Human Anatomy Exam 2
1/560
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
561 Terms
Osteocyte
mature bone cell that maintains the bone matrix
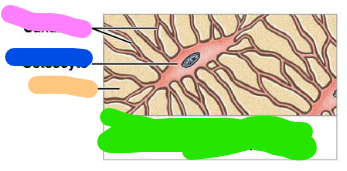
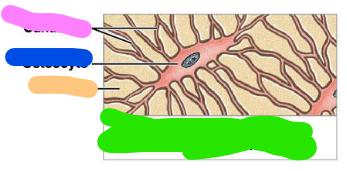
Canaliculi
pink
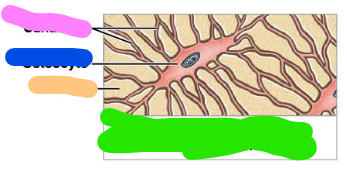
Osteocyte
blue
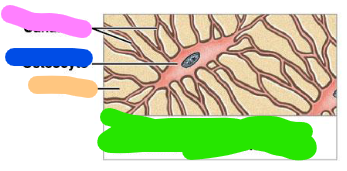
Matrix
orange
Osteoblast
immature bone cell that secretes osteoid, the organic bone matrix
Osteoprogenitor cell
stem cell that divides to produce osteoblasts
Osteoclast
multinucleate cell that secretes acids and enzymes to dissolve bone matrix
compact bone
external wall of bone
Spongy bone
internal layer; protects medullary cavity
Yellow marrow
tissue dominated by adipocytes (found in shaft and end of long bones)
Red marrow
Tissue dominated by blood cells (found in flat bones and long bones)
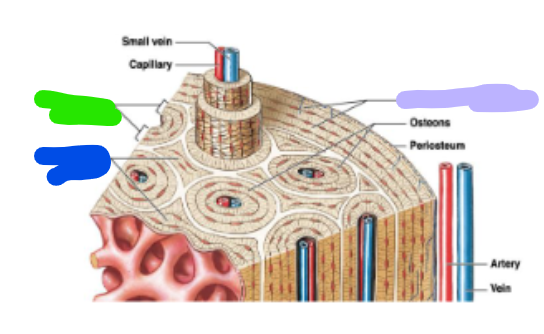
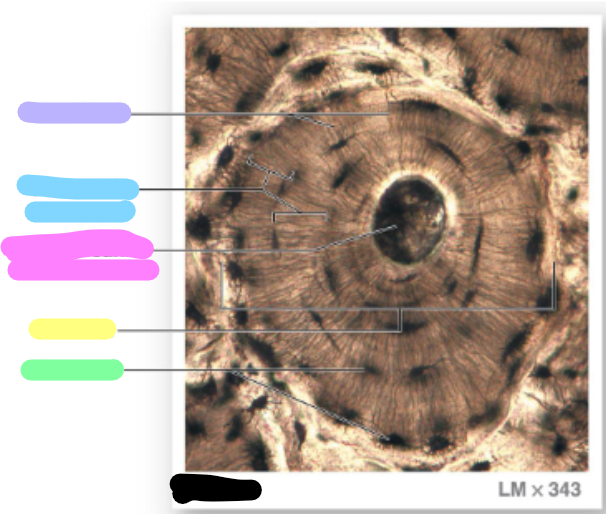
concentric lamellae
