Ch1: Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins (copy)
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Sickle Cell Disease
Glutamic acid to valine in RBC
Hemoglobin aggregate and precipitate
Amino Acids
Molecules with amino and carboxyl functional groups
a-Amino Acids
Amino, carboxyl, H, and R group bound to a-carbon
Side Chains
R group
Determine amino acid properties and functions
Proteinogenic Amino Acids
20 a-amino acids coded by human genome
Amino Acid Stereochemistry
All (not glycine) are chiral
All are L-amino acids (eukaryotes)
All (not cysteine) have S configuration
Amino Acid Weight
110 Daltons
Nonpolar Amino Acids
I Glided Low and Tripped Mr. Alan Phenyl Very Profanely
Isoleucine, glycine, leucine, tryptophan, methionine, alanine, phenylalanine, valine, proline
Aromatic Amino Acids
Tiger Tripped Pheonix
Tyrosine, tryptophan, phenylalanine
Polar Amino Acids
Sarah Thought Tyler Glued Asparagus to Cat
Serine, threonine, tyrosine, glutamine, asparagine, cysteine
Acidic/Negative Amino Acids
Aspartic acid (aspartate anion)
Glutamic acid (glutamate anion)
Mostly in deprotonated/anion form in the body
Basic/Positive Amino Acids
Lyzzie Argued Historically
Lysine, arginine, histidine
Isoleucine
I, Ile
Glycine
G, Gly
Smallest amino acid
Achiral
Leucine
L, Leu
Tryptophan
W, Trp
Double ring with N
Methionine
M, Met
S in side chain
Alanine
A, Ala
Phenylalanine
F, Phe
Benzyl (benzene + CH2)
Valine
V, Val
Proline
P, Pro
Cyclic
Reduce flexibility in secondary structure
Serine
S, Ser
OH in side chain
H bond
Threonine
T, Thr
OH in side chain
H bond
Tyrosine
Y, Tyr
Benzyl + OH
Glutamine
Q, Gln
Amide side chain
No charge change with pH change
Asparagine
N, Asn
Amide side chain
No charge change with pH change
Cysteine
C, Cys
Thiol (SH) group
Prone to oxidation
Aspartic Acid
D, Asp
Carboxylate side chain
Glutamic Acid
E, Glu
Carboxylate side chain
Lysine
K, Lys
Terminal primary amino group
Arginine
R, Arg
3 N (disperse charge)
Histidine
H, His
Aromatic ring with 2 N (imidazole)
Hydrophobic Amino Acids
Long akyl side chains
Inside protein
Hydrophilic Amino Acids
Charged side chains
Protein surface
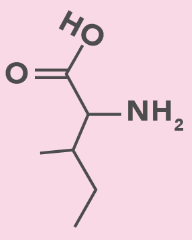
isoleucine
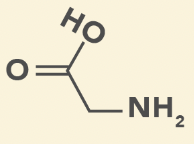
glycine
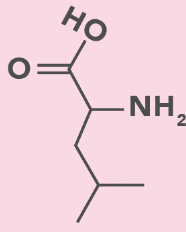
leucine
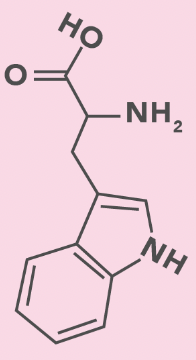
tryptophan
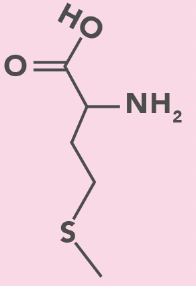
methionine
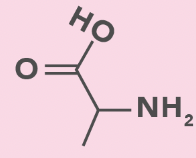
alanine
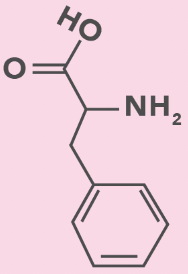
phenylalanine
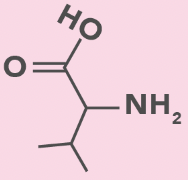
valine
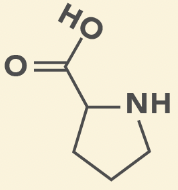
proline
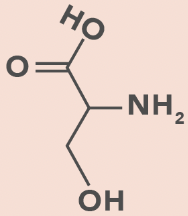
serine
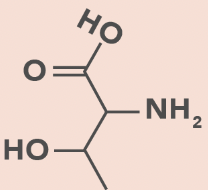
threonine
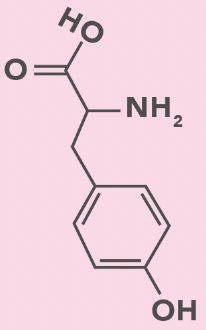
tyrosine
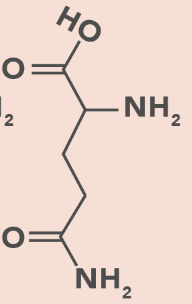
glutamine
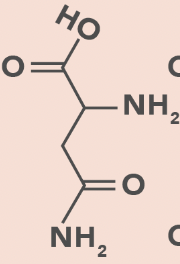
asparagine
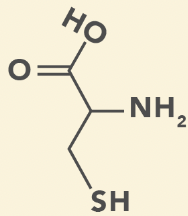
cysteine
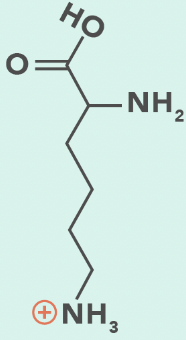
lysine (protonated)
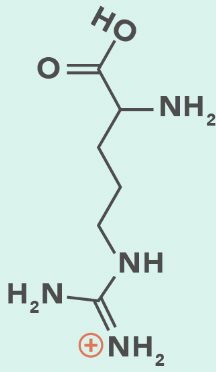
arginine (protonated)
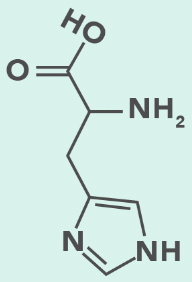
histidine (protontated)
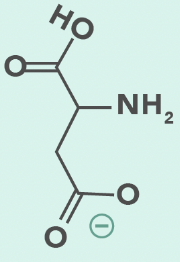
aspartate (deprotonated)
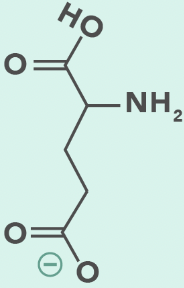
glutamate (deprotonated)
Amphoteric Species
Accept or donate proton depending on pH
Ex: Amino acids
Ionizable Groups
Acidic (low pH): Gain protons/protonated
Basic (high pH): Lose protons/deprotonated
