NURS 203: Unit 4 - Neurological System: Motor Response (Lab 4 Review)
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The portion of the nervous system that contains the brain and spinal cord cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The portion of the nervous system that contains both cranial and spinal nerves
Amount of Cranial Nerve Pairs
12
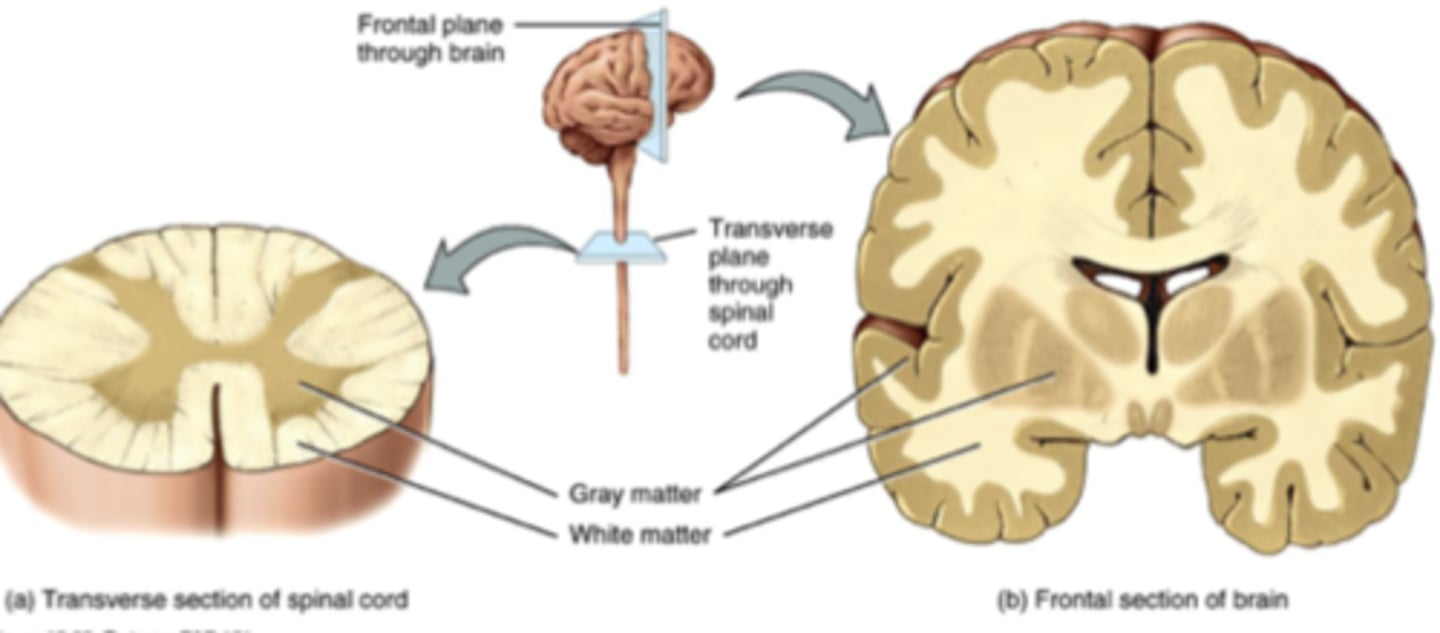
White Matter
Myelinated axons (Ex. Inner of brain, and outer of spinal cord)
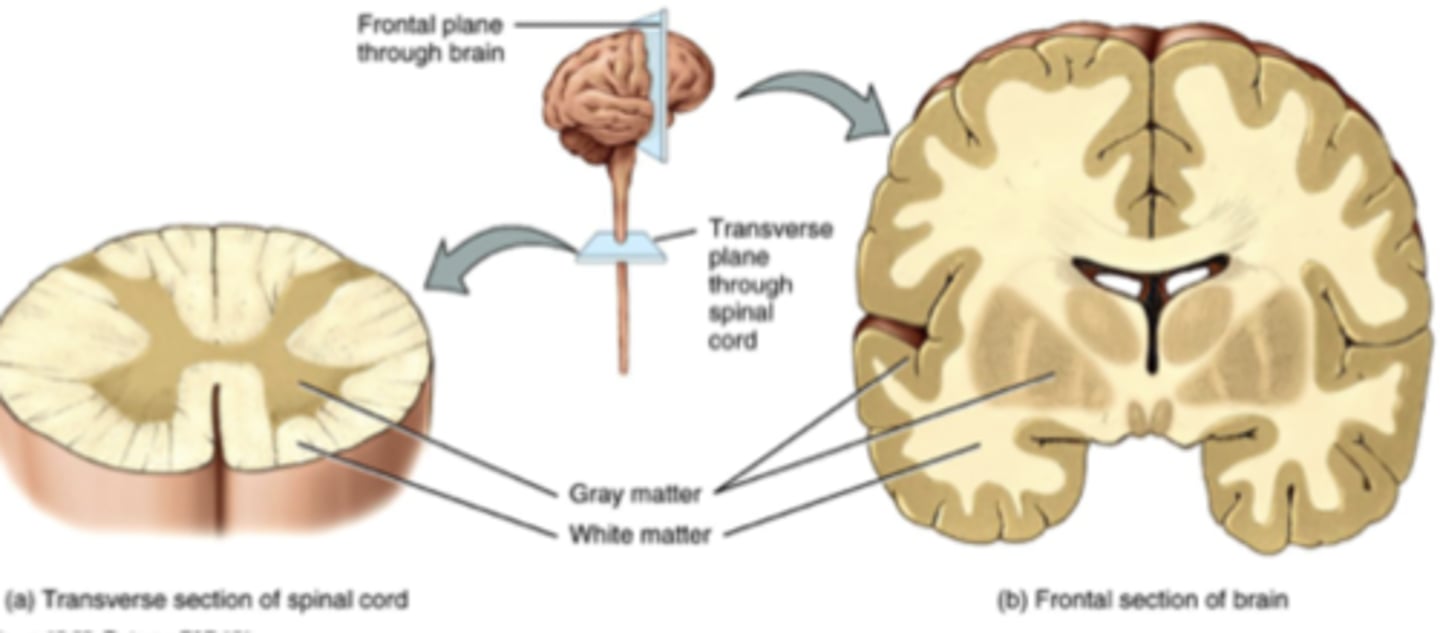
