lecture 5 concepts bchm
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Explain the acid and base mechanism of the Enolase reaction
Lys acts as a nucleophile and grabs a proton from active site via base catalysis . Mg2+ ions stabilize leading to an enolic intermediate
Glu kicks off the OH (the enzyme protonates OH, turning it to H20 so it can leave) by acid catalysis
What is a lysozyme and what does it do generally?
It cleaves the peptidoglycan leading to bacterial cell lysis
acts as antibacterial enzyme, key immune defense (targeting peptidoglycan easily degrades bacterial cell wall)
cleaves the glycosidic linkage (B1-4) between NAM and NAG
Explain the SN1 peptidoglycan cleavage by a lysozyme
*LESS STABLE CARBOCATION PATH
1.Glycosidic bond cleavage and carbocation formation.
2. Water general base catalysis of water leading to Reactivation of OH
3. Nuc (H20) attacks carbocation and leads to product formation
Explain the SN2 peptidoglycan cleavage by a lysozyme
1. Covalent Nuc Attack of Asp to OH
2. General Base catalysis of water/ H20 activation leading to product formation
List biological functions of nucleotides
Energy currency (ATP); enzyme cofactors (e.g., NAD⁺); second messengers (cAMP, cGMP), DNA (genetic info store), mRNA (transmission of genetic info), tRNA and r RNA (protein synthesis)
Define: gene.
A segment of DNA containing the information to synthesize a functional product (protein or RNA).
What are the Fxns of DNA vs RNA
DNA: store biological info and transmit that to next gen
RNA:
ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) = components
of ribosomes
messenger RNAs (mRNAs) =
intermediates in protein synthesis
transfer RNAs (tRNAs) = adapter
molecules that translate the information in
mRNA into a specific amino acid sequence
noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) = wide
variety of functions
Nucleoside vs. nucleotide—what’s the difference?
Nucleoside = nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) + pentose.
Nucleotide = nucleoside (purine or pyrimidine base, pentose) + ≥1 phosphate.
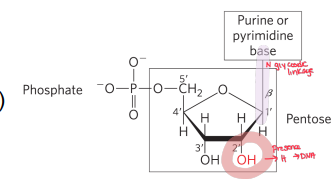
What is an anomeric OH
The OH that was the OG carbonyl in the 1‘ position, can be alpha or beta
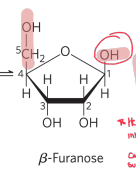
What is hemiacetal formation?
an aldehyde reacts with an OH on same molecule (intramolecular cyclization) to form 5 membered ring which can be alpha or beta forms.
natural reversible process
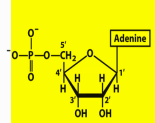
Name structure
Adenosine 5’ monophosphate
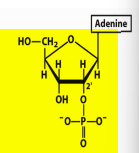
Name structure
Adenosine 2’ monophosphate
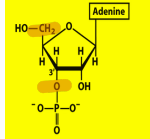
Name structure and importance
Adenosine 3’ monophosphate, end product of RNA hydrolysis
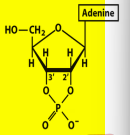
Name structure and importance
Adenosine 2’,3’ cyclic monophosphate
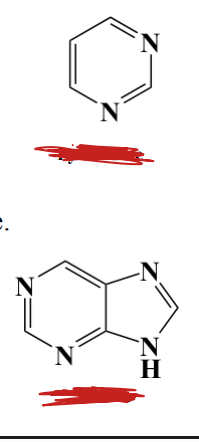
Label each, the nm they absorb light at, and which absorbs more in a uv system and why
TOP: pyrimidine
BOTTOM: purine
purines absorbs more in a UV system because of resonance
BOTH absorb UV around 250-270 nm
Name the pyrimidines and purines found in nucleic acids.
Pyrimidines: Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil. (Pyrimidine Calls Them Ugly)
Purines: Adenine, Guanine (Pure As Gold)
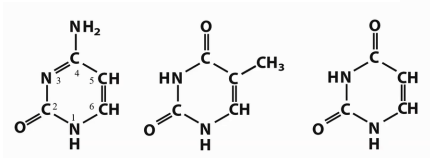
Which bases are DNA-only vs RNA-only vs both?
DNA-only: T (MIDDLE). RNA-only: U (LAST). Both: A, G, C(FIRST)
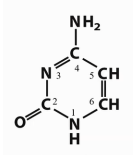
Which base is this?
Cytosine
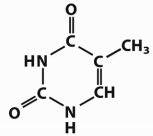
Which base is this?
Thymine
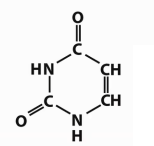
Which base is this?
Uracil
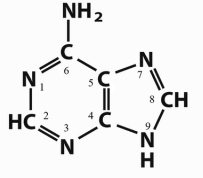
Which base is this?
Adenine
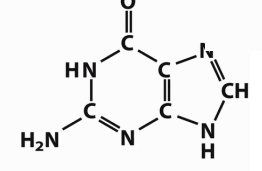
Which base is this?
