A&P1 Connective Tissues (Tissues 3)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Cells far apart
at least two different cell types
Highly Vascularized
Contains large amounts of extracellular matrix
Classified based on type of extracellular matrix and function
Extracellular matrix contains 3 components (in varying amounts)
protein fibers, ground substance, fluid
Ground substance: proteins and sugars
What are the characteristics of Connective Tissues?
Classified based on type of extracellular matrix and function
How are Connective Tissues Classified?
protein fibers
ground substance
fluid
3 components of the extracellular matrix?
Ground substance
Protein and sugars are?
Collagen and Elastic Fibers
What are typically considered protein fibers?
Loose
Dense
Adipose
What are the 3 types of Ordinary Connective Tissue?
Loose (areolar) connective tissue
Adipose tissue
Dense connective tissue
Cartilage
Bone
Blood
What are the 6 types of connective tissues?
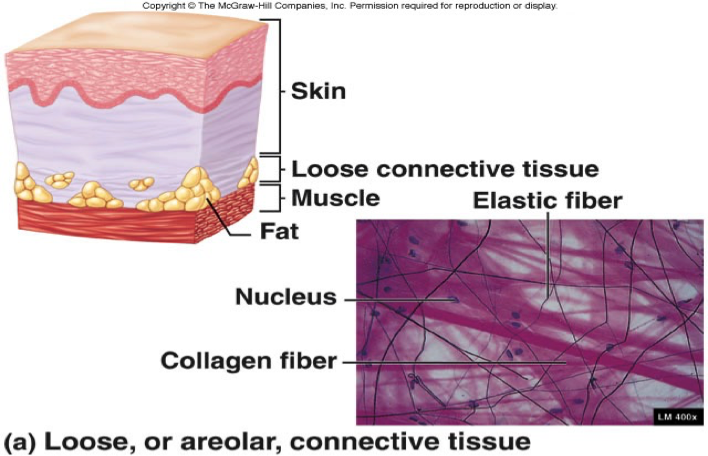
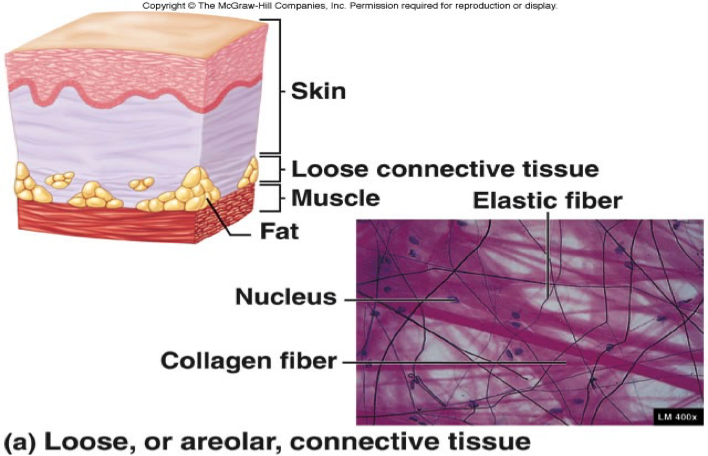
Collagen = strength
Elastic = elasticity
Loose (areolar) connective tissue
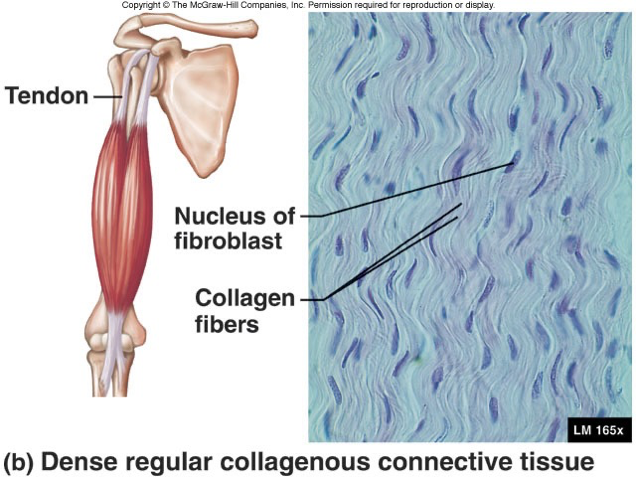
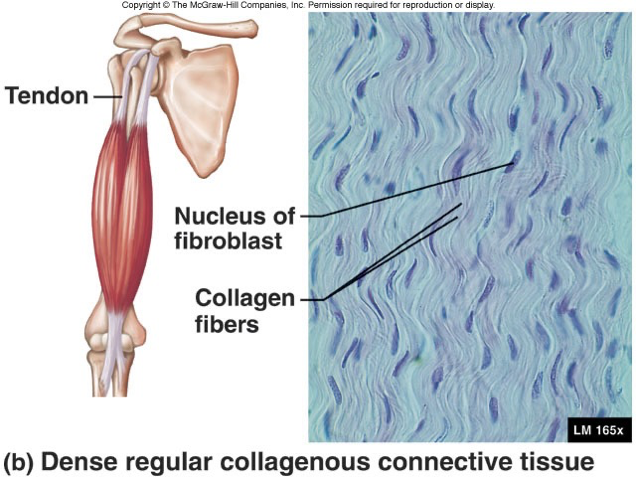
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue
Collagen fibers are densely connected and packed together. They run parallel.
