IB BIOLOGY TOPIC 2
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
carbon compounds
carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid, proteins
Metabolism
the chemical processes (enzyme catalyzed) that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life.
Anabolism
the synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones, including ther formation of macrolmes from monomers by condensation reactions
Catabolism
the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules, including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers.
Insulin
protein hormone that facilitates the movement of glucose form the bloodstream to the interior of cells
organic chemistry
the study of all chemicals containing carbon
Subcomponent of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
subcomponent of lipids
Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphate groups
Subcomponent of proteins
amino acids
subcomponent of nucleic acids
nucleotides
carbohydrate subcategories
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
Lipid subcategories
triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
Protein examples
enzymes, antibodies, peptide hormones
Monosaccharide examples
glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose
Disaccharide examples
sucrose, lactose, maltose
polysaccharide examples
starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
triglyceride examples
fats in adipose tissue
phospholipid example
bilayer of cell membrane
Steroid examples
cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen
nucleic acid examples
DNA, RNA, ATP
Enzymes
molecule that increases the likelihood that a collision will lead to a useful reaction
hydrogen bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
polar covalent bond
bond between the oxygen atom and the two hydrogen atoms of a signle water molecule; A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
Electrons
Negatively charged particles
covalent bond
A chemical bond formed when two atoms share electrons
Dipolarity
Polarity only on two poles
e.g. water molecules
ephermal
short-lived
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
high specific heat
A property of water. Water can absorb lots of heat before changing temperature
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
Pholem
type of vascular tissue that carries nutrients, food , and dissolved sugars from place to place inside the cell
Hydrophilic
water loving
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
Methane
non polar substance example
monosachharides
monomer of carbohydrates; linked together by condensation reactions to form disaccharides
Types of fatty acids
saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated
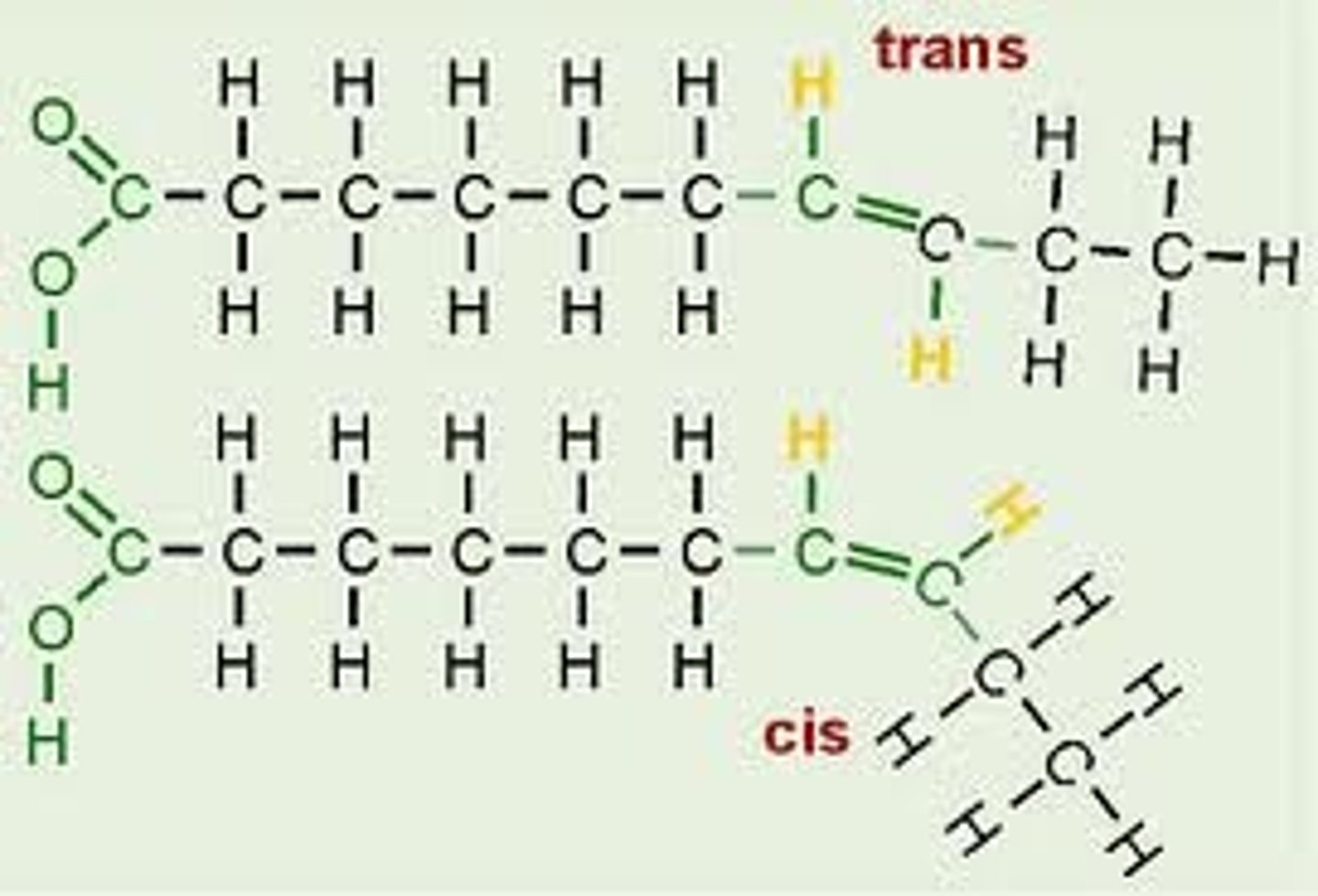
Unsaturated Isomers
cis and trans
Triglycerides
formed by condensation from three fatty acids and one glycerol
dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction)
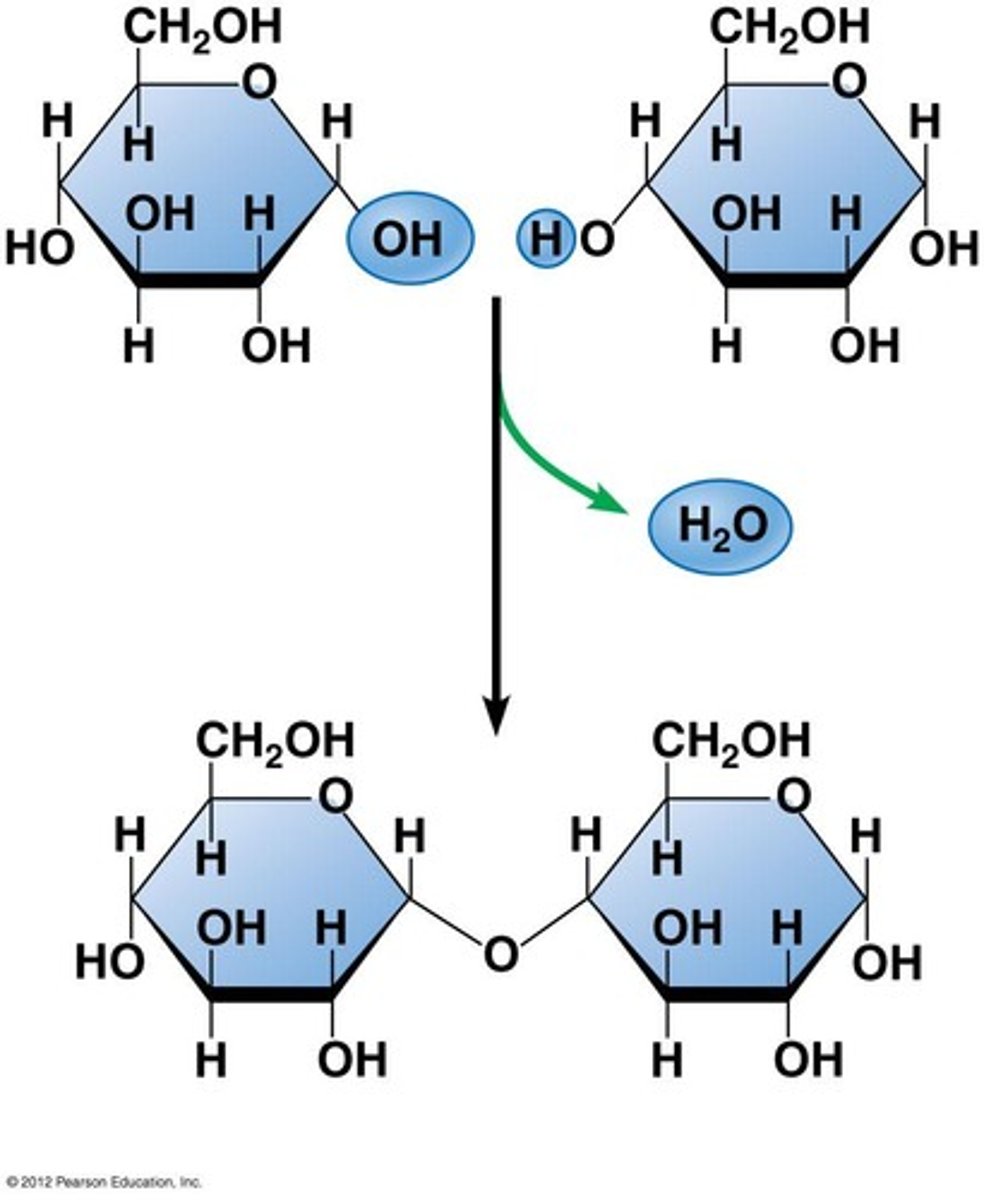
examples of polysaccharides (all made of glucose)
starch, glycogen, cellulose
Cellulose
major component of cell walls, helps give rigidity support to roots, stems, and leaves
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose; usually located in roots
Glycogen
Storage form of glucose in animals; usually located in liver and muscle tissue
saturated fatty acid
carbons are saturated with hydrogen atoms; generally solid at room temperature; no double bonds
monounstaturated fatty acids
one double bond exists in the chain of a hydrocarbon; cause one "kink" or bend in the molecule
polyunsaturated fatty acid
two or more double bonds in the carbon chain; usually liquid at room temperature
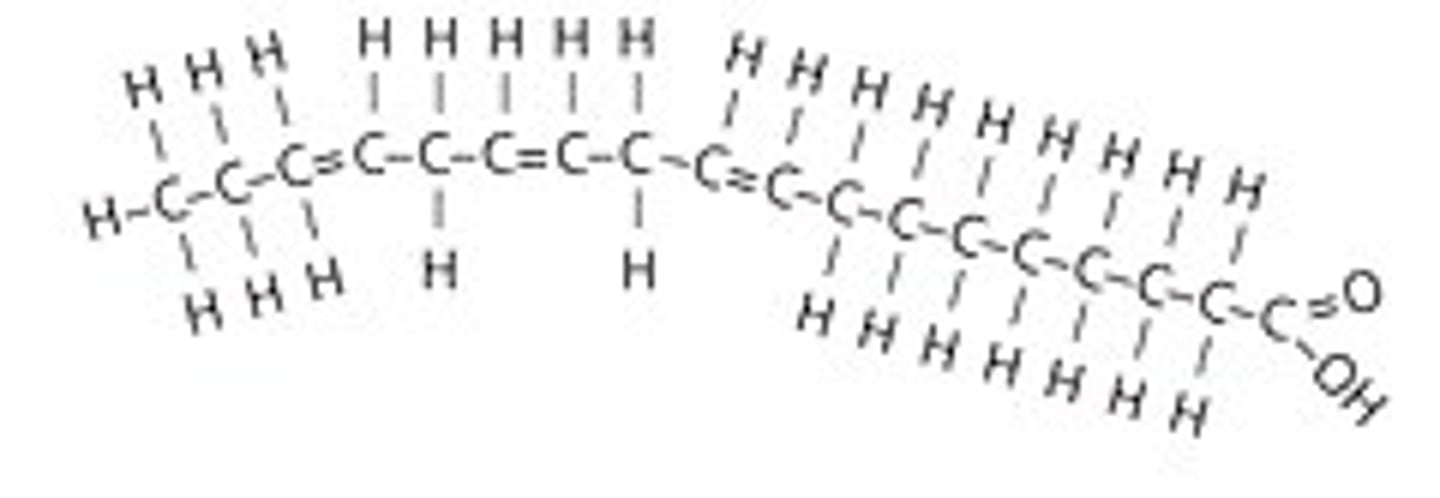
Hydrogenation
The process of converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen
cis fatty acids
Two covalent single C-C bonds angle in the same direction adjacent to the C=C double bond
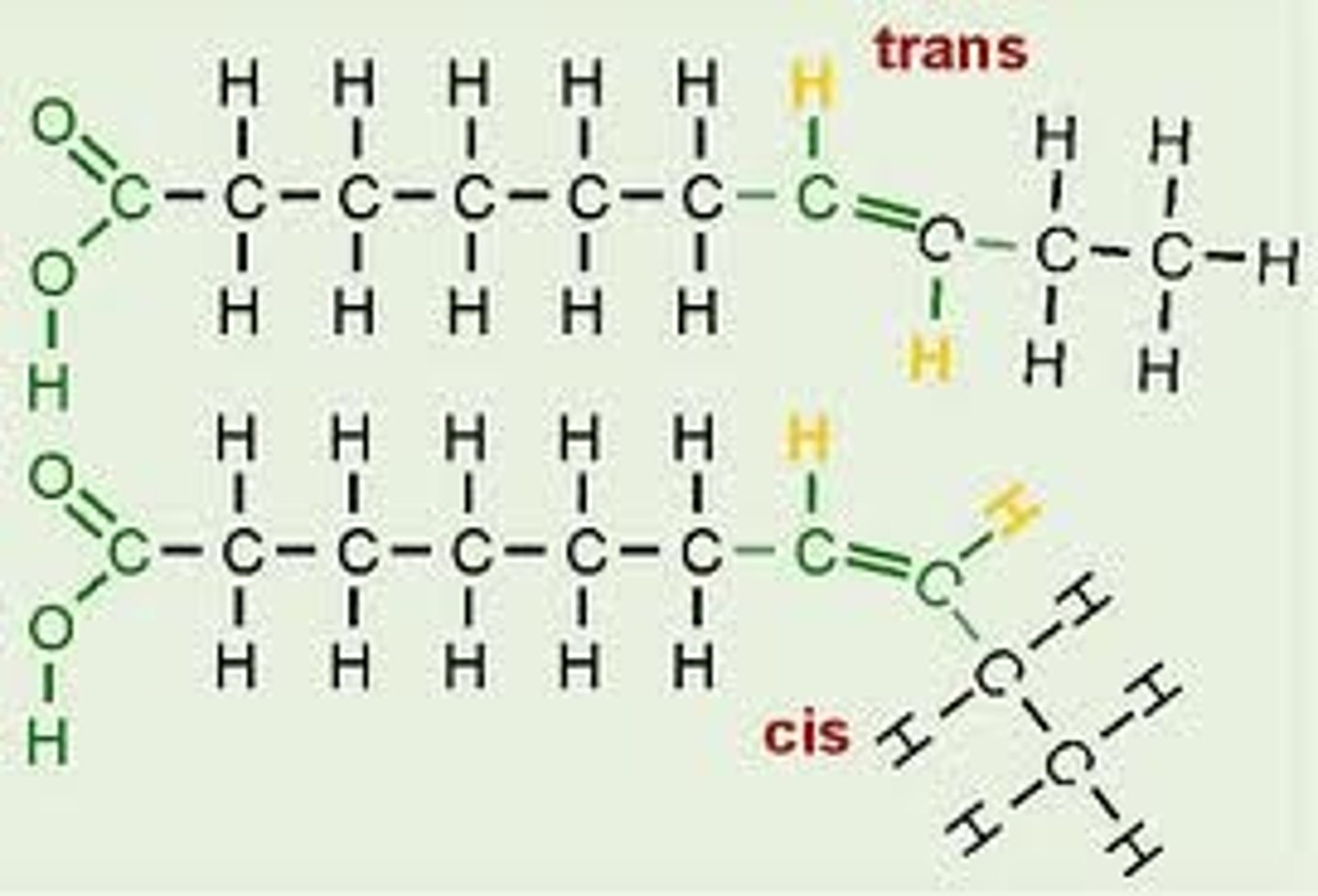
trans fatty acids
fatty acids with hydrogens on opposite sides of the double bond
adipose tissue
Tissue that stores fat (triglyceride lipids).