Grey Matter
Unmyelinated axons (Ex. Soma, dendrites, neuroglia, outer part of brain and inner part of spinal cord)
Amount of Hemispheres in the Brain
2
4 Lobes of Each Hemisphere in the Brain
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Occipital
- Temporal
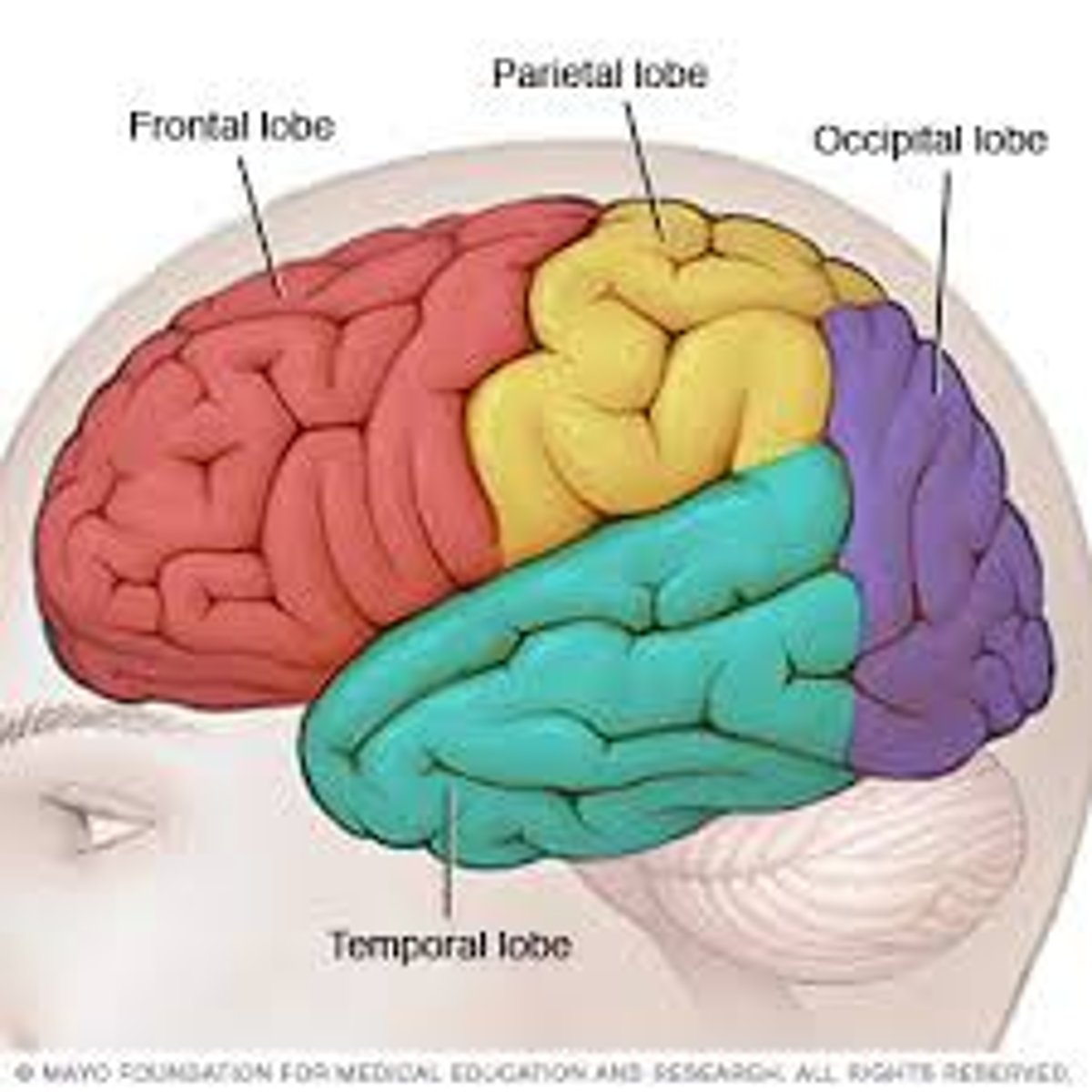
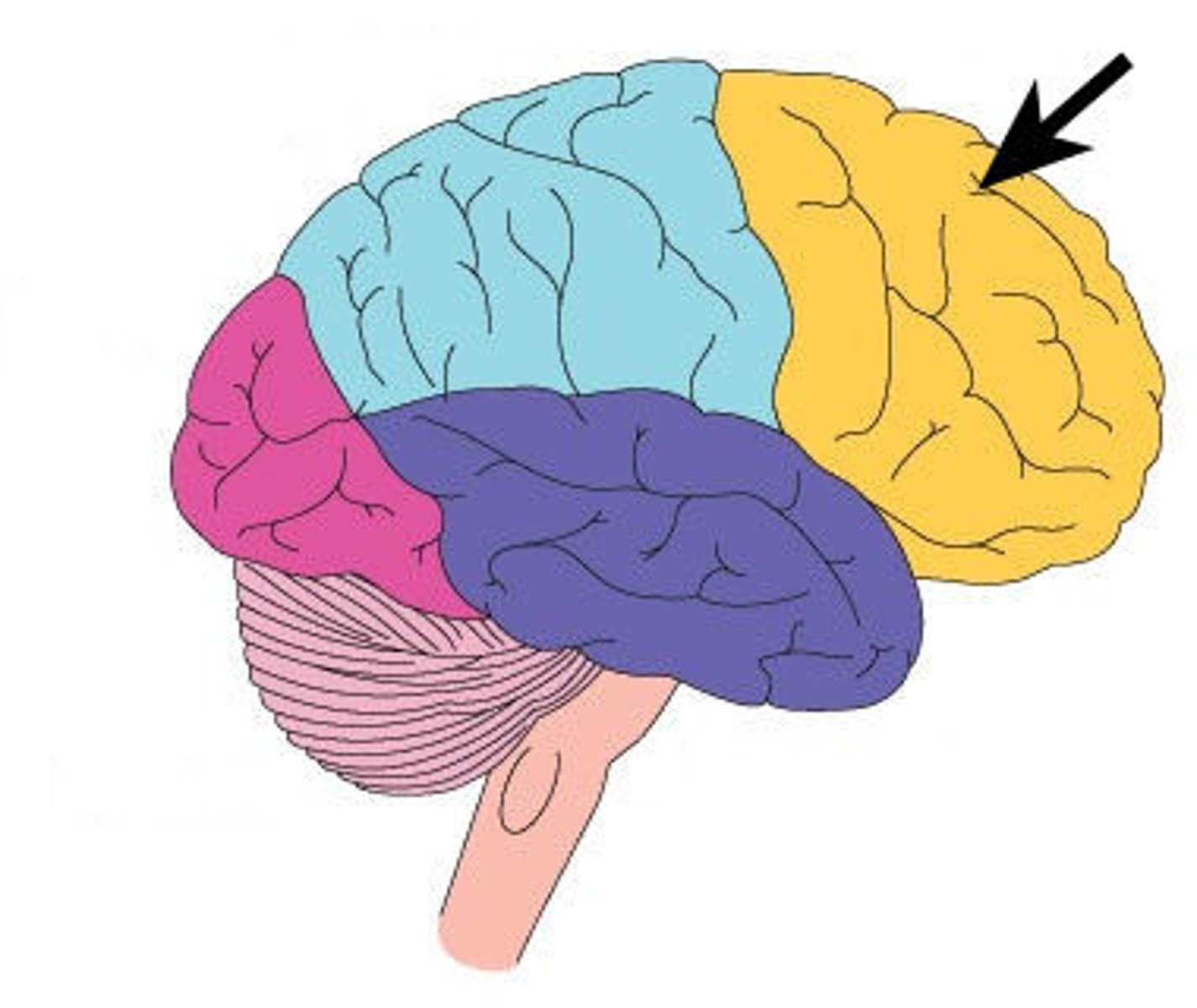
Frontal Lobe
Lobe of the brain concerned with personality, behaviour, emotions, and intellectual function
Parietal Lobe
Lobe of the brain responsible for sensation
