Intro to Communication Disorders
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 1 (Done), Ch. 2 (in progress)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Give some examples of developmental communication disorders.
Autism
Cerebral palsy
Dyslexia
Down syndrome
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Give some examples of acquired communication disorders.
Car accident
Brain injury
Cancers
Surgeries
Medical events
What is a communication disorder?
Impairs the ability to both receive, send, and also process and comprehend concepts or verbal, nonverbal, and graphic information.
What is a speech disorder?
Atypical production of speech sounds, interruption in the flow of speaking, or abnormal production and/or absences of voice quality, including pitch, loudness, resonance, and/or duration.
What is a language disorder?
An impairment in comprehension and/or use of spoken, written, and/or other symbol systems.
What is a hearing disorder?
Impaired sensitivity of the auditory or hearing system.
What do CSD professionals target/treat?
Auditory processing disorders
Augmentative/alternative communication
Feeding disorders
Swallowing disorders
Hearing loss
What do SLPs target?
Developmental disorders
Genetic disorders
Stroke and brain injury
Progressive neurological disorders
What are some examples of SLP clinical settings?
Schools
Skilled nursing facilities
Private practices
Hospitals
NICU
Acute care
What’s the key to improved outcomes when diagnosing a communication disorder?
Early identification and early intervention
What does EBP stand for?
Evidence Based Practice
EBP is based on 2 assumptions, what are they?
Clinical skills grow not just from experience, but from currently available data
An expert SLP or AuD continually seeks new therapeutic info to improve efficiency
Define anatomy
The study of structures of the body and the relationship of these structures to one another.
Define physiology
The branch of biology that is concerned with the functions of organisms and bodily structures.
What are the 3 physiological subsystems involved in speech production?
Respiratory system
Laryngeal system
Articulatory/resonatory systems
What is the primary biological function of the respiratory system?
Supply O2 to the blood and remove CO2
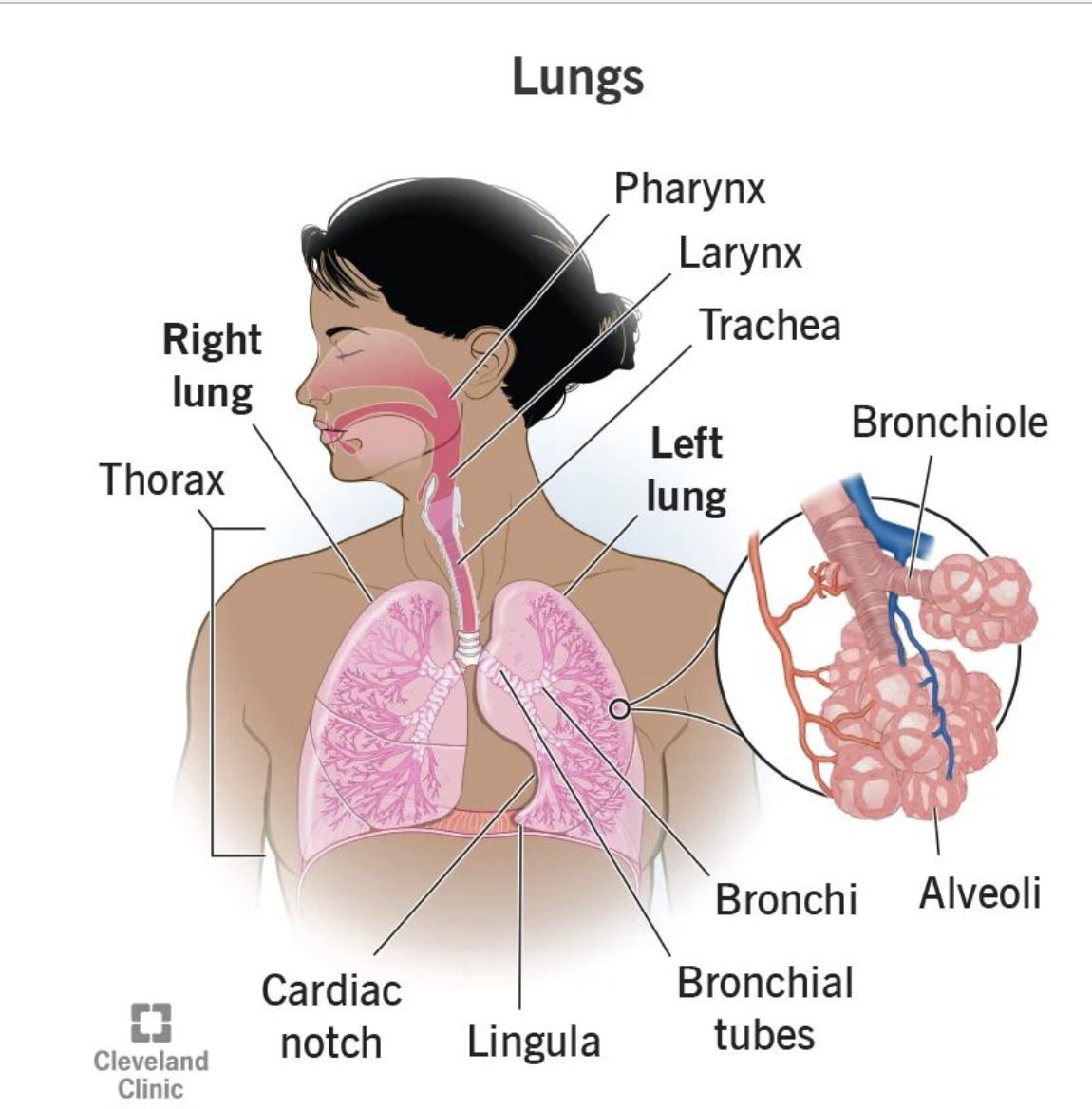
What is the overlaid function of the respiratory system?
