ARC 1013 Jones Final
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
needs
art
Architecture responds to the __________ of its users and rises to the level of __________.
geography
climate
surroundings
Architecture is connected to a particular place and relates to the specifics of __________, __________ and the __________.
Because it permanently records a civilization's aesthetic tastes, material resources, political and social aspirations.
Why is architecture important?
place
Architecture helps define __________.
Three principles Vitruvius felt essential to architecture
Firmness (structure)
Commodity (function)
Delight (beauty)
Representative
Abstract
Symbolic
Different types of architecture sletches
Solids, Rhythm, Voids, Color, Scale, Texture, Massing, Light, Proportion
Architects shape space using the following elements: (9)
Solids
Voids
The relationship between __________ and __________ creates architectural space.
Asymmetry
Architectural elements that are unevenly spaced in size, shape and/or position
Scale
The size or proportion a building element appears to have relative to other elements of known or assumed size
Proportion
A quantified relationship among the parts of an element, as well the relationship of that element to the whole
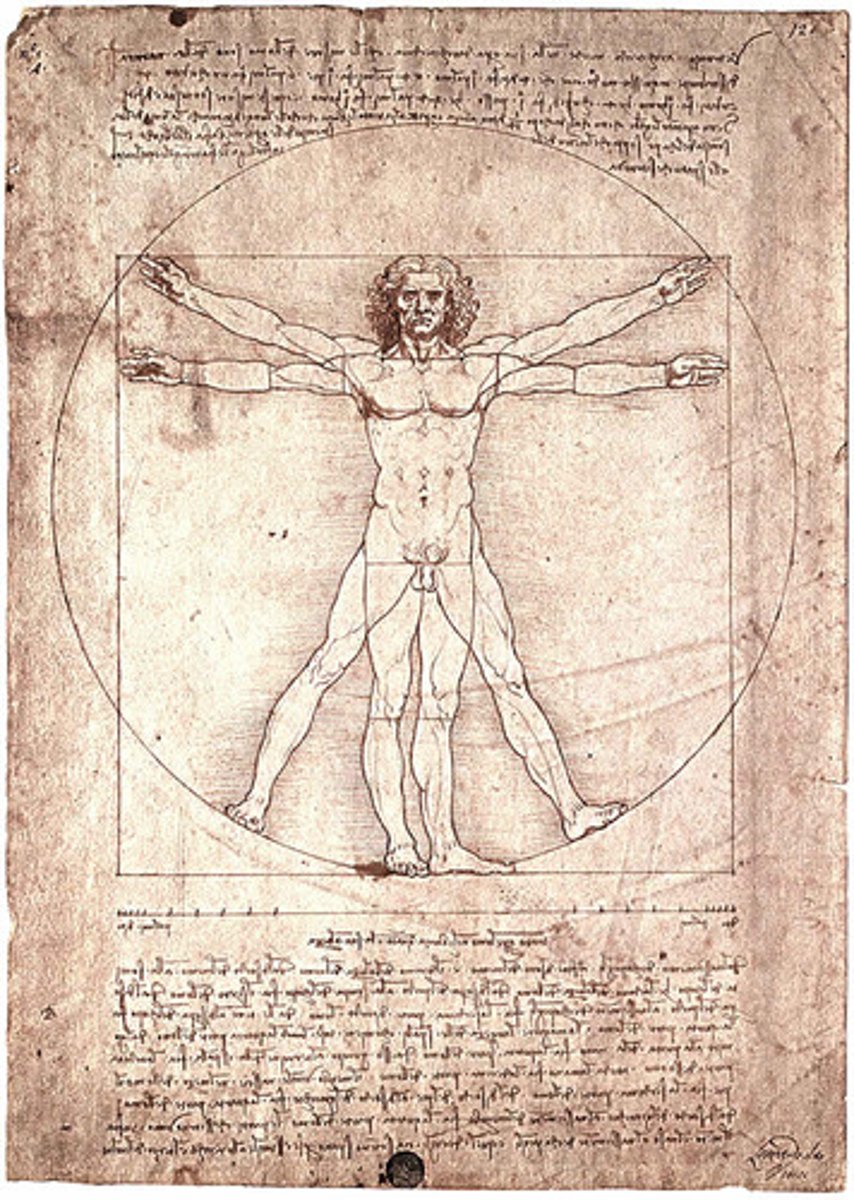
Golden Section
Known since the Greek mathematician Euclid, an irrational proportion with special mathematical and spatial relationships applicable to a wide variety of phenomena, including aesthetics, art, music, and nature:
"A line cut in such a way that the smaller section is to the greater as the greater is to the whole"
Approximately 8:5 ratio
Leonardo da Vinci's drawing of body's balanced proportions
Le Corbusier's Modular
Le Corbusier created a series of harmonic numbers: one was the average height of the human being, the other was the height of a man with raised arms
Massing
composing 3D shapes or volumes into a building design
Context
the built or natural environment that surrounds new buildings
Style
A particular or distinctive form of artistic expression characteristic of a person, people, or period
Mies van der Rohe
"God is in the details"
Shed Roof
A roof having a single slope
Hipped Roof
Sloping ends and sides that meet at a ridge
Mansard Roof
a roof that has two slopes on all sides, with the lower slope being steep and the upper slope almost flat
Named for French architect François Mansart
Flat Roof
A horizontal roof; often found on commercial or industrial occupancies.
Half-timbered
Wall having a timber framework with the spaces filled with masonry or plaster
Clapboard Siding
Wall with wood siding laid horizontally
Masonry
brickwork or stonework
Concrete
building material made by mixing small stones and sand with limestone, clay, and water
poured in place
pre-cast
tilt up panels
Palladian Window
a round headed window flanked by two smaller windows
Double Hung Window
a window having two vertically hung sashes, each in separate tracks
Dormer Window
a vertical window in a projection built out on a sloping roof
Bay Window
Window projecting from the surface of the wall to allow light from three sides
Ribbon Window
horizontal band of windows
Casement Window
a window sash opening on hinges generally attached to the vertical side of the frame
Clerestory
part of an interior wall rising above the adjacent roof with windows admitting light
Arched Doorways
Doorways associated with Romanesque and Gothic architecture
Venetian Door
a door opening with a semicircular window (fanlight) above and flanked by vertical windows (sidelights)
French Door
door having rectangular glass panes extending throughout its length often hung in pairs
Building Type
an architectural form which has become accepted by society through repeated use
Cathedral, Skyscraper, Bank, Temple, Train Station, Airport, Palace, Factory, Castle
Examples of Building Types: (9)
Need
Land (site)
Financing
What 3 things are required for any architectural project?
Architecture today is very complex
"An architect is different from an engineer or an interior designer because he or she creates both the exterior and interior of a building - not just the structure or the decoration of the rooms."
- Deborah Dietch, Architecture for Dummies
The Building Program
A client's list of practical requirements for a design project
Steps required to become a licensed architect
-5-year BARC
or 4+2 MARC
or 3+ year MARC
- Minimum 3-year internship (minimum weeks of exposure to various aspects of practice)
- Pass 7 part ARE 4.0 exam
15
25
35
5
20
Basic Architectural Services consist of the following phases:
Schematic Design - __________% of fee
Design Development - __________% of fee
Construction Documents - __________% of fee
Bidding & Contract Negotiation - __________% of fee
Construction Phase - __________% of fee
Orthographic
Axonometric
Perspective
3 Types of Architectural Drawings
Orthographic
"straight" + "writing"
depict and require measurement in two dimensions
- Plan
- Section
- Elevation
Axonometric
Good drawing type to make quick design
Easy to draw - to scale
Perspective
- Depict and require measurement in 3 dimensions (like axonometric)
- "Foreshortening" - parallel lines in the object appear to recede in depth (unlike axonometric)
- This is how we see (realistic)
Dead Loads
Forces from all the "immovable" elements of a building [weight of building materials, walls, floors, built-ins, etc.]
Live Loads
Forces from all the movable elements of a building [people, equipment, furniture, etc.]
