IB MYP 8 Science electricity unit
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Lightning
an example of static electricity on a much larger scale in nature.
Static electricity
charge, typically produced by friction, which causes sparks or crackling or the attraction of dust or hair.
uncharged
state in which something isn’t charged by electricity.
charged
state in which something is charged by electricity.
Attraction
The object gets closer to another object because of differing electrical charges.
Repulsion
The object gets farther away from another object because of being the same electrical charge.
Electrical charge and magnetic charge
They are only the same concept, they are completely different and distinct things.
Coulombmeter
Digital meter that finds out whether a charged object has positive or negative charge
Otto van Guericke
One of the scientists that discovered static electricity
free electrons
electrons that reside in an atom’s valence shell as valence electrons and are easily plucked off and carried around, when ac ted upon by an ‘outside force’.
Describing static electricity material
We describe them similarly to how we describe heat transfers; conductors and insulators.
Conductor
they let electrons move freely throughout the solid.
Insulators
they hold to electrons tightly, limiting their flow.
wood
an example of a static electricity insulator
Negative charge
Too many electrons
positive charge
Too little electrons
Law of conservation of electric charge
It says that you can never create a net electric charge. Instead, charge can only move from one place to another.
Triboelectric effect
happens when rubbing two neutral objects and forming one positive charged object and one negatively charged object
humidity on static electricity
The extra water in the air makes the air more conductive, constantly leaking the buildup of electrical charge
Neutral objects
they have net zero charge
Thunderstorm formation
When warm, moist air rises high into the atmosphere
updraft
vocabulary used for when warm, moist air rises high into the atmosphere
Cloud formation
when water vapour in the air cools into water drops called cloud droplets
cloud droplets freezing
They freeze into ice crystals
graupel formation
when cloud droplets and ice crystals collide with each other
storm cloud electrical charge buildup
With the collision of graupel and ice crystals, they form electrical charges of positive and negative
cloud electricity locations
ice crystals with positive charges are located higher within the clouds due to updraft, meanwhile graupel with negative charges are within the nether regions.
lightning electrical discharge
When the cloud forces build up enough electrical charge, the discharge happens with the surface.
Cloud to ground lightning
lightning often connects the negative charge of the clouds with the positive charge of the ground
lightning hitting tall structures
They are the closest to the clouds high up in the skies
Intracloud lightning
when lightning from a negative charge goes to a positively charged cloud
Friction significance
it separates the positive and negative charges that lead to static electricity.
friction electrons
it transfers a valence electron from one atom to the another
electron nucleus attraction
the electron is attracted to the nucleus because of the opposite charges.
electron weakening attraction
Valence electrons lose their attractiveness to an atom the farther away the valence shell is from the nucleus.
neutral attraction explanation
They are attracted because of the mere presence of electrons and protons
everything electric
everything is electric
static electricity imbalance
it is the imbalance of positive and negative charges
difference in materials holding electrons
materials have different attractions with their valence electrons
Difference in materials holding electrons example
silk holds their electrons more tightly than glass
More friction more power
the more the object is interacted through friction (rubbing), the more powerful the charge.
Conductor
Material that allows electricity to pass through them
Conductor variation
Not all conductors are equal; some conductors are better than others.
Copper wire
Example of a conductor
Insulator
Material that do not allow electricity to pass through them
Plastic
This is an example of an insulator
conductor of electricity atomic structure
all of them have an electron that can change between atoms.
electric current
Specific word used to define electricity when utilised.
electric circuit requirements
complete circuit of metal around which the current can flow, a cell (a battery) to make the current flow
Circuit Diagrams
Method in which how different components are connected together in an electric circuit is shown.
Circuit Symbol
symbol for a component within a circuit
Conventional current flow
opposite of the electron flow and comes out from the postiive battery
Electron flow
opposite of the conventional current flow and comes out from the negative battery
Switch Symbol
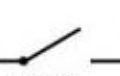
Light bulb symbol

Wire symbol
simple line. Never curved.
battery Long line
Long line is the positive side of the battery
Battery orientation
The orientation of the battery matches the schematic’s orientation
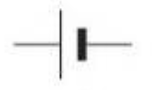
Battery
composition of two cells
Battery symbol
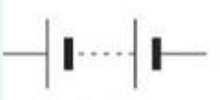
Cell symbol
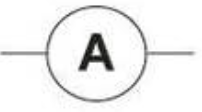
Anmeter symbol
Voltmeter symbol

Motor symbol
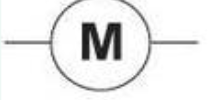
Resistor symbol
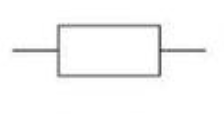
Variable Resistor Symbol
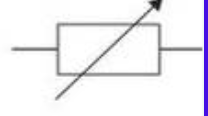
Reason for electric circuits
We can’t rely on static electricity as a source of energy because it is instant and happens all at once, meanwhile we can utilise electric circuits because of its steady flow of energy.
Current
steady flow of electrons
Circuit
Path that a current can follow
Power source
source that provides a steady source of electrons
Hot slot
Where electrons come from within a wall outlet
Load
Device that utilises electricity
Negative terminal
where electricity leaves and goes for the load
Positive terminal
Where the electrons enter in an electric circuit
Neutral slot
where positive charges go within the wall outlet
Electron flow within wall outlet
They flow out of the hot slot and into the load, and goes again back to the wall outlet through the other prong and goes into the neutral slot
Switch
Device that controls electric circuits by opening them or closing them.
Switch off
This means that the circuit is open.
Switch on
This means that the circuit is closed.
Current magnitude
If a brighter lamp lights up, a bigger current is present.
ammeter
used to measure electric current in a circuit
Amp
unit of electric circuit
A
Amp symbol
Ammeter connection
To connect an ammeter in a circuit, it is necessary to make a break in the circuit. Then the current can flow through the ammeter.
Ampere
Unit of measure of the rate of electron flow or current in an electrical conductor
ampere representation
one ampere of current represents one coulomb of electrical charge moving past a specific point in one second.
Current equal
The current is the same all the way round each circuit.
Current usage
It doesn’t get used up as if goes through the lamps.
Series circuit
Components are connected end-to-end. Current flows through the components one after another.
Series circuit same current
The current is the same all the way round a series circuit.
Metal usefulness
Metal contains a lot of electrons which can move about inside the metal. It allows for useful conducting
Metal electron attachment
These electrons are no tightly attached to their atoms. That is what makes this material different from others.
Cell making current flow
The positive end of the cell attracts electrons meanwhile the negative end repels electrons.
Cell meaning
provides energy for many electrical devices to function
electrochemical cell
Cell which uses chemical reactions to transfer energy.
Voltage
Pressure from an electrical circuit’s power source that pushes charged electrons through a circuit, enabling them to do work.
Volts
Measurement of voltage
V
Symbol for volts
Voltage scaling waterfall analogy
If voltage was a waterfall, the voltage would be the height of the waterfall: the higher it is, the more potential energy the water because of its distance from the bottom of the falls, and the more energy it will possess as it hits the bottom.
Current waterfall analogy
It represents how much water was going over the edge of the falls each second