Generating source for speech function.
What is the primary biological function of the laryngeal system?
To prevent foreign objects from entering trachea and lungs
Impound air for forceful expulsion of foreign objects that threaten lower airways (cough, hack, val salva)
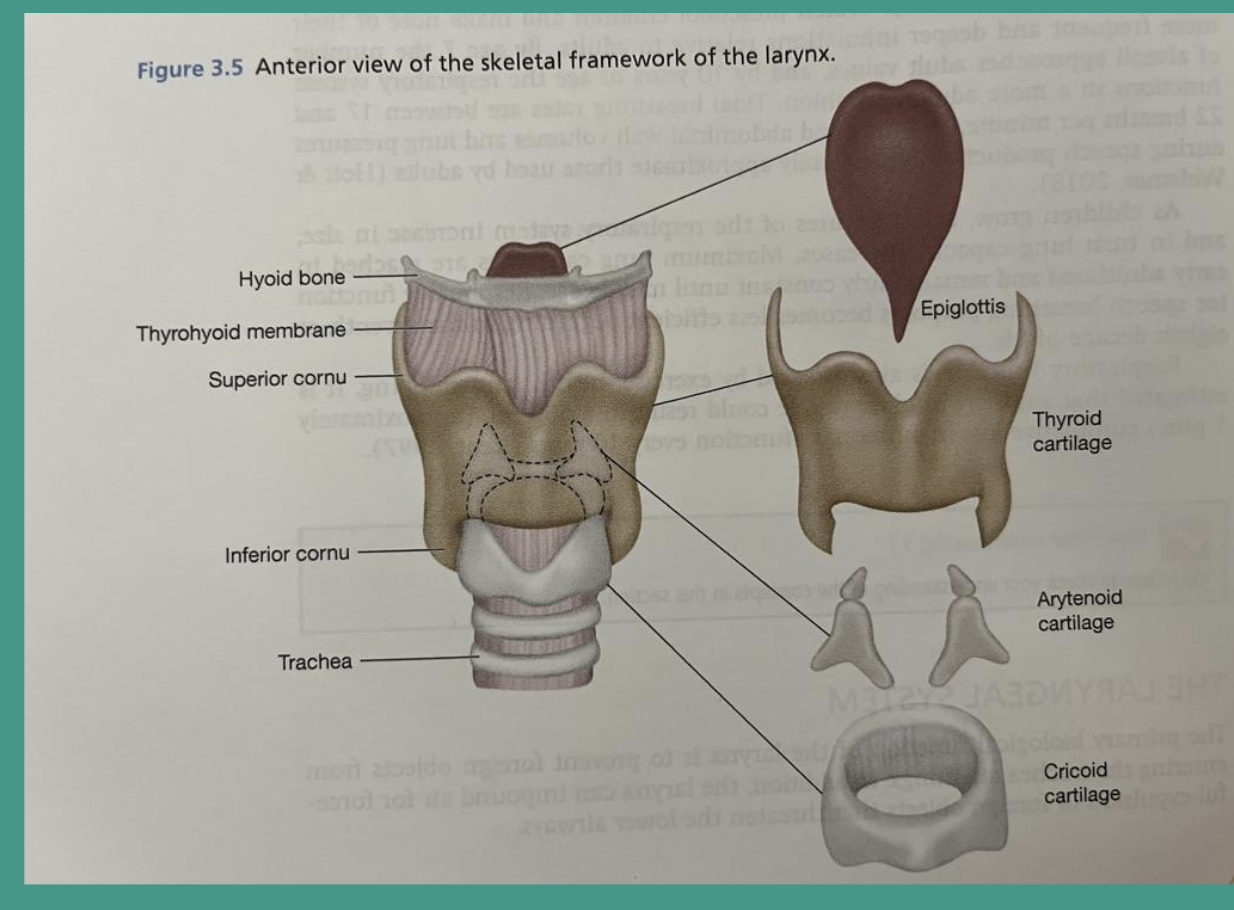
What is the overlaid function of the laryngeal system?
Produce voicing