L3: Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors and Acetaminophen
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
NSAID
anti inflammatory actions wo being a steroid
aspirin is the prototype
the one we compare the others in the class to
does not include COX2 specific or selective agents nor acetaminophen
prototype
the one we compare the others in the class to
traditional NSAID
aspirin
ibuprofen
naproxen
naproxen sodium
indomethacin
ketorolac
risk of heart attack and stroke
COX 2 agents
celecoxib
meloxicam
risk of heart attack and stroke
the other one
acetaminophen

in between is risky

aspirin chemical class
salicylic acid derivative
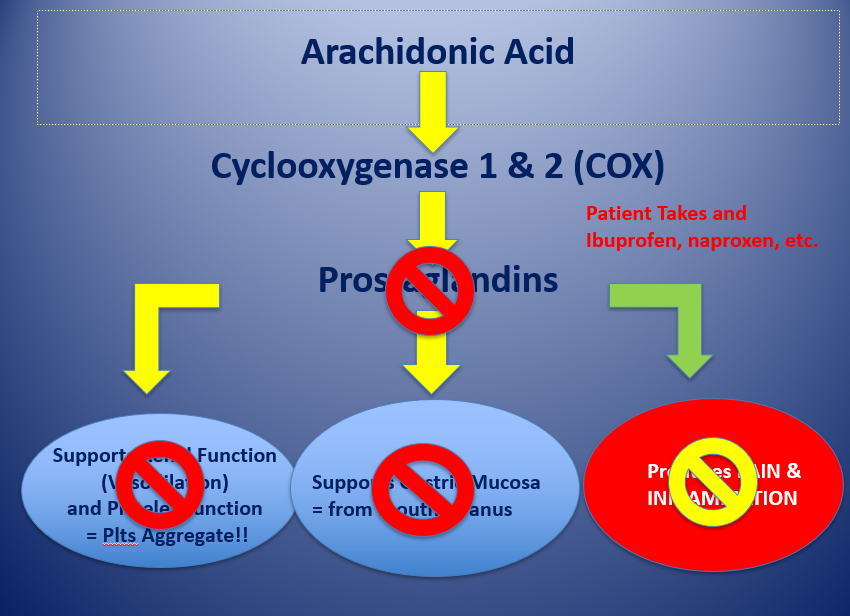
arachidonic acid cascade - inflammation and pain
arachdonic acid
releases cytokines
cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (COX)
prostaglandins
supports renal fxn (vasodilation) and platelet fxn = platelets aggregate
supports gastric mucosa = from mouth to anus
INDUCIBLE — produces pain and inflammation
= patient takes ibuprofen, naproxen, etc
when do kids become a pharmacological adult
12
ibuprofen
traditional NSAID
decreases the synthesis of pain and inflammation
inflammation-promoting prostaglandins via nonselective inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2
NSAID fxn (outcome of inh the various enzymes (cox 1/2))
decrease:
fever (antipyretic)
pain (analgesic)
inflammation (anti-inflammatory)
COX 1 inhibition
stomach problems (mouth to anus)
vasoconstriction in the kidneys
inhibition of platelets
all the BAD == more side effects
asprin = _______ inh of platelets
irreversible
cardiac protective drug
a dose kills 50%
other NSAIDs = __________ inh of platelets
reversible
can you separate cox 1/2
no
reversible vs irreversible inh of platelets
irreversible = half dead and half fine
reversible = chaos
cox 2 inh
therapeutic GOOD —> only benefit is a slight decrease in GI tox, no inh of platelets
decrease in pain and inflammation
what COX2 agents were pulled off the market bc they showed an increase in CV thrombotic events
Valdecoxib (Bextra) and rofecoxib (vioxx)
inh of which enzyme gives side effects
COX 1
cox 2 agents side effects?