Menhirs
single stone standing upright
Dolmen
several stones supporting a stone slab
Henges
circular ditches around which some megalithic monuments are arranged
Cromlech
circle of stones
Straight-sided Pyramids
Cheop's Pyramid - Giza, Egypt
Khafre's Pyramid - Giza, Egypt
Great Pyramid
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus
The Statue of Zeus
Mausoleum of Halicarnassus
The Lighthouse of Alexandria
The Colossus of Rhodes
7 Wonders of the Ancient World
Imhotep
First recorded architect
- Egyptian - "the one who comes in peace"
- Born a commoner
- Between 2700-2600 BC Zoser hired him to design and build his tomb
- "Translated" traditional building materials of mud, wood, and reeds into stone
- Also an astronomer, magician, and a doctor
- Later worshipped as a god
Egypt - Pyramids
- Tombs for kings built on the west bank of Nile River
- Covered in reflective limestone - quarried from the east bank
- Gold veneer found at the top
- Thought king would walk on sun rays to eternity - if the king lives forever, the people do too
- Sealed the tomb, not a public place
- Sculptural objects on the landscape
Greeks
- United by language
- Founded on:
- Private property
- Individual freedom (less than 35% of people)
- "Democracy"
Doric Order
-oldest, simplest, most massive
-columns placed close together, often no bases
-plain capitals
-entablatures have metopes and triglyphs
Ionic Order
The middle size of Greek classical columns, with capitals decorated with scrolls
- Temple of Athena Nike
Corinthian Order
the most decorative of the classical Greek architectural styles, featuring a fluted column shaft, capitals with flowers and leaves below a small scroll, and a large base; used more by the Romans
Elgin Marbles
- Lord Elgin purchased marbles from Turks
- British Museum - London
Caryatids
- a sculptured female figure used as a column
- architects use images of these to convey shamed, imprisoned women to the world
Atlas
- A sculptured male figure used as a column
Greeks
- Made objects in the landscape
- balance
- harmony
- refinement of form
- not structural innovation
- Post and Beam
Romans
- Conquered the Greeks
- Brought classical architecture to Empire
- 1/5 of the world was under Roman Rule
- Made spaces
- made images in context
- made innovations in construction and
technology
- The arch
- vault
- dome
- concrete
Tuscan Order
-unlike Doric, supports an entablature with no decoration
-used to create wooden temple with pitched roof
Composite Order
- Combines Ionic volutes with Corinthian acanthus
leaves
- A Roman innovation
Pantheon
- 125 CE
- Pediment: triangle shape over colonnade
Constantine I
- AD 306-337
- Edict of Milan 313 AD
- Proclaimed tolerance of all religions
Early Christian Churches
These churches were based on timber-roofed basilicas
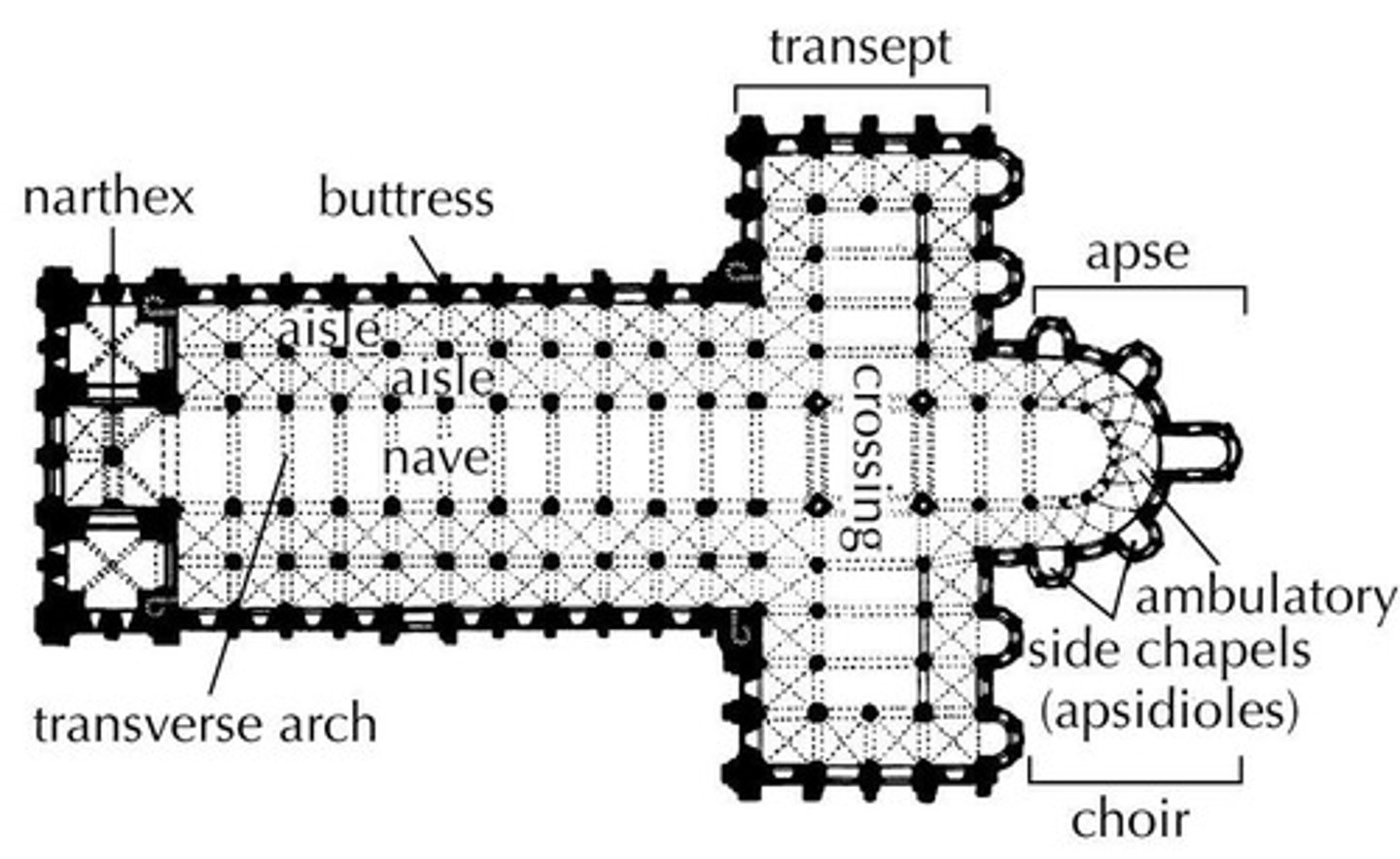
Apse
A recess, usually semicircular, in the wall of a building, commonly found at the east end of a church.