green; each osteon are parallel to the long axis of the bone (bull’s eye target)
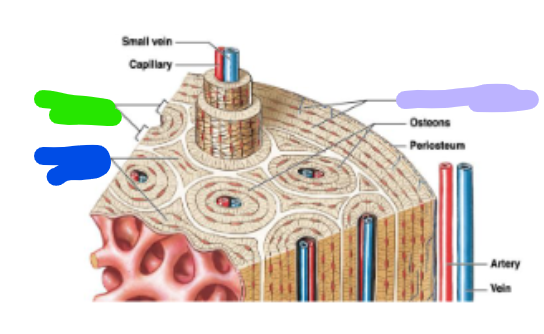
Circumferential lamellae
lavender; located at the internal and external surface of the bone
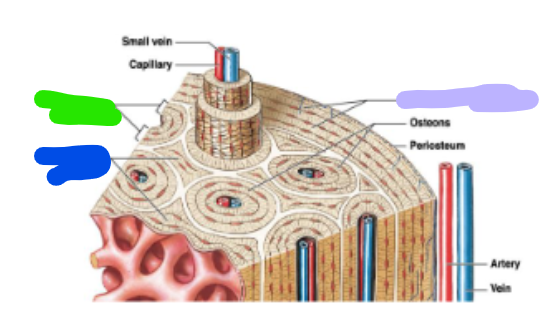
Interstitial lamellae
blue; fill the space between osteons
canaliculi
lavender
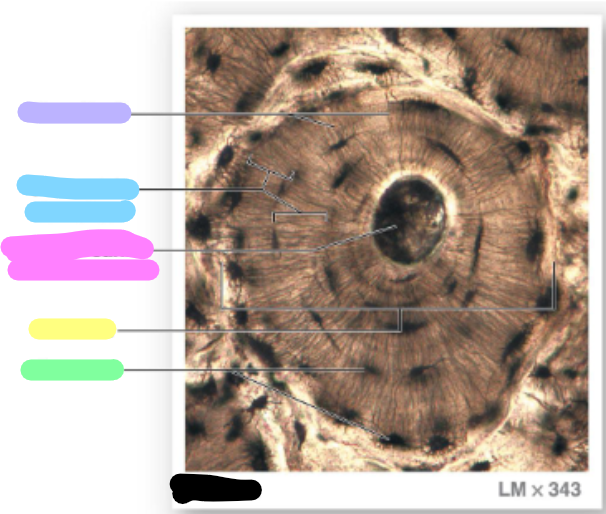
concentric lamellae
blue
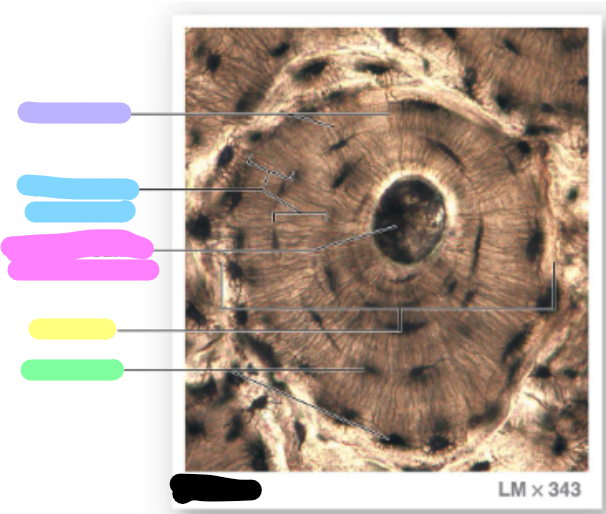
central canal / harvesian canal
pink
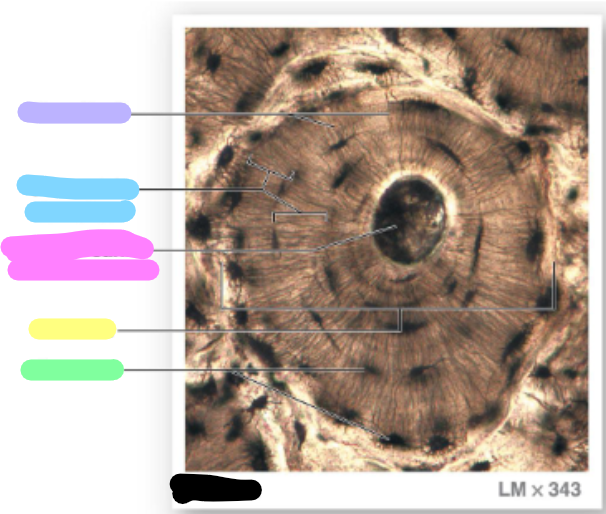
osteon
yellow
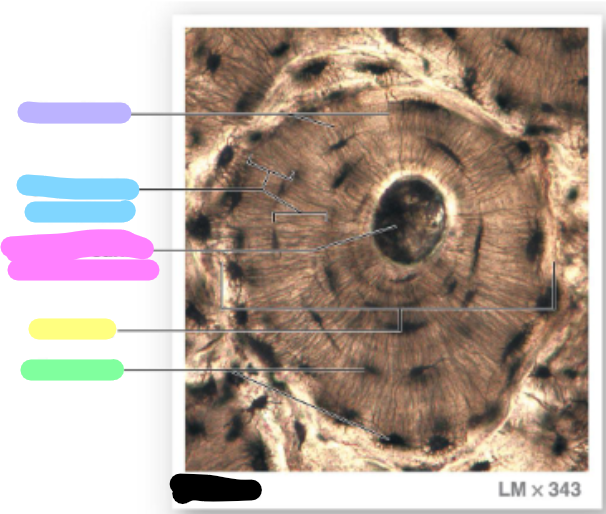
lacunae
green
trabeculae
Arrangement of spongy bone is into parallel thick branching plates of bars
epiphysis
purple
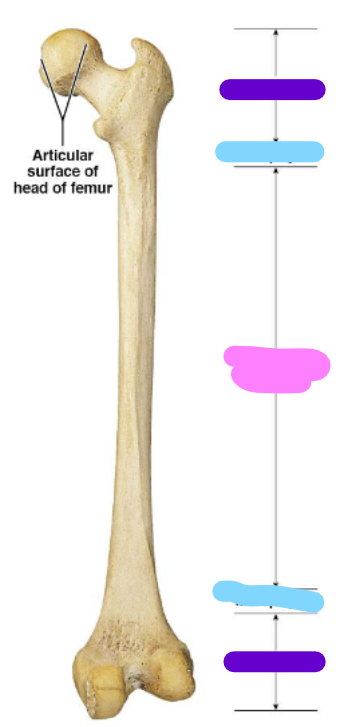
metaphysis
blue
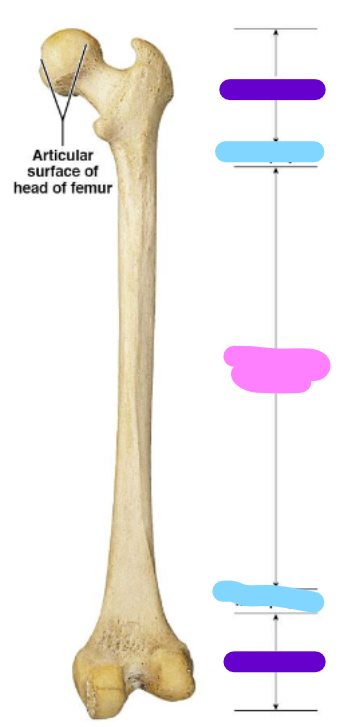
diaphysis
pink
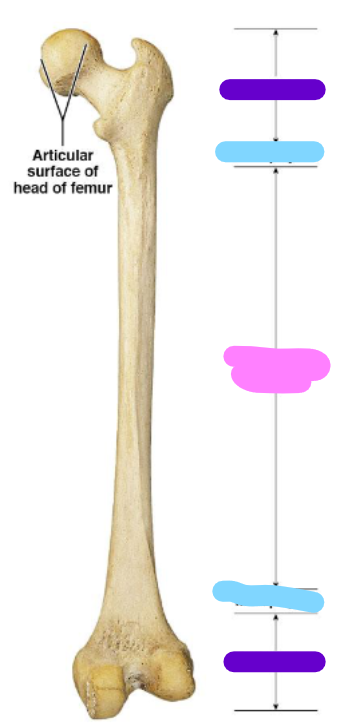
Periosteum
Function: Isolates and protect the bone. Provides a route and attachment point for insertion of tendons and ligaments, which Is Important in bone growth and repair.
