AP HUG - Unit 2 (Population and Migration)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Demography
The study of populations and how they are distributed around the world.
Population Distribution
Refers to the way people are spread across a given area, highlighting the patterns of where people live, such as in urban versus rural settings.
-Helps explain why people live in certain places.
Ecumene
Portions of the Earth's surface with permanent human settlements.
Megacities
Cities with over 10 million people
Developed Country (or Industrialized Country)
A nation with a high level of economic growth, advanced technological infrastructure, and a high standard of living for its citizens.
Developing Country (or Industrializing Country)
A nation with a lower level of industrialization, lower income levels, and generally poorer infrastructure.
Characteristics of developed and developing countries (as they pertain to the Demographic Transition Model)
-Developed countries: In Stages 4 or 5 of the DTM, have low birth and death rates, slow or negative population growth, and aging populations.
-Developing countries: In Stages 2 or 3, have high or declining birth rates, falling death rates, rapid population growth, and younger populations.
Population Density
The average amount of people per square mile/kilometer
3 Types of Population Density
1. Arithmetic (crude) density
2. Physiological density
3. Agricultural density
Arithmetic (Crude) Density

Physiological Density
Total amount of PEOPLE divided by the total amount of arable land (farmable land).
-E.g.: Egypt only has 3% arable land. It is highly concentrated along the Nile River so the physiological density would be quite high.
Agricultural Density
Total amount of FARMERS divided by the total amount of arable land.
-E.g.: India has an agricultural country with many farmers making their living growing crops. Their agricultural density would be high because so many people are using the land to farm.
Carrying Capacity
The relationship between the population size and the amount of resources available to them.