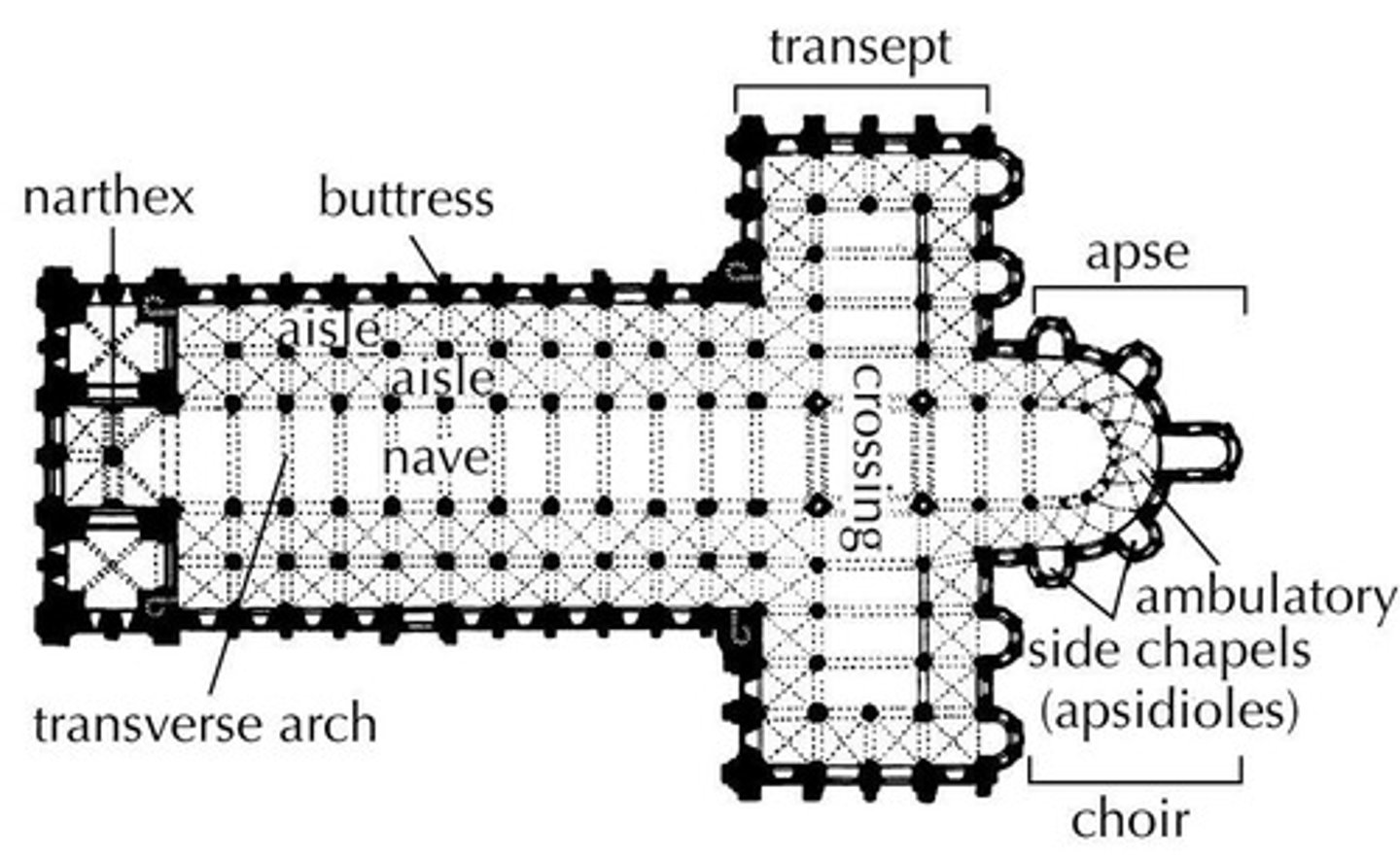
Nave
The long central part of a church, extending from the entrance to the altar, with aisles along the sides.
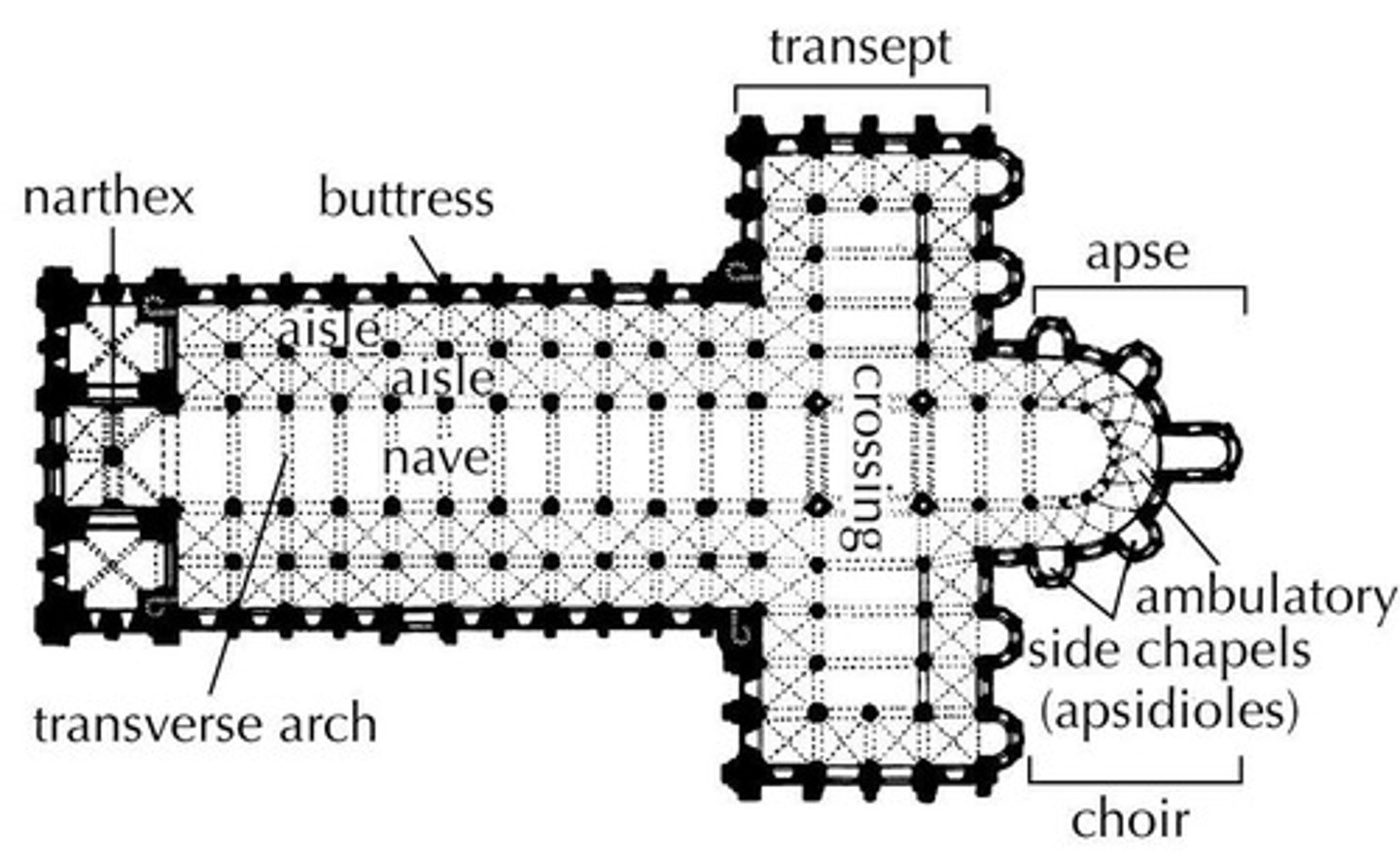
Aisle
the portion of a basilica flanking the nave