Dense irregular connective tissue
What kind of tissue is the periosteum?
Endosteum
Lines the medullary cavity (marrow). Lines the inner surfaces of the central canals and perforating canals. Covers the trabeculae of spongy bone. Important in bone growth and repair.
Epiphyseal vessels
pink; Supply medullary cavities of the epiphyses (through foramina)
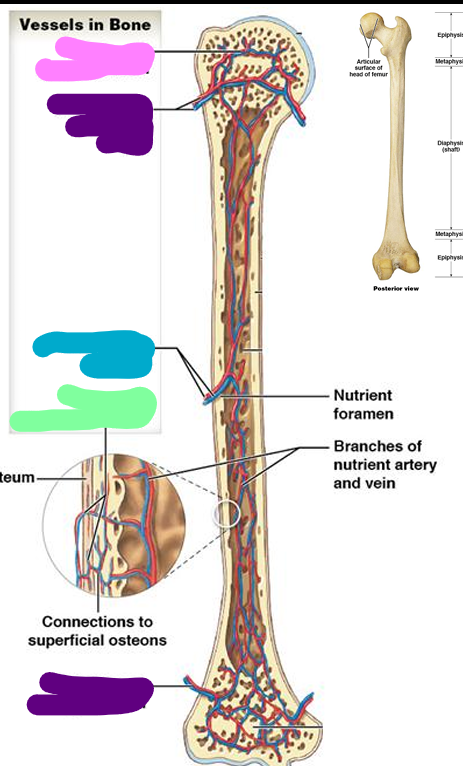
Metaphyseal vessels
purple; Supply to diaphyseal surface (bone is replacing cartilage)
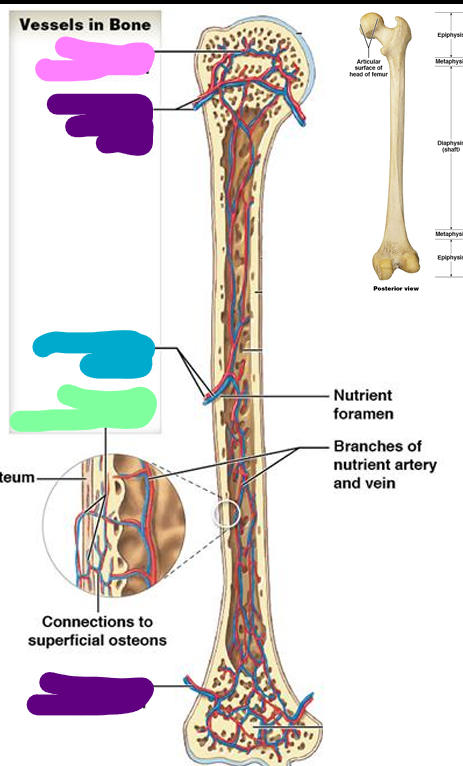
Nutrient vessels
blue; enter through nutrient foramen
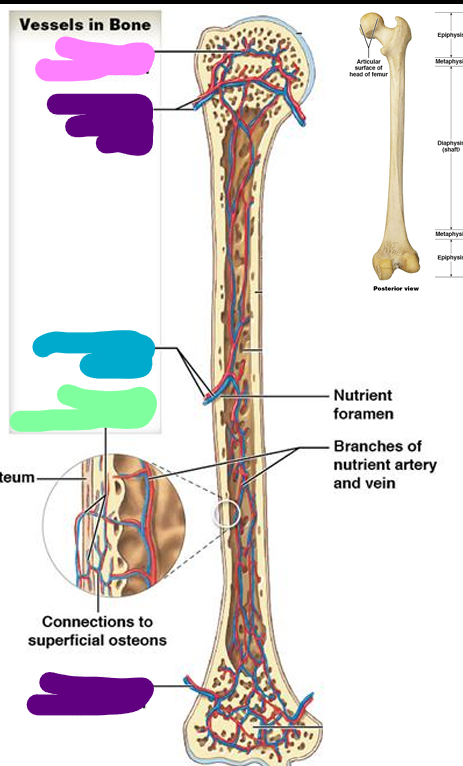
Periosteal vessels
green; Supply superficial osteons (compact bone)
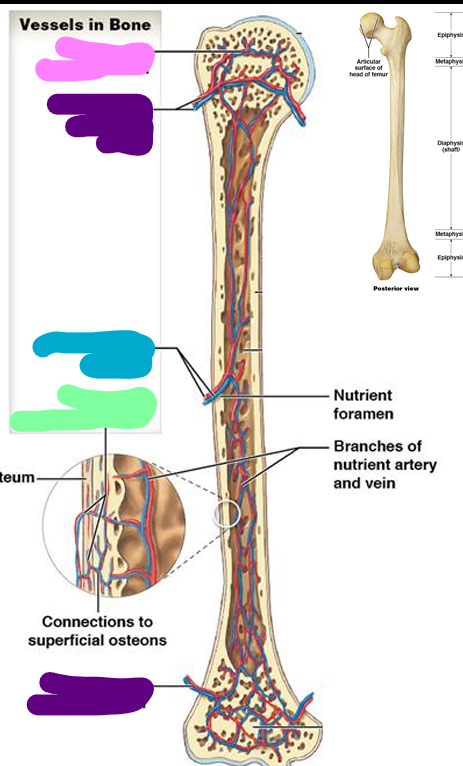
Sutural bones
small, flat, oddly shaped bones found between the flat bones of the skull along the sutures. They develop from separate centers of ossification.
Pneumatized bones
bones that are hollow or contain numerous air pockets, such as the ethmoid bone.
Short Bones
Their external surfaces are covered by compact bone, but the interior contains spongy bone. Examples of short bones include the carpal bones (wrists) and tarsal bones (ankles)
Irregular Bones