Resources < population: The country is over its carrying capacity.
Resources > population: The country is under its carrying capacity.
Resources = population: The country is at its carrying capacity.
Problems that countries with aging population face
1. Labor shortages: As many older people retire, there aren't enough young workers to replace them.
2. Economic slowdown: Fewer workers mean less productivity and slower economic growth.
3. Increased healthcare and pension costs: Governments must spend more on medical care and social support for the elderly.
4. Generational imbalance: A smaller youth population must support a much larger elderly population, creating financial strain (high dependency ratio).
5. Smaller tax base: With fewer working-age people, there's less tax revenue to support growing expenses.
Population Composition
The makeup of the population by age, sex, ethnic, racial, income, and educational background.
-Exactly what demographers study!
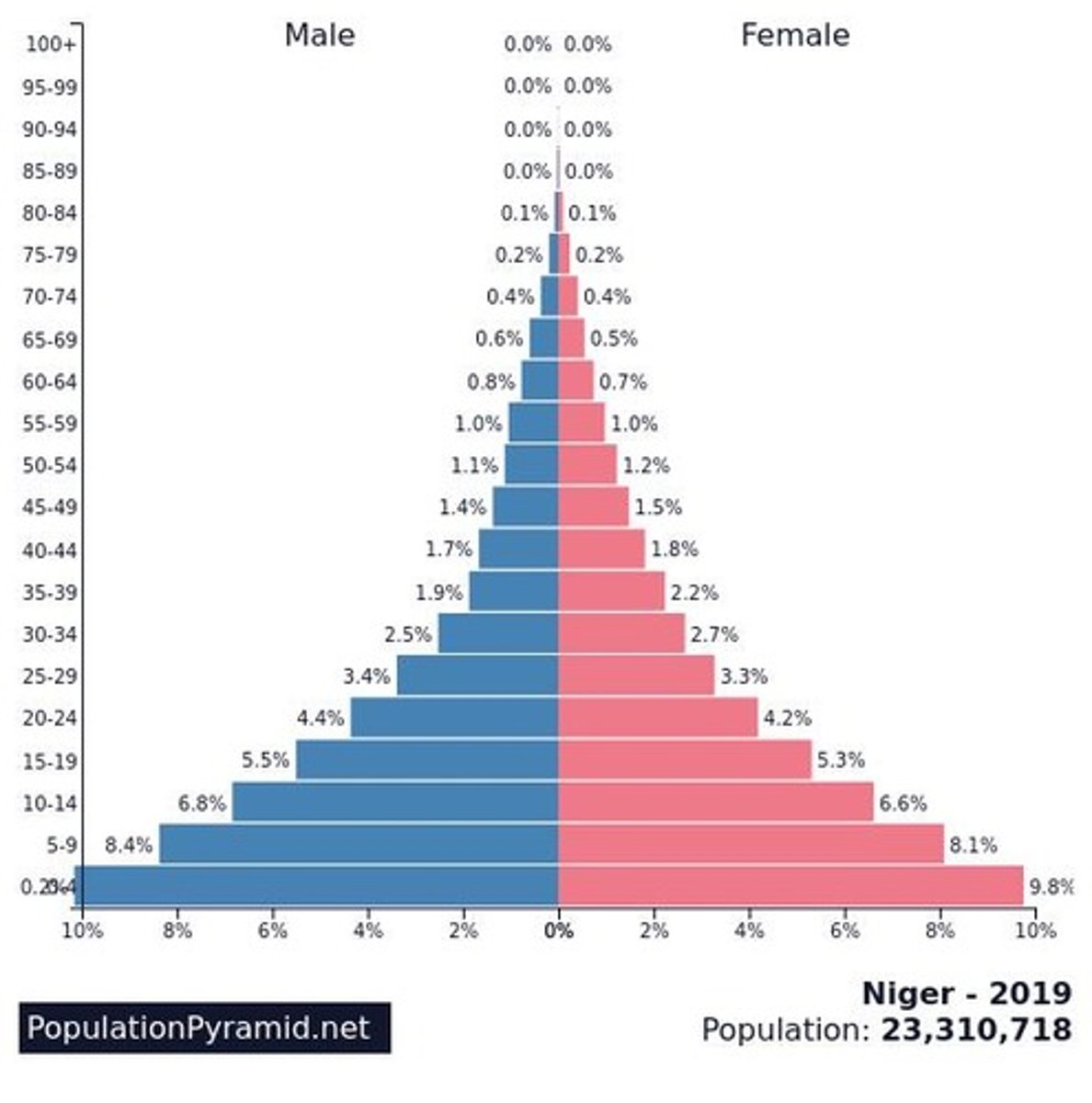
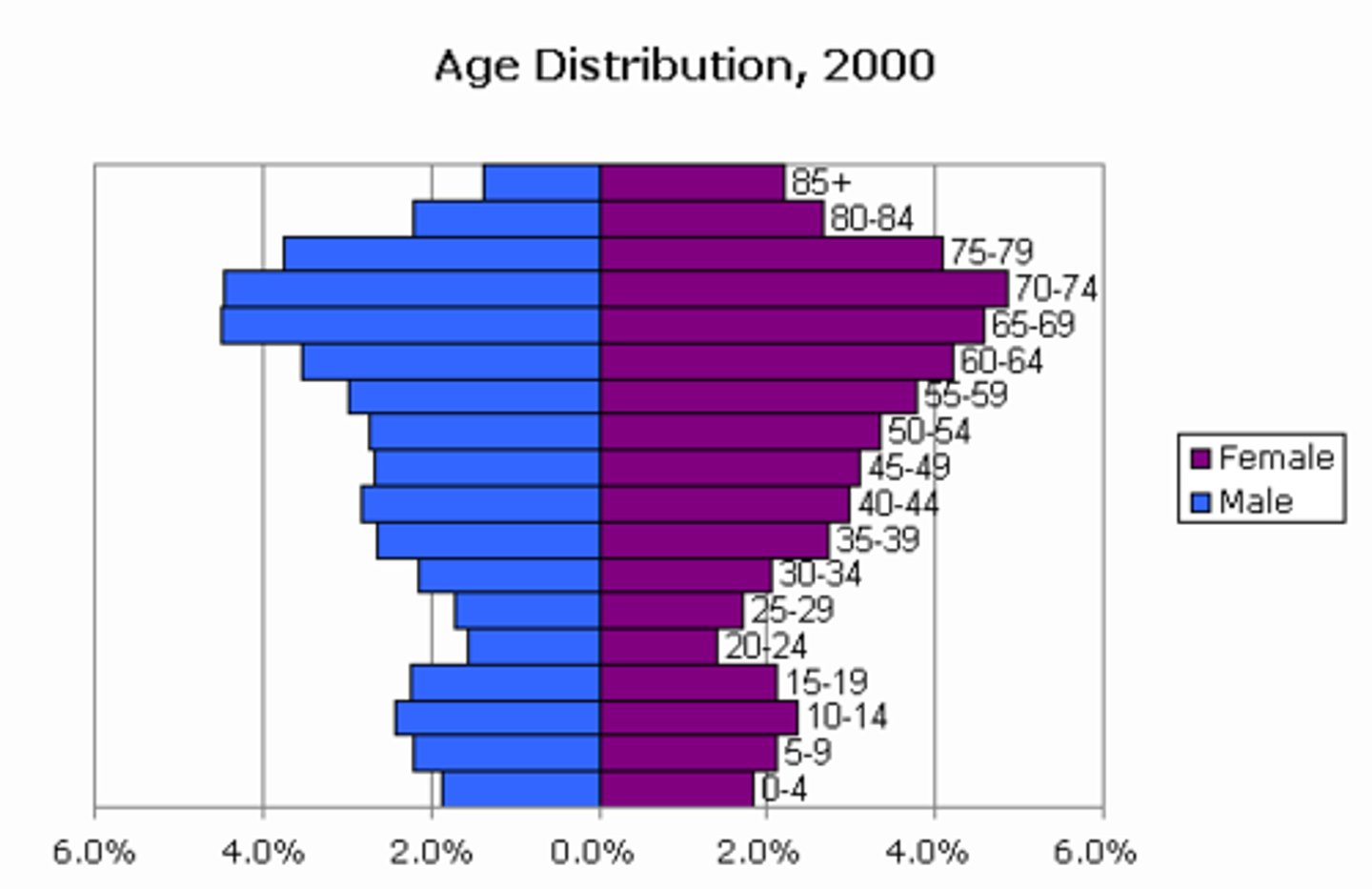
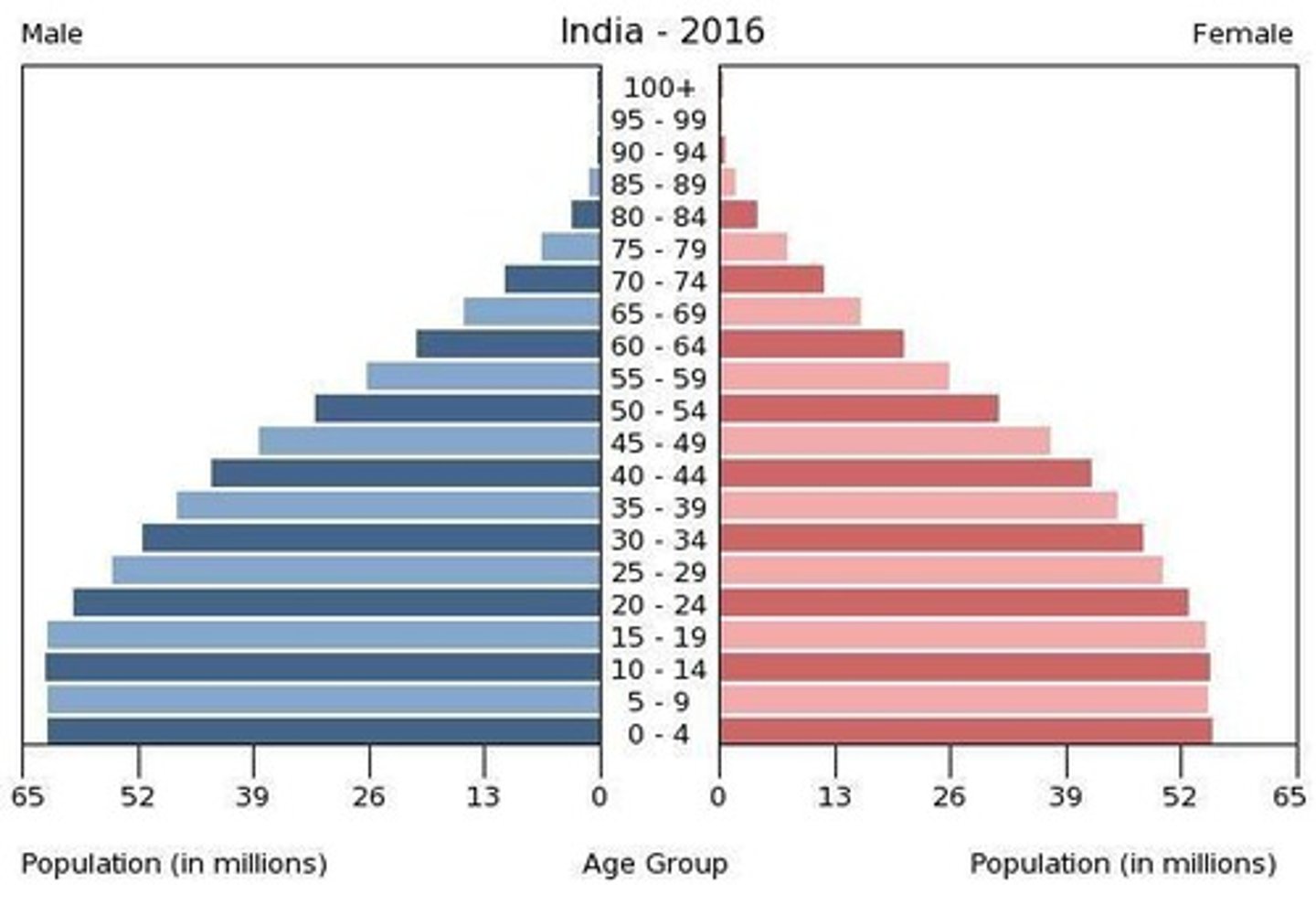
Population Pyramids
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
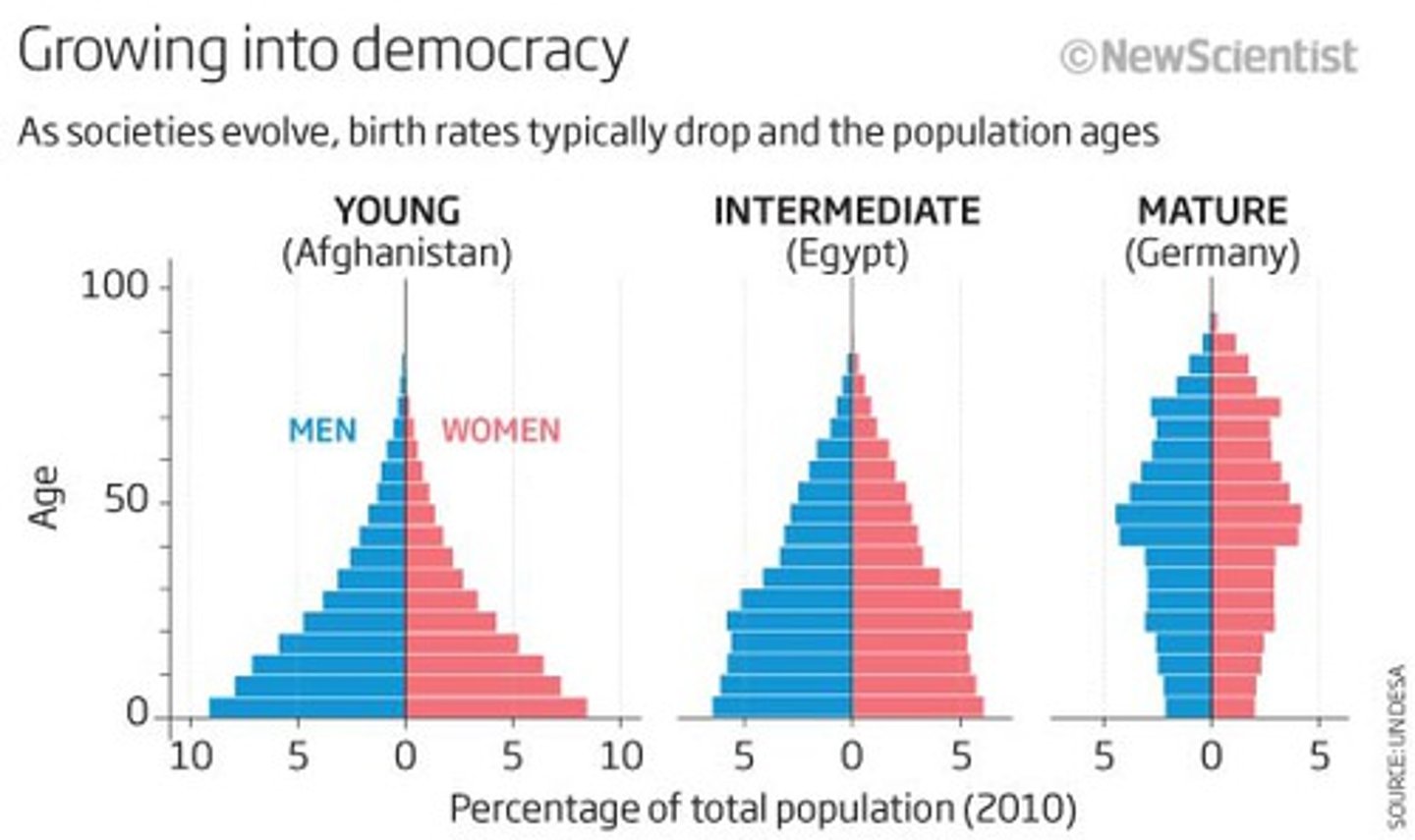
(Population pyramid) When the base is much wider than the rest of the pyramid it means that...
there are many more young people and the population is increasing fast.
(Population pyramid) When the base is a little bit wider than the rest of the pyramid it means that...
the population is growing, but slowly.
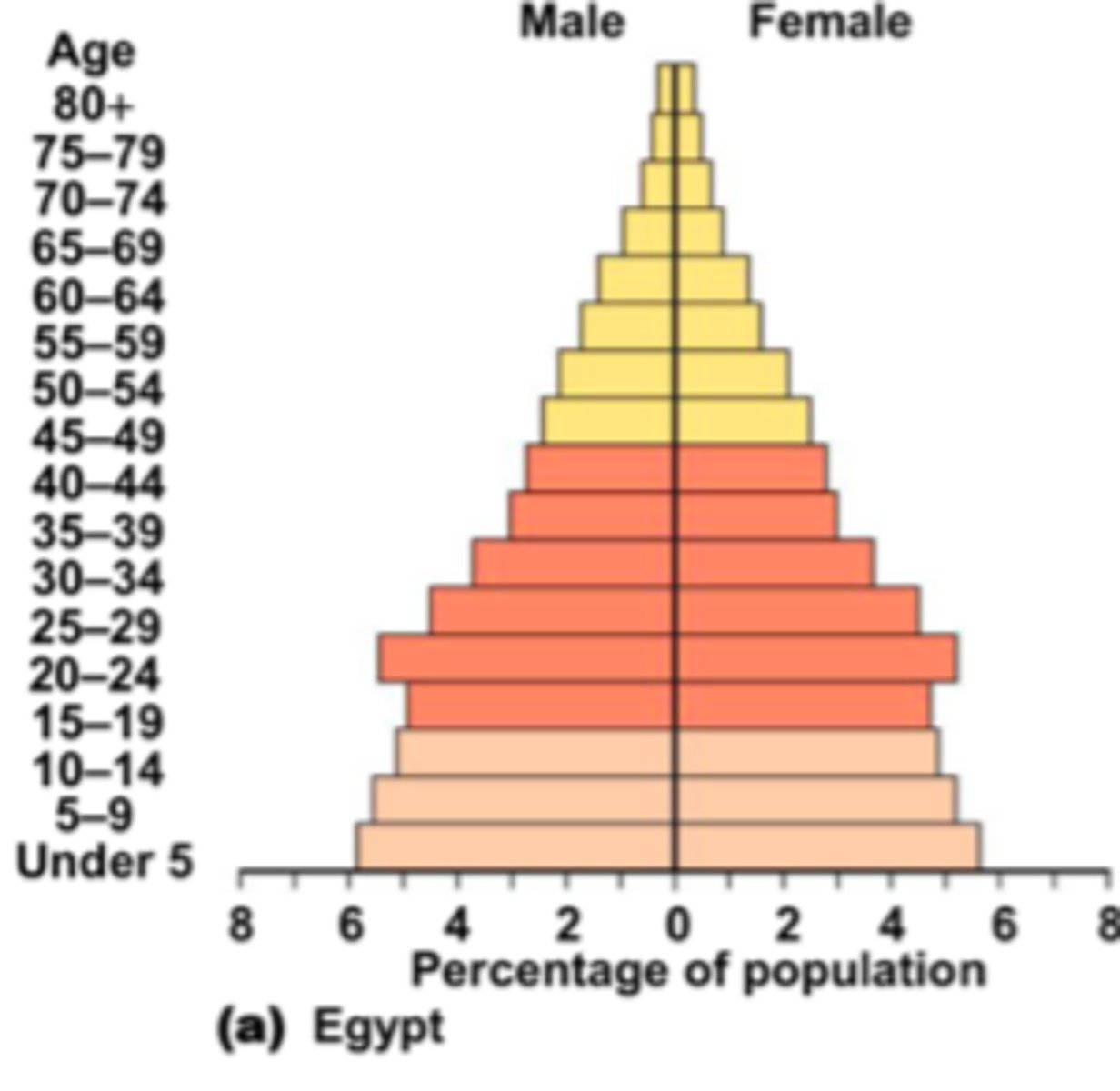
(Population pyramid) When the middle of the pyramid is the widest, it means that...
the population is slowing down.
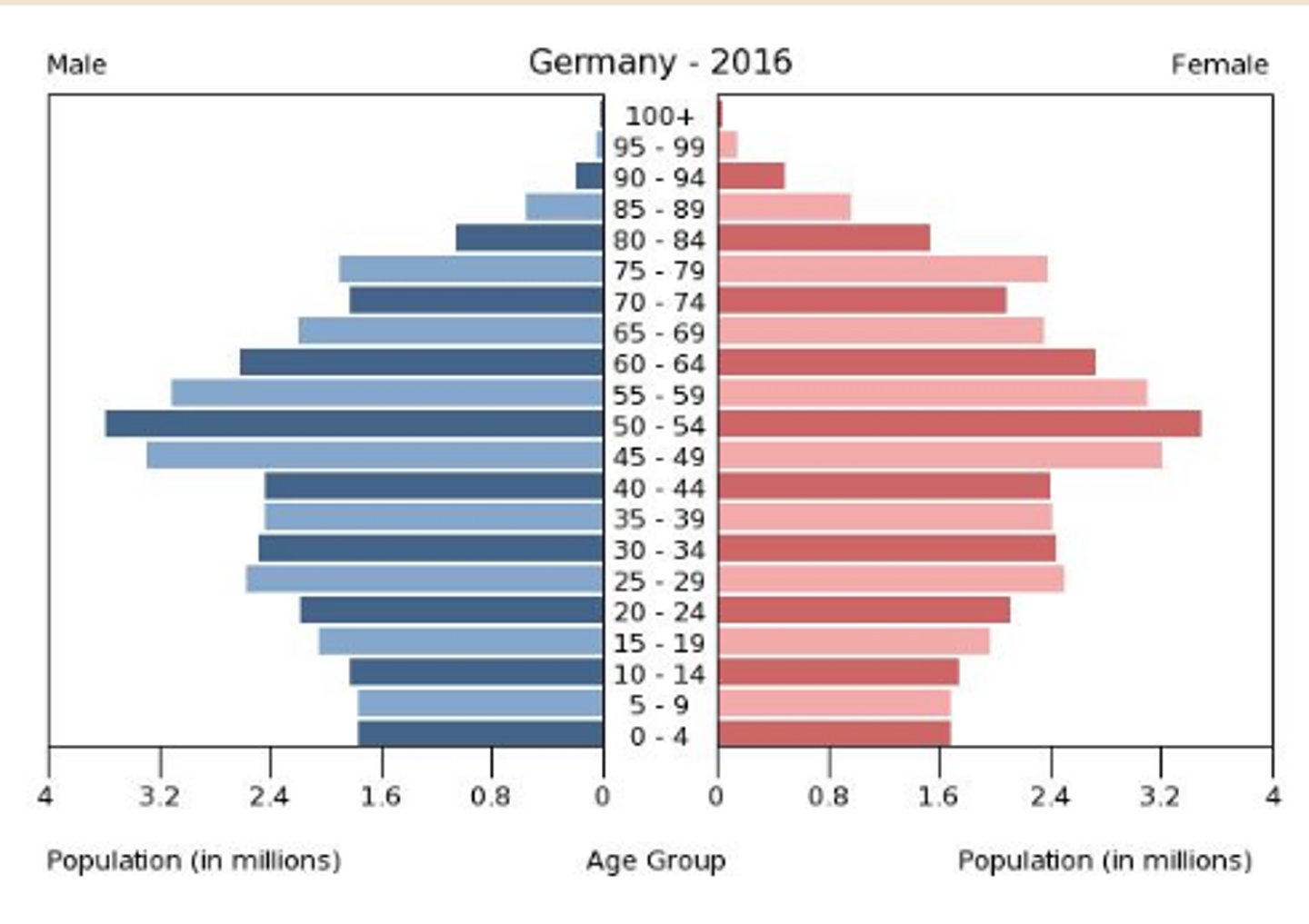
(Population pyramid) If the base is narrow and the top is wide, that means...
the population is decreasing.
Sex Ratio
The number of males per 100 females in the population
Androcentrism
Male centered; the belief that the male is the norm
-Some countries have a much higher sex ratio towards males.