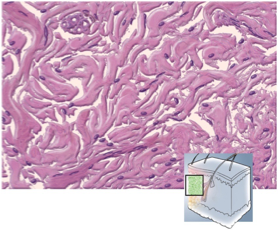
Dense Irregular Connective Tissues
Densely packed, randomly arranged, collagen fibers and few visible cells.
Withstands unpredictable stresses
Deeper layer of skin; capsules around organs
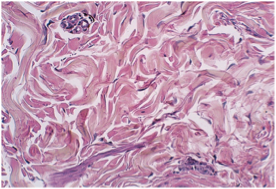
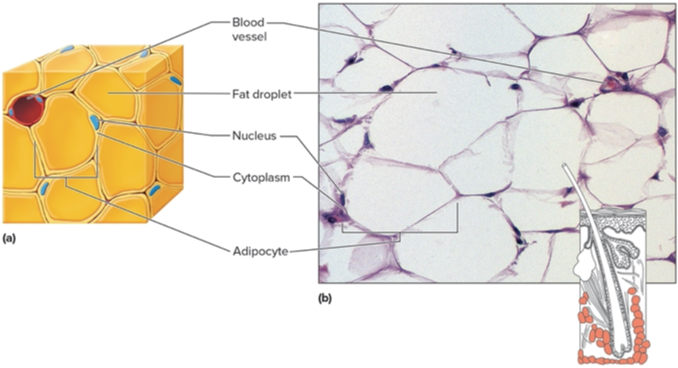
Adipose Tissue
Type of tissue?
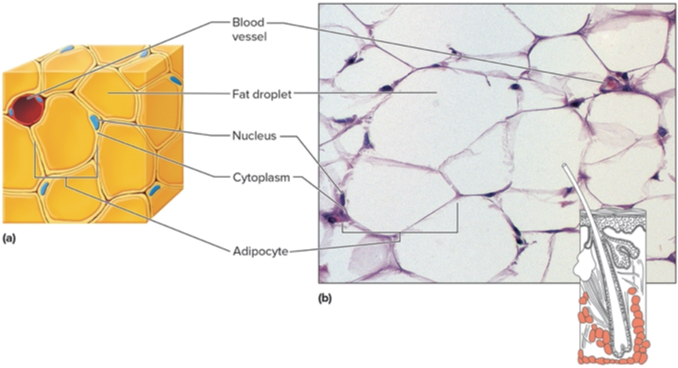
Adipocytes
Fat cells are called? They are one big cell with a fat droplet. Provide cushion and energy storage.
Cartilage
Bone
Blood
What are the 3 specialized connective tissues?
Cartilage
Composed of chondrocytes
Contains collagen
Withstands compressions
Provides support, flexibility, strength
Chondrocytes
What is collagen composed of?
Hyaline Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Elastic Cartilage
What are 3 types of Cartilage?
