Lecture 3: Central Endocrine Glands
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
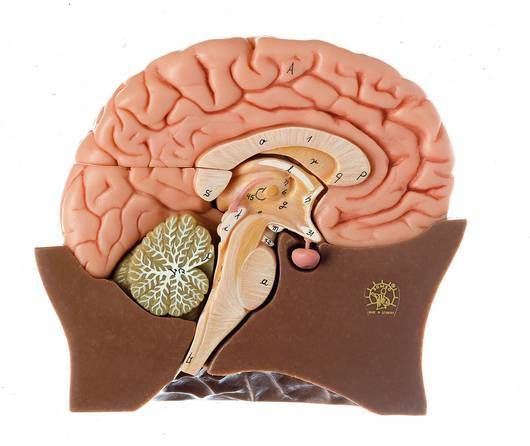
Where are the hypothalamus and pituitary gland?
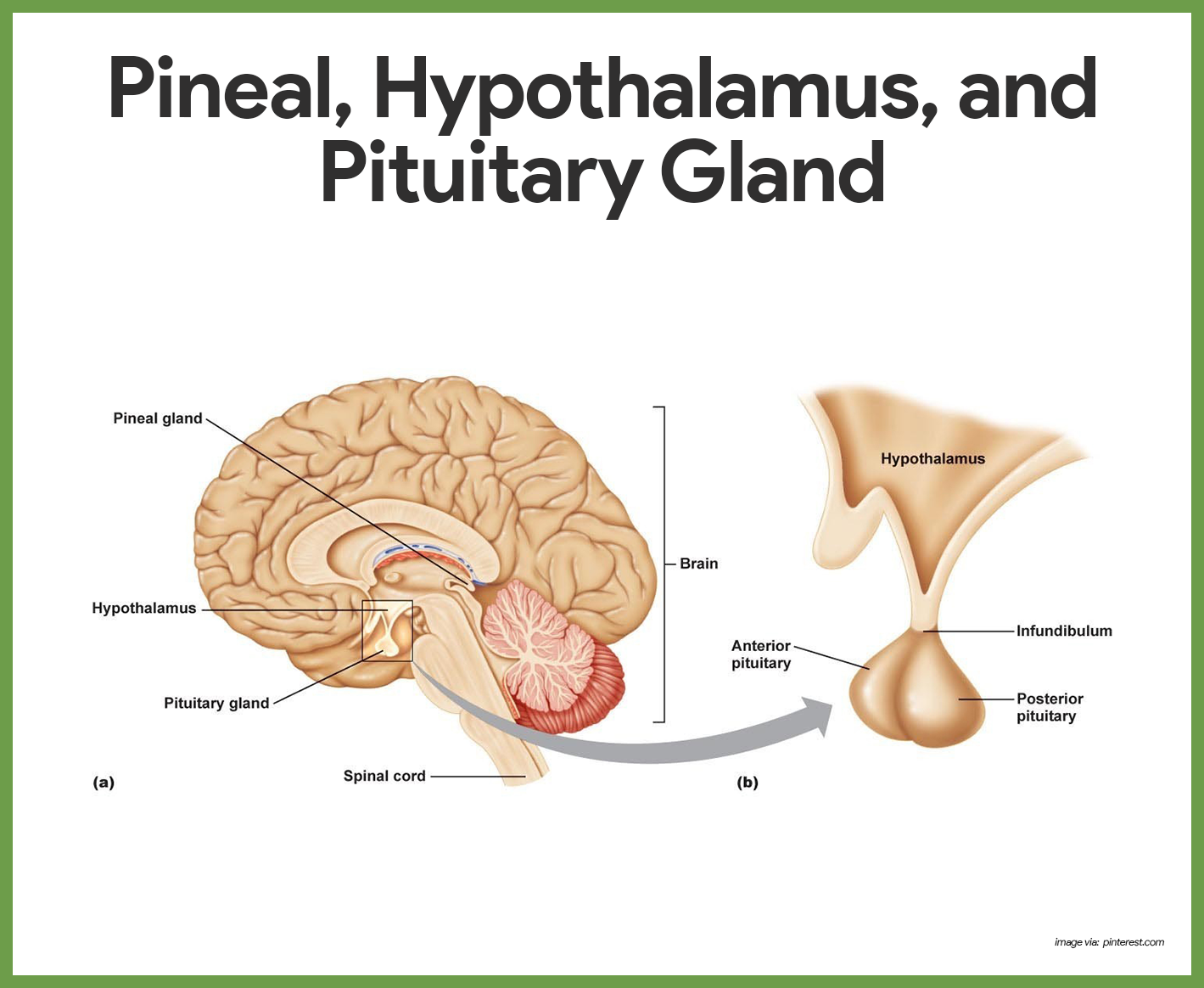
What is the hypothalamus made up of?
brain nuclei: paraventricular nuclei (PVN) and supraoptic nuclei (SO)
synthesise hormones that are important in the posterior part of the pituitary gland
brain nuclei
collections of cells that
what does the hypothalamus do?
a collection of brain nuclei that have important control and integrative functions
important for homeostasis and primary functions
controls autonomic function via the brainstem autonomic centres
controls endocrine function via the pituitary gland
what does the hypothalamus respond to?
environmental factors:
light (circadian rythym)
stress (fear, noise, etc)
neural signals:
visceral afferents from the intestines, heart, liver, stomach (mediated by neurotransmitters)
hormones: -ve
which pituitary hormones does TRH correspond to?