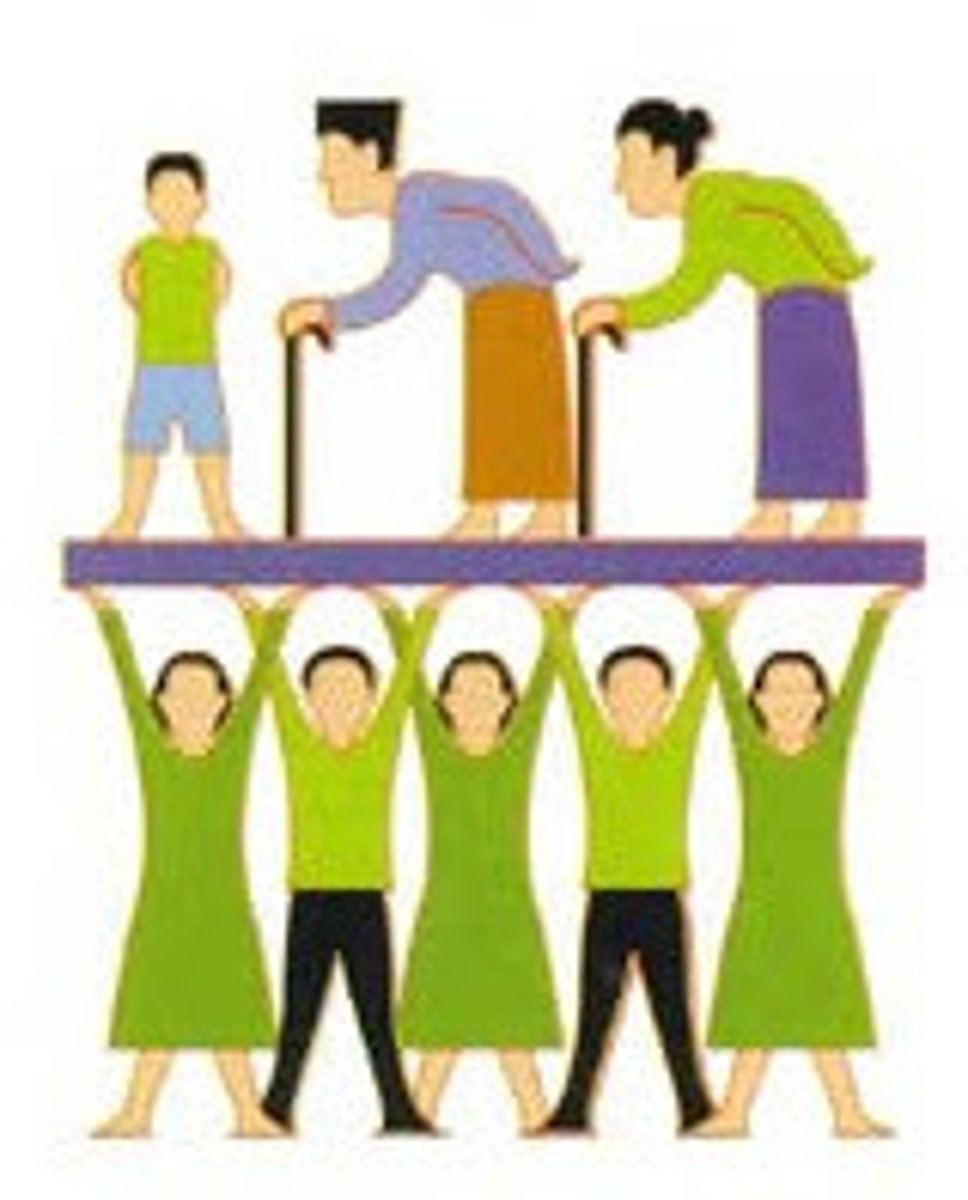
Dependency Ratio
A demographic measure that compares the number of people who are typically not in the labor force (dependents) to those who are (the working-age population).
-Used to assess the economic pressure on the productive population.
-A HIGH dependency ratio means more dependents per working-age person, which can strain sources for healthcare, education, and pensions.

Baby Boomers
People born between 1946 and 1964, result of men coming back from WWII and having a bunch of babies.
-The largest generation in America

Infanticide
The killing of an infant, often occurring due to cultural preferences for male children and leading to imbalanced sex ratios.

Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
Tells us per 1,000 people in a place, how many babies have been born in a year.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
Tells us how many babies are born per woman over her lifetime.
-Developing countries usually have higher TFR.
-Countries are considered to have low birth rates if their CBR is between 10-20 births per 1,000 people, while countries with more than 30 births per 1,000 people are considered to have high birth rates.
Infant Morality Rate
Shows how many babies die per year before the age one out of 1,000 babies born.
Crude Mortality Rate (Death Rate)
Tells us how many people in a country die per year out of every 1,000.
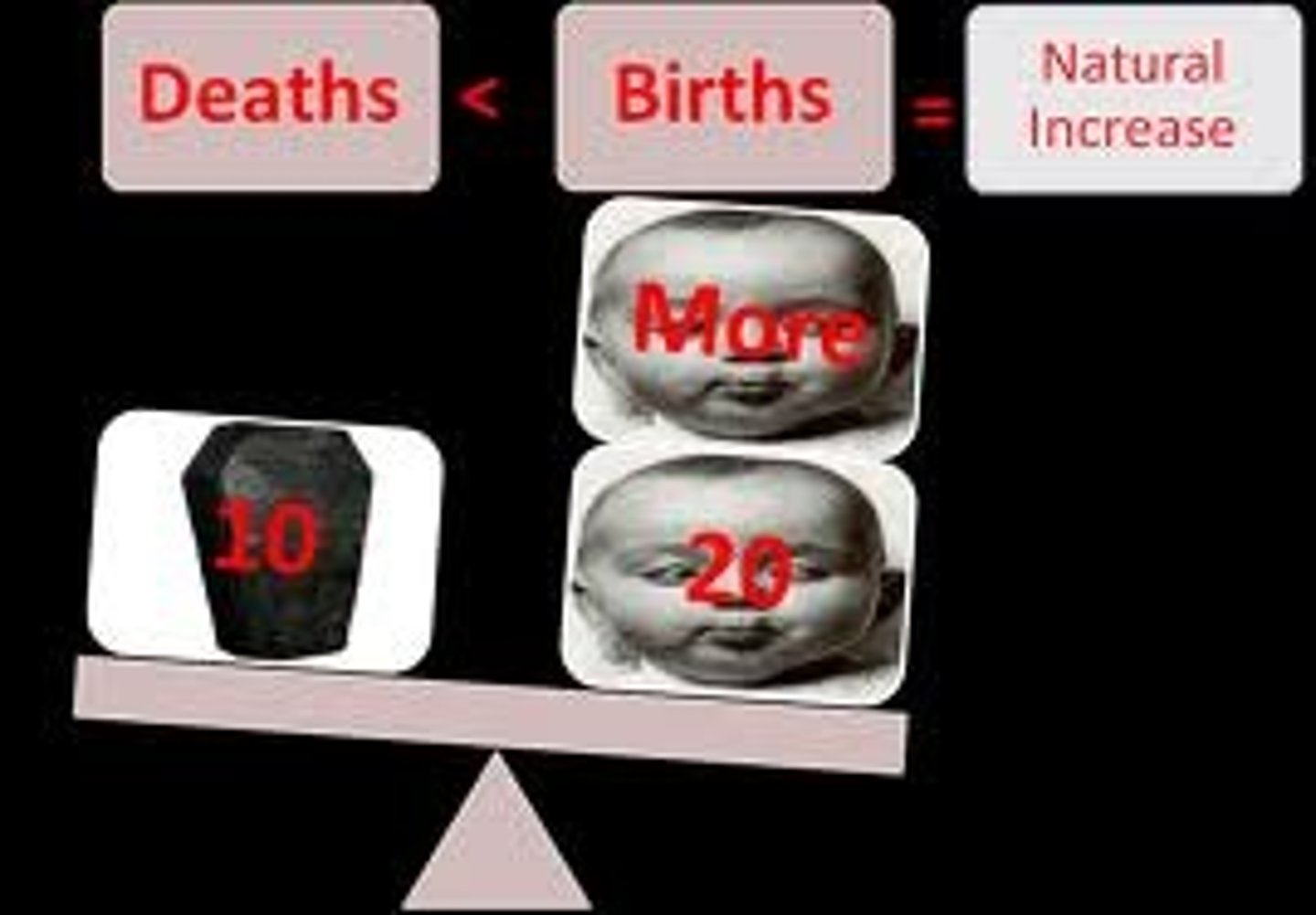
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
The percentage by which a population grows in a year.
Crude Birth Rate - Crude Death Rate
Life Expectancy
The average number of years a person is expected to live, based on current mortality rates.
-Reflects the overall health and quality of life in a country or region and is influenced by factors like: Healthcare access, Nutrition, Sanitation, Living conditions, Education.
Population Doubling Time
The amount of time it takes for a population to double.
Rule of 70
Trick to calculate the population doubling time of a country: 70 / NIR
Replacement Level Fertility / Replacement Rate
The average number of children needed to replace both parents and keep the population stable with no increase or decrease.
-TFR in the country needs to be 2.1. If a country is above or below 2.1, they will experience population shifts.