and separated from it by a row of columns or piers
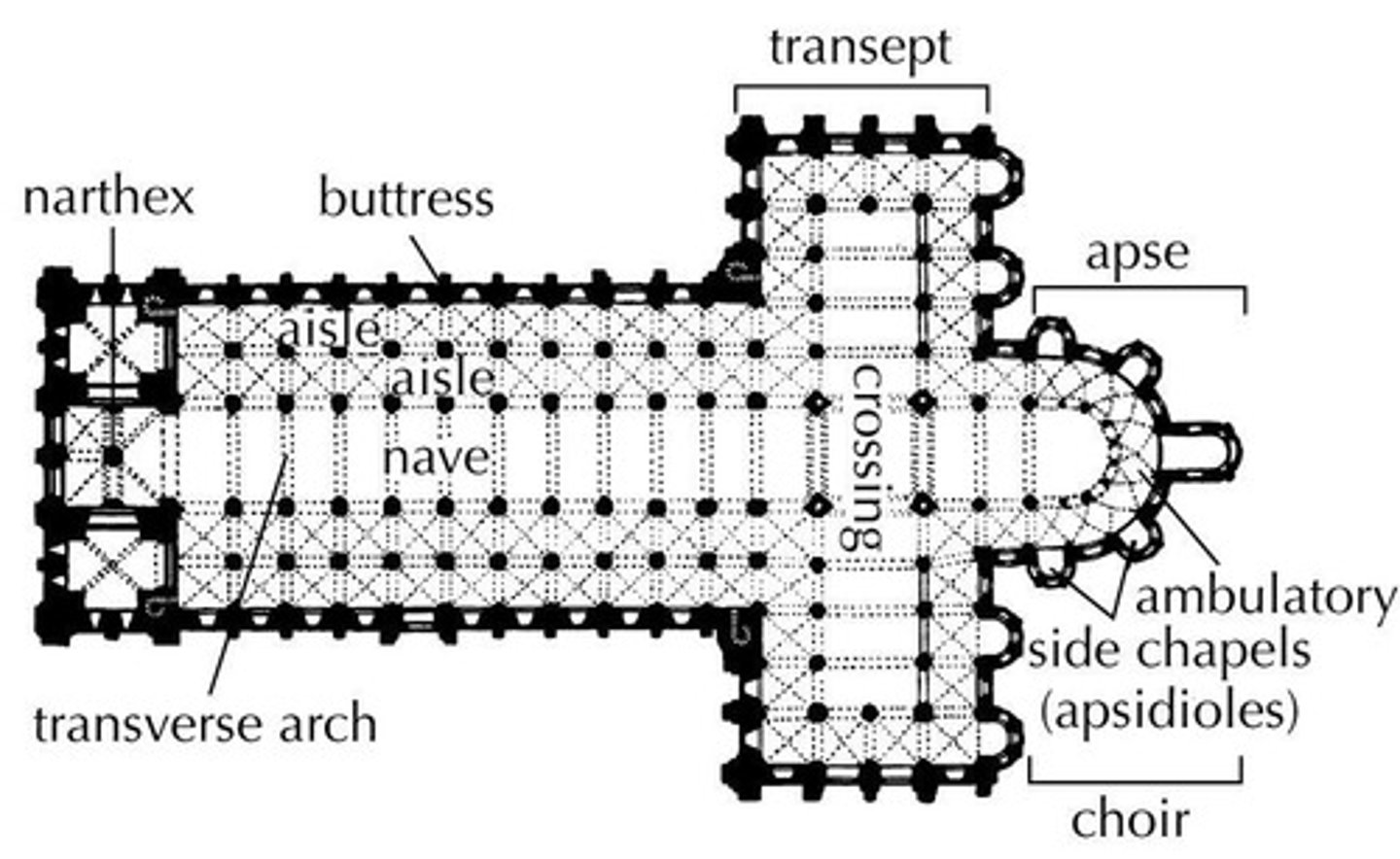
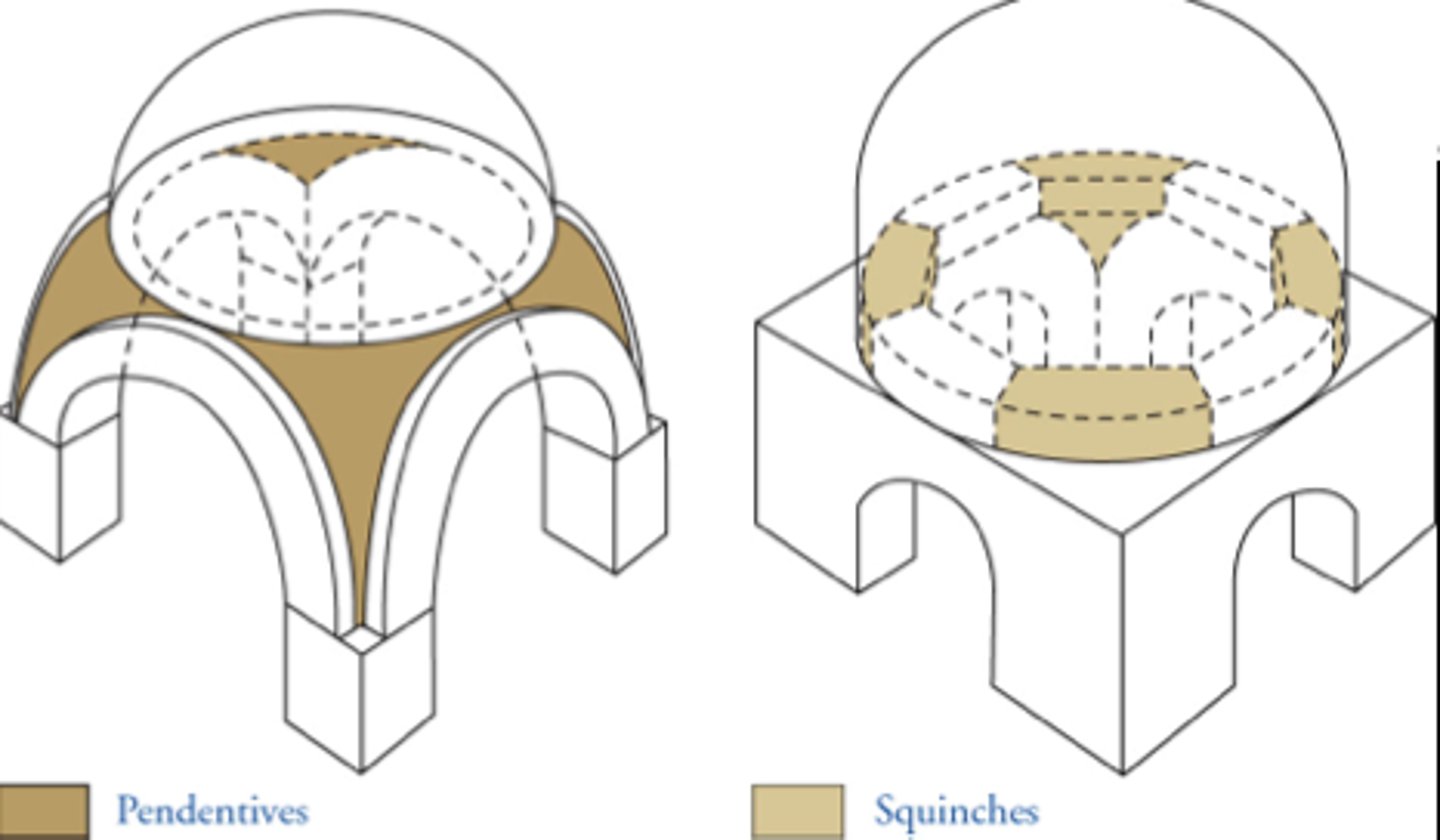
Pendentives
a curved triangle of vaulting formed by the intersection of a dome with its supporting arches.