Guanine
What atoms form the N-glycosidic bond in pyrimidines vs purines?
Pyrimidines: N1-C1′(β); Purines: N9-C1′(β)
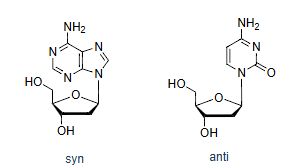
Syn vs anti around the glycosidic bond; which is typical in B-DNA?
Both exist; anti (The nitrogenous base is rotated away from the sugar ring) predominates in B-DNA.
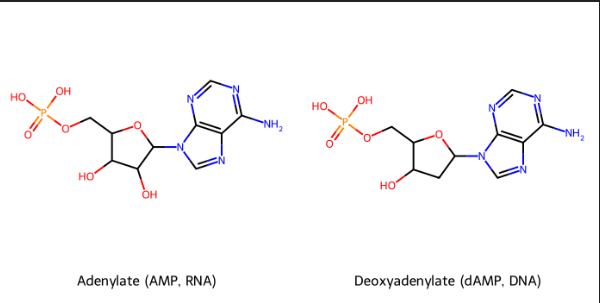
identify→nucleoside→nucleotide names→ symbols (DNA AND RNA).
DNA
Nucleotide: Deoxyadenylate (deoxyadenosine 5’ monophosphate)
Symbols: A, dA, dAMP
Nucleoside: Deoxyadenosine
RNA
Nucleotide: Adenylate (adenosine 5′ monophosphate)
Symbols: A, AMP
Nucleoside: Adenosine
Give guanines→nucleoside→nucleotide names→ symbols (DNA and RNA ).
DNA
Nucleotide: deoxyguanylate (deoxyguanosine 5′ monophosphate)
Symbols: G, dG, dGMP
Nucleoside: deoxyguanosine
RNA
Nucleotide: Guanylate (guanosine 5′ monophosphate)
Symbols: G, GMP
Nucleoside: Guanosine
Give cytosines→nucleoside→nucleotide names→ symbols (DNA and RNA).
DNA
Nucleotide: deoxycytidylate (deoxycytidine 5′ monophosphate)
Symbols: C, dC, dCMP
Nucleoside: deoxycytidine
RNA
Nucleotide: Cytidylate (cytidine 5′ monophosphate)
Symbols: C, CMP
Nucleoside: Cytidine
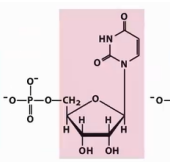
Identify →nucleoside→nucleotide names→ symbols (DNA).
Nucleotide: Uridylate (uridine 5′ monophosphate)
Symbols: U, UMP
Nucleoside: Uridine
Two common DNA base modifications and where.
5-methyl-deoxyCytidylate (eukaryotes, also bacteria); N⁶-methyl-deoxyAdenylate (bacteria, not eukaryotes).
Name two widespread RNA modifications and their roles.
Inosine (tRNA wobble), pseudouridine (tRNA/rRNA); both stabilize structure/folding
Define epigenetics in one sentence.
Heritable regulation of gene activity via DNA methylation, histone modification, and ncRNAs—no base-sequence change; environment-influenced; often reversible.
What links nucleotides and what direction do we read sequence?
3′OH–5′ phosphate- phosphodiester linkages; read 5′→3′.
Which backbone is more chemically stable: DNA or RNA—and why?
DNA. RNA’s 2′-OH promotes base-catalyzed cleavage, forms 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate intermediates → cleavage; DNA lacks 2′-OH
How many H-bonds in A·T vs G·C?
A·T = 2; G·C = 3
What produces major/minor grooves in B-DNA?
Offset pairing of antiparallel strands in the helix.
Two main contributors to duplex stability.
Cation shielding of the backbone; base stacking (G≡C stacks > A=T).
Name A, B, Z DNA and a key feature of each.
B: . Watson Crick structure/most stable;
A: right-handed double helix, wider, favored when dehydrated
Z: left-handed, , zig-zag backbone, slender looking.
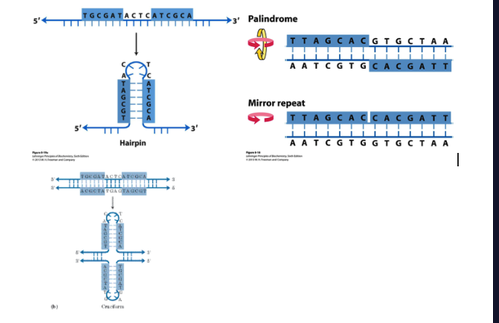
non-Watson–Crick structures DNA can adopt?
Hairpin/cruciform from inverted repeats on opposite strands
Palindrome- same forwards and backwards
Mirror- Mirror repeat on same strand
What are the Hoogsteen positions in purines, and what role do they play in unusual DNA structures?
N-7, O6, and N6 of purines; they participate in hydrogen bonding with a third DNA strand, allowing Hoogsteen pairing and formation of triplex DNA.