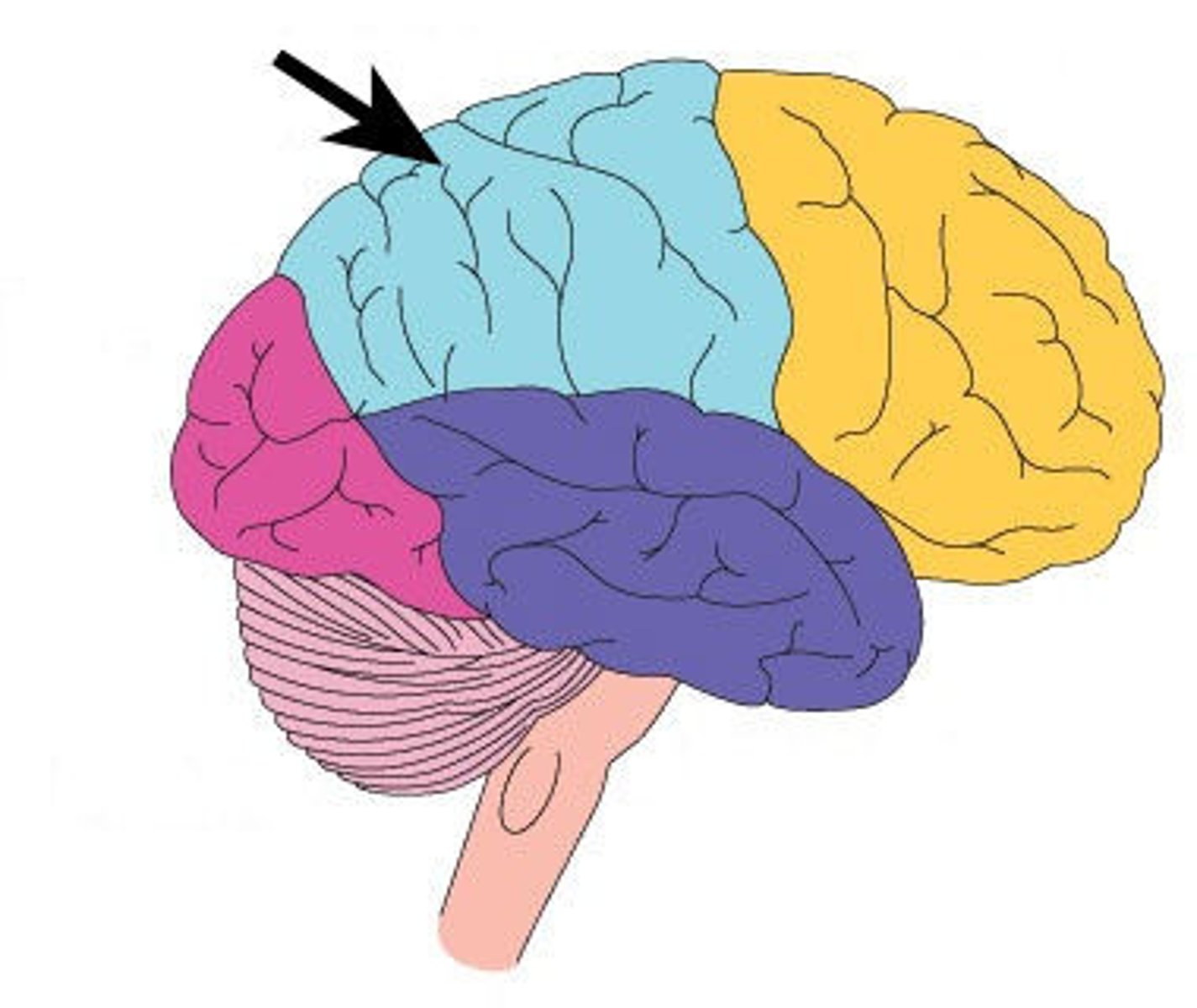
Occipital Lobe
Lobe of the brain that acts as the primary visual receptor centre
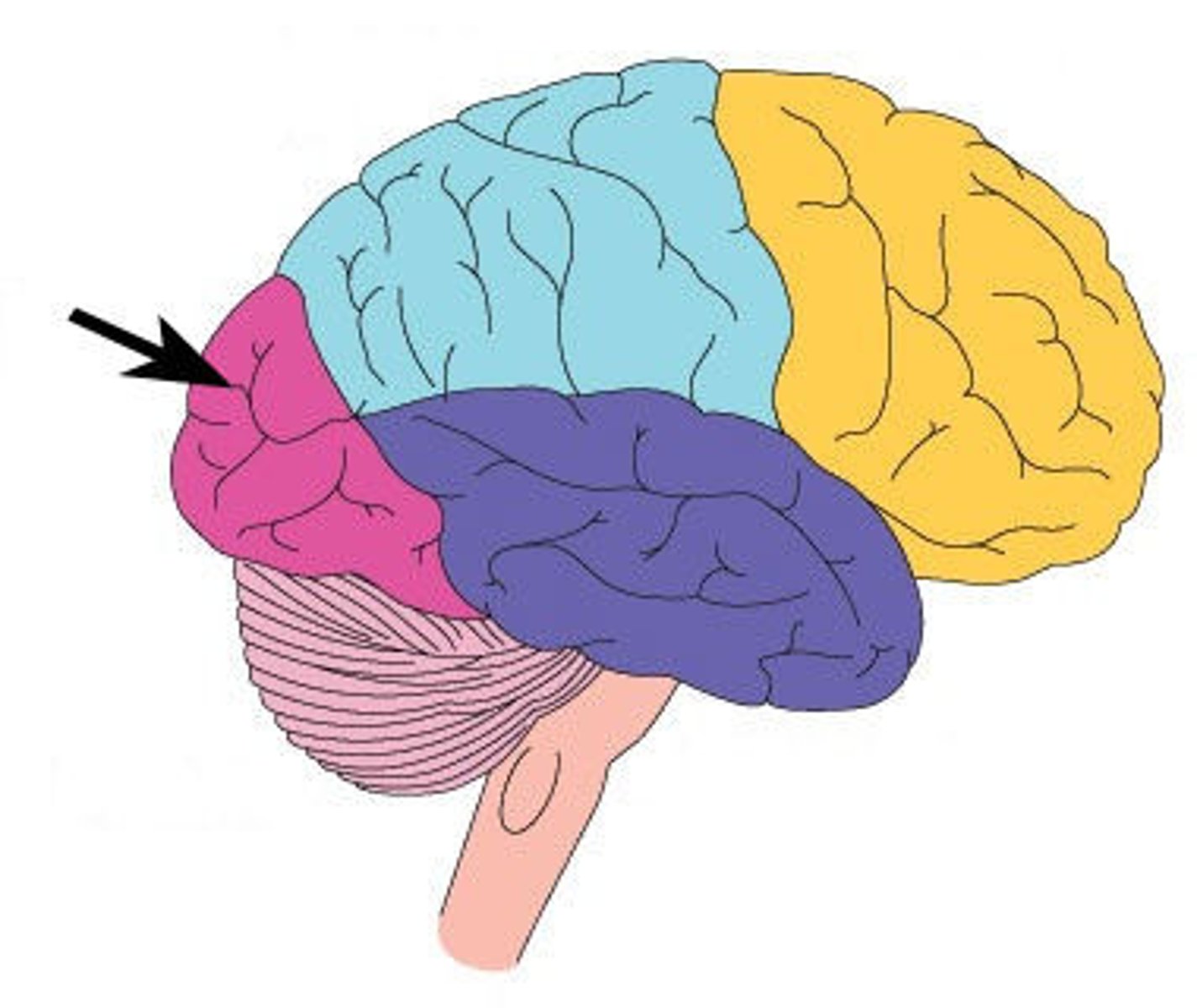
Temporal Lobe
Lobe of the brain located behind the ear and contains the primary auditory reception centre
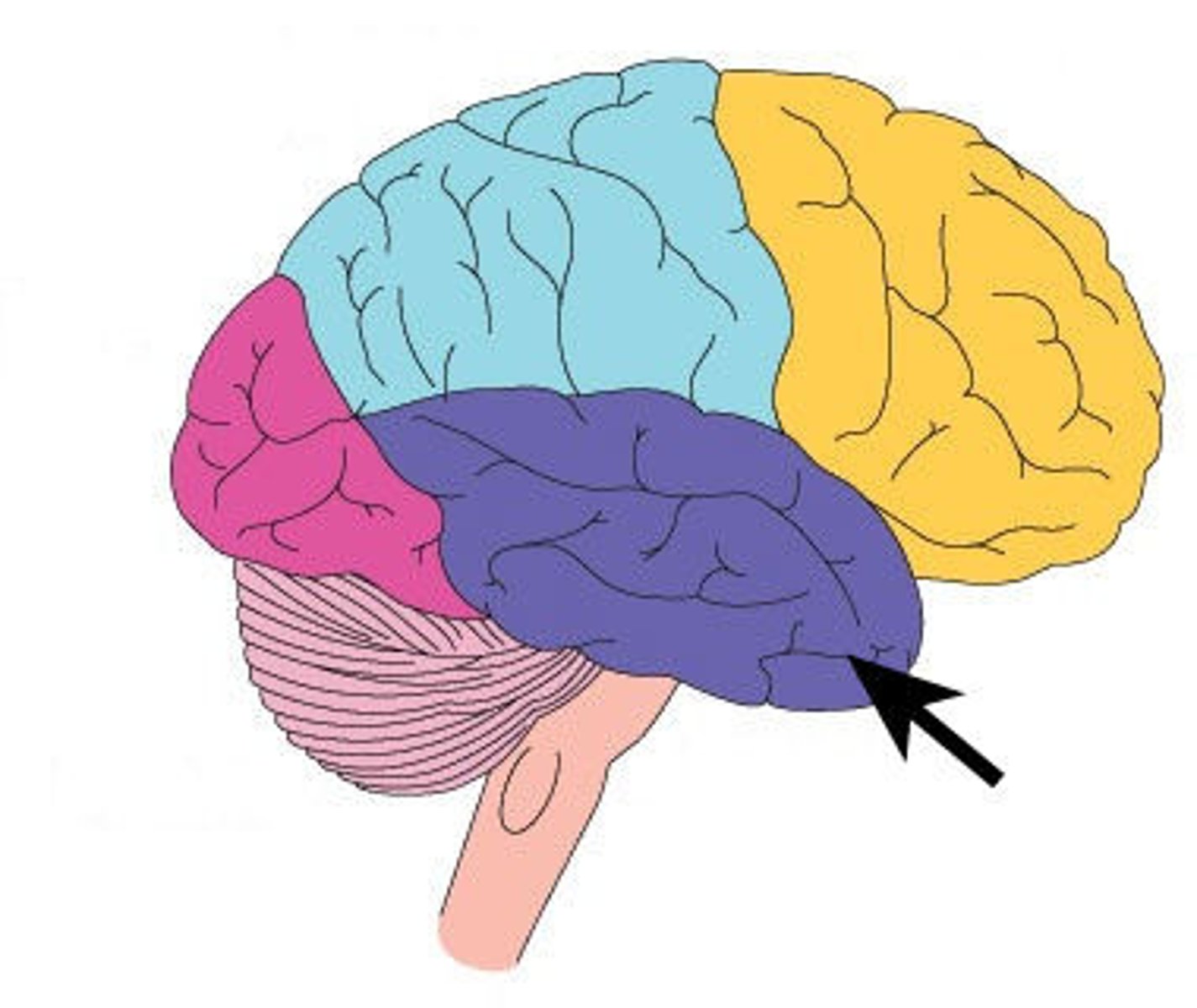
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary muscular activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, thought, and memory
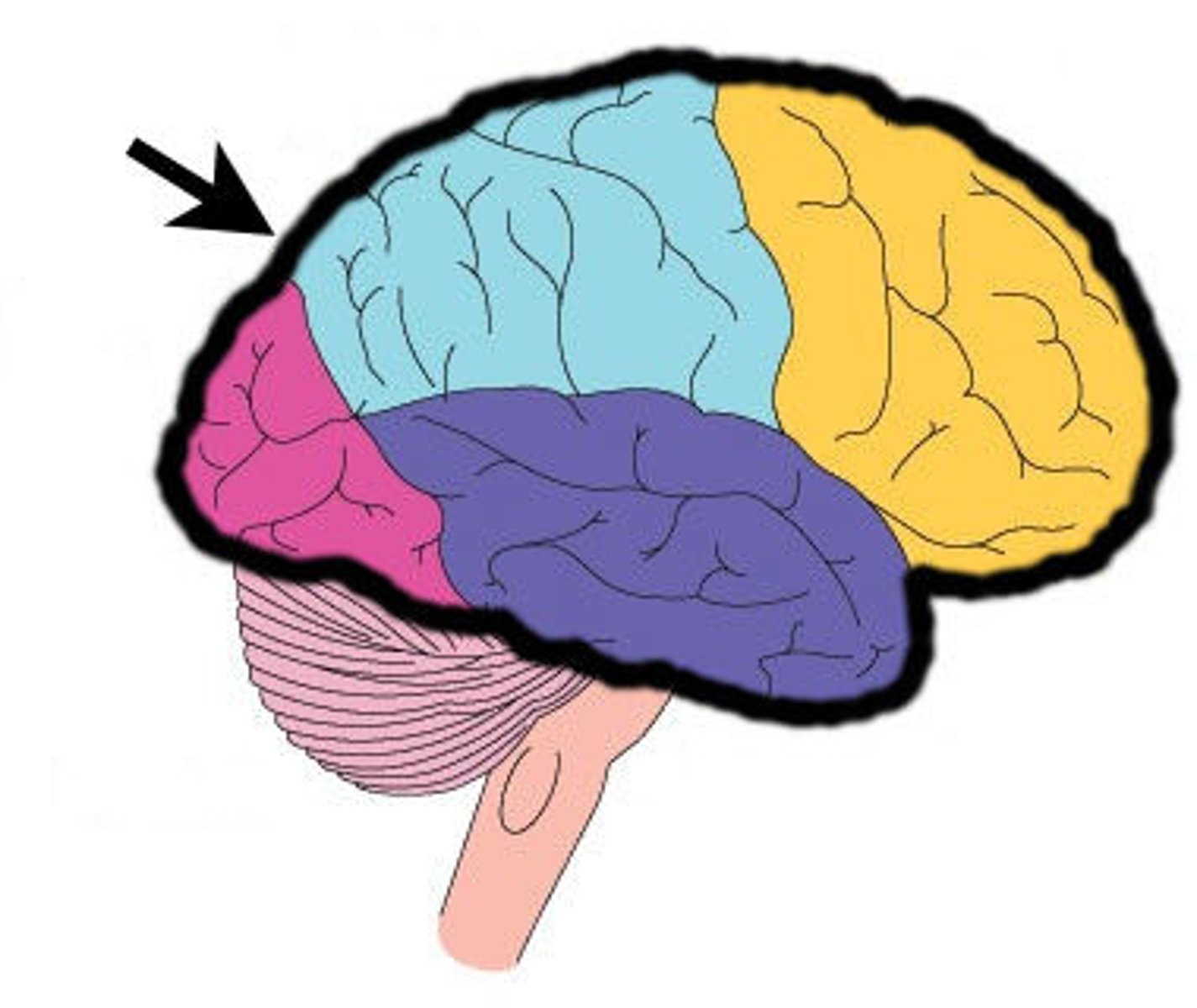