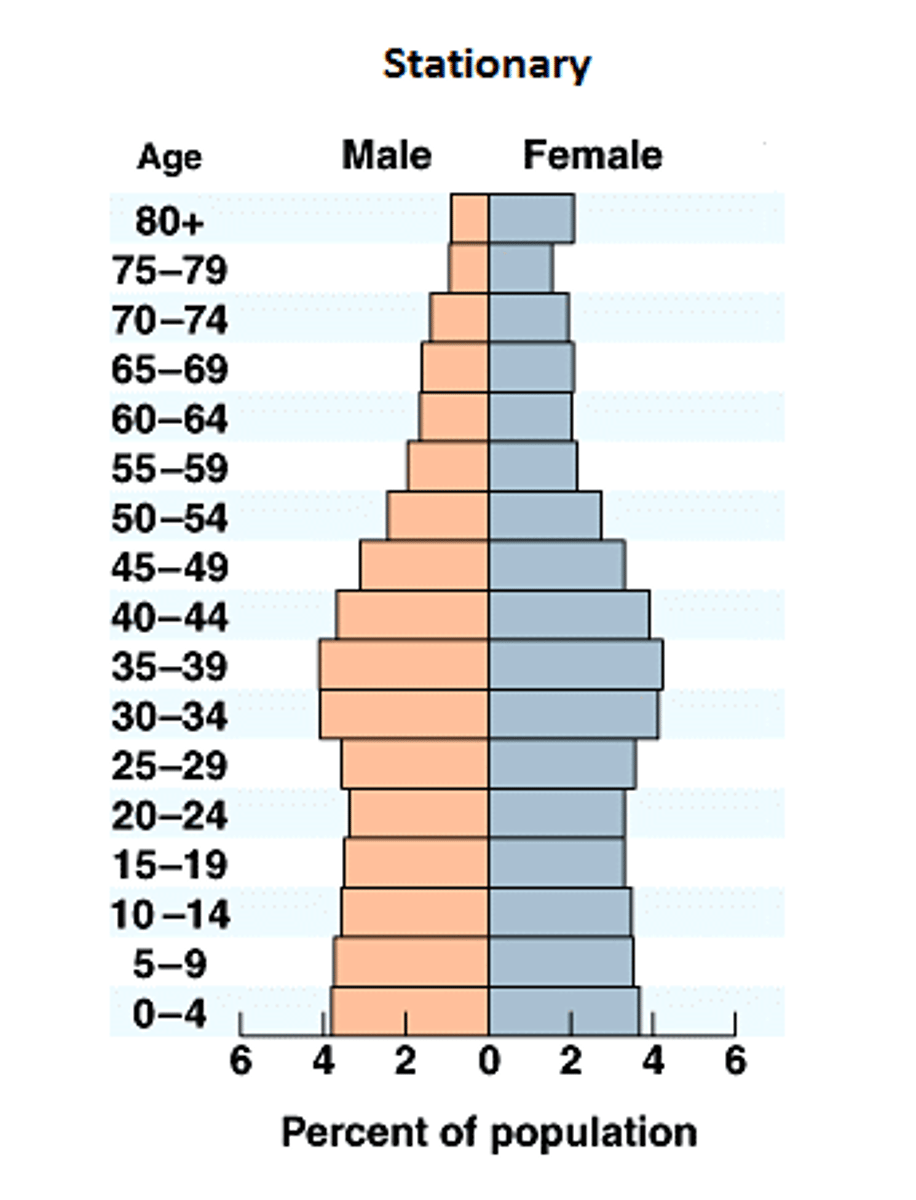
Low Birth Rate
Any time the TFR is below 1.5.
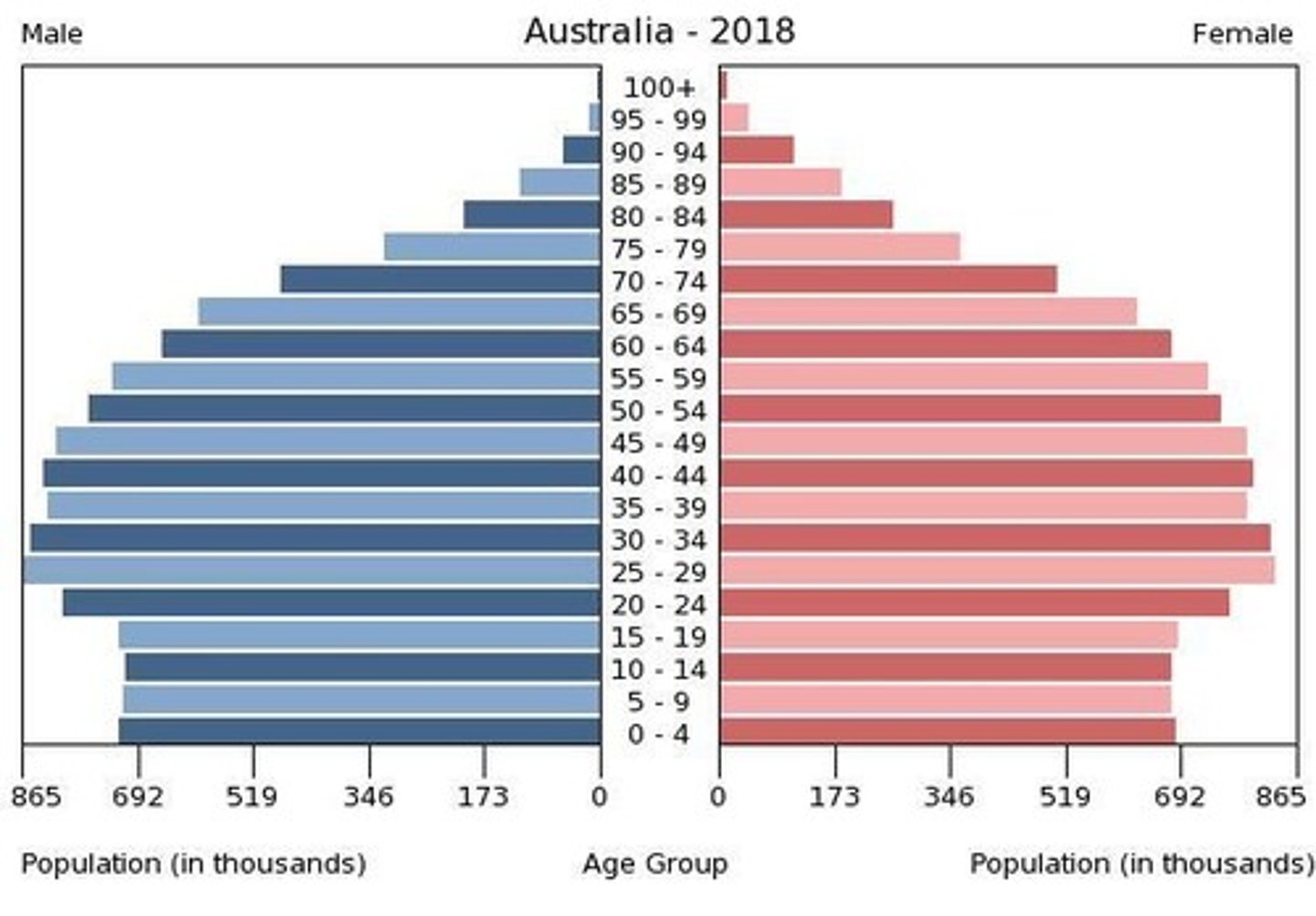
High Birth Rate
Any time the TFR is above 3.5.
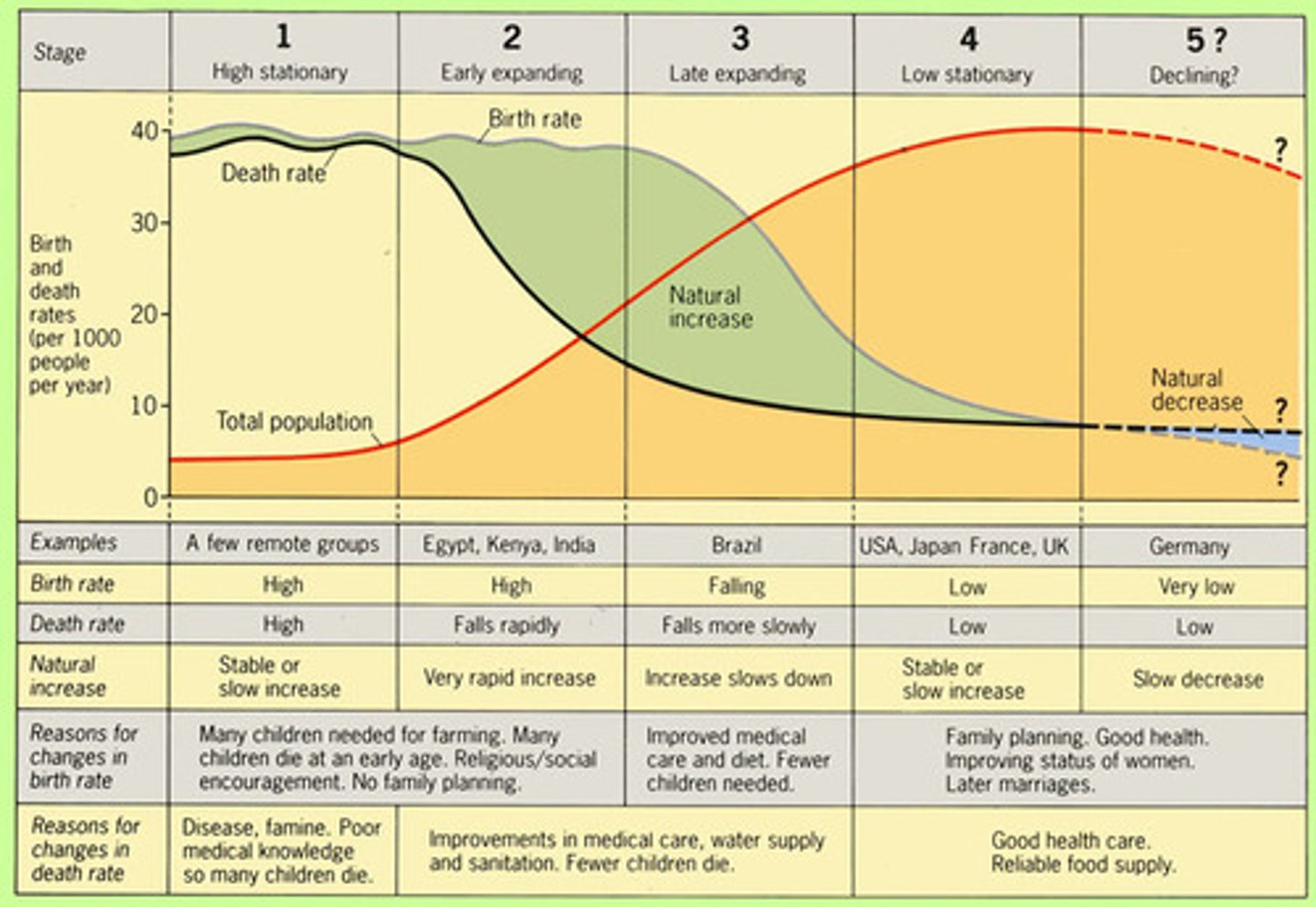
Demographic Transition Model
A model that shows how a country's population changes over time as it develops.
-It is based on birth rates and death rates, to suggest that a country's total population growth rate cycles through stages as that country develops economically.
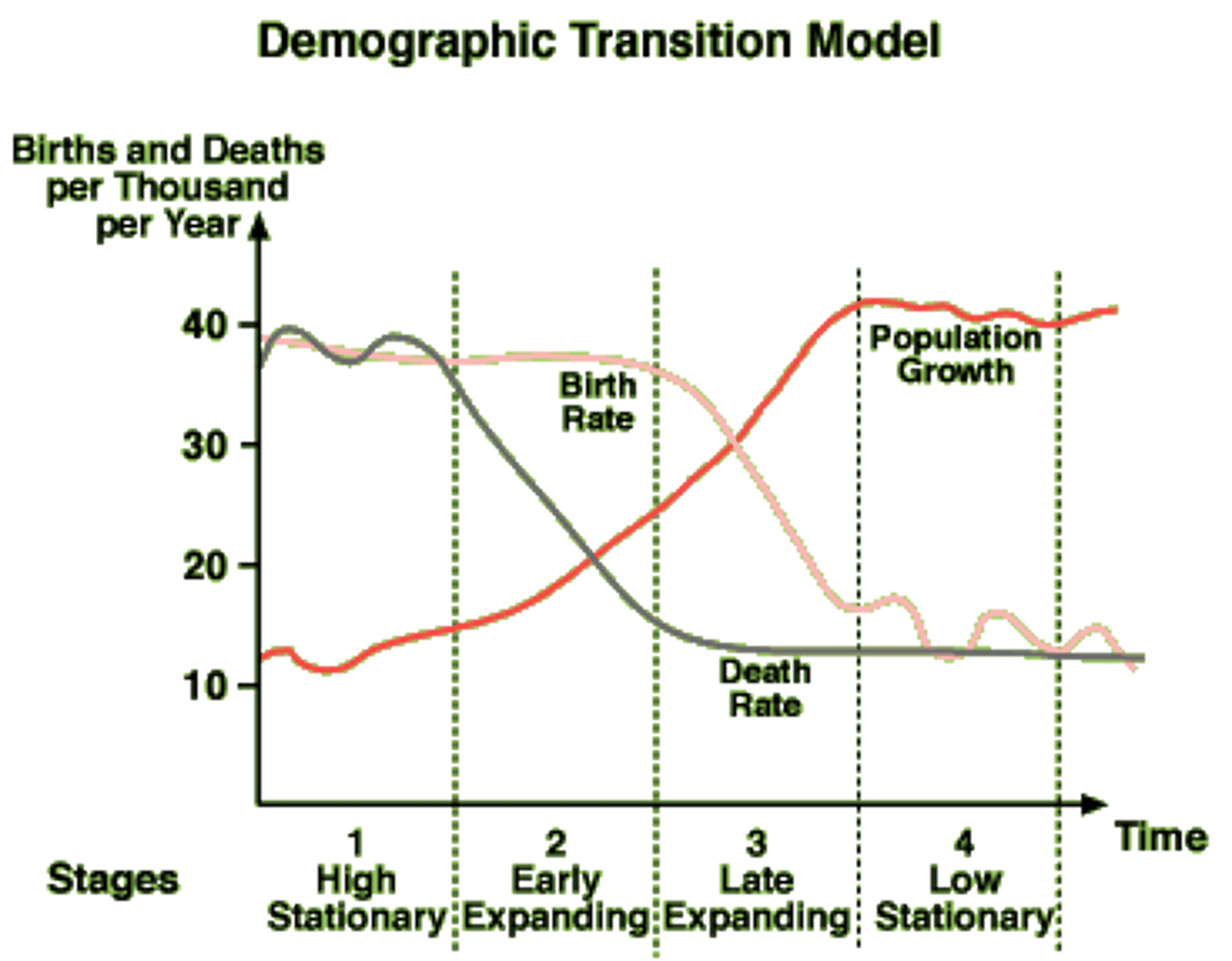
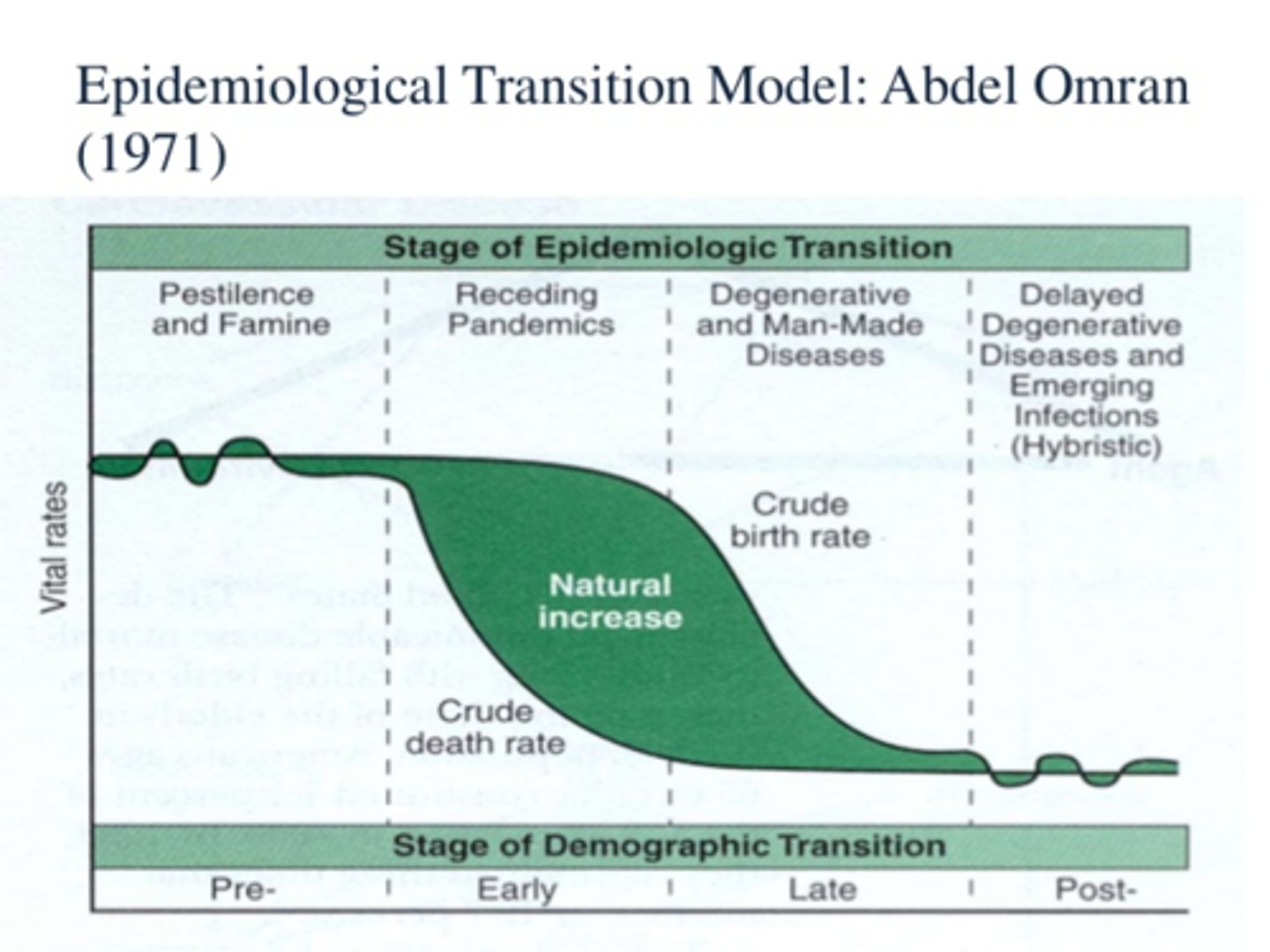
Epidemiological Transition Model
A framework used by geographers, demographers, and public health experts to understand how patterns of disease and causes of death change over time in relation to economic development and social progress.
-Tells us what the leading causes of death are in each stage of the demographic transition model.
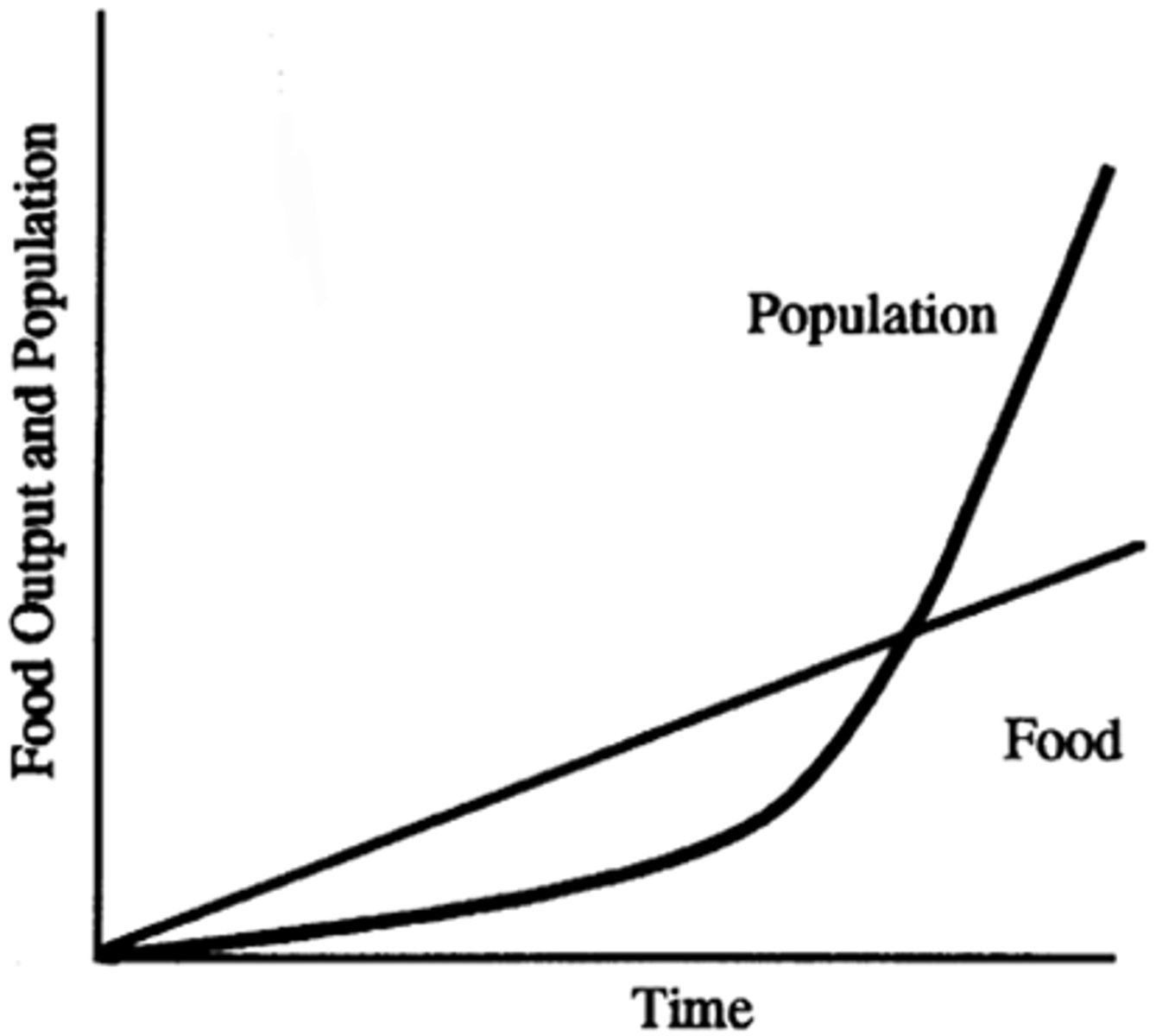
Malthusian Theory
Developed by Thomas Malthus, states that population growth tends to outpace food production, leading to periodic checks like famine, disease, and war.
Overpopulation
When population exceeds the food supply.
Cornucopians
Individuals or theorists who believe that human ingenuity and technology can overcome any resource limitations and that population growth can lead to increased prosperity.
-They argue that advancements in science and technology will enable humanity to find solutions to challenges like food shortages and environmental issues, often opposing the pessimistic views of resource scarcity.