How does Hoogsteen pairing differ from Watson–Crick pairing, and what DNA structure can it produce?
Hoogsteen pairing is non-Watson–Crick hydrogen bonding, which can result in triplex DNA.
Compare triplex DNA and tetraplex DNA in terms of strand number, pairing mechanism, and sequence requirements.
Triplex DNA = 3 strands, formed by Hoogsteen pairing.
Tetraplex DNA = 4 strands, forms readily in G-rich sequences, producing a very stable G-tetraplex.
Compare the stability of triplex DNA, tetraplex DNA, and canonical duplex DNA.
Duplex DNA (Watson–Crick) → the most stable and default form.
Triplex DNA → less stable than duplex because Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds are weaker and steric/electrostatic strain is higher.
Tetraplex DNA (G-quadruplex) → more stable than triplexes, due to stacked G-quartets and cation stabilization, but not necessarily more stable than a well-matched duplex.
What is DNA “denaturation” and a cause?
Strand separation from pH extremes or heat disrupting H-bonds and stacking.
Define “annealing” of nucleic acids.
Complementary strands re-pair on returning to favorable T/pH (nucleation → zippering).
Hypochromic vs hyperchromic effect at 260 nm
Hypo: ↓absorbance when duplex forms; Hyper: ↑absorbance on denaturation.
What is Tm, and how does %G≡C affect it?
Tm (denaturation temp)= temperature where half the DNA is single-stranded; ↑G≡C → ↑Tm.
Which regions “melt” first on heating?
A=T-rich regions (bubbles).
Two spontaneous DNA damage types.
Deamination (e.g., C→U) and depurination- hydrolysis of the N-β-glycosyl bond between the base and the pentose (AP/abasic sites).
What problematic alkylation product forms on guanine?
O⁶-methylguanine—mispairs and blocks correct pairing.
Which bases are methylated more often and the methyl donor?
A and C; donor is S-adenosylmethionine (SAM).
Introns vs exons; what % of human DNA is coding?
Introns = non-translated- dont code for anything; exons = coding; coding ≈1.5% of DNA.
PCR?
Amplifying DNA segments of interest.
denature, anneal, use DNA polymerase which add nucleotides to the 3’
ends of primers (marking the starting point for DNA synthesis).
end up making many copies of DNA
What are SSRs and ~how much genome?
Simple sequence repeats (≤10-bp units); ~3% of the human genome; often at centromeres/telomeres. Are non coding and highly repetitive
Satellite DNA?
simple sequence DNA. migrates as satellite bands in a cesium chloride density gradient
What is a centromere; distinctive feature in yeast?
Attachment site for kinetochore/spindle; essential region ~130 bp and A=T-rich.
Describe the Human telomere repeat and replication behavior?
(TTAGGG)n; telomeres shorten each replication without telomerase, that extends them. Telomeres help stabilize the chromosome
Define chromatin and nucleosome details.
Chromatin = DNA+proteins+RNA.
Nucleosome = DNA wrapped around a histone octamer (H2A, H2B, H3, H4) in a left-handed solenoidal supercoil.
Which histones make the octamer core? What is a histone.
Two copies each of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Histones= proteins tightly asc w chromatin and package/order DNA
Define DNA supercoiling.
“Coiling of a coil”—tertiary overwinding/underwinding to compact/manage DNA
closed-circular DNA?
small-circular DNAs that have no breaks in either strand
Define topoisomers and linking number (Lk).
two forms of a circular DNA that only differ only in topology (e.g., Lk);
Lk =describes how many times one strand of DNA winds around the other in a closed circular DNA molecule (coiling pattern/ how many times DNA strand will coil around itself). Relaxed DNA will have a constant Lk # unless the strand breaks
Type I vs Type II topoisomerases in bacteria?
Type I (Topo I & III) relax negative supercoils (increase Lk). Type II (DNA gyrase or Topo II ) introduces negative supercoils (decrease Lk).
Vertebrate Type II topoisomerases?
Eukaryotic Topo IIα/IIβ relaxes (+/−) supercoils but cannot introduce negative supercoils
Fluoroquinolones—targets and effect?
Inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase (Topo II) and Topo IV → block replication → bactericidal; e.g., ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, ofloxacin.
Key features of mRNA.
Ribose; uracil (not thymine); single-stranded; mono (code for one protein)- or polycistronic (code for multiple).
Connect methylation to function in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
Prokaryotes mark self DNA (N⁶-mA/5-mC) so restriction systems attack foreign DNA; eukaryotic 5-mC regulates gene expression / mark which genes should be active, negative regulation (epigenetic mark).
Why does DNA use thymine instead of uracil?
Spontaneous C→U deamination would be undetectable if U were normal; thymine lets repair systems flag U as damage.
Why is inhibiting bacterial gyrase bactericidal, whereas broad Topo II inhibition is toxic to us?
Bacteria need gyrase to introduce negative supercoils for replication; blocking it stalls forks and kills cells. Humans lack gyrase but require Topo II—global inhibition harms dividing human cells