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebrum's outer layer of nerve cell bodies; this layer looks like "grey matter"
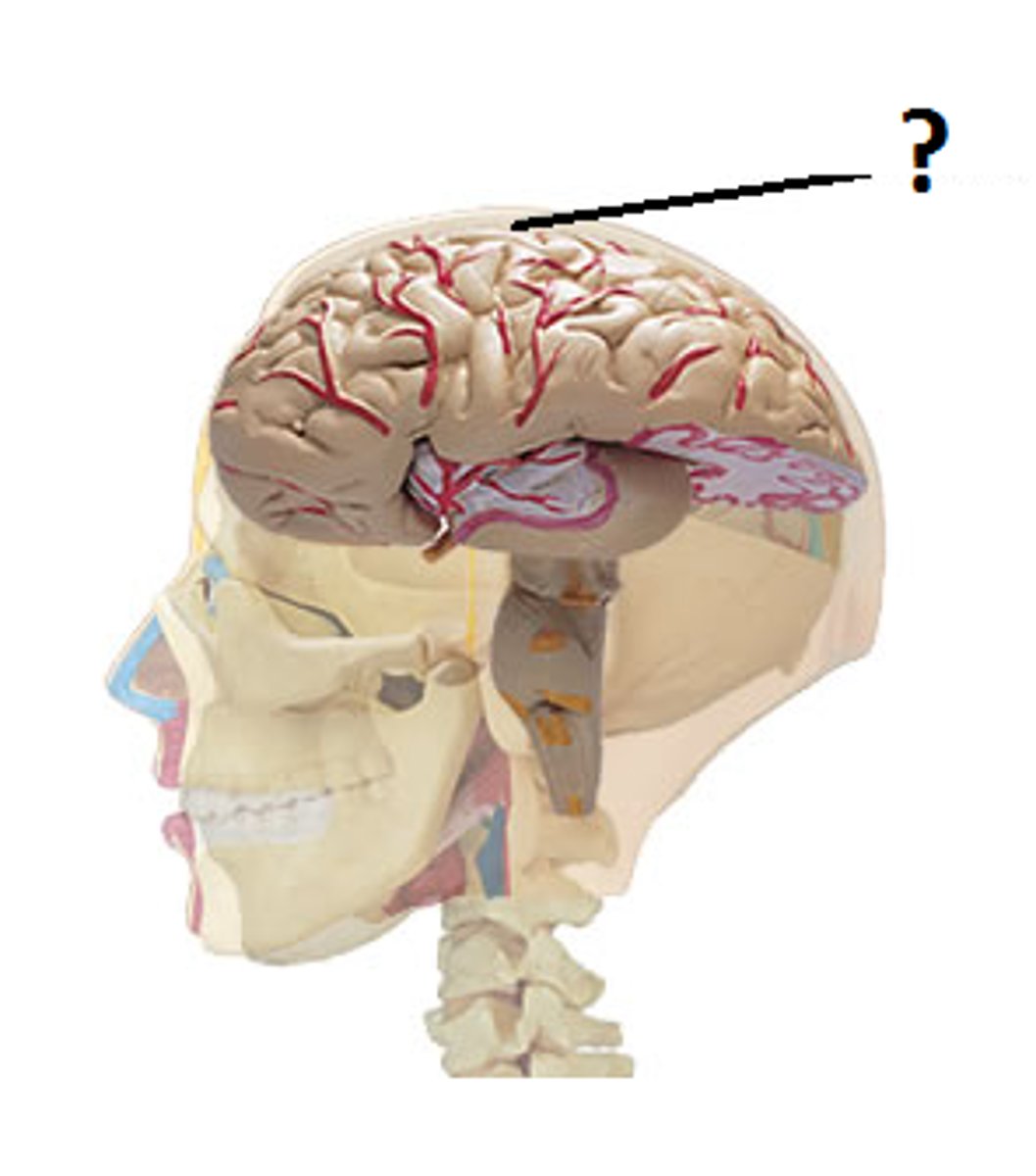
Basal Ganglia
Part of the brain that controls automatic associated movements of the body (Ex. Alternating swinging of arms and legs)
Thalamus
Part of the brain that acts as the main relay station for the nervous system
Hypothalamus
Part of the brain that regulates hormones, temperature, apetite, pleasure, pain, rage, sleep/wake cycle, and emotional status