no side effects
cox 2 specific inhibitor
celecoxib (Celebrax)
more Cox 2 than Cox 1 inh
cox 2 selective inhibitor
meloxicam (mobic)
parents of celebrex and mobic
Bextra and Vioxx showed an inc in CV thrombotic events in clinical data
parents are serial killers so maybe the kids are bad
cox 2 agents are only used for
pain
Celebrax and mobic
max dose of ibuprofen
800 mg every 6 hours = 3,200 mg
min mg amount for anti—inflammatory effects of NSAID
1,200 mg
for any itis
ketorolac
outlier
max of 5 days
longer duration = inc risk of serious renal effects and bleeding
very common parenteral NSAID
this is what you took for those kidney stones
adult ibuprofen age
12 years and older
otc dose of ibuprofen
200
rx doses of ibuprofen
400, 600, 800
infant ibuprofen (advil, motrin) should not be used in children less than
>/ 6 mo
babies less than 6 mo old should take what
acetaminophen
babies greater or equal to 6 mo can take
acetaminophen and or ibuprofen
infant iburpofen general
>/ 6 mo to 23 mo
use weight when possible for dosing, and age when weight is not possible
childrens ibuprofen
2-11 years old
use weight when possible for dosing, and age when weight is not possible
effects on platelets (adverse drug reactions)
aspirin causes irreversible inh of platelets; NSAIDs are reversible
BLOOD THINNERS
platelet life span is 7-10 days
see prolonged bleeding time
discontinue 1 week prior to surgery (aspirin) and 3ish days (NSAIDs)
in general, aspirin, NSAID, and COX2 agents are to be discontinued a minimum of 7 days prior to a procedure
what is the minimum amount of time necessary to discontinue aspirin, COX1, COX2 prior to sx
7 days
what is the minimum amount of time necessary to discontinue traditional NSAID
3 days
renal effects - NSAIDs and COX2 specific
prostaglandin needed to maintain vasodilation and blood flow to the kidneys; other wise VASOCONSTRICTION occurs
hypersensitivity rxns
if someone is allergic to aspirin then they are probably allergic to NSAIDs and Cox 2 agents
can cause bronchoconstriction, nasal polyps
celecoxib has what cross sensitivity
sulfa
chance is slim bc celecoxib is a non antibiotic sulfa drug
CNS side effects
salicylates - aspirin is the prototype
aspirin is a salicylate
aspirin is most likely to cause CNS issues = tinnitus = ringing in ears
Reye syndrome
what happens if we give aspirin to kids less than or equal to 14 years old when they have a viral infection:
influenza
varicella (chicken pox)
reye syndrome can cause hepatitis and cerebral edema - so we avoid aspirin
kids are given acetaminophen or ibuprofen
GI issues
15% of pt treated chronically w NSAIDs will go on to develop major GI event
take w food —> helps w GI issues
Acetaminophen (tylenol)
non NSAID analgesic
APAP
prostaglandins are not impacted
only an antipyretic and analgesic —> NOT an anti inflammatory drug
•non-NSAID analgesic: believed to exert its effects via CNS COX inhibition and activation of central serotonergic pathways
max daily does for acetaminophen
3000 mg (or 4000 mg for a couple of days)
ADR w acetaminophen
hepatic injury
more likely to occur in chronic alcohol users
many OTC and Rx products contain acetaminophen
hepatically metabolized to sulfate and glucuronide conjugates
small amount is metabolized by CYP450 into a hepatotoxic metabolite (NAPQI)
more regullary a person drinks = shift towards more hepatotoxic metabolites
NAPQI normally binds to glutathione
if glutathione stores are depeleted = NAPQI is not detoxified = hepatotoxicity
kidney issues too
antidote for tylenol toxicity (acetaminophen overdose)
NAC
TIME SENSITIVE = must be given wi 8 hours of ingestion of acetaminophen
fever drugs: birth to 6 mo are given
acetaminophen
fever drugs: 6 mo to adult are given
acetaminophen and or ibuprofen
aspirin mech of action
irreversible acetylation of enzyme cyclooxygenase = inhibition of the synthesis of thromboxane A2
Irreversibly inhibits platelet aggregation
primarily given to prevent arteriolar lots
anticoagulants are given to prevent venous clots
low dose aspirin (LD ASA) is ___ mg
81
men 45 - 79 to prevent heart attack
women 55- 79 to prevent stroke
men/women > 80 - recommended only if they have high CV risk and no additional GI bleeding risk
take them off it bc now risk for GI bleed is higher
should aspirin and other NSAID be taken w food
yes, w largest meal of day
thienopyridine derivatives
clopidogrel (plavix)
mech of action
irreversibly inhibit ADP
NOT effecting prostaglandin
ticagrelor (brilinta)
mech of action
only ADP inh that binds reversibly to platelets