Boserup Effect
The idea that humans constantly come up with innovative farming methods.
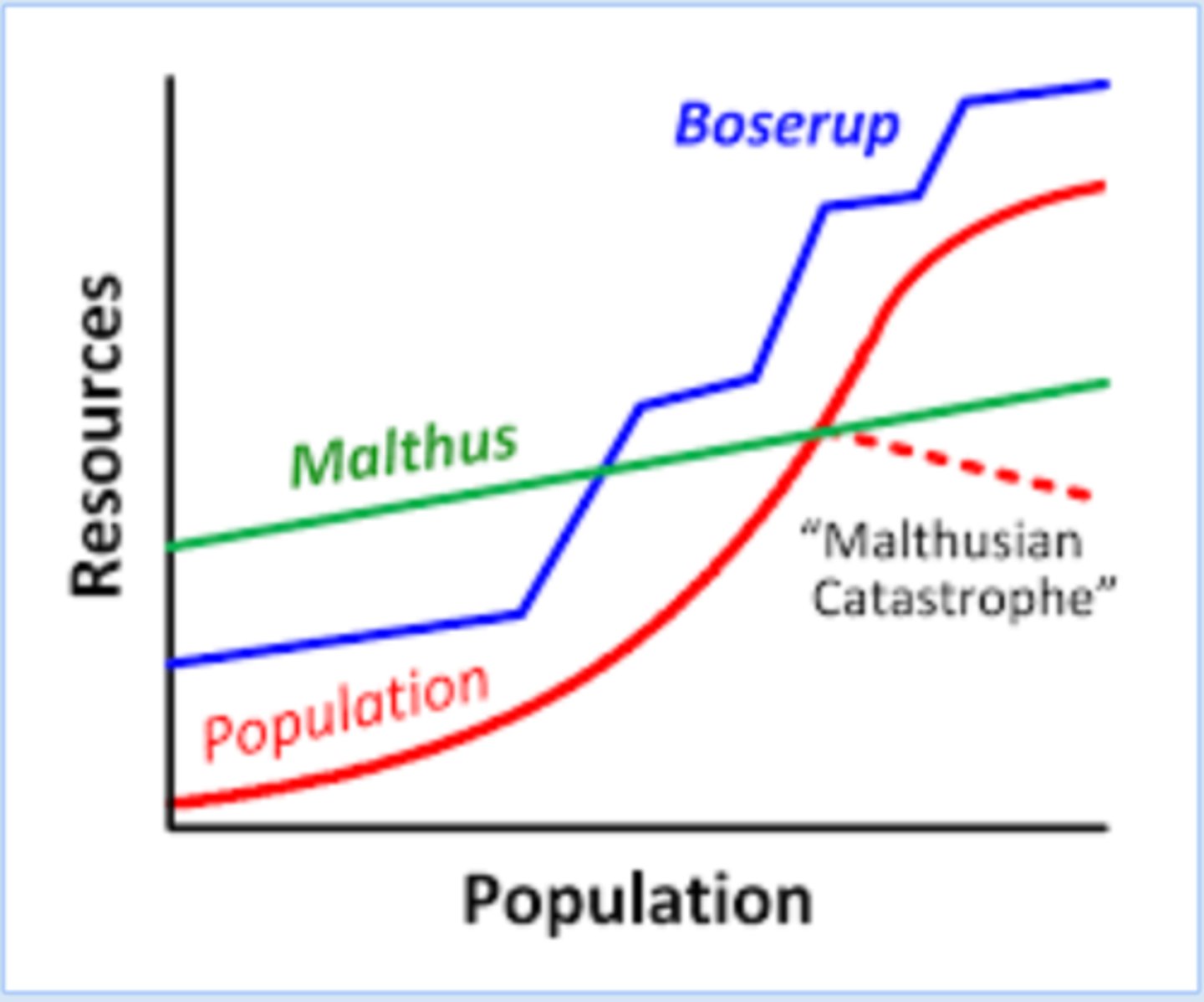
Anti-Natalist
Government policies concerned with LIMITING population growth.

