BOTAFUN Long Exam 1
1/386
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Modules 1-4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
387 Terms
\
\*botane = plant
* Eukaryotic
* More complicated cell parts
* Multicellular
* Cellulosic cell walls
* Contains chloroplasts with chlorophylls a and b that enables photosynthesis
* Photosynthetic
* Lacks the power of locomotion/movement from one place to another by step
* They move in the sense that pollen grains can get dispersed
* Produces embryos that are parts of seeds
Psychotic mushrooms
Food: alternative sources of food
Energy: renewable energy sources
Environment: environmental conditions
Interact with plants
Grow your own plants
Be open-minded to novel interest on plants
Photosynthesis-Calvin Cycle
Melvin Calvin (Chemistry, 1961)
Chlorophyll-Photosynthetic Reaction Center
Richard Martin Willstatter (Chemistry, 1915)
Artemisinin: Cure against the Malarial parasite
Youyou Tu (Physiology or Medicine, 2015)
Green Revolution
Norman Borlau (Nobel Peace Prize, 1970)
Genetic Transposition in Maize
Small RNAs that silence genes (for viral diseases) Discovered in plant cells
1. Recognize a problem
2. Develop a hypothesis
3. Design and perform an experiment
4. Analyze and interpret the data
5. Share new knowledge
1. consistent
2. observable
3. natural
4. predictable
5. testable
6. tentative
Scientists are _______, among others?
Honest
Plants have trace elements of the following EXCEPT:
A. Boron
B. Iron
C. Manganese
D. Zinc
E. Copper
F. Molybdenum
G. Tin
G. Tin
All organisms are composed of _____
Matter
What 4 elements make up around 96 to 99.5% of living matter?
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Carbon
Nitrogen
Water is ____ of the entire plant body
70%
What are inorganic molecules?
A group of molecules/compounds that have no carbon
How does polarity work?
“Electrons in a polar covalent bond are unequally shared between the two bonded atoms, which results in partial positive and negative charges. The separation of the partial charges creates a dipole. The word dipole means two poles: the separated partial positive and negative charges. A polar molecule results when a molecule contains polar bonds in an unsymmetrical arrangement”
“Since oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the two bonds that are formed will be polar covalent, which means that a partial negative charge will be on the more electronegative atom - oxygen - and two partial positive charges will be on the less electronegative atoms - hydrogen”
Benefits of being polar
Being attracted to a lot more compounds
Involved in more reactions
_____________ form when a covalently-bonded H is attracted to a negatively-charged atom in a neighboring molecule
Hydrogen bonds
Characteristics of water that benefit living things
Liquid at room temperature
Universal solvent for polar molecules
Water molecules are cohesive, which means they really stick together
Slow temperature change
Is water an organic or inorganic compound?
Inorganic
What is produced when water dissociates?
Hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-)
These are molecules that contain a carbon
Organic compounds
Are all compounds with carbons organic? What are examples of such?
No, not all carbon compounds are organic. Some examples are:
CO2, CO (carbon oxides)
CO3, HCO3 (carbonates/bicarbonates)
HCN (cyanides)
Compounds with one C and usually with no H
What are the four basic types of organic molecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
What are the building blocks of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
What are the building blocks of lipids?
Glycerol and fatty acids
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What is the ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in carbohydrates?
1:2:1 respectively
Sugars and starches are called what
Saccharides
Where does the name “carbohydrate” come from?
ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen to form C6H12O6
What makes most carbohydrates water-soluble?
Alcohol (-OH) groups attached
How can carbohydrates be classified?
Number of sugar molecules
Location of carbonyl group
Size of carbon skeleton
Differentiate monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides with each other
Monosaccharides: simple sugars
Disaccharides: condensation synthesis required to link two monosaccharides with each other through glycosidic bonds
Polysaccharides: bound together through polymerization of covalent bonds of 3 or more monosaccharides
What are carbohydrates used for?
Energy production, storage, and structure
This is the main food molecule used by most living things that is produced through photosynthesis
Glucose
[T/F] Glucose can be assembled into starch and cellulose
True
Fruit sugar used to sweeten food products
Fructose
What are examples of monosaccharides?
Glucose
Fructose
Ribose, Deoxyribose
Vitamin C
If monosaccharides have the same chemical formula, what differentiates them from each other?
Their structure, specifically ISOMERS
What are isomers?