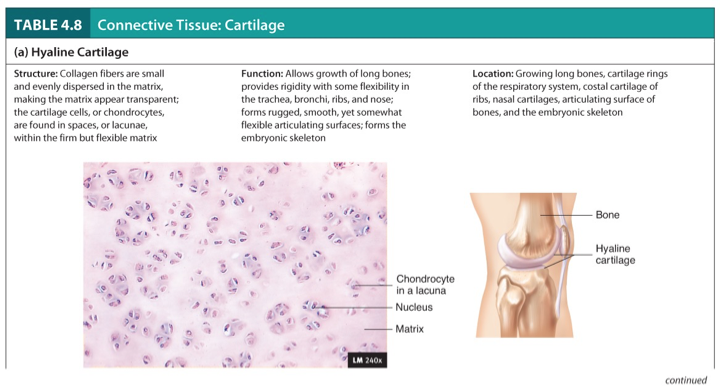
Hyaline Cartilage
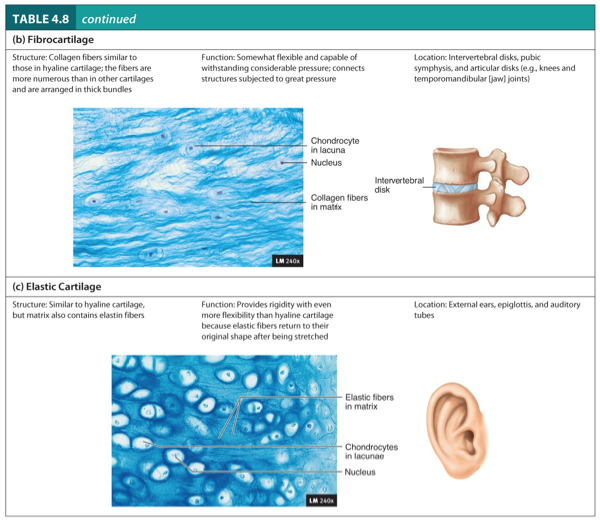
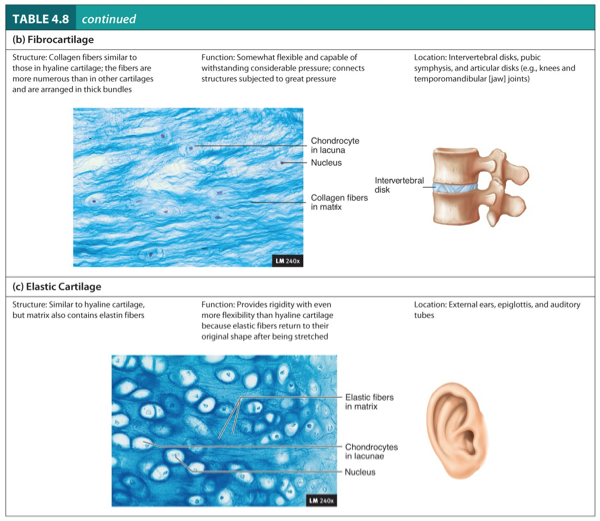
Fibrocartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Bone
Composed of osteocytes
The matrix is made of calcium phosphate
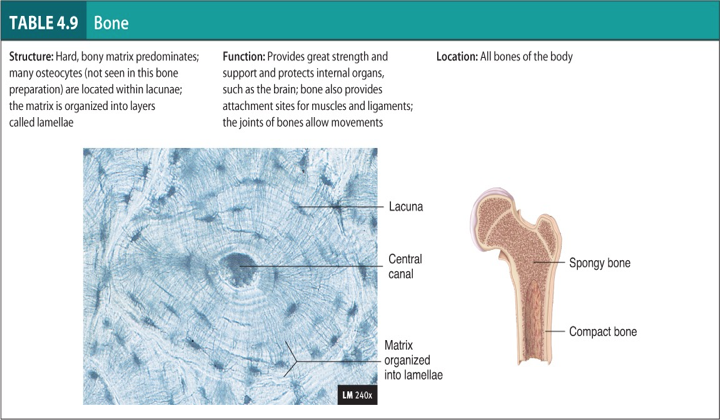
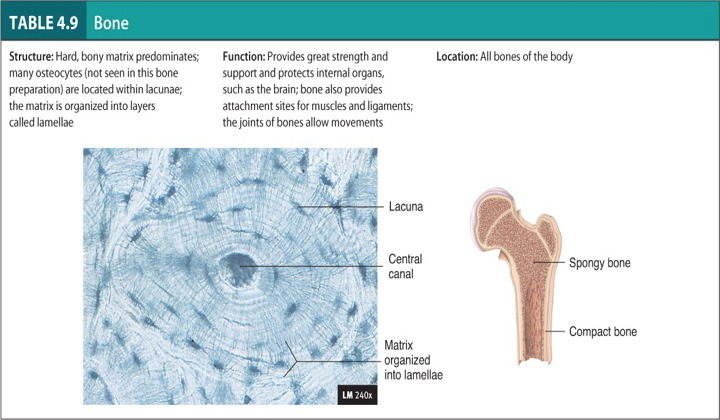
Bone
Know the Lacuna and Central Canal
Bone
Know the Lacuna and Central Canal
Blood
Liquid matrix: Plasma - 90% Water
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
Transport food, oxygen, waste, hormones