Cerebellum
Part of the brain that is concerned with motor coordination of voluntary movements, equilibrium, and muscle tone (Ex. Posture/balance)
3 Components of the Brain Stem
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla
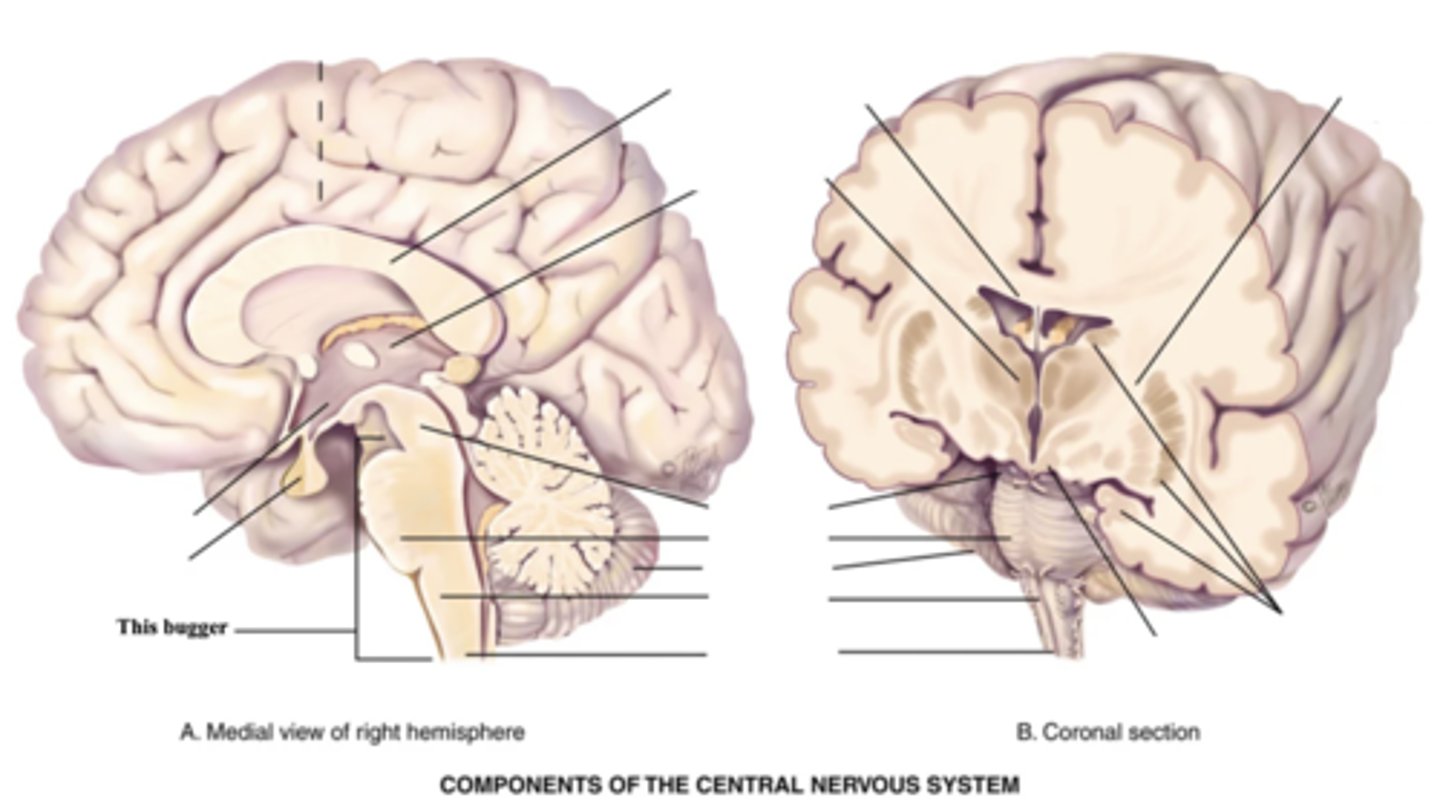
Midbrain
Part of the brain stem that connects the spinal cord to the thalamus and hypothalamus
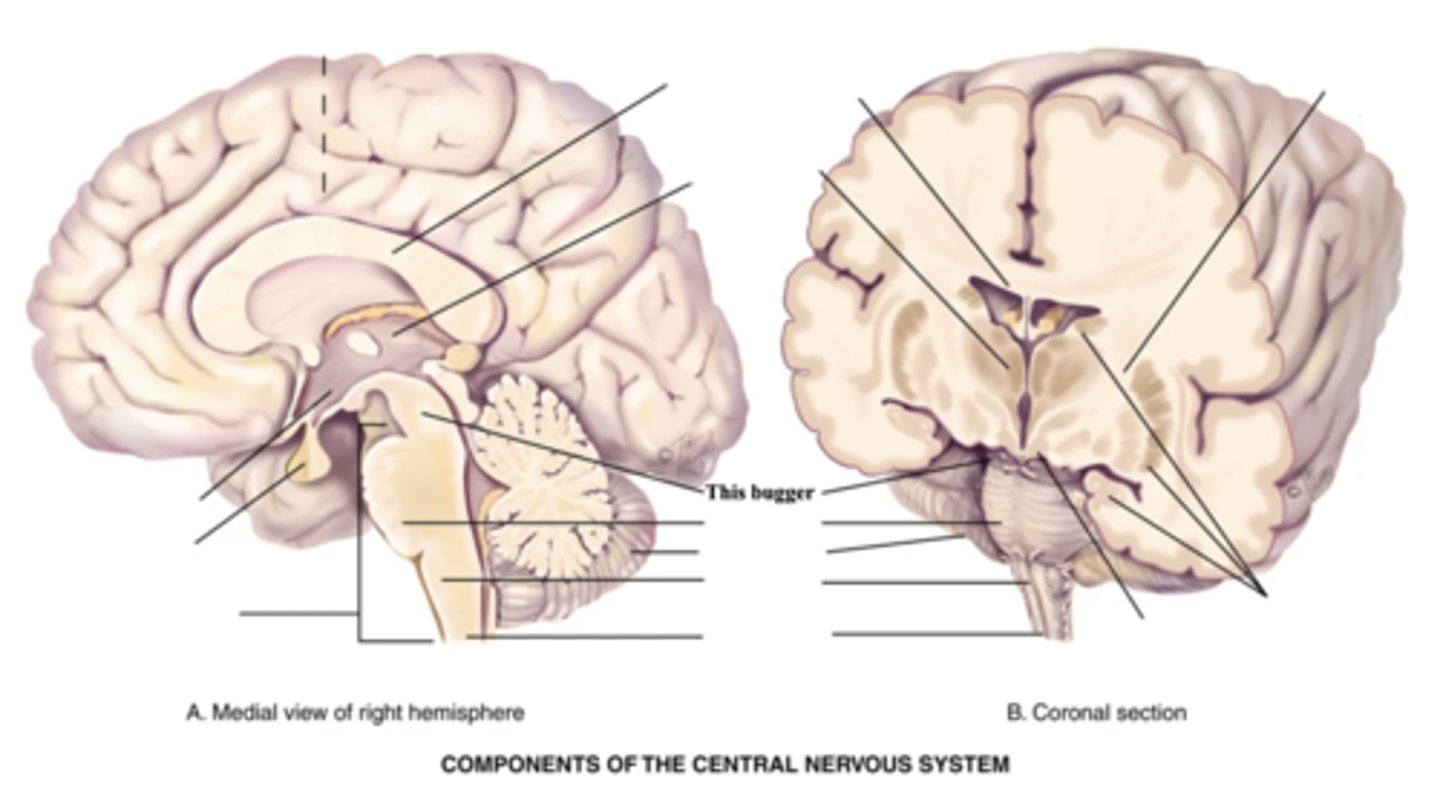
Pons
Enlarged area of the brain stem containing ascending and descending fibre tracts
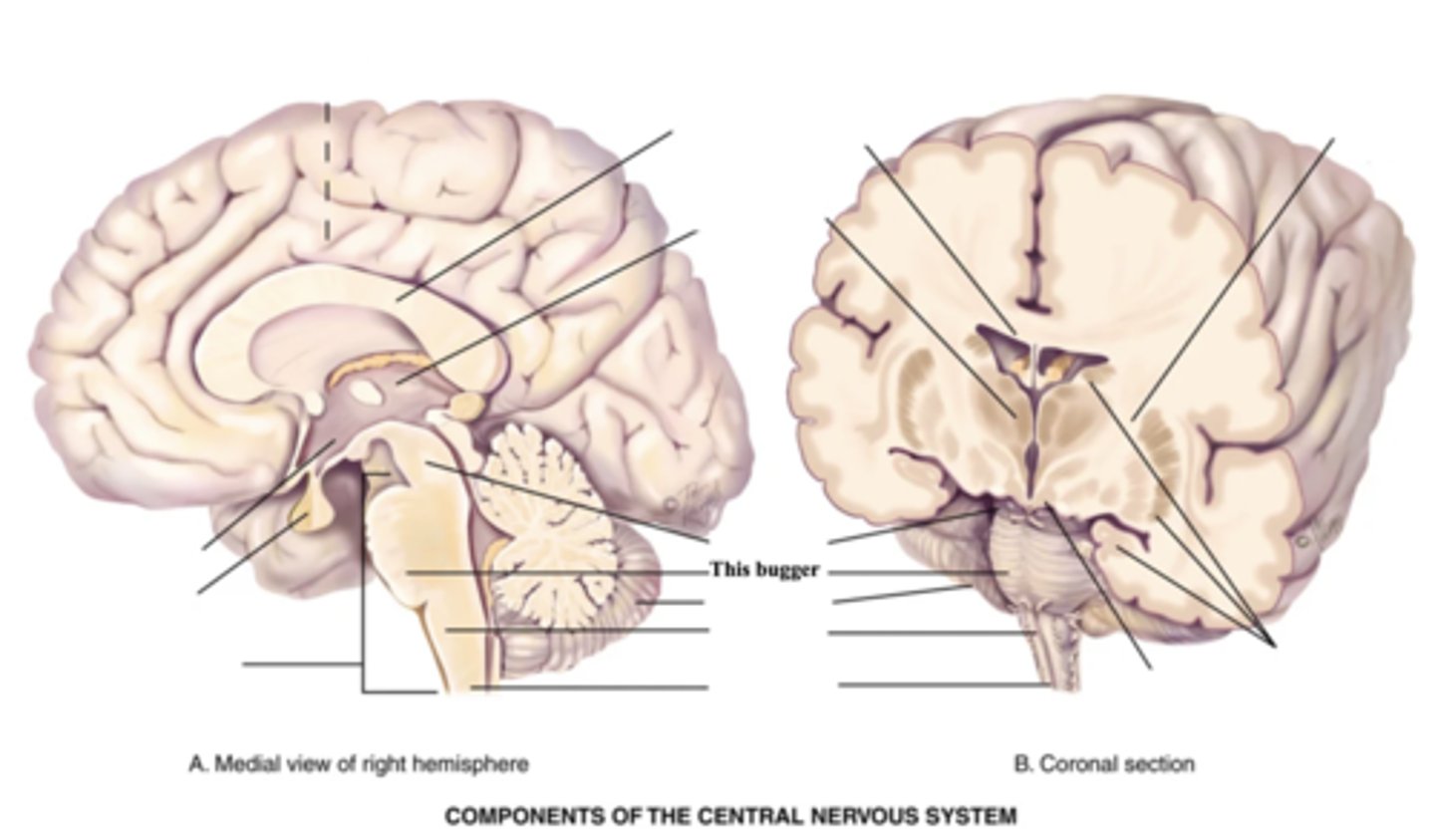