TSH, PRL, FSH
RH (ex: TRH)
releasing hormone (ex: thyroid releasing hormone)
which pituitary hormones does GnRH correspond to?
LH, FSH
which pituitary hormone/s does GHRH correspond to?
GH
which pituitary hormones does somatostatin correspond to?
GH
which pituitary hormones does CRH correspond to?
ACTH
which pituitary hormones does dopamine correspond to?
PRL
Outline the regions of the pituitary gland
Anterior + posterior
Anterior = pituitary hormones regulated by secreted hypothalamic factors
capable of making and storing its own hormones
Posterior = pituitary hormones synthesised in hypothalamus and transported via neuronal projections
Structurally continuous with the hypothalamus of the brain, to which it remains attached by the hypophyseal/pituitary stalk
cannot make its own hormones, stores hormones made in the hypothalamus
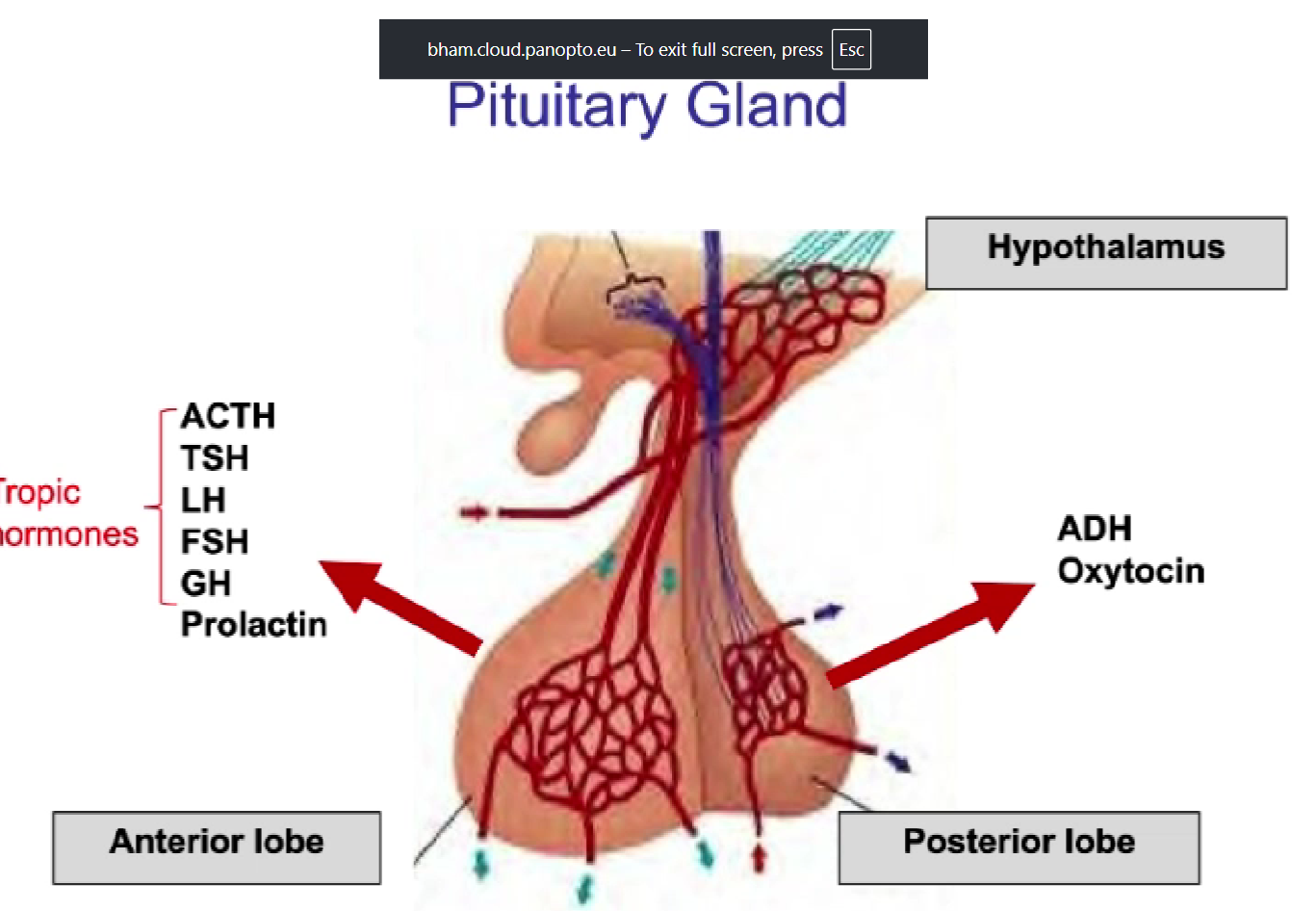
tropic hormones
a hormone that activates another gland- have other endocrine glands as their target
most of the hormones produced by the hypothalamus = tropic
ADH
antidiuretic hormone
produced in PVN (left side of the pituitary gland)
list the anterior pituitary hormones
TSH, ACTH, LH/FSH, GH, PRL
list the posterior pituitary hormones
ADH/vasopressin, neurophysins, oxytocin
trophic
cell types that can produce their own hormone (ex: thyrotroph)
outline thyrotrophs
anterior
Hormone = TSH
function = thyroid hormone regulation
rare to have functional tumors
outline corticotrophs
anterior
ACTH
regulation of adrenal cortex
functional tumors such as cushing’s
outline gonadotrophs
anterior
LH/FSH
reproductive control
outline somatotrophs
GH
growth
anterior
functional tumors = acromegaly
outline lactotrophs
anterior
PRL
milk production
functional turmors = prolactinoma
outline ADH
water regulation
outline neurophysins
important in ADH synthesis
outline oxytocin
important in birth and breast milk expression
what makes up the majority (half) of all cell types in the anterior pituitary?
somatotrophs
the proportion of the remaining cell types can change during breastfeeding, pregnancy, etc
list the glycoproteins of the anterior pituitary hormones