BMI (body mass index)
a measure of body weight relative to height
amino acids
a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group; linked together by condensation to form polypeptides.
Gene
specific region of DNA that codes for a particular protein (polypeptide)
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis; amino acid linkage
Rubisco
The most abundant protein on earth; enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction of the carbon-fixing reactions of photosynthesis
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues; results in decrease of blood sugar levels and an increase of sugar inside body cells
immonuglobulins
another name for an antibody that recognizes an antigen(s) as part of immune response
rhodopsin
a pigment found in the retina of the eye that is particularly useful in low light conditions
Collagen
main protein component of connective tissue, which is abundant in skin, tendons, and ligaments.
spider silk
the fibrous protein spun by spiders for making webs, drop lines, nest building, and other uses; has incredible tensile strength.
primary structure of protein
the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain; determines the three dimensional shape
secondary structure of protein
repetitive shapes of either an alpha helix (spiral staircase) or beta pleated sheet (corrugated folds); e.g. spider silk
tertiary structure of protein
protein structure is formed when the twists and folds of the secondary structure fold again to from a larger globular 3D structure; e.g. enzymes
quaternary structure of a protein
A number of polypeptide chains linked together, and sometimes associated with non-protein groups to form a protein; e.g. hemoglobin
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
Proteome
the unique and entire set of proteins expressed by a given cell or group of cells
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things).
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
Enzymes
proteins that act as biological catalysts; speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells by lowering the activation energy; act on specific substrates
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14; each number on the scale presents an increase/decrease by a power of 10
nucleic acids
examples DNA, RNA, ATP;
nucleotides
monomers of nucleic acids; contains phosphate, sugar (deoxyribose/ribose), a nitrogenous base (A,T,G,C,U); DNA and RNA involved in genetic aspects of the cell; ATP involved in energy transfer
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
DNA
A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule capable of replicating and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins.
antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
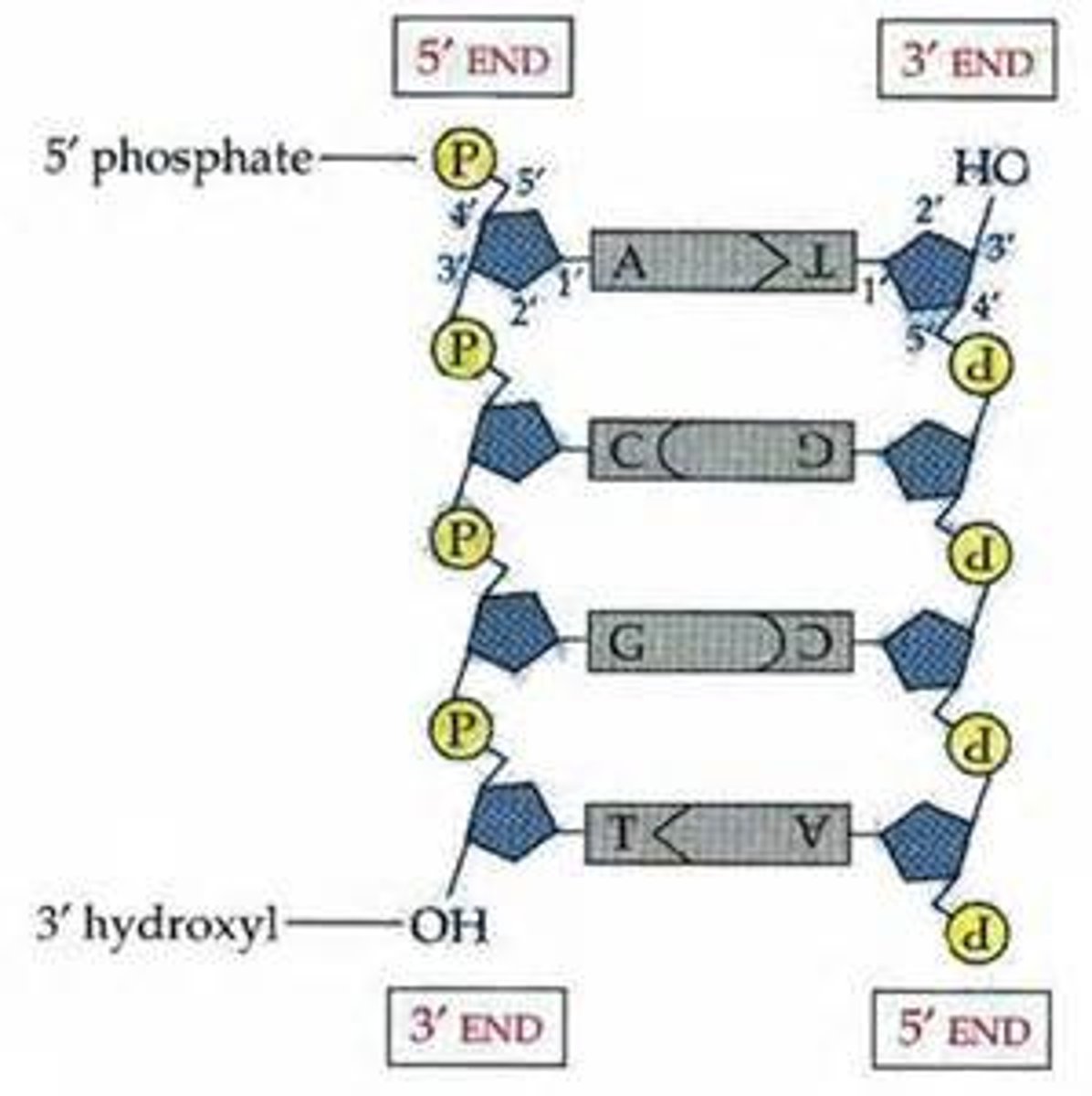
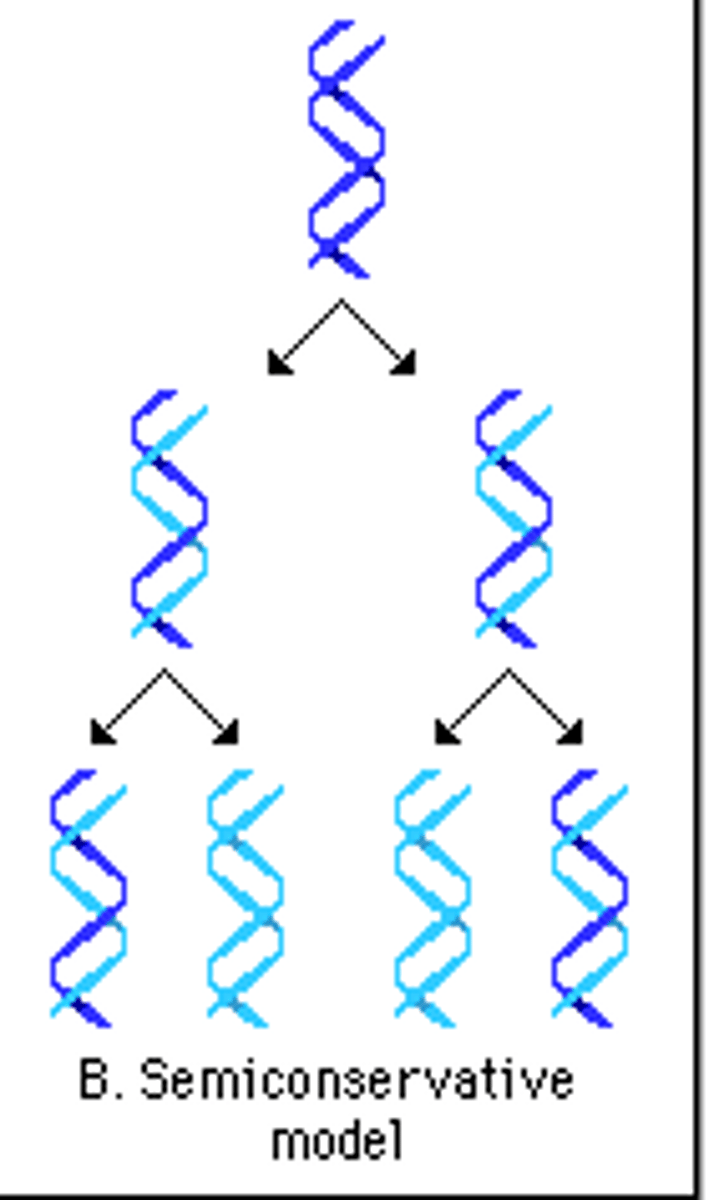
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself; occurs in nucleus
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix at the replication forks, separating the two parental strands and making them available as template strands.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
free-floating nucleotides
nucleotides that are present in the nucleus and are used during DNA replication and mRNA synthesis
Nucleoplasm
Fluid inside the nucleus
semiconservative replication
each new DNA molecule consists of one new strand and one old strand
protein synthesis
the formation of proteins by using information contained in DNA and carried by mRNA; transcription (in the nucleus) and translation (on the ribosome)
RNA polymerase
enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
Codon (triplet)
three sequential bases of RNA that code for an amino acid
mRNA (messenger RNA)
a single-stranded RNA molecule that encodes the information to make a protein; complementary copy of a DNA gene and has enough genetic information to code for a single polypeptide
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
type of RNA that makes up the major part of ribosomes
tRNA (transfer RNA)
type of RNA molecule that transfers one of the 20 amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis (polypeptide synthesis)
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
a way DNA replication can be carried out artificially; A technique for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers, DNA polymerase molecules, and nucleotides.
Thermus aquaticus (Taq)
a bacterium that contains an enzyme that is not denatured at high temperatures (Taq polymerase)
cell respiration
the process in cells in which oxygen is used to release stored energy by breaking down sugar molecules (general)
cell respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 >>>> 6H20 + 6CO2 +ATP
Glycolysis
first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose (6 C) is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3C); occurs in cytoplasm of ALL cells
anaerobic respiration (fermentation)
breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen; small ATP yield
alcoholic fermentation
A process used by yeast cells and some bacteria to produce carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol (2C): bakers and brewers use
lactic acid fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate (3C) to lactate with no release of carbon dioxide; used in human muscles
Aerobic cell respiration
respiration requiring oxygen, involving the oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide and water; occurs in the mitochondria
Production of human insulin in bacteria
Example of the universality of the genetic code allowing gene transfer between species