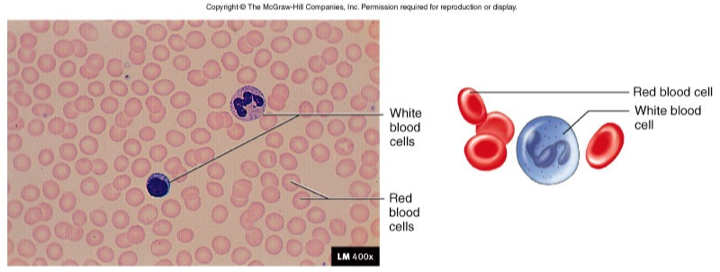
What does the White Blood Cell look like?
What does the Red Blood Cell look like?
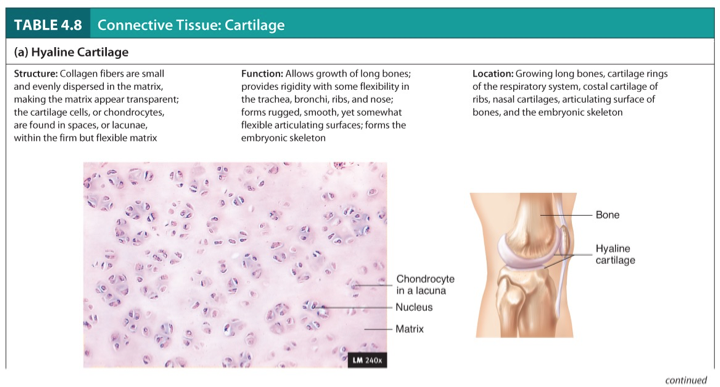
Hyaline Cartilage
Structure:
Collagen fibers are small and evenly dispersed in the matrix, making the matrix appear transparent; the cartilage cells, or chondrocytes, are found in spaces, or lacunae, within the firm but flexible matrix.
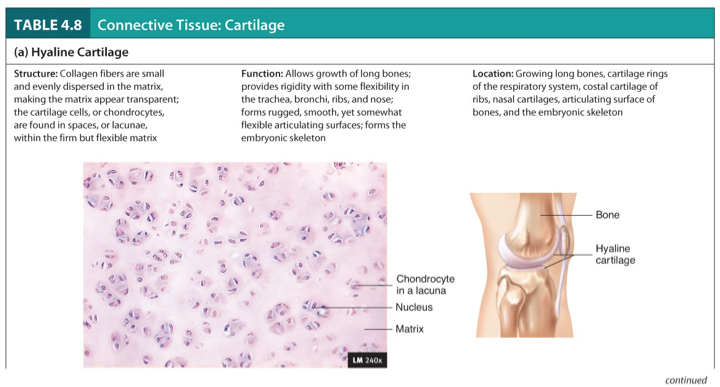
Hyaline Cartilage
Function:
Allows growth of long bones; provides rigidity with some flexibility in the trachea, bronchi, ribs, and nose.