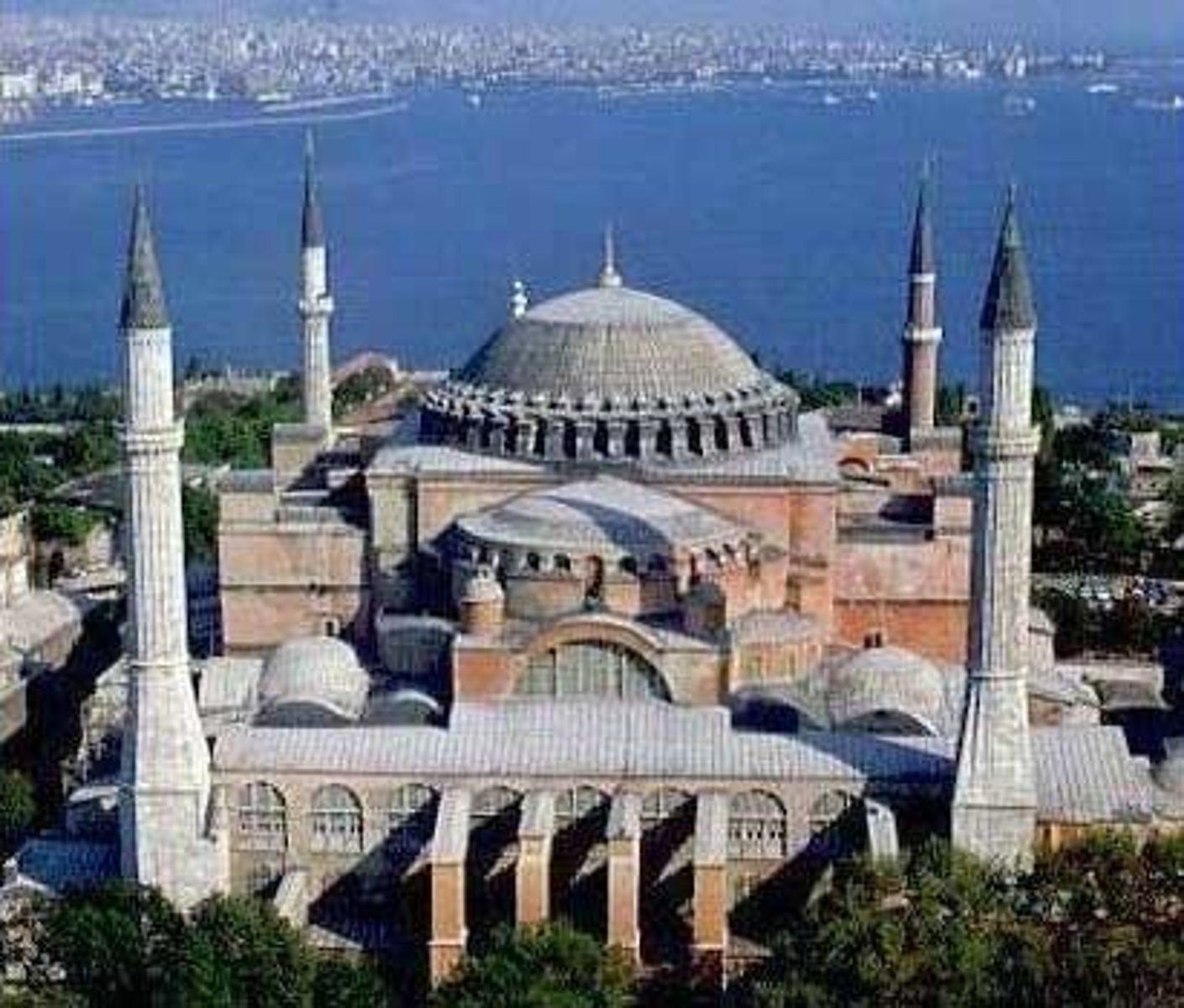
Hagia Sophia
Dome
- covered in mosaics
- appeared to float without support
- destroyed in earthquake

Buttresses
- projecting support of stone or brick built against a wall
- used at right angles to take collected pressures of a ribbed vault
Salisbury Cathedral
1220-1258
Tower 1334-1380
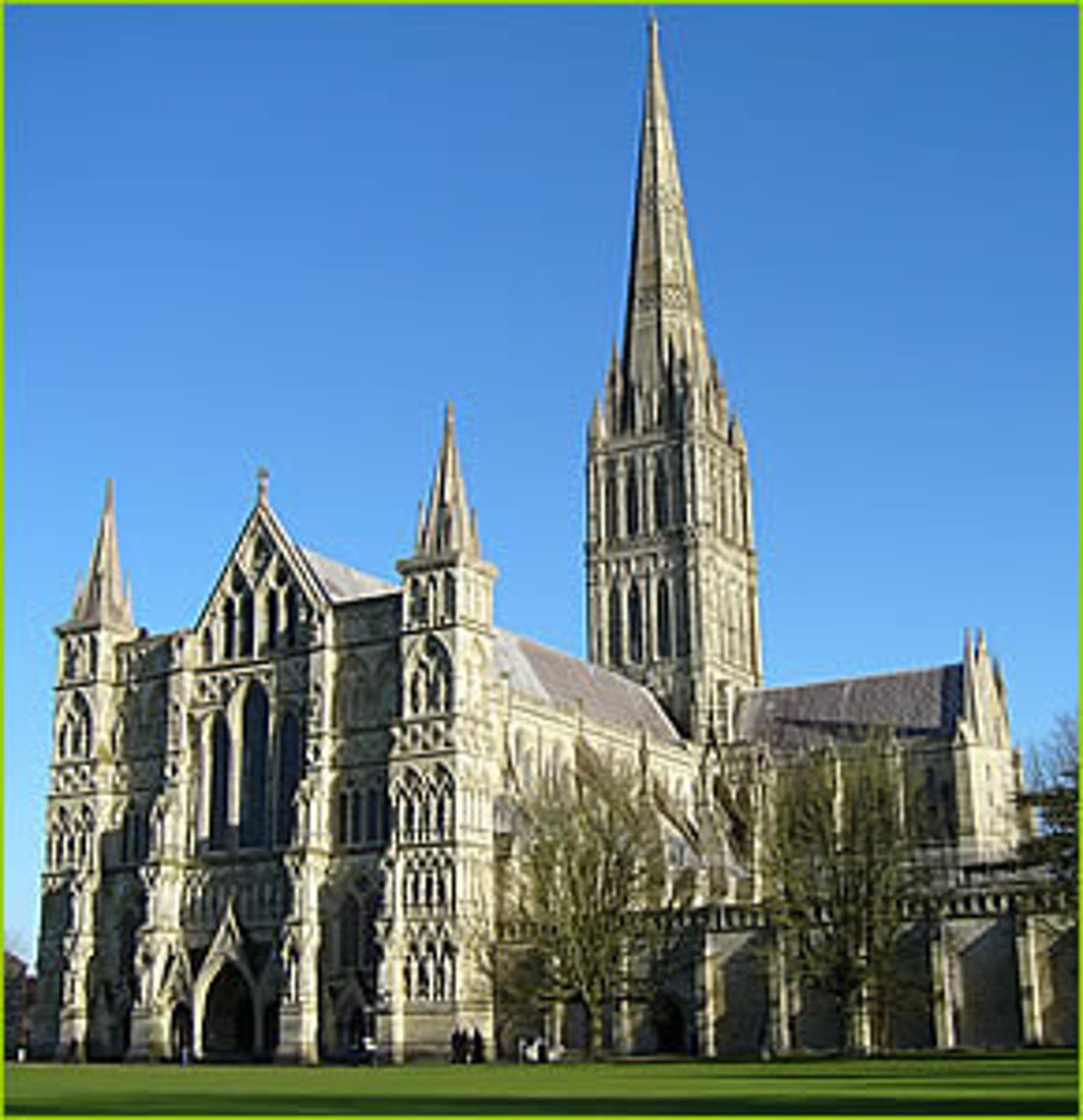

Transept
(in a cross-shaped church) either of the two parts forming the arms of the cross shape, projecting at right angles from the nave.
Renaissance
- Mathematics, rational, proportional, universal order
- Not aspire to heavens, grounded to Earth, human reason
- Symmetry
Gothic
- A-historical, asymmetrical
- Architecture in service to god
Renaissance 15th Century
- Began in Florence, Italy
- Authentic re-use of classicism, based in
understanding of perspective
- Represent human intellect
Renaissance
the activity, spirit, or time of the great revival of art, literature, and learning in Europe beginning in the 14th century and extending to the 17th century, marking the transition from the medieval to the modern world.