Medulla
- Part of the brain stem that contains all ascending and descending fibre tracts connecting the brain and spinal cord
- Controls HR, breathing, vomiting, hiccupping, and sneezing
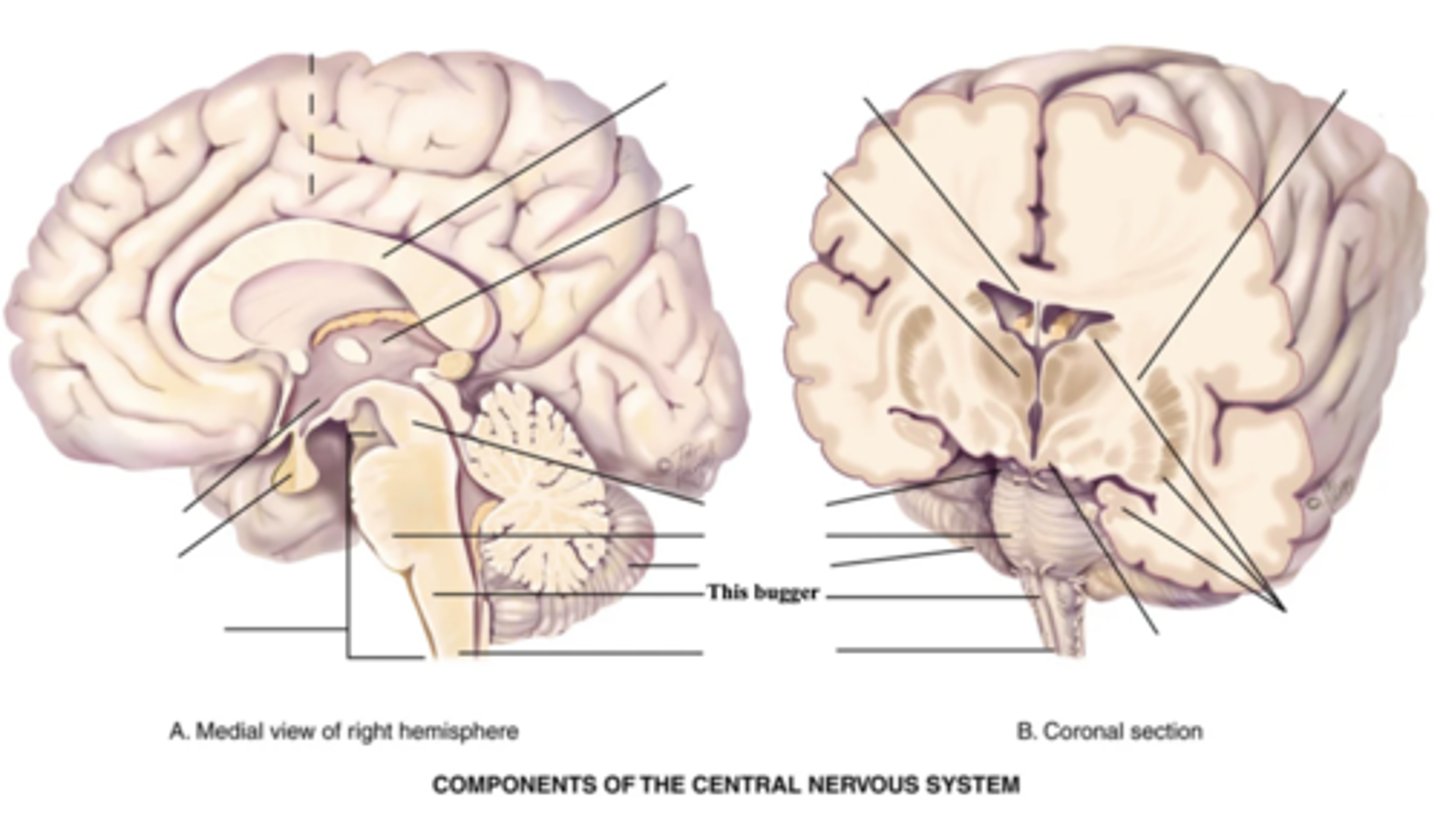
Spinal Cord
- Structure that connect the brain to the spinal nerves
- Mediates reflexes
4 Motor Pathways
- Corticospinal/Pyramidal tract
- Extrapyramidal tracts
- Cerebellar system
- Upper/lower motor neurons
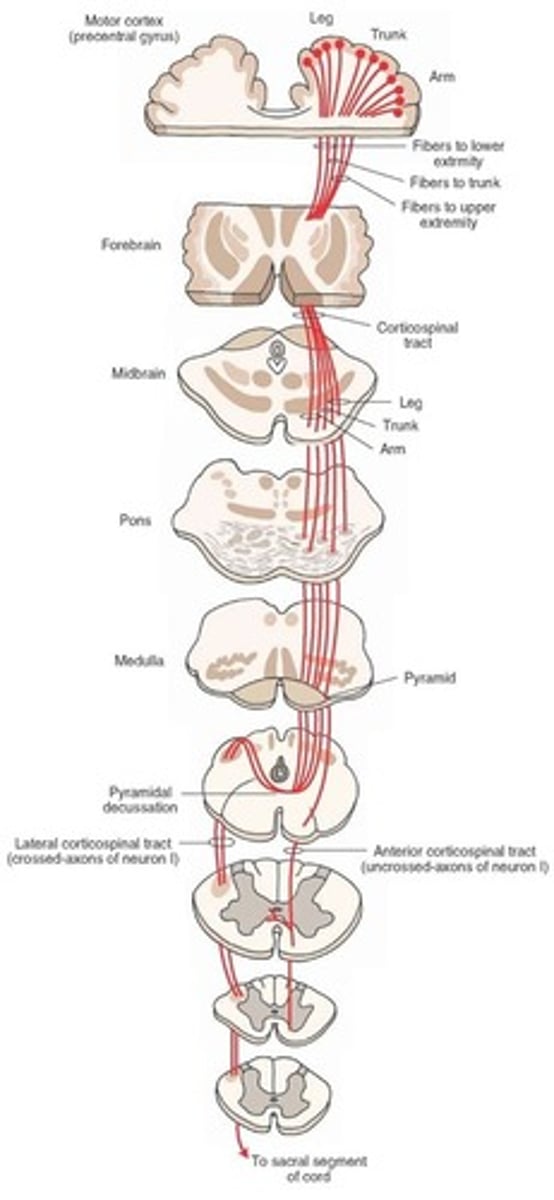
Corticospinal/Pyramidal Tract