Pronatalist
Government policies that ENCOURAGE people to have children.

Women Empowerment
Refers to an increased autonomy for women to make their own choices and shape their lives.
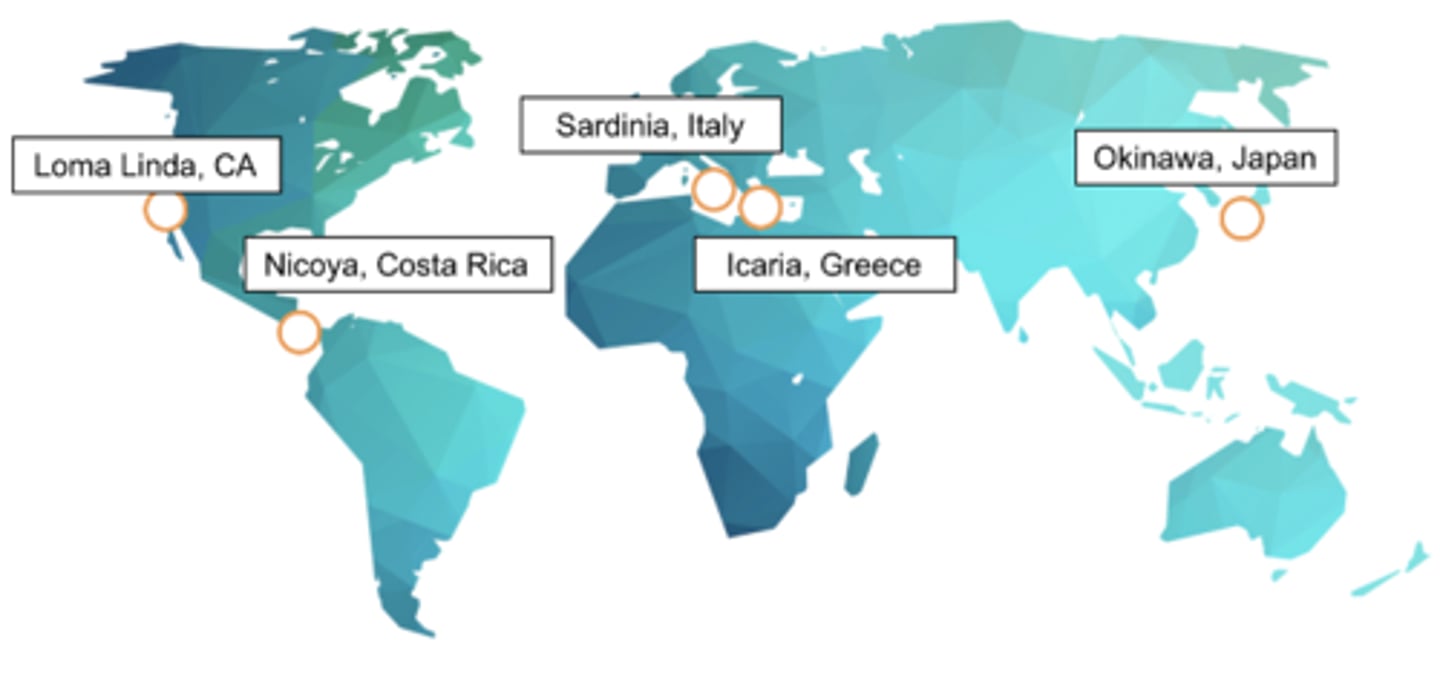
Blue Zones
Areas of the world where it is common for people to live to be over 100 years old.
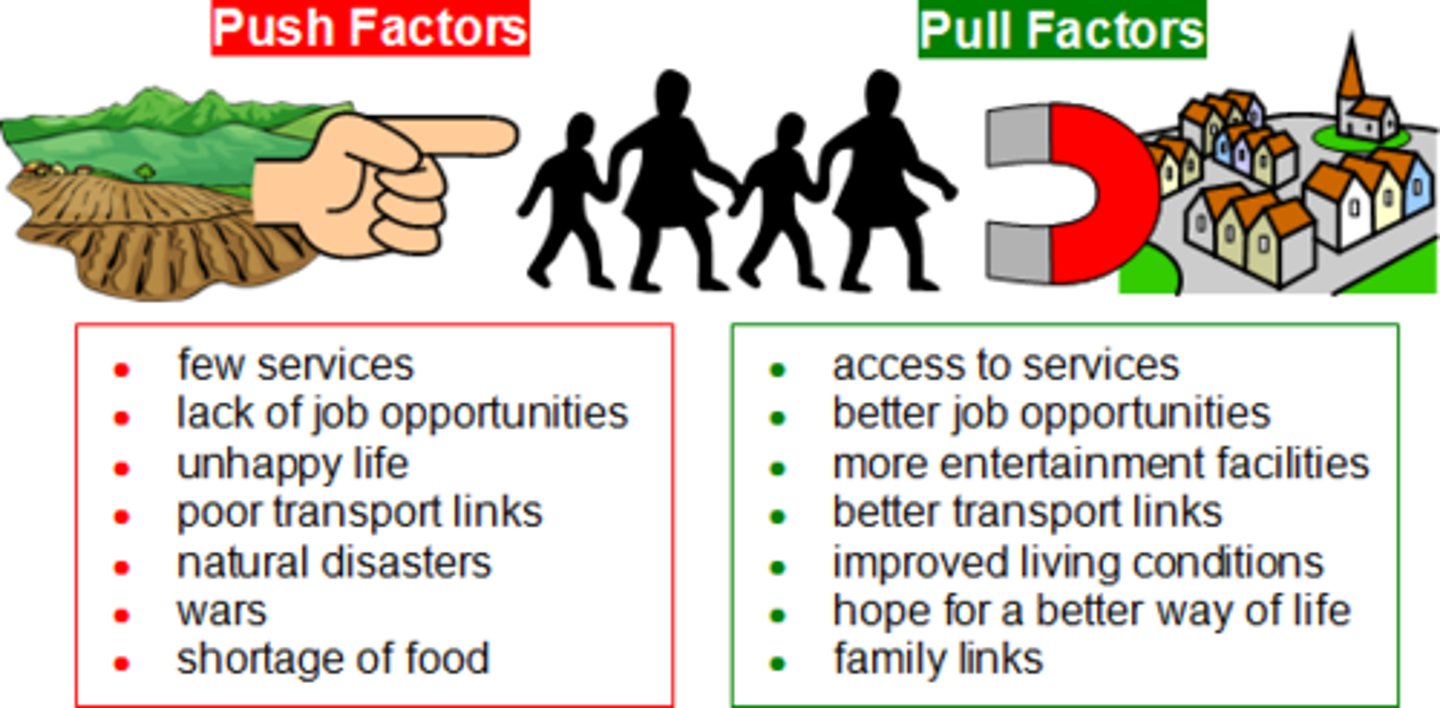
Push Factors
Factor that cause people to leave their homelands and migrate to another region.
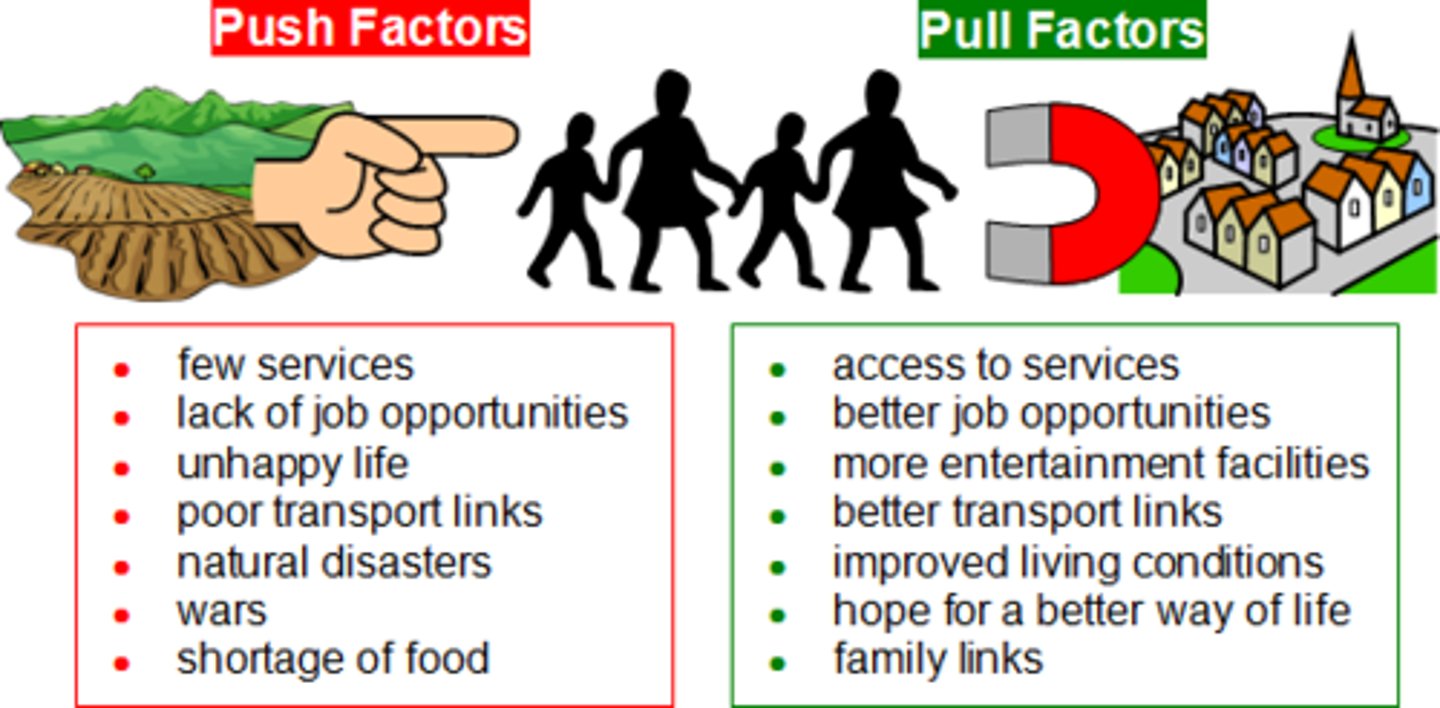
Pull Factors
Factor that draw or attract people to a certain location.
Immigrants
Individuals who move into a new country with the intention of settling there permanently or for an extended period.
Emigrants
individuals who leave their country of origin to settle in another.
-Often driven by "push" factors like poverty, conflict, or environmental issues in the home country, and influenced by "pull" factors such as job opportunities, better living conditions, or political stability in the destination country.

Intervening Obstacles
Any forces or factors that may limit human migration.

Intervening Opportunities
The presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away.
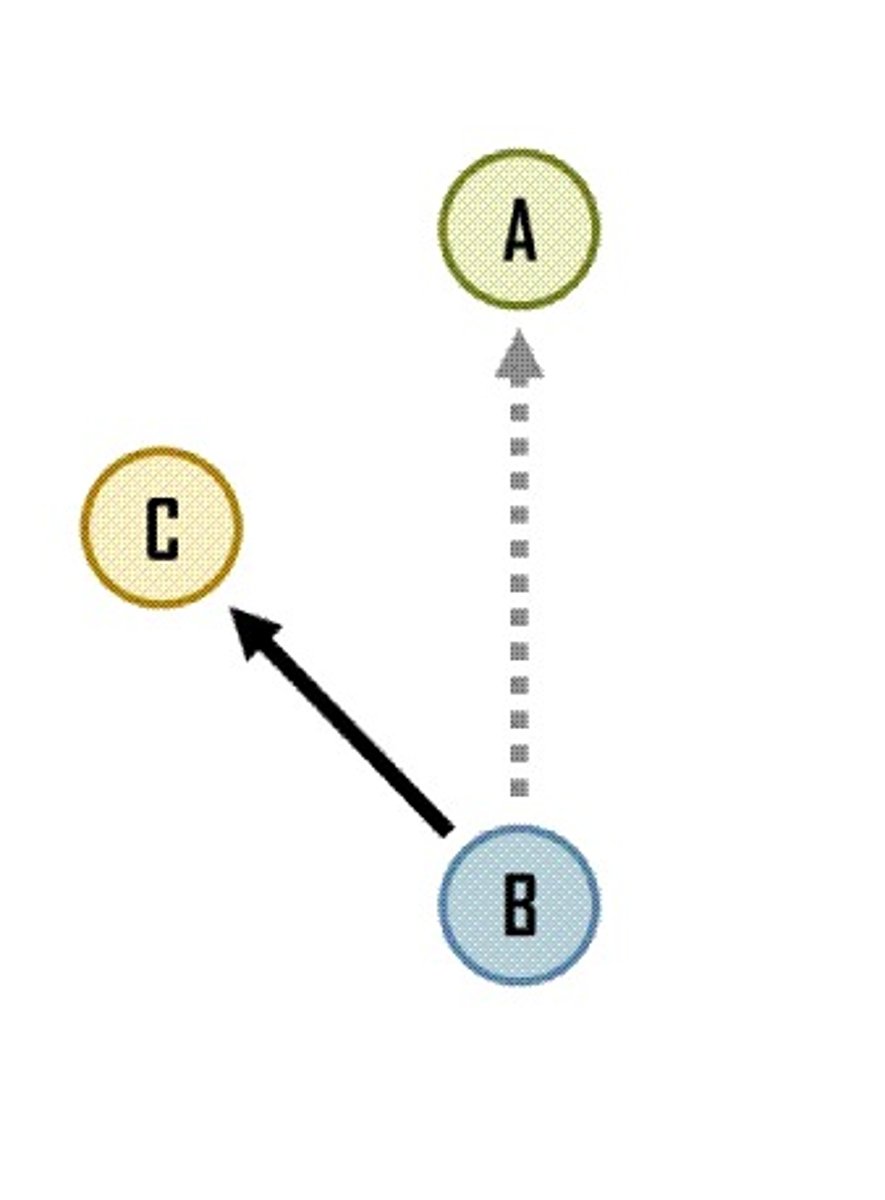
Asylum
Protection granted by a country to someone who has fled their home country due to fear of persecution based on race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or social group.

Refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster.

Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries
Net Migration
The difference between the number of people entering (immigrants) and leaving (emigrants) a country or region.
Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs)
People who have been forced to flee their homes due to conflict, violence, or disasters but remain within their country's borders.
-E.g.: Palestinians
Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
A set of "laws" that can be organized into three groups: the reasons why migrants move, the distance they typically move, and their characteristics.

Brain Drain
The loss of highly educated and skilled workers to other countries due to brighter opportunities.