Have complex shapes with short, flat, notched, or ridged surfaces. Their internal structure is equally varied. The vertebrae that form the spinal column and several bones in the skull are examples of irregular bones.
Flat Bones
Have thin, roughly parallel surfaces of compact bone. In structure, a flat bone resembles a spongy bone sandwich; such bones are strong but relatively light. Flat bones form the roof of the skull, the sternum, the ribs, and the scapulae. They protect underlying soft tissues and have an extensive surface area for the attachment of skeletal muscles.
Long Bones
Relatively long and slender. They have a diaphysis, two metaphyses, two epiphyses, and a medullary cavity. Found in the upper and lower limbs. Examples: humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, and fibula
Sesamoid Bones
Usually small, round, and flat. They develop inside tendons and are most often encountered near joints of the knee, the hands, and the feet. Few individuals have sesamoid bones at every possible location, but everyone has patellae, or kneecaps
Foramen
Round or oval opening through a bone
Groove
Furrow
Fissure
Narrow, slit like opening
Notch
Indentation at the edge of a structure
Fossa
Shallow basin like depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
Meatus
Canal-like passageway
Sinus
Cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
Head
Red; bony expansion carried on a narrow neck

Facet
orange; Smooth, nearly flat articular surface

Condyle
yellow; Rounded articular projection, often articulates with a corresponding fossa

Tuberosity
green; large rounded projection; may be roughened
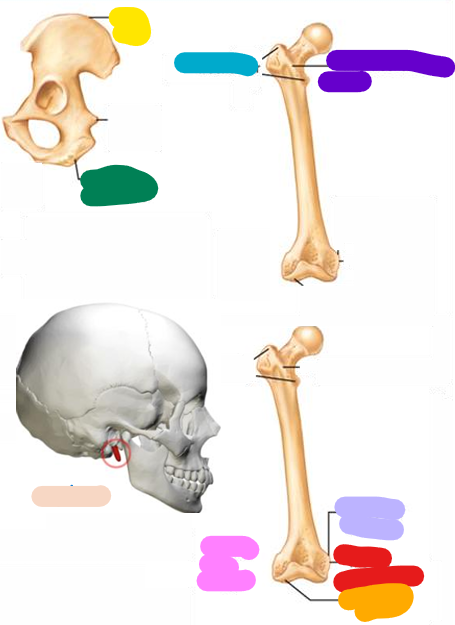
Crest
yellow; Narrow ridge of bone, usually prominent
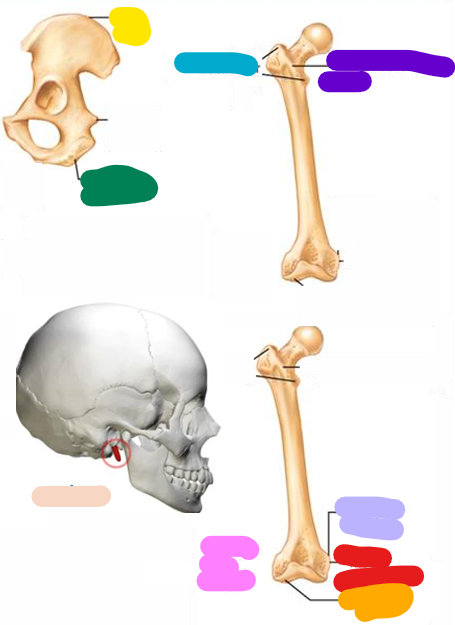
Trochanter
blue; Very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process (the only examples are on the femur
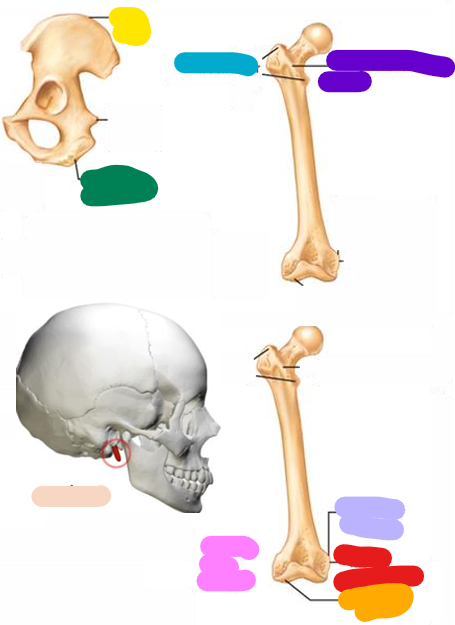
Line
Purple; Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
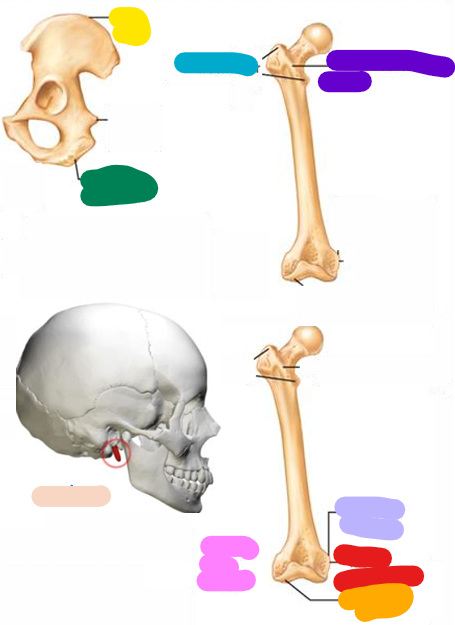
Tubercle
Lavender; Small rounded projection or process
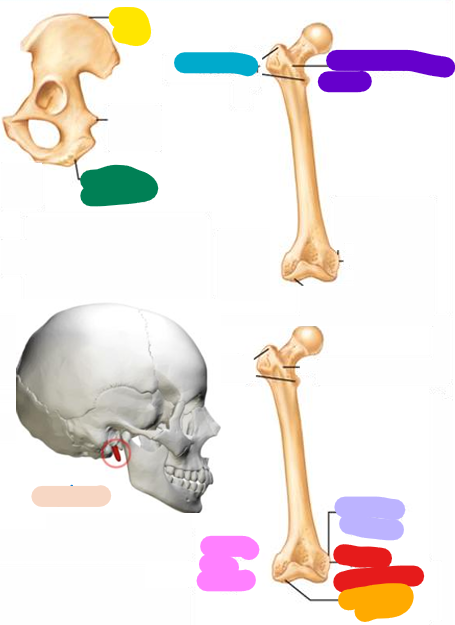
Epicondyle
Red; Raised area on or above a condyle
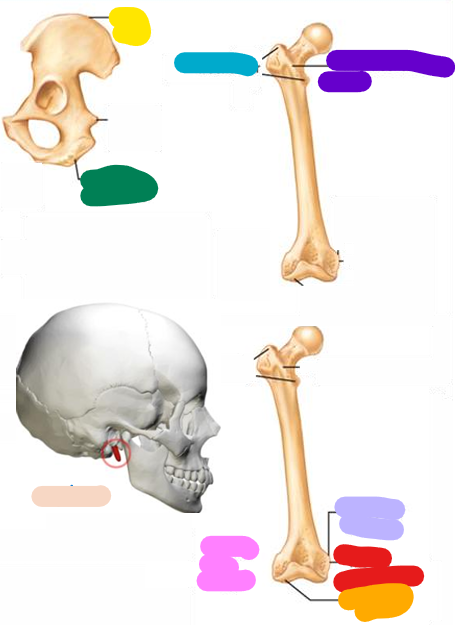
Spine
beige; Sharp, slender, often pointed projection
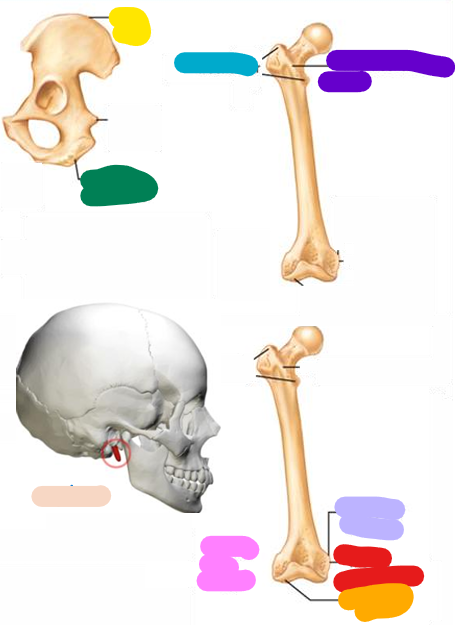
Process
Any projection or bump
Ramus
An extension of a bone that forms an angle with the rest of the structure
Comminuted
Bone fragments into three or more pieces. Particularly common in the aged, whose bones are more brittle.