TSH = thyroid stimulating
FSH = follicle stimulating
LH = luteinising
all tropic
list the proteins and polypeptide hormones of the anterior pituitary
ACTH = adrenocorticotrophic
GH = growth
prolactin
all share common alpha subunit, differ in their specialised subunit
what is a glycoprotein
a protein that has been glycosylated
what are the single chain protein hormones?
prolactin, growth hormone
what are the two-chain glycoprotein hormones?
TSH, LH, FSH
have a common alpha subunit and unique beta subunit
outline TSH
thyrotropin and thryotrophin
made in thyrotrophs in response to pulsatile TRH release from the hypothalamus
+ve: production of thyroid hormone TRH by hypothalamus, act on anterior pituitary, to release TSH, acts on thyroid to produce T4 prohormone, converted to T3 hormone and acts on TT
-ve: T3 acts on TT, feedback to ant. pituitary and hypothalamus to tell them to stop
T4 acts on ant. pituitary and hypothalamus as well
what happens when the cells in the anterior pituitary are damaged
secondary hypothyroidism- pituitary failure
secondary hyperthyroidism- pituitary tumor
primary disorder vs a secondary disorder
primary: gland itself is damaged/has an issue
secondary: disorder is caused by issue elsewhere than gland
gonadotrophins
LH and FSH
made in the gonadotrophs of the anterior pituitary in response to gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH)
LH and FSH
good examples of g-protein receptors! use cAMP and protein kinase a
regulate reproduction (testosterone biosynthesis, menstruation, fertility)
adenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) aka adrenocorticotrophin
synthesised in corticotrophs
influences the adrenal cortex
synthesised from POMC = processing of POMC produces ACTH which acts on the adrenal cortex to produce adrenal hormones
effects of ACTH
stimulates g-protein receptor coupled to cAMP
this stumulates the enzymes that convert cholesterol to cortisol or sex steroid precursers
prolactin
made in lactotrophs
regulation: prolactin production inhibited by dopamine (also produced by hypothalamus).
