module 7 - taxes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
tax revenue
the total amount of money a firm receives from selling its goods or services
price x quantity sold
accounting profit
total money a firm makes after subtracting ONLY explicit costs
explicit costs
direct, recorded costs
implicit costs
opportunity costs of using resources the firm already owns, rather than spending money directly
not paid out in cash
can be time, wages, rent, supplies, etc
economic profit
measure of profit that takes into account both explicit and implicit costs
total cost
sum of all costs in a firm incurs in the production of goods and services
implicit and explicit costs
variable cost
the costs tat change with the level of output
more a firm producers, the higher this cost
cost per unit x number of units produced
fixed cost
the costs that do not change with the level of production
rent
salaries
insurance
property taxes
equipment
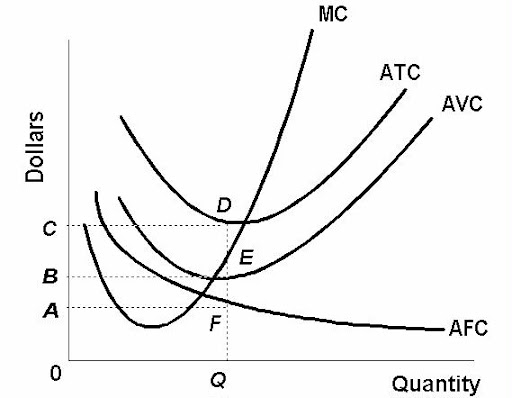
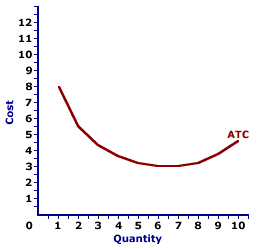
average total cost (ATC)
the total cost per unit of output
total cost/quantity
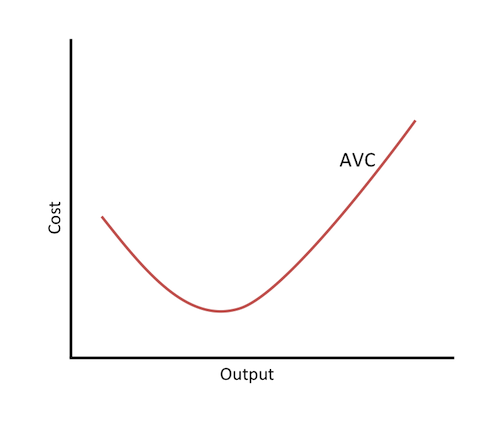
average variable cost
the variable cost per unit of output
variable cost/quantity
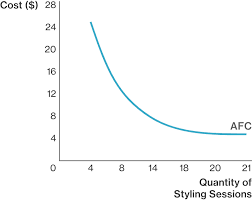
average fixed cost
the fixed cost per unit of output
total fixed cost (TFC)/quantity
marginal cost (mc)
fundamental concept in economics that refer to the additional cost incurred by producing one more unit of a good or service
formula: change in total cost/change in quantity produced
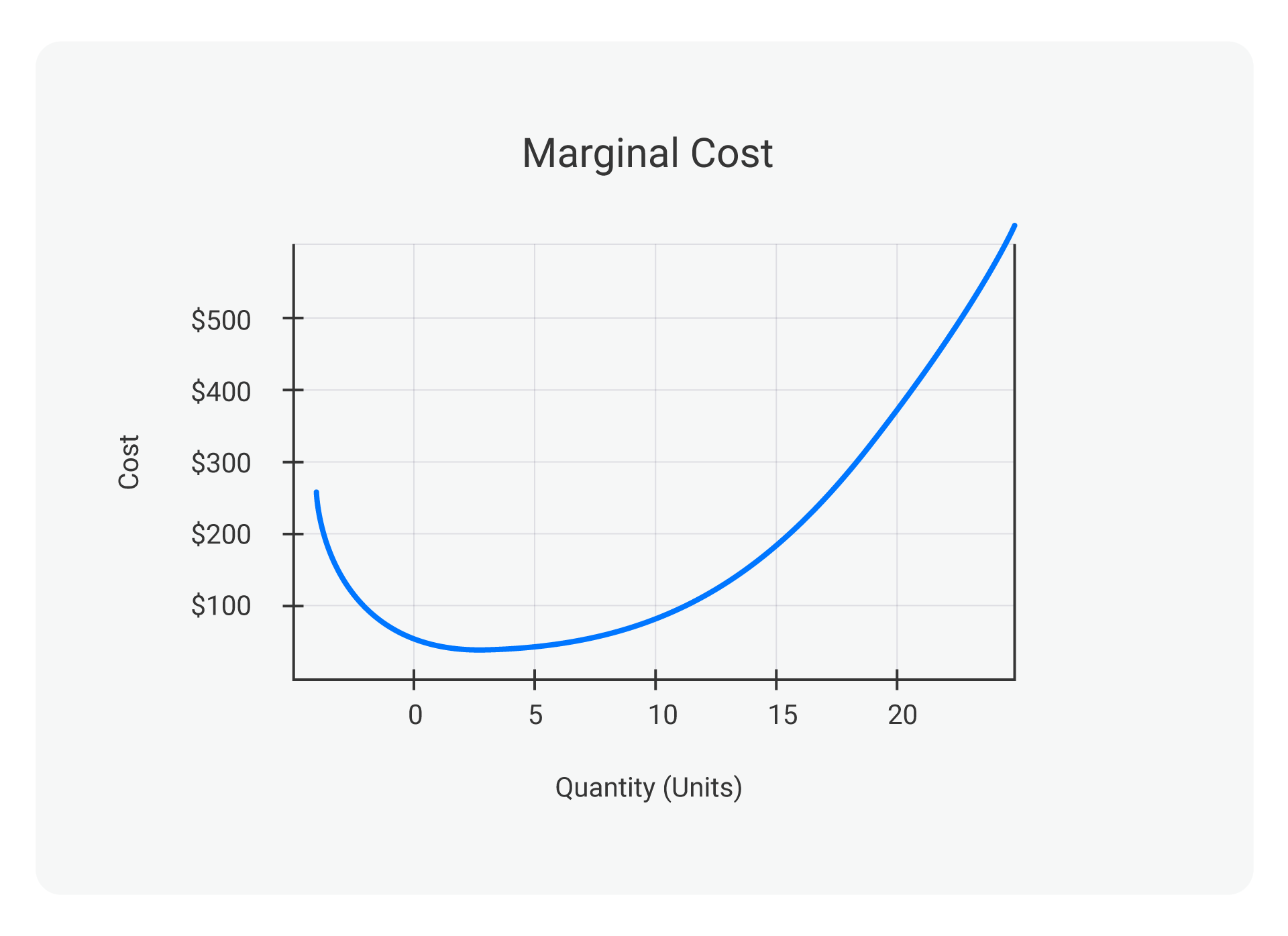
decreasing (marginal) returns - law of diminishing marginal returns
fundamental economic principal that describes what happens to output when you continuously add more of one input to production while holding all other inputs constant
hiring more workers (place can become too cramped with too many people)
decreasing returns to scale
a situation in which a proportional increase in all inputs leads to less than proportional increase in output
long run
occurs when a firm expands its production capacity; changing all its factors of production proportionally
increasing returns to scale
long run production phenomenon where a proportional increase in all inputs leads to a more than proportional increase in output
specialization and division of labor
technological advantages
bulk purchasing and discounts
managerial efficiencies
constant returns to scale
occur in the long run when a proportional increase in all inputs leads to an equally proportional increase in output
goal of firms
maximize profits (total revenue minus total cost)
all costs on a graph together