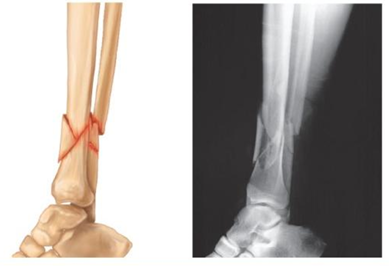
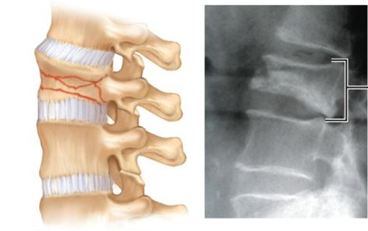
Compression
Bone is crushed. Common in porous bones (i.e., osteoporotic bones) subjected to extreme trauma, as in a fall.
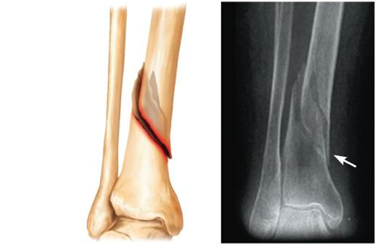
Spiral
Ragged break occurs when excessive twisting forces are applied to a bone
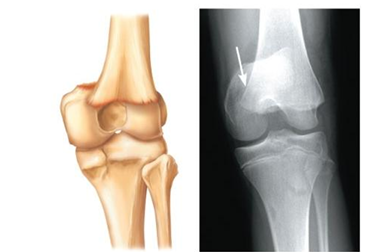
Epiphyseal
Epiphysis separates from the diaphysis along the epiphyseal plate. Tends to occur when cartilage cells are dying and calcification of the matrix is occuring
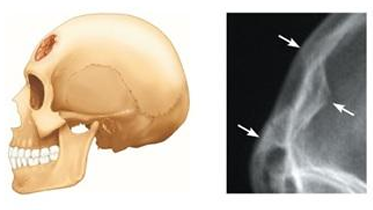
Depressed
Broken bone portion is pressed inward. Typical of skull fracture
Greenstick
Bone breaks incompletely, much in the way in the way a green twig breaks. Only one side of the shaft breaks; the other side bends. Common in children, whose bones have relatively more organic matrix and are more flexible than those of adults
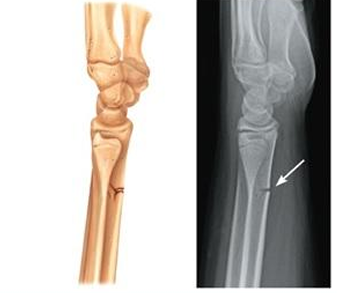
206
Number of bones
80