Early Renaissance
a style of Italian Renaissance art and architecture developed during the 15th century, characterized by the development of linear perspective, chiaroscuro, and in buildings, by the free and inventive use of classical details
Chiaroscuro
a style of painting using only light and shadow
Brunelleschi
- Father of the Renaissance Architecture
- Symmetrical forms
- Proportions relate one element to another
- Application scientific perspective
- Employed ribs and double shells in domes
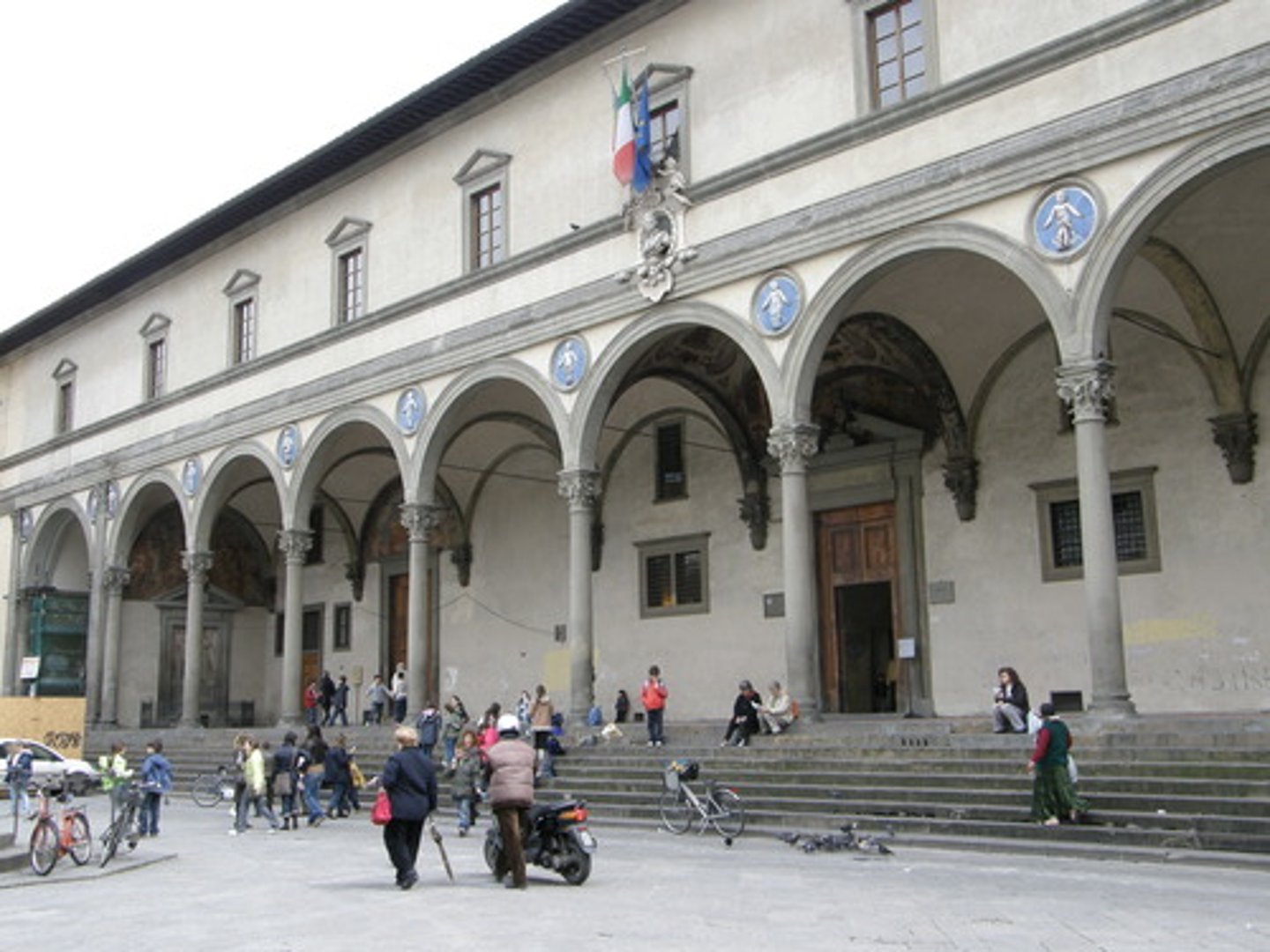
Foundling Hospital
Brunelleschi
Florence, Italy 1422

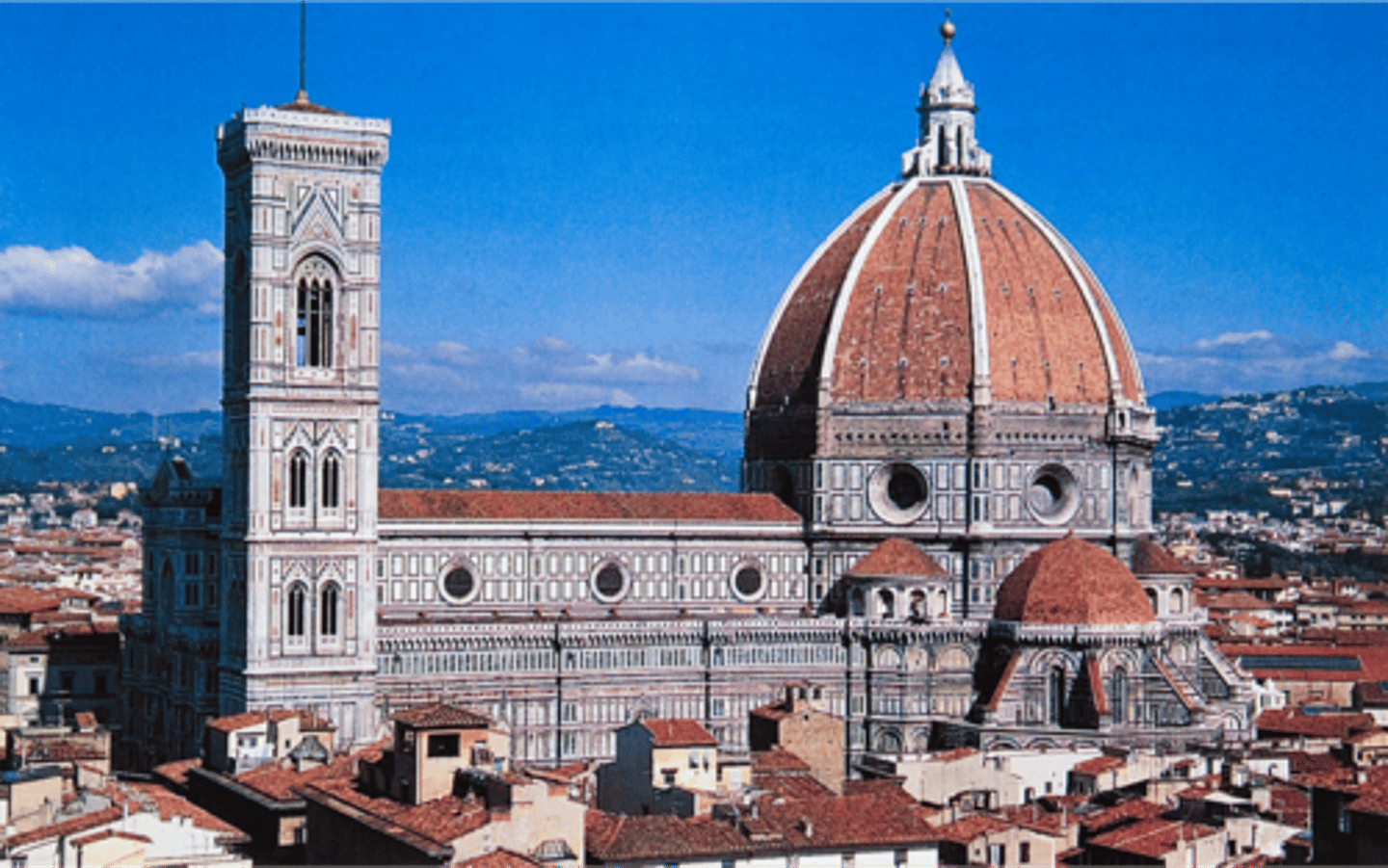
The "Duomo" Dome of the Cathedral
Brunelleschi
Florence, Italy 1418-36
-Largest dome built since the Romans
- No "centering" - built to be self-supporting as it was constructed

Vitruvius
- Wrote "Bible" for Renaissance architects
- The Ten Books of Architecture
- Firmness, commodity, and delight
Villa Rotunda
- Andrea Palladio
- Supreme example of theoretically inspired
design
- Completely symmetrical
- Elements all governed by proportional -
relationships
- Turned house into a temple
Pope Julius II