Forms rugged, smooth, yet somewhat flexible articulating surfaces; forms the embryonic skeleton.
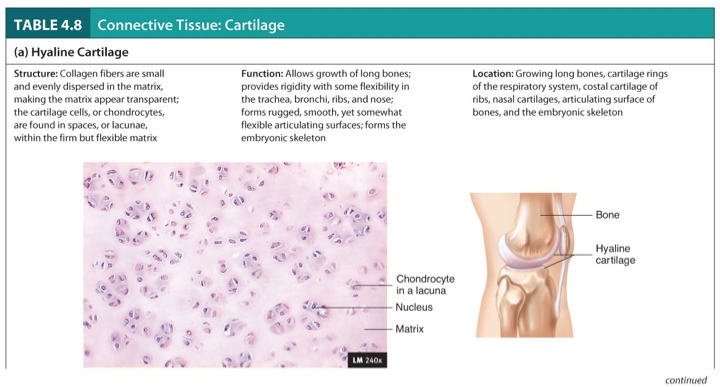
Hyaline Cartilage
Location:
Growing long bones, cartilage rings of the respiratory system, costal cartilage of ribs, nasal cartilages, articulating surface of bones, and the embryonic skeleton
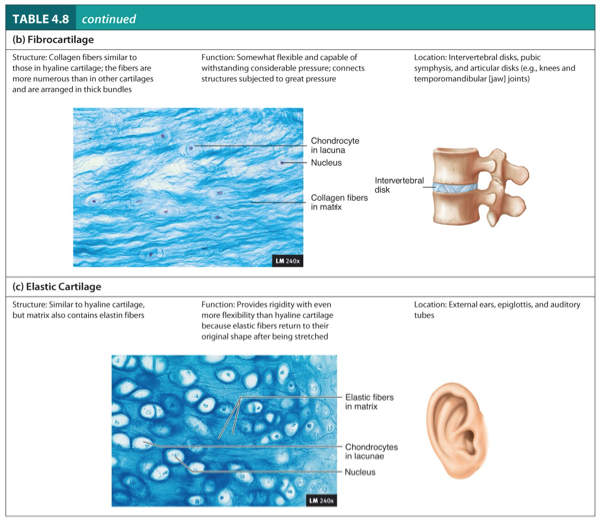
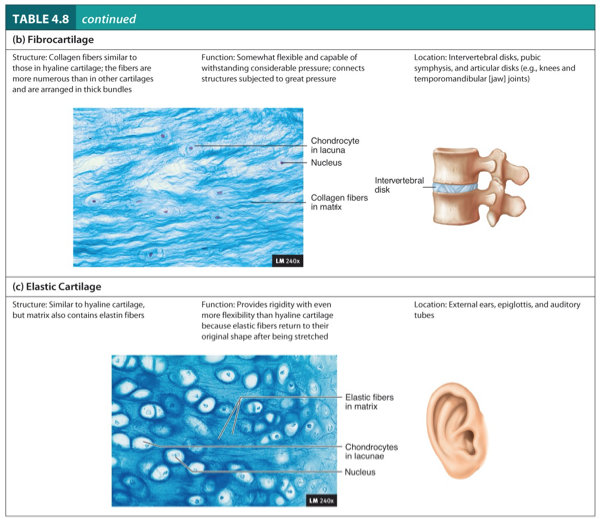
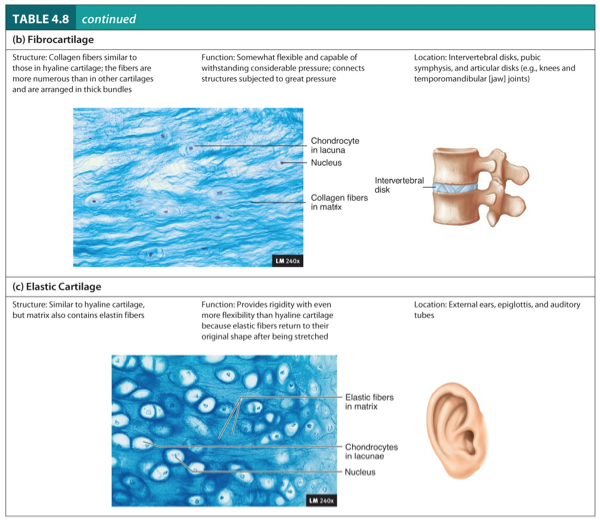
Fibrocartilage
Structure:
Collagen fibers similar to those in hyaline cartilage.
