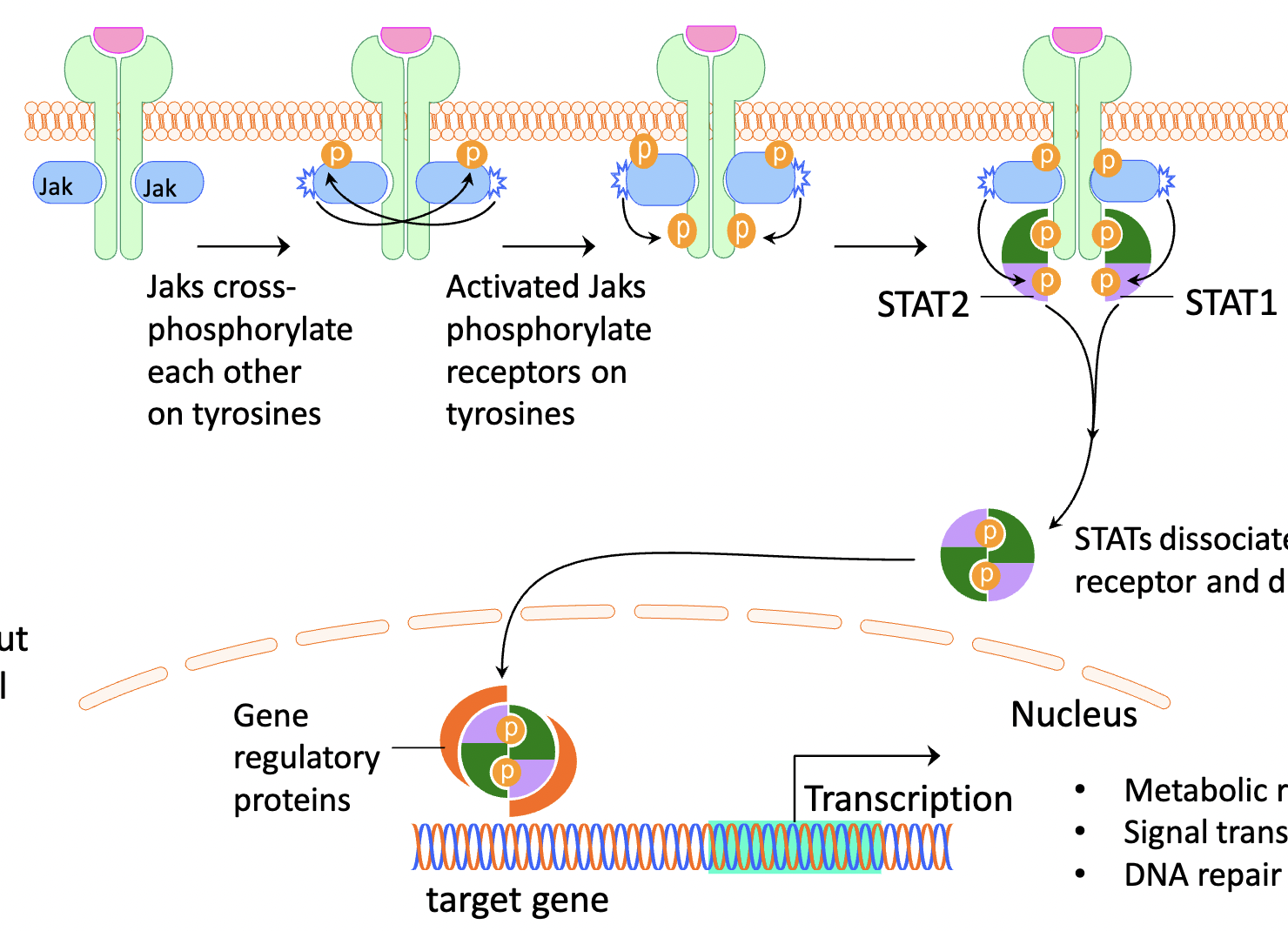
what effects of the STAT1 and 2 have once transcription at the gene occur?
metabloc regulation(IGF-1; IGFBs) , signal transducers (stats), DNA repair genes
which target has MOST receptors of GH (responds to GH the most when GH is present)
LIVER!!!