- Humanist ideals introduced into the Papal court
- Rome Queen city - consolidate temporal power
- Return to glory from Roman antiquity
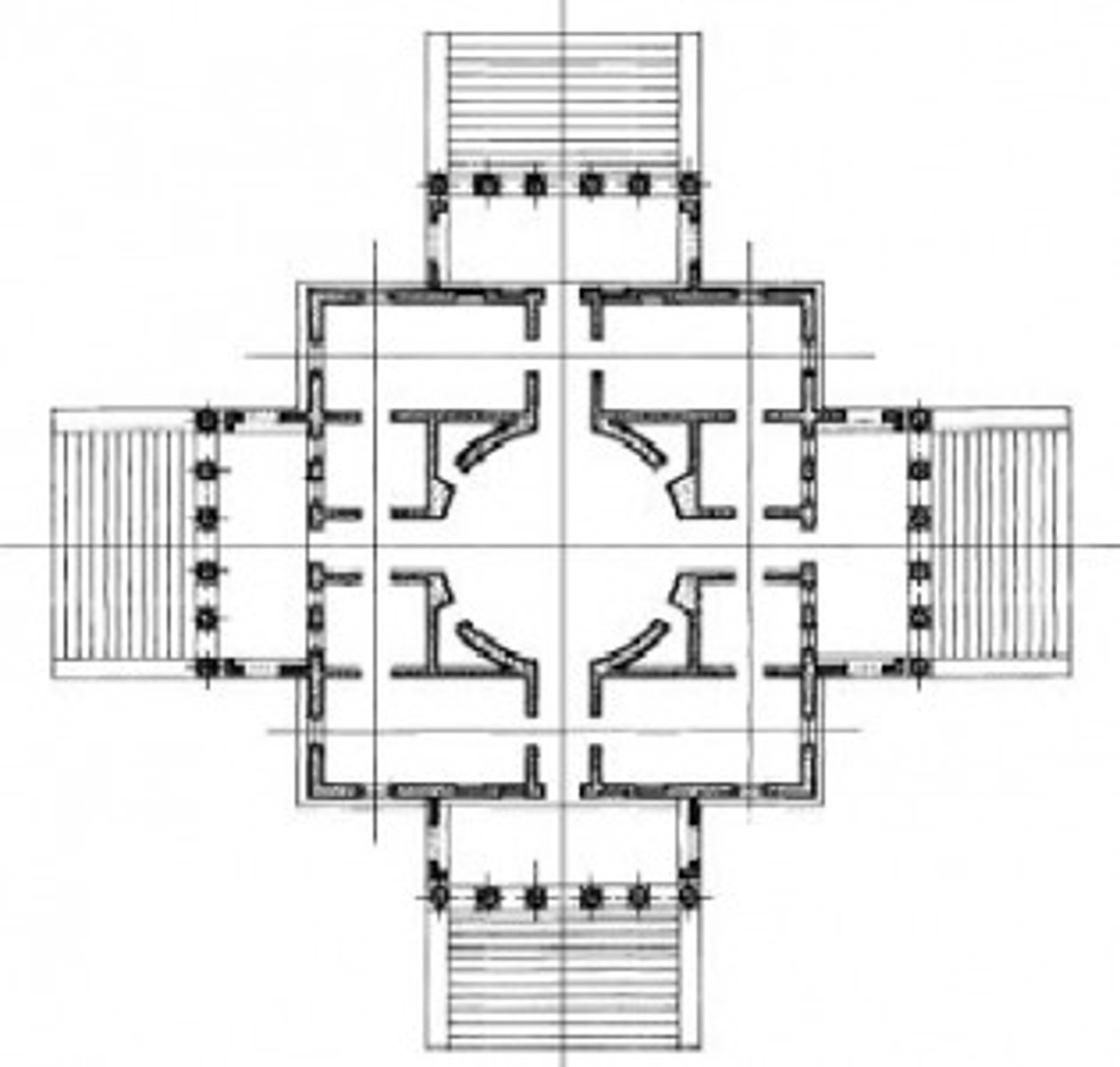
Saint Peter's
- Bramante: started a symmetrical plan with a
dome, after his death
- Michelangelo changed it
- A magnificent new church over the crypt of St.
Peter
- Battle over "centralized" and "linear" plans
- "Greek" cross - short arms, equal length
- "Latin" cross - crossing with a long nave
Mannerism
A transitional style in European architecture in the late 16th century, particularly in Italy, characterized by the unconventional use of the classical elements. In the fine arts, it was chiefly characterized by distortion of perspective, elongated forms, and intense, often strident color.
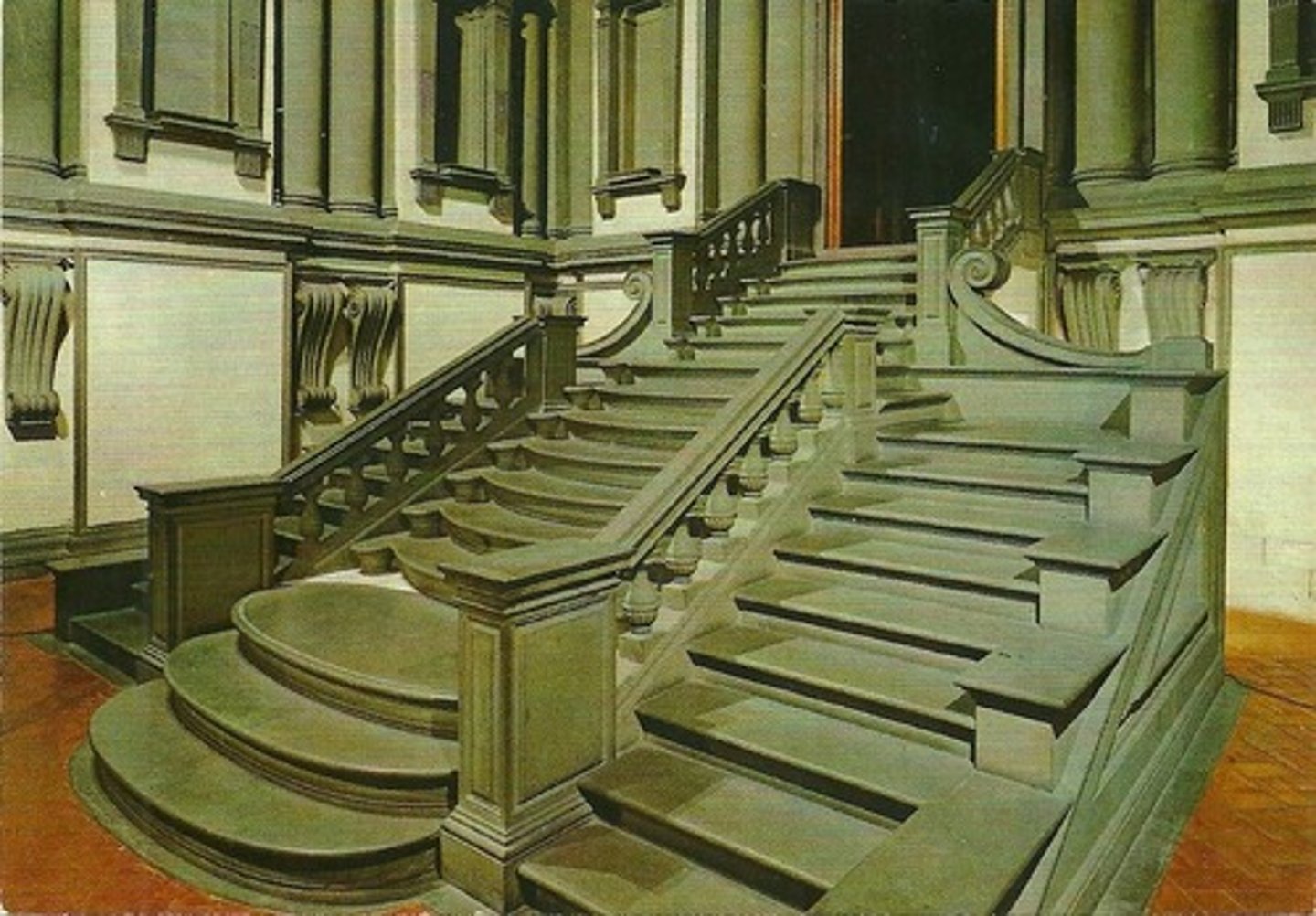
Laurentian Library
- 1524
- Exaggerated proportions
- Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475-1564) -
rebelled against Renaissance decorum
- Inventive combinations of elements that
purposefully play with classical rules

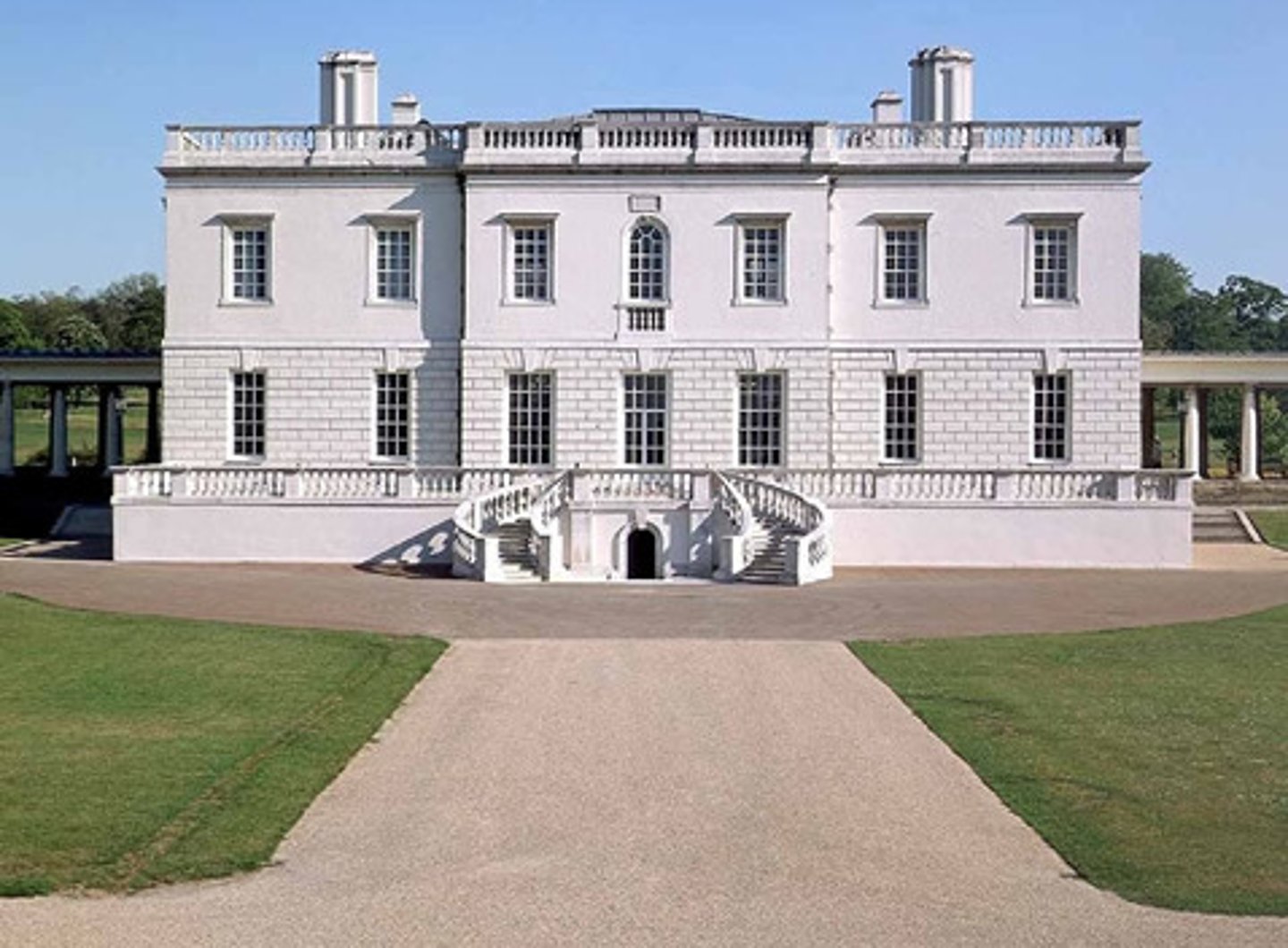
Inigo Jones
- 1572-1652 Englishman
- Self-taught (son of a clothmaker)