upregulated by thyroid hormones
suckling, sleep and stress stimuli impact hypothalamus, dopamine levels drop, prolactin produced
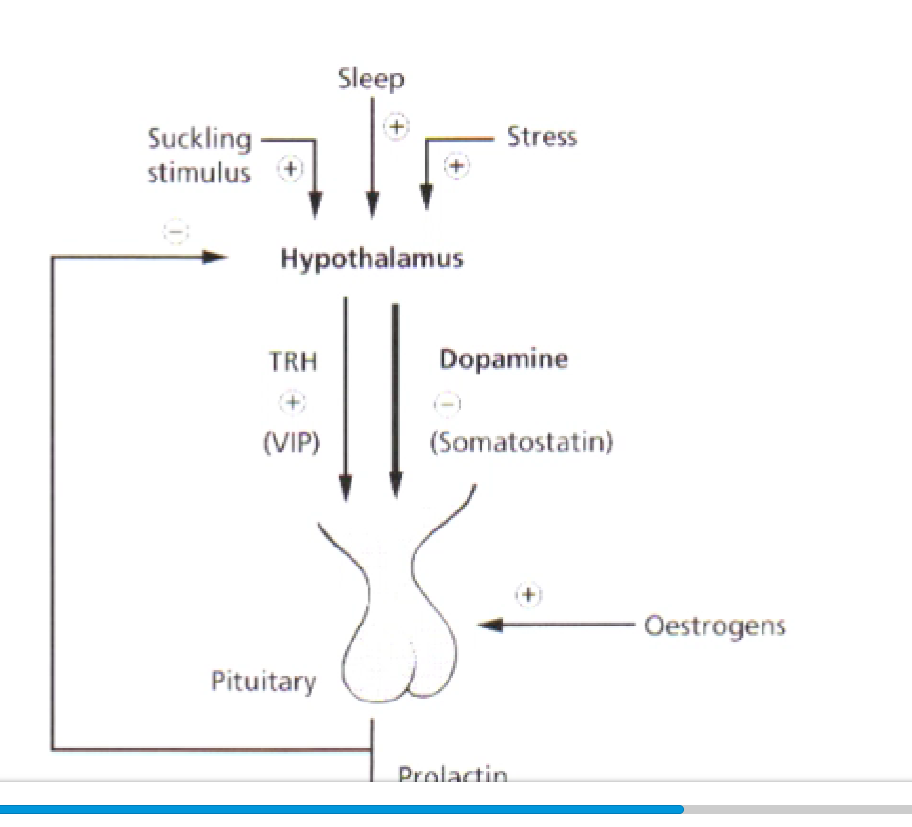
outline some effects of prolactin
stimulates mammary gland development
DNA synthesis, epithelial cell proliferation, synthesis of lactose + free fatty acids
maintains lactation
synergised by glucocorticoids
inhibited by oestrogen and progesterone
prolactinomas
tumor in pituitary gland, causes prolactin production
causes inappropriate expression of milk
interferes with the HPG axis- causes infertility, amenorrhoea, galactorrhoea
treated with dopamine agonists
NB hypothyroidism —> hyperprolactinaemia due to elevations in TRH
growth hormone
pulsatile secretion w/many inputs
released throughout life, stimulated by low glucose, exercise, sleep
DOES NOT act upon bones and growth itself- stimulates liver to produce IGF1 to allow for growth
list the stimulatory factors that regulate growth hormone release
GHRH
Dopamine
Catecholamines
Excitatory amino acids
Thyroid hormone
list the inhibitory factors regulating growth hormone release
somatostatin
IGF-1
glucose
FFA
what can go wrong if you have incorrect levels of GH?
deficiency/resistance: due to receptor mutations such as Laron syndrome dwarfism, treated with IGF-1
deficiency: treated w/recombinant hGH
excess: acromegaly in adults or children, large jaw and hands
list some causes of hypopituitarism
pituitary tumor
brain surgery
trauma such as road accidents
radiotherapy
blocked blood supply, bleeding, inflammation
autoimmunity
infection
arginine vasopressin/antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
nonapeptide (9 peptides) secreted from the PP
synthesised and packed with a carrier protein called neurophysin in secretory granules in the magnocellular neurones of the PV and SO nuclei
granules move down to the ends of the fibres
both released upon stimulation of the nerves
how does ADH secretion and plasma osmolarity work?
ADH acts on the collecting ducts of the kidney
collecting ducts intrinsically impermeable to h2o
ADH stimulates the production of water channels and their incorporation into the walls of the collecting ducts
this allows for the reabsorption of free water from tubular fluid
can convert very dilute urine into very concentrated urine
ADH excess
caused by damage to head, secreting tumors, etc
syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH)
water retention (low serum sodium conc) leads to highly concentrated urine
hyper
ADH deficiency
hypo- excess water excretion
diabetes insipidus
ADH needed for water absorption in the renal collecting ducts
ADH controls serum osmolarity- during water deprivation, ADH levels should rise to allow water reabsorption with an associated increase in urine concentration and reduced urine volume
if the PP is damaged, ADH may be reduced or urine cannot be concentrated
secondary to generalised pituitary disease or isolated/idiopathic
causes: polyuria (peeing too often), polydipsia (drinking too often), hypernatraemia and increased serum osmolarity
oxytocin
stimulates contraction of smooth muscle (myoepithelial cells) of breast and uterus
POSTIVE FEEDBACK!
roles in milk ejection reflux and birth (parturition)
neuro-endocrine reflexes: neuro-endocrine cells secrete hormones from the neural axon terminals into the blood in response to some neural signal