pKa
pH when half molecules are deprotonated (buffer)
[HA] = [A-]
Amino acids have at least 2
Flat titration curve
pH < pKa
More protonated
pH > pKa
More deprotonated
pKa1
pKa for carboxyl
~2
pKa2
pKa for amino
9-10
Positive Charge in Acidic Conditions
pH < pKa1 and pKa2
Carboxyl protonated (neutral)
Amino protonated (positive)
Amino and carboxyl groups fully protonated
Positive molecule
Zwitterions at Intermediate pH
pH > pKa1: Carboxyl deprotonated (negative)
pH < pKa2: Amino protonated (positive)
Neutral molecule
Negative Charge in Basic Conditions
pH > pKa1 and pKa2
Carboxyl deprotonated (negative)
Amino deprotonated (neutral)
Negative molecule
Isoelectric Point (pI)
pH when amino acid is electrically neutral
Average of 2 closest pKa values
Vertical titration curve
Acidic Side Chains
Low pI
Negative charge
Average of pKaR and pKa1
Basic Side Chains
High pI
Positive charge
Average of pKaR and pKa2
Peptides
Composed of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds
Peptide Bond
Special amide bond between -COO- and NH3+
Form functional group -C(O)NH-
Dipeptide
2 amino acid residues
Tripeptide
3 amino acid residues
Oligopeptide
Small peptides (≤20)
Polypeptide
Long peptides
Peptide Bond Formation Reaction
Condensation/dehydration (release H2O)
Acyl substitution
Electrophilic carbonyl C attack nucleophilic amino group
Peptide Bond Resonance
Restrict rotation around C-N amide bond
N-Terminus
Free amino end
Left
C-Terminus
Free carboxy end
Right
Peptide Bond Hydrolysis
Trypsin and chymotrypsin cleave amide bond
Add H to amide N and OH to carbonyl C
Protein
Polypeptide with important biological functions (enzymes, hormones, membrane pores and receptors, cell structure)
Primary Protein Structure
Linear amino acid arrangement
N- to C- terminus
Primary Structure Stabilization
Covalent peptide bonds
Determining Primary Structure
Sequencing with DNA or protein
Secondary Protein Structure
Local structure determined by neighbouring amino acids
a-helices
b-pleated sheets
Secondary Structure Stabilization
H bonds
a-Helix
Clockwise-coiled peptide chain
H bonds every 4 residues
Side chains point away from core
Form keratin
b-Sheet
Parallel or antiparallel peptide chains
Side chains point above or below sheet plane
Form fibroin
Secondary Structure: Proline
Proline cause kinks
Found in a-helix start and b-sheet turns
Fibrous Protein
Sheets/strands
Collagen
Globular Proteins
Spherical
Myoglobin
Tertiary Protein Structure
3D protein shape
Tertiary Structure Stabilization
R group interactions
Electrostatic interactions
H bonds
Acid-base interactions form salt bridges
IMF
Tertiary Structure: Hydrophobic Residues
Protein interior
Pull in hydrophilic N-H and C=O bonds to form electrostatic interactions and H bonds
Tertiary Structure: Hydrophilic Residues
Protein surface
Tertiary Structure: Disulfide Bonds
Between cysteines to form cystine
Molten Globules
Intermediate states from secondary to tertiary structure
Solvation Layer
Solvent molecules lining solute in solution
Hydrophilic amino acids on exterior increase entropy and decrease Gibbs energy
Quaternary Protein Structure
1+ polypeptide chains (not present in all proteins)
Aggregation of globular subunits
Quaternary Structure: Stability
Decrease surface area = more stable
Quaternary Structure: DNA
Decrease DNA needed to code protein
Quaternary Structure: Catalytic Sites
Bring close together