Chapter 18 Rates of reactions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
How do chemists measure the rate of a reaction?
Rate = change in concentration/change in time
What are the units for rate of reaction?
mol dm3 s-1
What is the rate of reaction proportional to?
The concentration of a particular reactant
What is the order with respect to a reactant?
A measure of how the change in the concentration of that reactant will affect the overall rate.
What is zero order?
When the concentration has no effect on the rate
What is first order?
When the rate depends on the concentration of a reactant raised to the power of one
What is second order?
When the rate depends on the concentration of a reactant raised to the power of two
What does the rate equation do?
It gives the mathematical relationship between the concentrations of the reactants and the reaction rate
What is the rate constant?
The proportionality constant. It is the number that mathematically converts between the rate of reaction and concentration and orders
What is the overall order of reaction?
The value that gives the overall effect of the concentrations of all reactants on the rate of reaction. It is the sum of orders with respect to each reactant.
What is the initial rate?
The instantaneous rate at the beginning of a reaction when t = 0
What is continuous monitoring?
Continuous measurements taken during the course of a reaction. This can be monitored by gas collection and mass loss.
What is a colorimeter?
A device that measures the absorbance or transmittance of specific wavelengths of light by a solution to determine its concentration or quantify its colour
What is the gradient of a concentration-time graph equal to?
The rate of reaction
What does the concentration-time graph for a zero order reaction look like?

A straight line with a negative gradient
What does the concentration-time graph for a first order reaction look like?
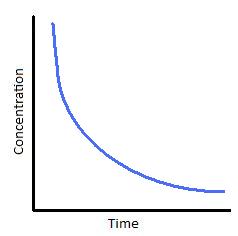
Downward curve with a decreasing gradient over time. The time for the concentration of the reactant to halve is constant
What does the concentration-time graph for a second order reaction look like?
A downward curve, steeper at the start but tailing off more slowly

What is the half-life of a reaction?
The time taken for half of a reactant to be used up. Constant half-life is called exponential decay
How can you calculate the rate constant from the half-life?
k = ln2/t1/2
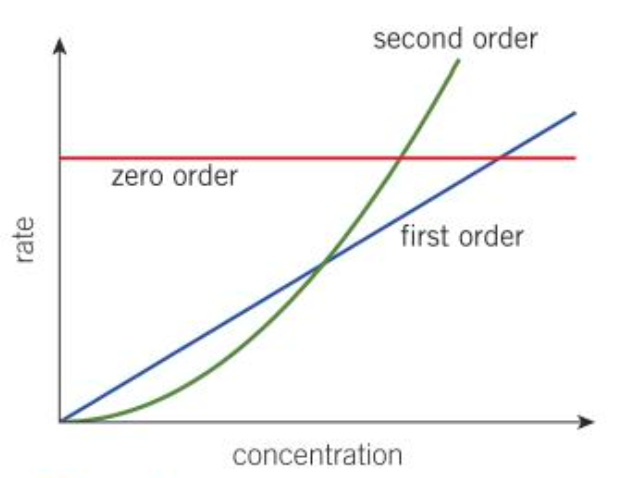
What are the different shapes of a rate-concentration graph?
What is observed in a clock reaction?
A visual change, and the time it takes for this to happen is measured
What are you measuring in a clock reaction?
The average rate during the first part of the reaction
What assumptions are made in a clock reaction?
The average rate of reaction is constant and is the same as the initial rate
Why are clock reaction results more accurate when there is a shorter time taken for a colour change?
Because that means there are less rate changes over that period of time
What is the reaction mechanism?
The series of steps that make up an overall reaction
Why is the following reaction likely to take place in a series of steps?
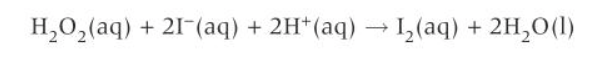
Because all of the reactants colliding at once would be an extremely unlikely event
What is the rate-determining step?
The slowest step in a reaction mechanism.
How do you know whether a reaction mechanism is likely to be correct?
The rate equation only includes reacting species involved in the rate-determining step
The orders in the rate equation match the number of species involved in the rate-determining step
What is the Arrhenius equation?
k = Ae-Ea/RT
What does the exponential factor (e-Ea/RT) represent?
The proportion of molecules that exceed Ea and that have sufficient energy for a reactio