Number of bones in the axial skeleton
29
Skull and associated bones
Skull
Cranium and facial bones
8
Number of cranium bones
14
number of facial bones
Associated bones
Auditory ossicles and hyoid
6
Number of auditory ossicles
25
Number of thoracic cage bones
Thoracic cage
Sternum and ribs
24
Number of rib bones
26
Number of bones in the vertebral column
Vertebral column
Vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
24
Number of bones in the vertebrae
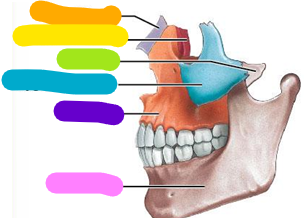
Maxillae
Purple; 2 bones
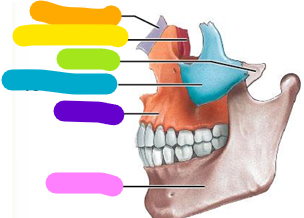
Nasal bone
Orange; 2 bones
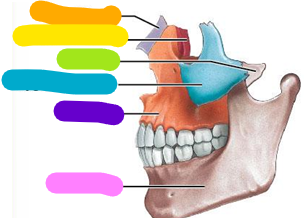
Zygomatic bone
Blue; 2 bones
Lacrimal bone
Yellow; 2 bones
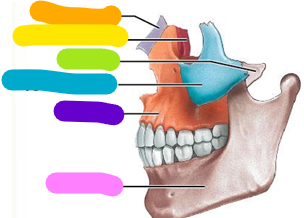
Vomer
Green; 1 bone
Mandible
Pink; 1 bone
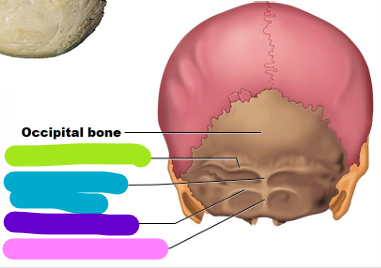
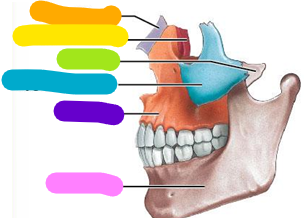
Occipital bone
Yellow; 1 bone
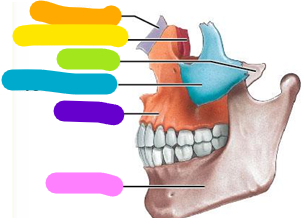
Parietal bone
green; 2 bones
Frontal bone