The fibers are more numerous than in other cartilages and are arranged in thick bundles.
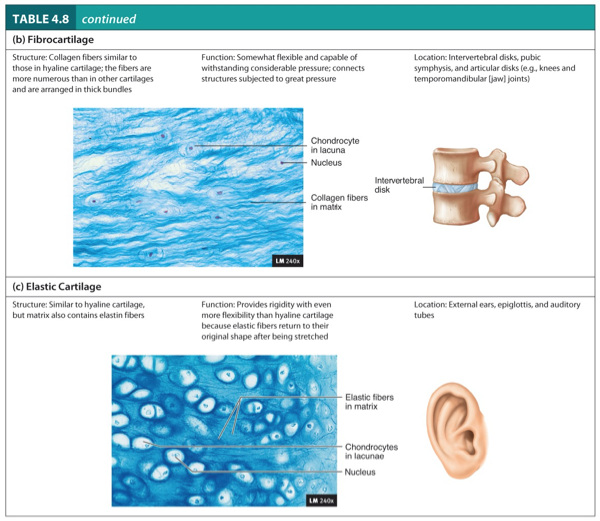
Fibrocartilage
Function:
Somewhat flexible and capable of withstanding considerable pressure.
Connects structure subjected to great pressure.
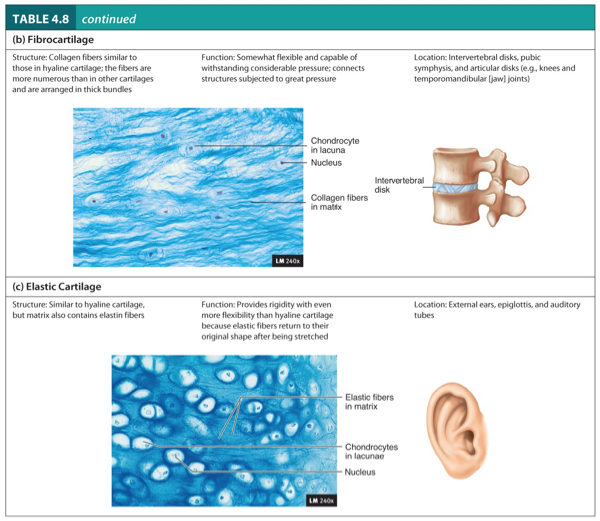
Fibrocartilage
Location:
Intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis, and articular disks (e.g., knees and temporomandibular (jaw joints).
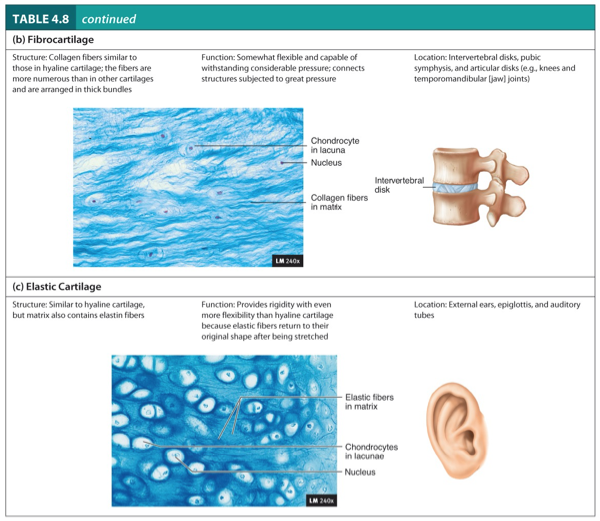
Elastic Cartilage
Structure:
Similar to hyaline cartilage, but matrix also contains elastic fibers.
Elastic Cartilage
Function:
Provides rigidity with even more flexibility than hyaline cartilage because elastic fibers return to their original shape after being stretched.
Elastic Cartilage
Location:
External ears, epiglottis, and auditory tubes.