so it has a shorter duration of effect than clopidogrel or prasugrel
might have to take 2 doses a day bc of this
prasugrel (effient)
mech of action
irreversible inhibits ADP receptor
as we go down the list the potency increases
whats more potent as an antiplatelet med aspirin or thienopyiridine derivs
thienopyridine derivs
dosing of clopidogrel (plavix)
can be taken alone or w aspirin
duration of antiplatelet effect is 7-10 days = that is the lifespan of a platelet
adverse effect of clopidogrel (plavix)
thrombocytopenia
low platelet amount
min amount of time to discontinue clopidogrel (plavix), ticagrelor (brilinta) before a sx
5 days
dosing of ticagrelor (brilinta)
MUST BE TAKEN W LOW DOSE ASPIRIN
if a pt takes more than 100 mg of aspirin it will impair ticagrelor (brilinta) MECH OF ACTION
ADRs of ticagrelor (brilinta)
dyspnea - shortness of breath
bradycardia
bleeding
dosing of prasugrel (effient)
must be taken w aspirin as well
any dose works
prasugrel (effient) ADR
bleeding BLACK BOX WARNING
most potent of the 3
prasugrel (effient) durg interactions
other drugs that increase bleeding risk
warfarin
NSAIDS
how long before a sx should you stop prasugrel (effient)
7 days
Just because the bleeding risk is higher
glycoprotein 2b/3a inh
given parenterally
no oral ones available
most potent
anti platelet potencies ranked
most —> GP 2b/3a inhibitors
thienopyridine derivs
effient
brillinta
plavix
aspirin
what are the anticoagulants
warfarin (coumadin) - introduced as coumadin in 1950
MOA
inhibits vit K dependent liver coagulation factors: 2, 7, 9, 10, and protein C and S
sometimes a pregnant women needs an anticoagulant, what do we use for that
heparin
NOT WARFARIN
whats the half life of warfarin
40-72 hours
what do we use to adjust the dose of warfarin
INR - international normalized ratio
used to check their PT - but that has variability
how do we monitor warfarin
monitor INR weekly for the first few weeks
then every 2 weeks
eventually every month
how long do we hold warfarin before a procedure
5 days
what INR do we want w Warfarin
2-3 = ideally 2.5
what must we maintain w warfarin
a consistent amount of vit K in kiet
avoid sporadic ingestion of foods high in vit K = beef liver, pork liver, green tea, green leafy vegs
does Warfarin interact w a lot of drugs
yes - we need to watch this
adverse rxn for warfarin
bleeding
warnings/precautions w warfarin
use w vitamin K may decrease the anticoagulant effects
vit K could be an antidote
use w NSAIDs and aspirins
NSAIDS = NO
aspirin - may be intentional
USE ACETAMINOPHEN TYLENOL FOR PAIN/FEVER
miscellaneous PO anticoagulants
dabigatran (pradaxa)
MOA
direct thrombin inh
first oral anticoagulant approved in US in over 50 years
for reducing stroke risk and systemic embolism in pt w non valvular atrial fibrillation
used in place of warfarin
does not require monitoring of INR
rivaroxaban (xarelto)
apixaban (eliquis)
MOA for both
factor Xa inhibitor
dabigatran (pradaxa)
MOA
direct thrombin inh
first oral anticoagulant approved in US in over 50 years
for reducing stroke risk and systemic embolism in pt w non valvular atrial fibrillation
used in place of warfarin
does not require monitoring of INR
dabigatran (pradaxa) ADR
bleeding
dyspepsia - heart burn
contains cream of tartar to help w absorption = this is what causes heart burn
precautions w dabigatran (pradaxa)
compliance is key
if a dose is missed the effectiveness starts to wane wi 15 mins of the missed dose
what do rivaroxaban (xarelto) and apixaban (eliquis) replace
warfarin or low molecular weight heparin
what are ADRs of rivaroxaban (xarelto) and apixaban (eliquis)
bleeding
eliquis might be worse for this
heparin types
traditional heparin therapy = unfractionated heparin
SC or IC
LARGE STRUCTURE
from pig and cow sources = more of a chance for allergies
low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)
enoxaparin (lovenox)
can be given every 12 - 24 hours
used for pregnancy
MOA for traditional/UFA heparin
inactivates thrombin and factor Xa
compare the half lives of traditional/UFA heparin and LMWH
traditional has shorter half life
how do we monitor UFA/traditional heparin efficacy
aPTT
ADR of UFA/traditional heparin and LMWH
bleeding
ADR of UFA/traditional heparin
allergic rxn - bc from animal source
HIT - heparin induced thrombocytopenia
all the platelets stick together in clumps (hypercoagulable) so it looks like theres a decrease in platelets
with long term use:
alopecia
cataracts
osteoporosis
LMWH MOA
only inhibit factor Xa
so they have a longer half life