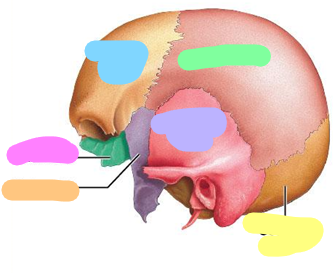
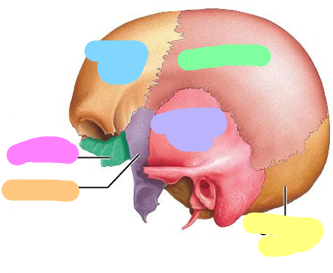
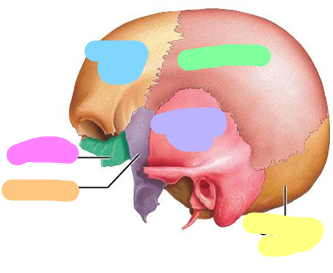
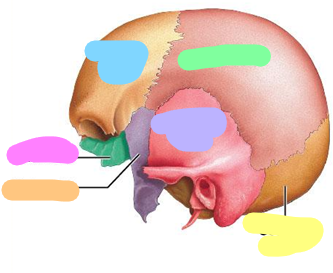
Blue; 1 bone
Temporal bone
Purple; 2 bones
Sphenoid
orange; 1 bone
Ethmoid
Pink; 1 bone
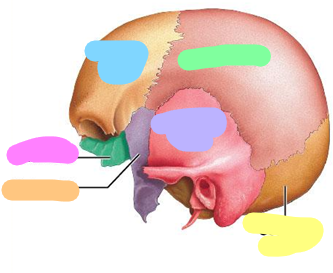
Hyoid

Cranial cavity
Fluid filled chamber that supports the brain
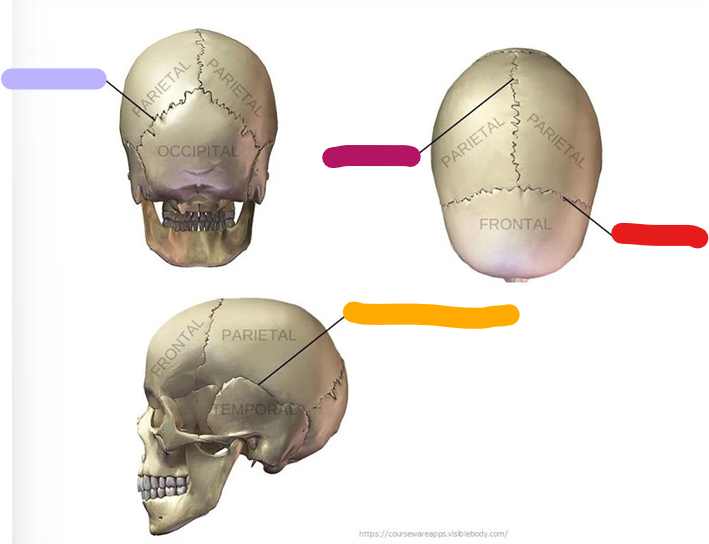
Lambdoid suture
purple
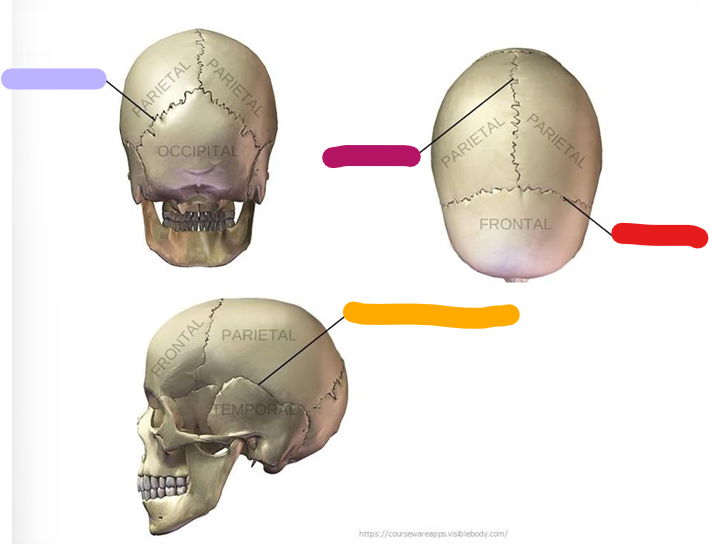
Sagittal suture
magenta
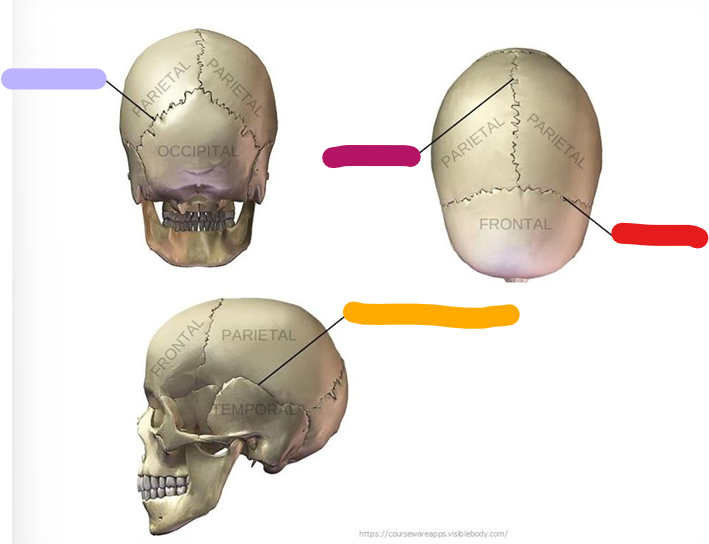
Coronal suture
Red
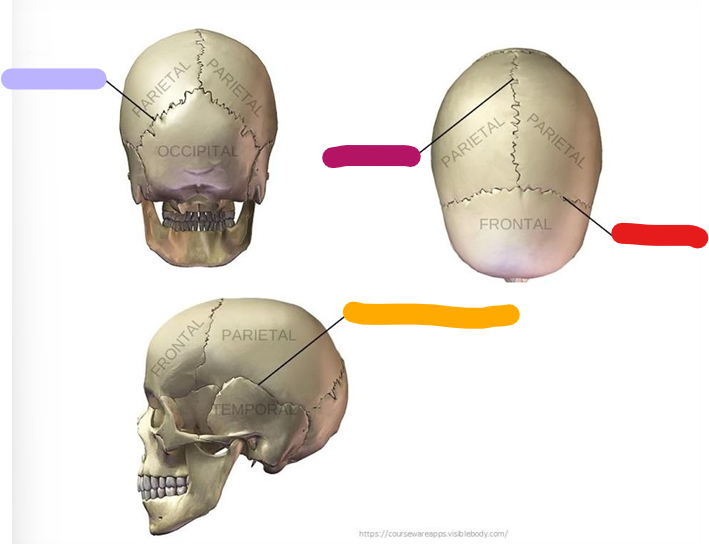
Squamous suture
orange
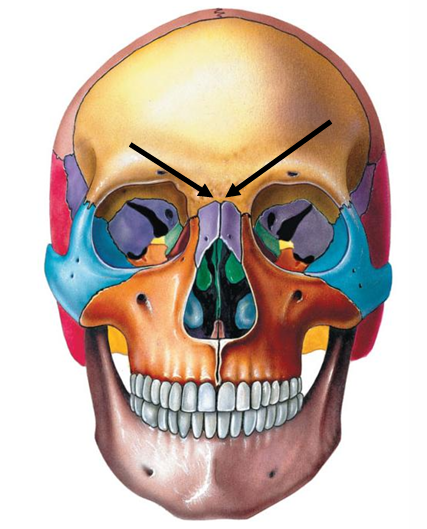
Frontonasal suture
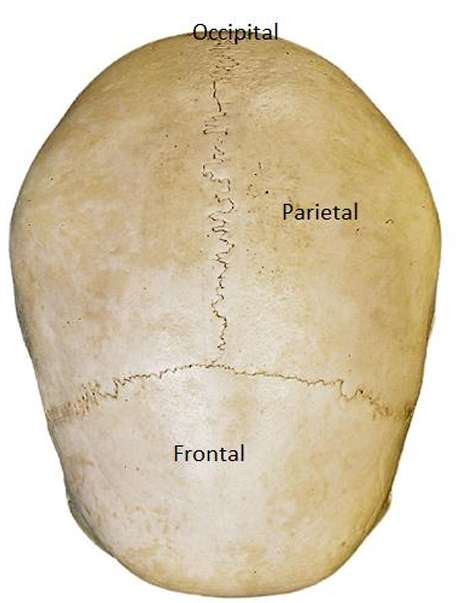
Calvaria
Cranial vault
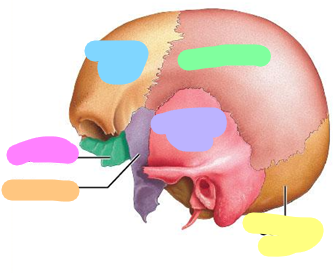
Hypoglossal canal
Orange
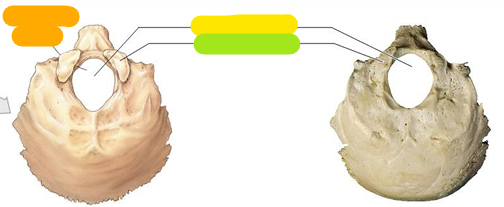
Foramen magnum
Yellow
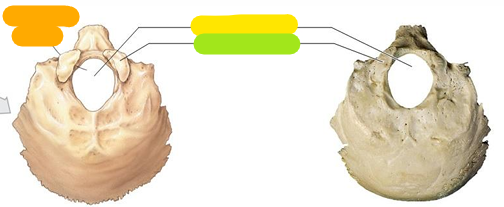
Occipital condyle
Green
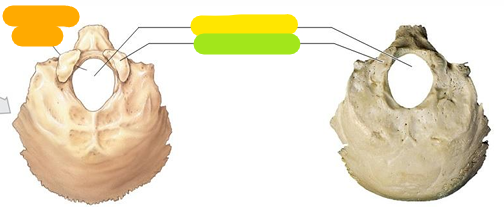
Superior nuchal line
green