International Migration
Moving across a border.
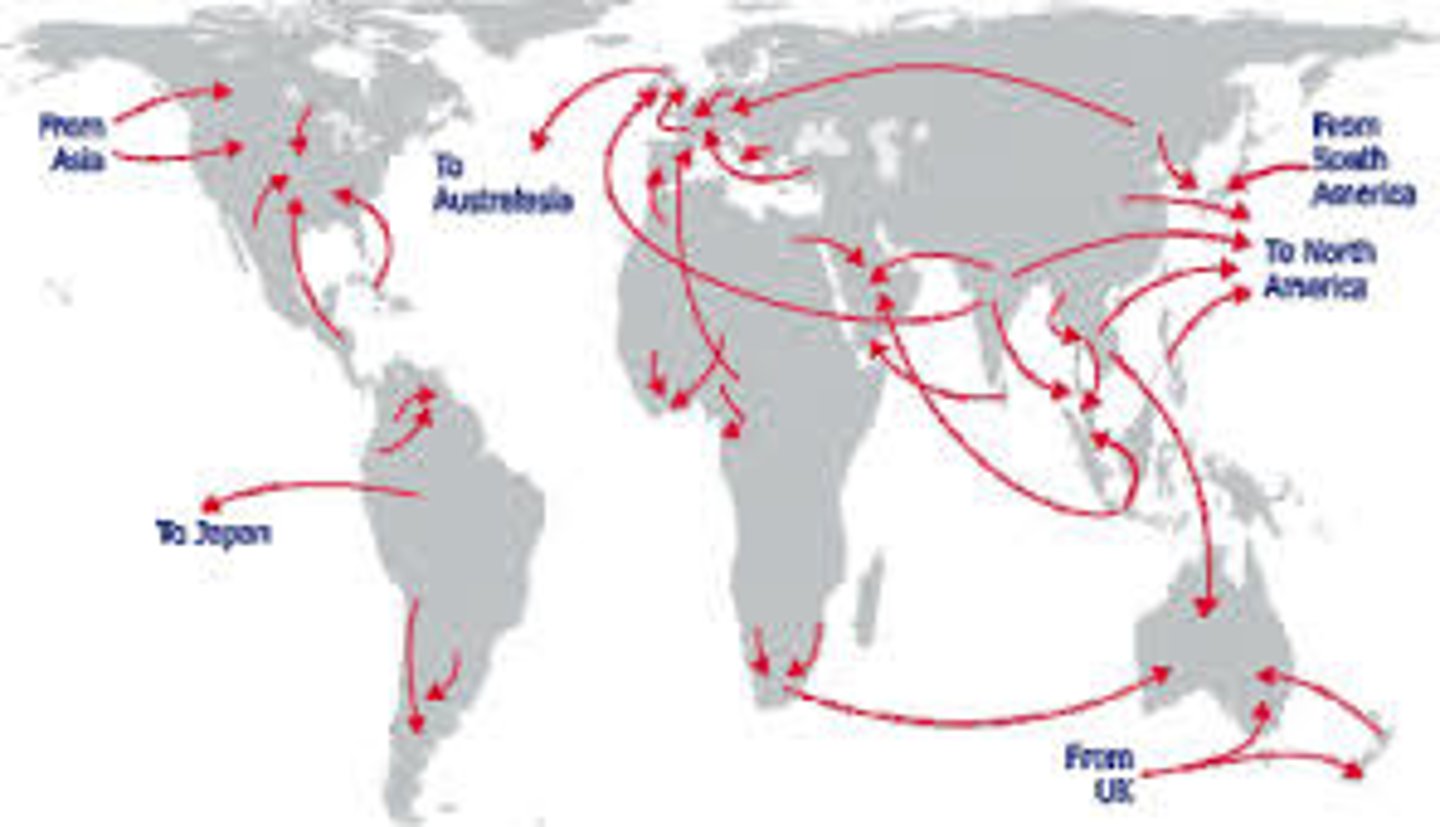
Guest Worker
Moving for temporary employment.
Transnational Migration
Moving back and forth repeatedly between two countries.
Internal Migration / Interregional Migration
Moving within a country from one region to another.
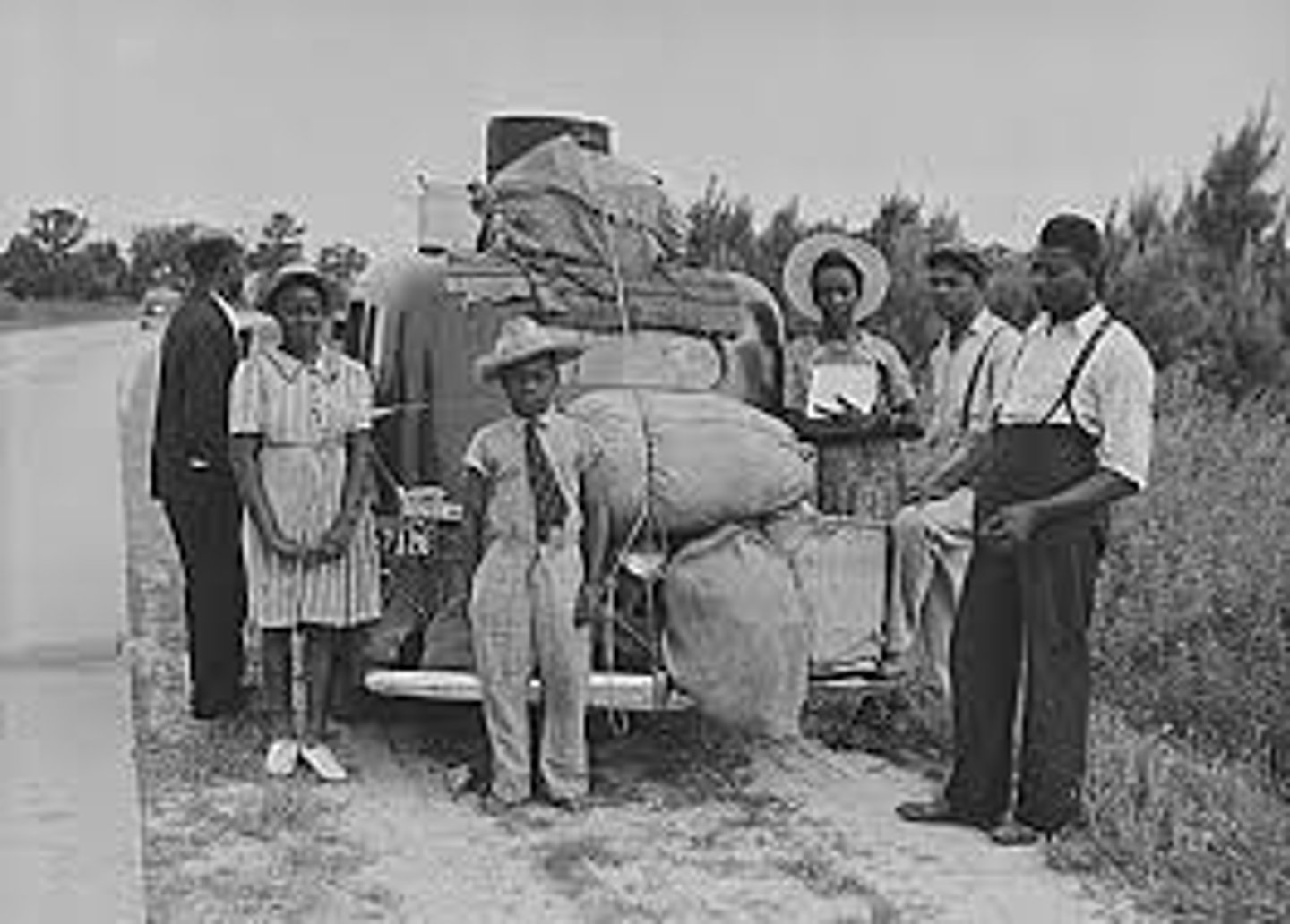
The Great Migration
Famous historic migration in America when the black population in the U.S. moved to the northeast or west to escape racist laws of the South.

Rural to Urban Migration
Moving from a farm to a city.

Residential Mobility
Moving within a city from one house to another.
Step Migration
Moving a long distance, but making temporary stops along the way to live and work periodically.
Chain Migration
Moving to a place where your family members have already moved.
Return Migration
Moving back to the country you previously moved away from.
Seasonal Migration / Circular Migration
Moving based on the time of year.
Transhumance Migration
The seasonal migration of people and their livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures.

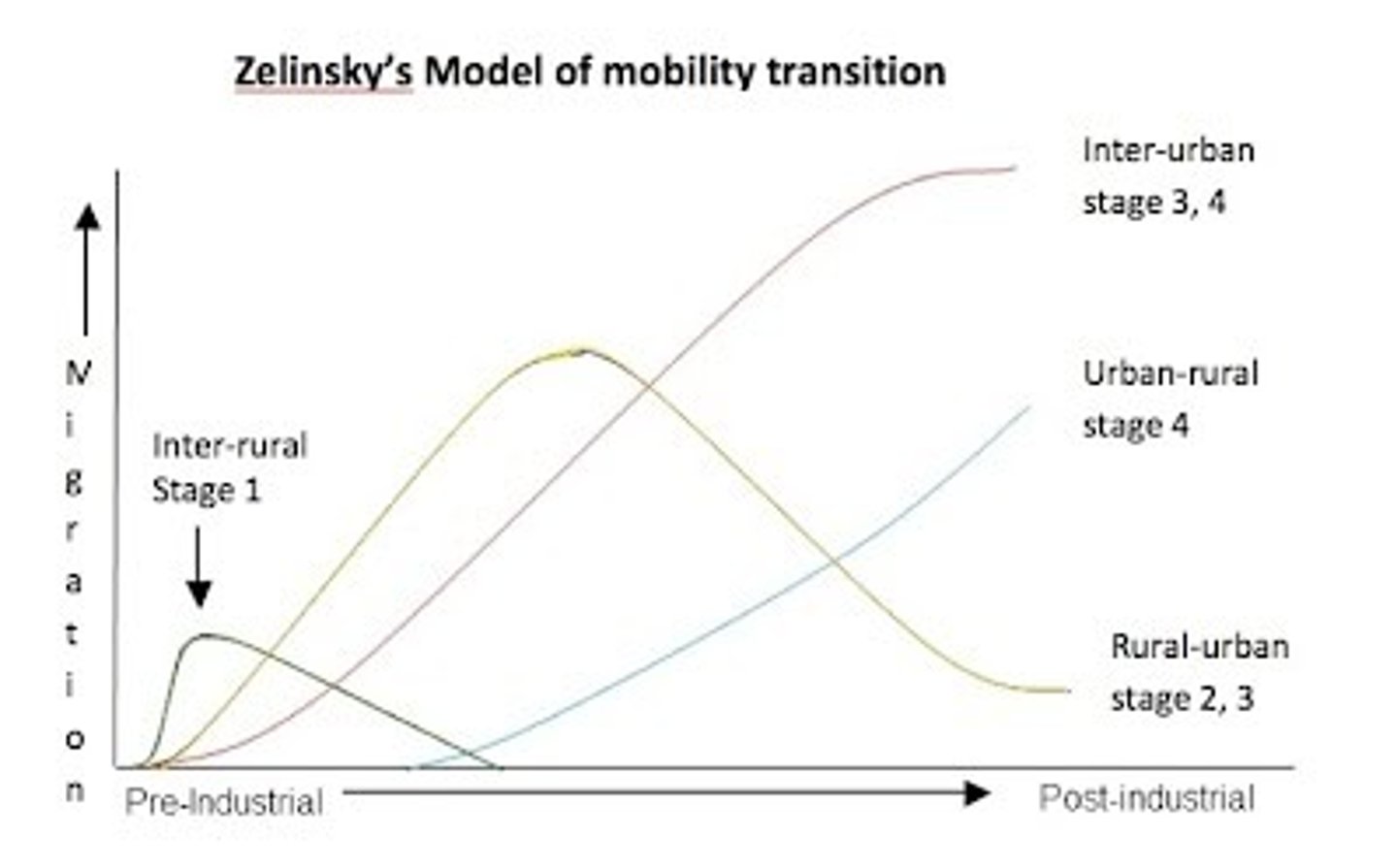
Zelinsky's Migrant Transition Model
A model that consists of five distinct stages of migration corresponding to the demographic transition model: pre-modern, transitional, industrial, post-industrial, and future.