C3.1 Integration of body systems
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
System Integration
Coordination between and within systems
Define tissues
Group of cells
State the two cell types of alveoli in lungs
AT1 (alveolar type 1)
AT2
Define organs
Group of tissues working together to carry out specific functions of life
Draw trachea and label
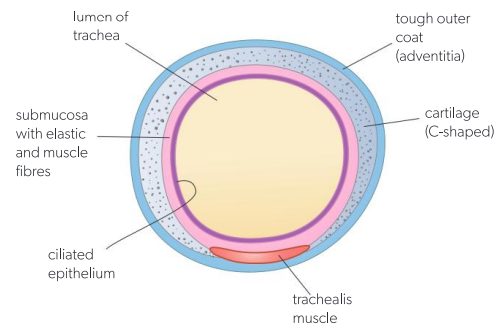
List the 11 organ systems
Ciculatory
Digestive
Endocrine
Gas exchange
Integumentary
Lymphatic
Muscular
Nervous
Reproductive
Skeletal
Urinary
Hormones and relation to integration
Chemicals produced by endocrine glands
Travel through blood stream
Slower
Only affects target cells (with right receptor protein)
Nervous signals and relation to integration
Electrical impulses
Transmitted by neurons to a specific location
Affects muscles or glands only
Rapid
Very short
Functions of brain
Receives information from one of our sensory organs
Process and stores that information
Brain processes information
Brain may send signals to effector organs if a response is required
Parts of brain
(check labelled diagram)
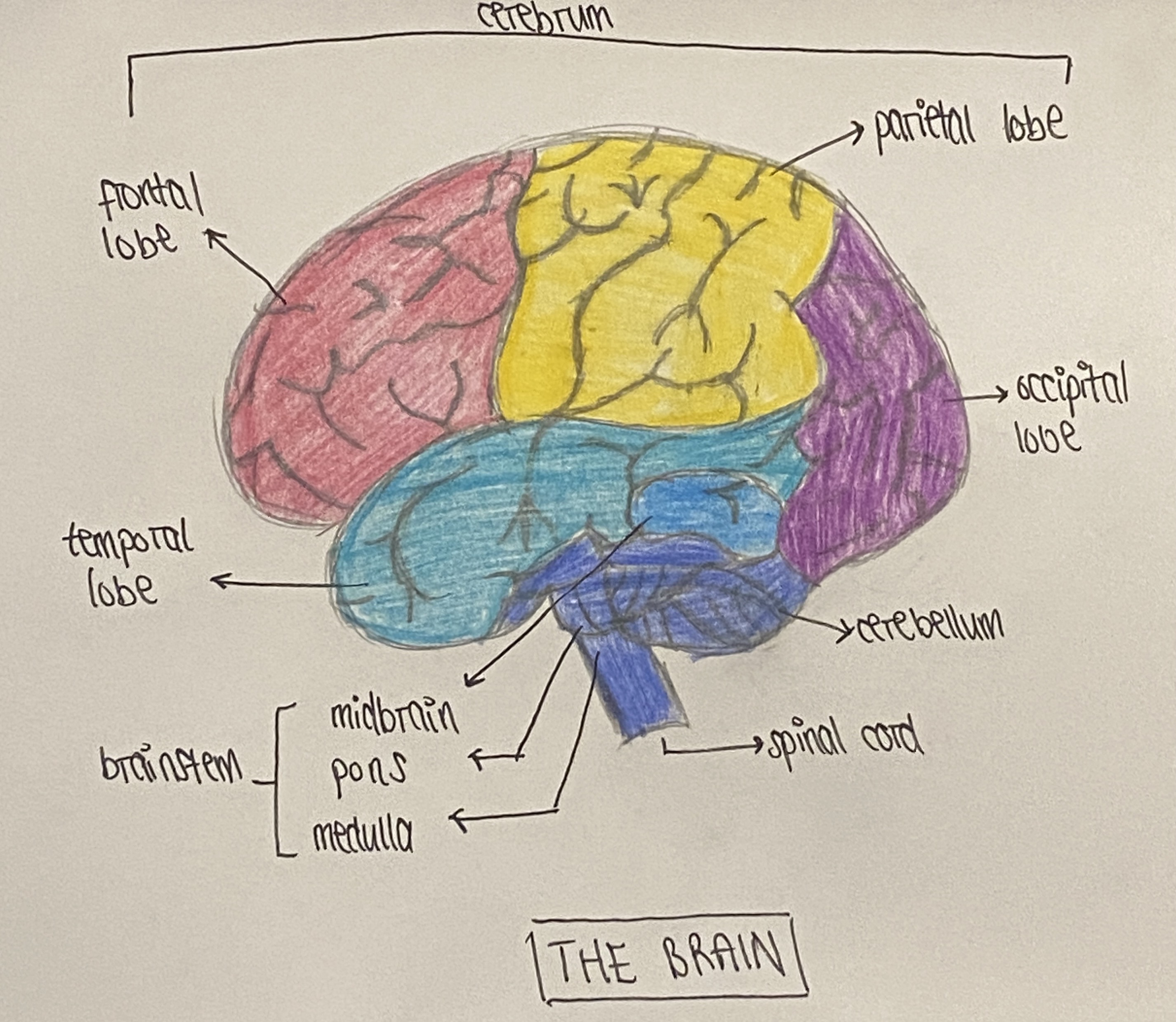
Define CNS
Central Nervous System, consisting of spinal chord and brain
White matter tissue in spinal chord
Transmits signals from:
Sensory receptors to brain
Brain to other organs
Grey matter tissue in spinal chord
Contains cell bodies and synapses
Processing information
Decision making
Unconscious processes only
Types of sensory receptors
External and Internal
External sensory receptors examples
Touch
Heat
Light
Internal sensory receptors examples
Stretch receptors (think of expanding stomach)
Chemo receptors
Motor cortex of brain
Has motor neurons originated, but axons go other places
Nerve + what it contains and transmits
Bundle of nerve fibres surrounded of a sheath
Contains both sensory and motor neurons
Can only transmit signals one way
Reflex arc
Rapid, involuntary response to a specific stimulus
Steps of a reflex arc
Receptor picks up the stimulus (touch, heat, light, smell…)
Pain message is carried along sensory neuron
Gets to CNS and passes along to an interneuron
Message is transmitted along a motor neuron, goes away CNS
Goes into effector organs- initiates movement, etc
Interneuron
Goes between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron
Cerebellum
Back/bottom of brain, coordinates the timing of muscle contractions
List 3 things the cerebellum coordinates
Balance
Posture
Things that require muscle memory
Melatonin
Hormone secreted by pineal gland that control circadian rhythm
Circadian rhythm
Pattern of sleep/wake cycles that organisms are adapted for
Effects of apinephrine secretion
Hydrolysis of glycogen → glucose
Decrease blood flow to gut and kidneys (vasoconstriction)
Increase diametre of bronchi and bronchioles
Increases heart rate