- Two trips to Italy - studied Palladio's work first
and through Palladio's "Four Books of
Architecture"
Queen's House
- Inigo Jones
- Introduced Palladian ideals to England

Renaissance vs. Baroque
- Engage intellect
- Pure forms
- Emphasize individual in isolation
- Architecture for wealthy
- Engage the emotions
- Illusionary effects
- Emphasize individual as part of society
- Architecture for all social classes
Baroque Architecture
a style of architecture originating in Italy in the early 17th century and variously prevalent in Europe and the new world for a century and a half characterized by free and sculptural use of the classical orders and ornament dynamic opposition and interpenetration of spaces, and the dramatic combined effects of architecture,sculpture, painting and the decorative arts.
Bernini and Borromini the Baroque in Rome
- Reaffirmation of Catholic Church after the
- Protestant led Reformation
- Buildings to awe, convert
- Counter reformation: reintroduce spiritual values
- Something greater than the individual
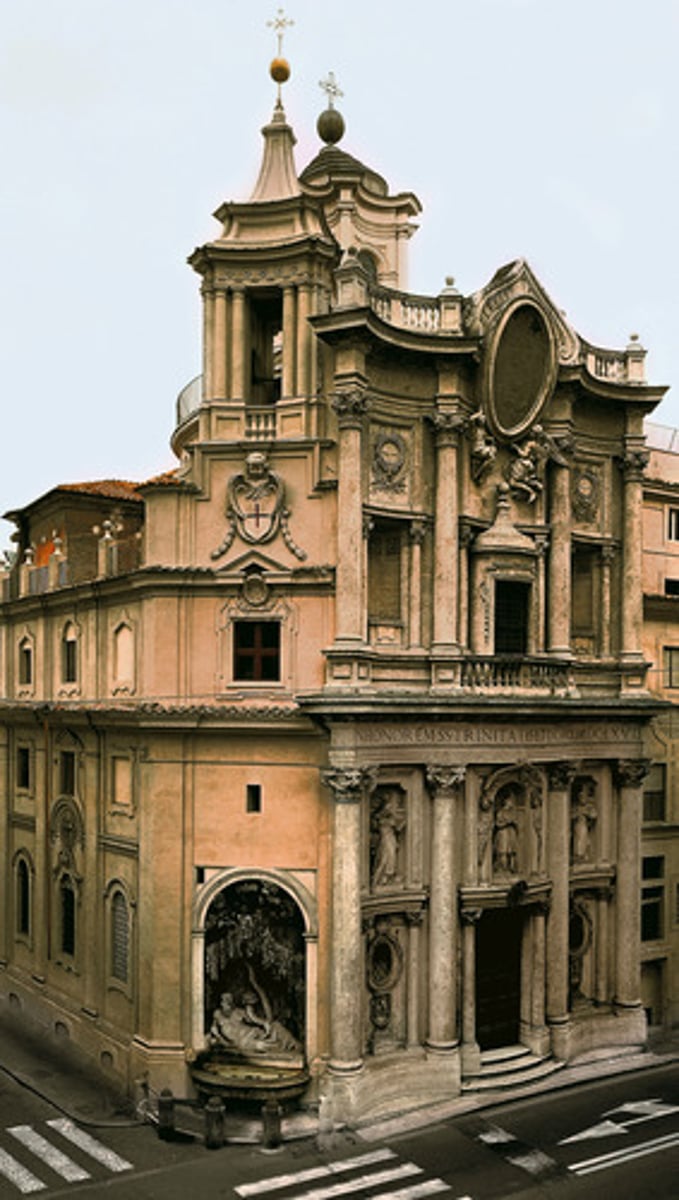
S. Carlo alle Quattro Fontane
- Bernini and Borromini
- Rome 1634