- Motor pathway that goes from motor nerve fibers - opposite side - lateral column of spinal cord - lower motor neuron in anterior horn of spinal cord
- Mediates purposeful voluntary movement (Ex. Writing)
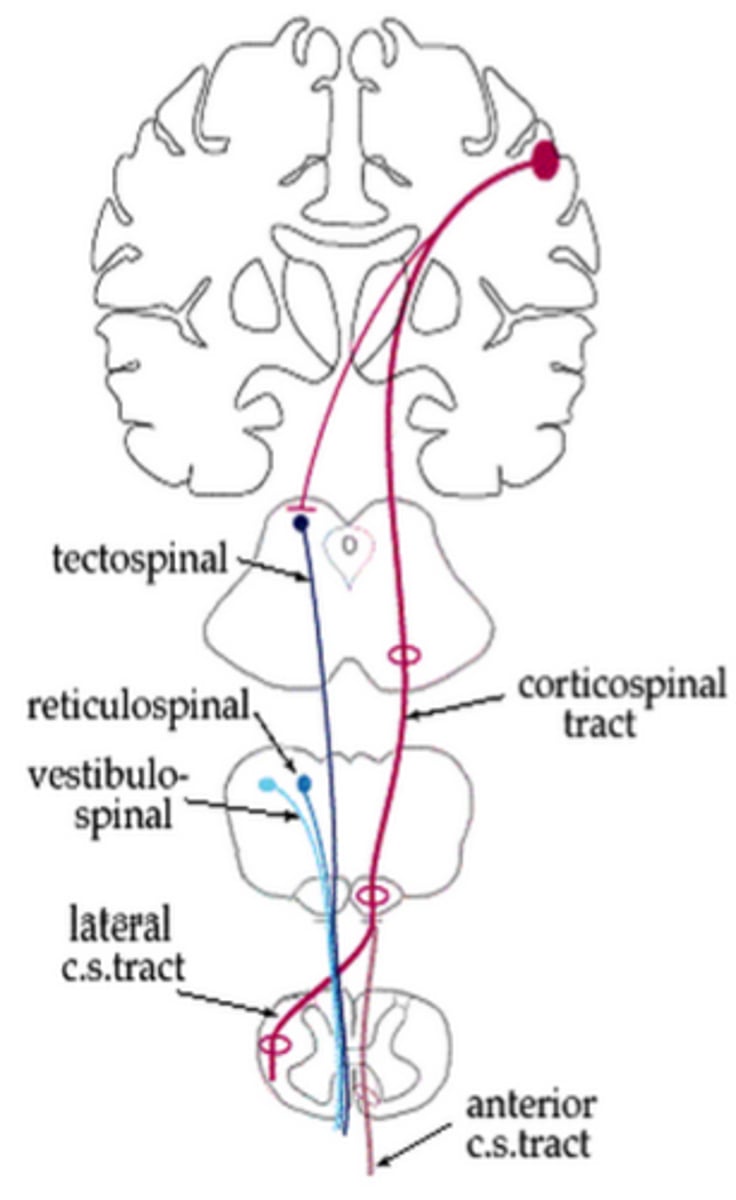
Extrapyramidal Tracts
- Motor pathway that originates outside of the pyramidal tract
- Maintains muscle tone and control of body movement (Ex. Walking, sitting, standing, twisting)
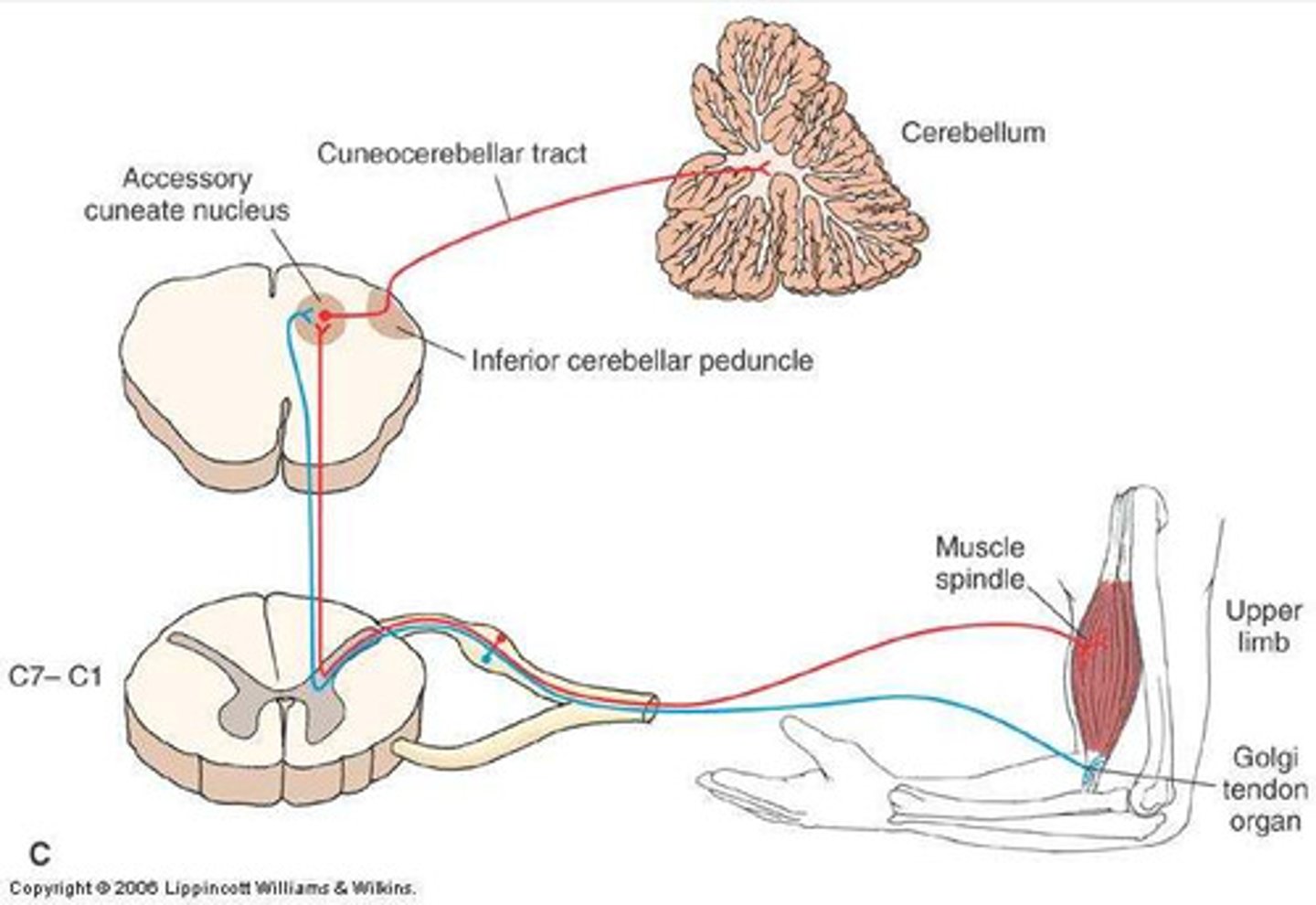
Cerebellar System
