Chapter 3 Theorems/ideas - Matrix Algebra
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Theorem 3 - Row operations on Determinants
Let A be a n x n matrix:
adding a multiple of one row to another does not change det A
Swapping two rows multiplies det A by -1
Multiplying a row by k multiples detA by k
Find det efficiently → row reduce, track swaps & scaling’s
Theorem 4 - Invertibility via Determinant
A is invertible ←> det A doesn’t = 0
Guarantees:
Zero determinant = no inverse
Links directly to the IMT
Theorem 5 - Determinant of a Transpose
det(AT) = det(A)
Lets you freely switch rows and columns in determinant arguments
Theorem 6 - Determinant of a Product
det(AB) = (detA)(detB)
Guarantees:
If either matrix is singular - product is singular
Used heavily in linear transformation arguments
Theorem 7 - Cramer’s Rule
If A is invertible and Ax = b, then:
where Ai(b) replaces column i of A with b
Mostly conceptual, not computational
Signals unique solution
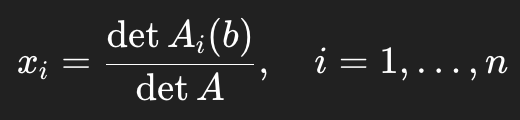
Theorem 8 - inverse via Adjugate
If A is invertible,
Guarantees:
Inverse exists only if det A doesn’t = 0
adjA = transpose of co-factor matrix
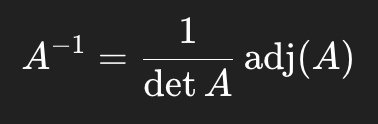
Theorem 9 - Determinant as Area / Volume
For 2 × 2 matrices:
|det A| = area of the parallelogram formed by columns
For 3 × 3 matrices:
|det A| = volume of the parallelpiped
Determinant measures geometric scaling
Theorem 10 - Determinant & Linear Transformations
If T(x) - Ax then:
“What does det mean geometrically?” → scaling factor

Determinant of a Triangular Matrix
For triangular matrices:
det A = product o diagonal entries
After row reduction, stop immediately
Zero Row → Zero Determinant
If A has a row or column of all zeros, then:
det A = 0
Also, if the rows are identical or linear dependent or the matrix is not invertible
Its a loss of dimension
Guarentee:
Matrix is singular
No Inverse