Explain how the hypothalamus works with osmoregulation
If body solute concentration is too high, pituitary gland is prompted to release ADH
Explain how hypothalamus works with puberty
Hypothalamus releases GnRH
Prompts pituitary to release LH and FSH
Initiate puberty
SA node
Sinoatrical node, at the top of the brain
Vagus nerve function
Causes SA node to slow down heart rate
Sympathetic nerve
Causes SA node to increase heart rate
State the two ways SA node is in feedback loops with
Chemoreceptors
Baroreceptors
Aorta
Distributes oxygenated blood to other parts of the body
Feedback loops
Series of inputs and responses
List what happens when an increase in (any) activity happens
More muscle movement
More ATP
More cellular respiration
More CO2
Less pH- causes nerve signals to be passed to muscles that control our breathing
Peristalsis
Muscle contractions that move food through digestive tract
List voluntary parts of digestive system
Initiation of swallowing
Defecation (later in life)
List involuntary parts of digestive system
Moving food through digestive tract
Defecation (early in life)
Tropism
Growth responses to stimulus
Positive tropism
Growing towards stimulus (e.g: roots)
Negative tropism
Growing away from the stimulus
Lateral
On the other side
Phytohormone and its functions
Plant hormone:
Growth
Promotes cell division/elongation
Development
Promotes differentiation of plant tissues
Response to stimuli
Control of tropisms
Auxin
Phytohormone that controls tropism
Auxin efflux carries
Transmembrane proteins that pump auxin into cells
Outlien how AEC help shoots frow away from the sunlight
Can move around withing membrane
If cells coordinate and move, the AEC to one side, high concentration of auxin can be established
Shoot away from the sunlight
Outline promotion of cell growth by auxin
Auxin promotes synthesis of proton pump
Pumps protons into apoplast (outside cell wall)
Lowers the pH of cell wall (acidification)
Weakens the cell wall, and causes wall to elongate
Elongation causes bending (positive phototropism)
Cytokinin
Another phytohormone; produced in roots and transported in shoots (opposite of auxin)
State a reason why seed disperal occurs
Parents don’t want to compete with offspring
Signals of ripening fruit
Colour change
Softening
Scent production
Sweetening
Ethylene
Phytochrome that works in a positive feedback look to ripen fruit
How does auxin exert its effect on plant cells
Binds to a receptor resulting in expression of genes
How auxin controls phototropism in plant shoots
Plant shoots bend towards light/sun
Auxin moves to shadier side from lighter
Moved by auxin efflux pumps
Auxin promotes cell wall acidification
Growth increases on shadier side
Binds to auxin receptors- they promote gene expression
Extension of stem in plants
Cell division of shoot/stem
Auxin stimulates stem extension
Elongation of cells causes stem to grow