Ch2- Electromagnetic Radiation
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is the formula for the energy (E) of a photon?
v= photon frequency
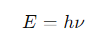
How is photon energy related to wavelength?
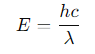
What is the formula for energy passing through a small area (dA) in time (dt)?
F =the energy flux
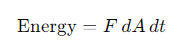
What is luminosity (L), and how is it related to flux?
Its the total energy emitted by a source per unit time
r =the distance from the source
F(r) =the flux at that distance.
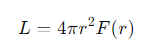
What is the inverse square law for flux?
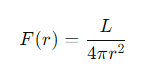
What is bolometric flux?
The total flux received over all frequencies
Calculated by integrating the flux density (Fv(v))
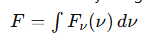
What is bolometric luminosity (L)?
It is the luminosity integrated over all wavelengths.
What is blackbody radiation?
Its the characteristic spectrum of radiation emitted by any object with a non-zero temperature, depending solely on its temperature.
What determines the shape of a blackbody’s spectral energy distribution?
The temperature of the body.
Why is it called a "blackbody"?
Because it reflects no light and absorbs all incident radiation.
What is the Planck function in terms of frequency (Bν(T))?
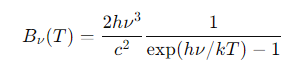
What is the Planck function in terms of wavelength (Bλ(T))?
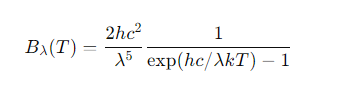
What is the Rayleigh-Jeans law for blackbody radiation at low frequencies (hν≪kT)?
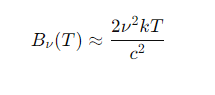
What is Wien's law for blackbody radiation at high frequencies (hν≫kT)?
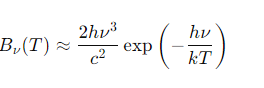
What is the Stefan-Boltzmann law for the flux of a blackbody?
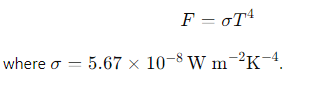
What is the formula for the luminosity of a star?
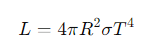
What is Wien’s displacement law for the wavelength of peak emission (λmax)?
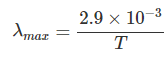
How does the frequency of peak emission relate to temperature (hνmax)?
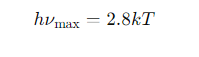
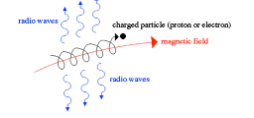
What is synchrotron radiation?
Synchrotron radiation is emitted when relativistic charged particles, such as electrons, spiral around magnetic field lines.
What causes synchrotron radiation?
Relativistic charged particles (usually electrons) spiralling around a magnetic field.
How does synchrotron radiation differ from blackbody radiation?
It is not isotropic and does not follow the Planck function.
Instead, it is beamed in the direction of the particle's motion and follows a power-law spectrum.
What is the formula for the power spectrum of synchrotron radiation?
s is the spectral index that depends on the energy distribution of the particles.
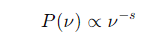
What causes bremsstrahlung radiation?
Its produced when electrons are decelerated by the electric field of ions in a fully ionised plasma, emitting photons in the process.
At what wavelengths is Bremsstrahlung radiation typically observed?
At high energies, particularly X-ray and gamma-ray wavelengths.
Under what conditions is bremsstrahlung the dominant continuum emission mechanism?
In thermal plasmas at high temperatures (T≫105K ), where the gas is fully ionized.
How does the bremsstrahlung spectrum behave at high temperatures?
It becomes a continuum, as atomic spectral lines are less important as coolants.
What is the formula for bremsstrahlung power (P(ν,T))?
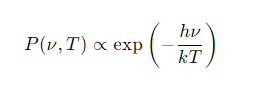
How does bremsstrahlung emission behave at low photon energies (hν≪kT)?
The emission is effectively independent of frequency (ν).
What happens at higher photon energies (hν≈kT)?
The exponential term becomes significant, reducing the emission.
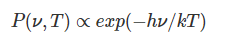
What causes spectral line emission or absorption?
Electrons transition between different energy states (orbitals) in an atom or ion, emitting or absorbing a photon in the process.
What is the relationship between the energy of a photon and the electron transition in bound-bound radiation?
The energy of the photon is given by:
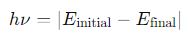
What happens during excitation and relaxation in atoms or ions?
Excitation: Electrons absorb energy and move to a higher energy state (orbital).
Relaxation: Electrons release energy as a photon and return to a lower energy state.
What is an emission line spectrum?
Its produced by an optically thin (transparent) volume of gas, where the gas emits light without any background light source.
What is an absorption line spectrum?
It occurs when cold gas lies in front of a source of radiation at a higher temperature, absorbing certain wavelengths of light.
What factors contribute to the finite width of spectral lines?
Natural linewidth
Collisional broadening
Doppler broadening
What is the natural linewidth formula?
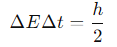
What causes collisional broadening of spectral lines?
Its caused by the number of collisions per second between particles in the gas, which increases with density.
Higher densities lead to broader spectral lines.
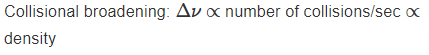
What causes Doppler broadening of spectral lines?
It occurs due to the motion of atoms with a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of velocities.
It can also result from large-scale motions of the gas, leading to shifts in the observed frequencies of the spectral lines.
What is the formula for the Doppler shift of spectral lines for non-relativistic motion?
v = the recession velocity along the line of sight
c =the speed of light.
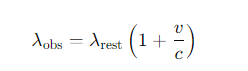
What is the formula for the Doppler shift of spectral lines for relativistic motion?
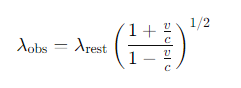
What is the formula for redshift z in an expanding universe?
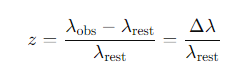
What does the redshift z tell us about the motion of galaxies?
A positive redshift z>0 indicates that a galaxy is moving away from us
A negative redshift (blueshift) indicates motion towards us.
What is circular velocity?
Its the velocity of an object undergoing uniform circular motion around a central mass.
What is the formula for circular velocity?
G = the gravitational constant
M =the central mass
r= the radius of the orbit.
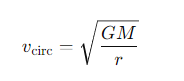
What is escape velocity?
The minimum speed needed for an object to escape from the gravitational influence of a body.
What is the formula for escape velocity?
M = the mass of the central object
r =the distance from the centre of the object.
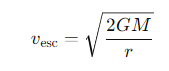
How does escape velocity compare to circular velocity?
Escape velocity is higher than circular velocity by a factor of root 2
It requires more speed to escape the gravitational pull than to remain in orbit.