Any two or more compounds with the same molecular formula but with different structures
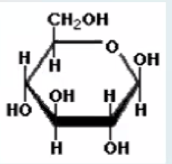
What is this molecule?
Glucose
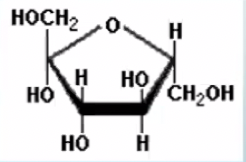
What is this molecule?
Fructose
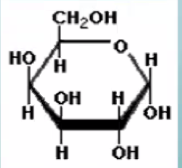
What is this molecule?
Galactose
Describe the two types of isomers
Structural: same constituent atoms but different bonding patterns
Stereoisomers: same molecular formula and sequence but differ in 3D (geometric isomers and enantiomers)
Differentiate geometric isomers from enantiomers
Geometric isomers: different spatial arrangements using the cis-trans
Cis - same molecules on the same side; Trans - same molecules on opposite sides
Enantiomers: mirror images
Carbohydrates as quick sources of energy
When we work, even when we sleep, all our cells are working
Cells use up energy when they work
Immediate source of energy are: carbohydrates
So if we want to lose weight, we go on carb-free diets
If we consume our carbs already, the stored carbs are the one that is lost
If we are active and we don’t eat carbs, the next source of energy are the lipids
Lipids provide us energy
Hence, we don't see the results of our diet immediatel
What are the monomers of carbohydrates?
Glucose, fructose, galactose
How do two monosaccharides link together to form disaccharides?
Process of condensation synthesis or dehydration synthesis, where two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water
How do you break up disaccharides?
Through hydrolysis, where a larger molecule forms two (or more) smaller molecules and water is consumed as a reactant. Water is introduced to break up the bond
Most common disaccharides are:
Maltose: malt sugar; glucose + glucose
Sucrose: common table sugar; glucose + fructose
Lactose: milk sugar; glucose + galactose
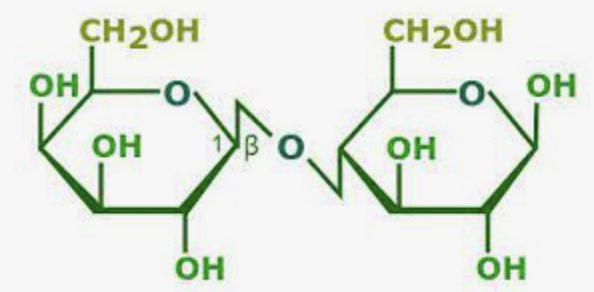
What is this molecule?
Lactose
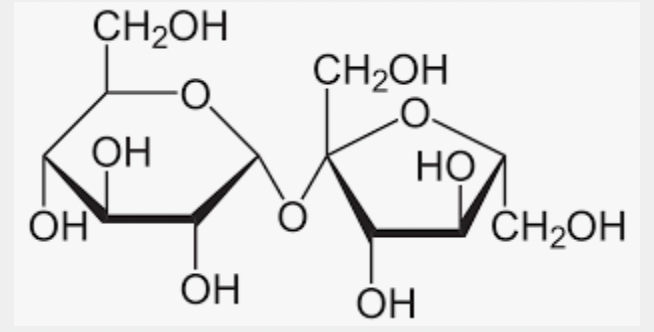
What is this molecule?
Sucrose
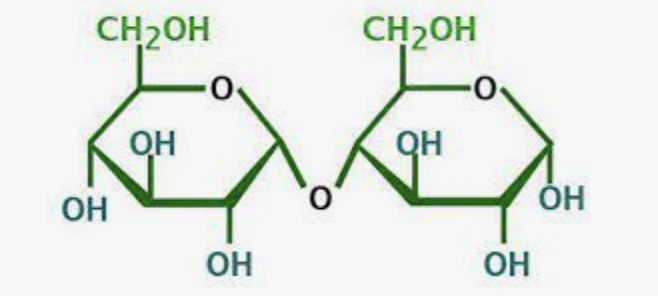
What is this molecule?
Maltose
These are bound together through polymerization
Polysaccharides
Most important polysaccharides for plants are
Cellulose
Starch
Polysaccharides can be classified into:
Structural polysaccharides
Storage polysaccharides
3 structural polysaccharides:
Cellulose
Chitin
Pectin
Also known as fibers
Cellulose
Most abundant organic compound on Earth
Cellulose
How much cellulose do plants produce per year?
100 billion tons
Toughest organic compound to digest
Cellulose
Insects, spiders, and crustaceans use this to build their exoskeletons
Chitin