what are other targets that have receptors of GH (responds to GH the most when GH is present)
muscle, adipose tissue, kidney, heart, Bone
IGF-1 is stimulated by :
GH
t/f: during fasting (not eating enough), GH effects are mediated by IGF-1
False!!! if you have no food, that means no energy so how can you make IGF-1!!
t/f: during fasting (not eating enough), GH effects are independent of IGF-1
yess that one is true
t/f: during fed state (you have food and energy), GH effects are mediated by IGF-1
yesss trueee! you can have storage of glycogen
Fasting state leads to (catabolism OR Anabolism)
catabolism
Fed states leads to (catabolism OR Anabolism)
anabolism
during fasting, is there IGF-1 production?? what does that mean??
NOO!! because there is no food so no energy in the body so GH cannot make IGF-1! So there will be no negative feedback on pituitary so it will lead to high GH
during fed state, is there IGF-1 production?? what does that mean??
YESS! there will be IGF-1 in the liver which will have a negative feedback on pituitary GH
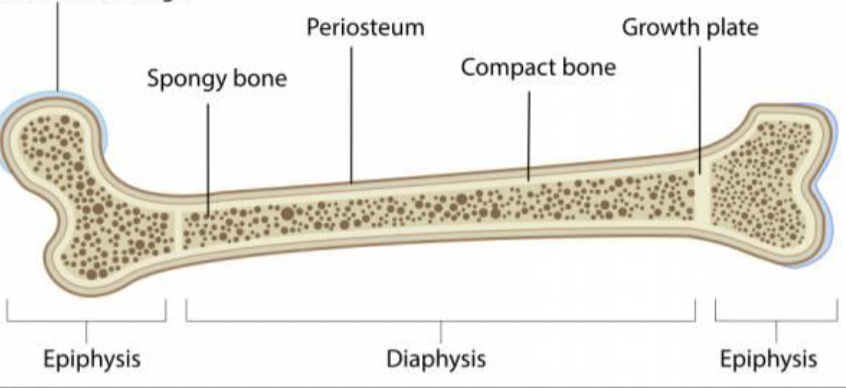
t/f: growth plate is the same as epiphyseal plate
yesss!! because if you add more cells, you elongate the bone
Since GH stimulates IGF-1 through the GH receptor (GHR), which zones of the bone does it affect?
(resting zone, proliferating zone, hypertrophic zone, ossification zone, or trabecular bone)
proliferating zone & hypertrophic zone
chondroblasts are present in the __________ (resting zone) which also activates what ?
epiphyseal plate, it stimulates GHR → IGF-1
Chondroblasts and Chondrocyte dictate what?
Bone length
Osteoblasts dictate what?
density
t/f: Bone length is dictates by osteoblast
FALSEE!! its by Chondroblasts and chondocytes
t/f: Density is dictated by Chondroblasts and chondocytes
FALSEE!! its by osteoblasts!! (scrubbies)
in a 13 yrs old, puberty is happeing! meaning more sex hormones like estrogen and androgens are being produced!! this stimulates the growth Hormones in which zone of the bone???
(resting zone, proliferating zone, hypertrophic zone, ossification zone, or trabecular bone)
resting zone!
What if estrogen is more predominant !!! how will that affect the growth Hormone ?
it inhibits growth and epiphyseal plate closes ☹
what zones of the bone does the thyroid hormone affect ?
(resting zone, proliferating zone, hypertrophic zone, ossification zone, or trabecular bone)
hypertrophic zone and ossification zone to elongate the bone
what is the role of cortisol in the bone growth? what two areas does it afffect
cortisol stops growth!! in the bone, it stops GHR in chondroblasts resulting in weak bones when high cortisol AND inhibits IGF-1R in chondrocytes in proliferating and hypertrophic zone, so even if there is high GH in resting zone, would not have IGF-1 bcuz all receptors are inhibited
t/f: prepubertal growth is the same for males and females
trueeee … until they grow up
t/f: closure of epiphyseal plate is more strongly regulated by androgens
FALSEE!!! its strongly regulated by ESTROGEN!!
what are 2 examples of dysregulation of GH???
Gigantism and Acromegaly
what is gigantism ?
before the closure of epiphyseal plates … so there was an excess GH before it closed
what is acromegaly?
after closure of epiphyseal plates …