- Motor pathway where messages are sent from the cortex to the muscles
- Coordinates movement/posture
- Subconscious process
Upper Motor Neurons (CNS)
A complex of all of the descending motor fibres that can influence or modify the lower motor neurons
Lower Motor Neurons (PNS)
The neurons that receive the signal from the upper motor neurons and transmits it to the muscles; "final common pathway"
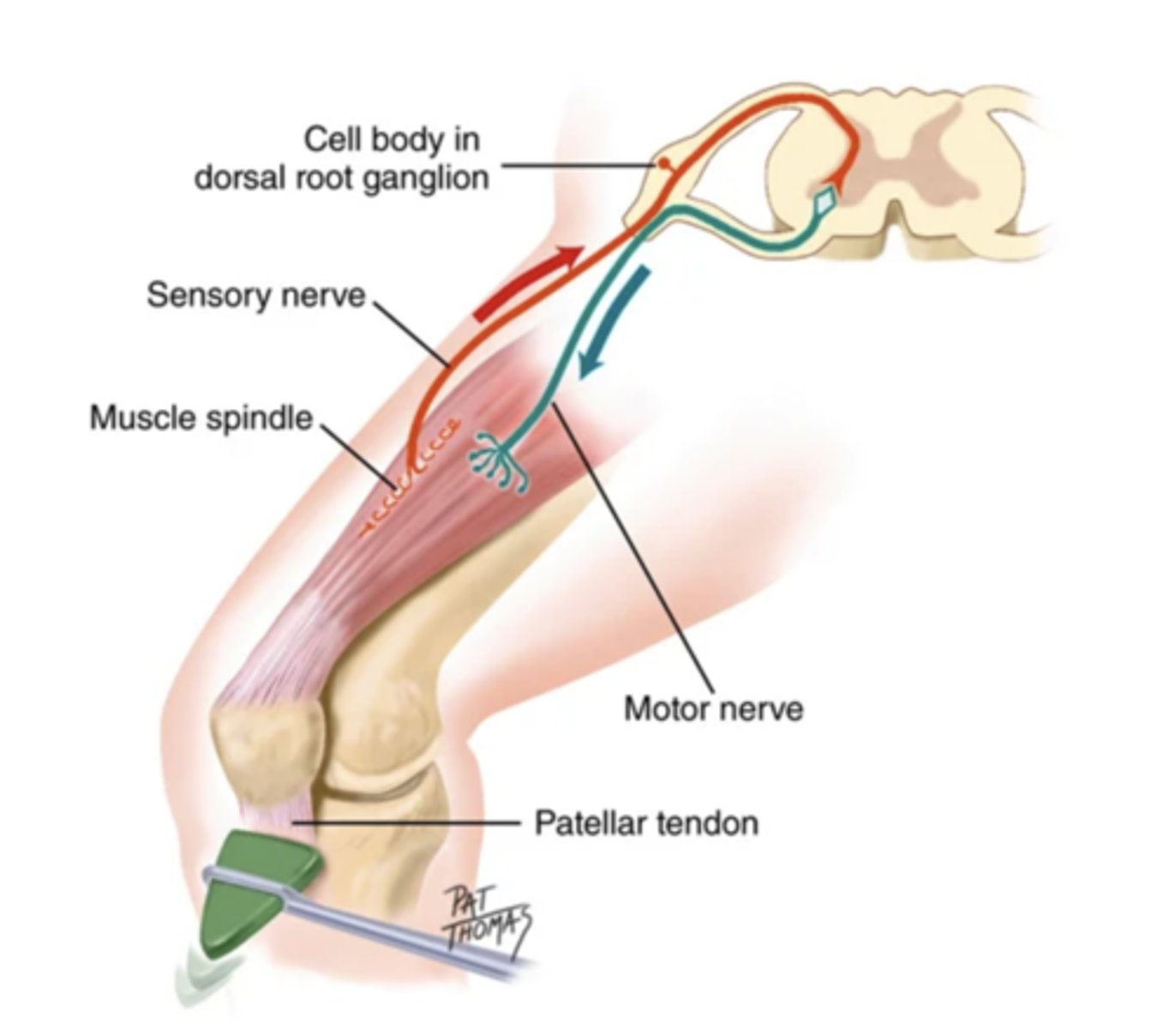
Reflex Arcs
- Neural circuits that control reflexive behavior
- Protects the nervous system
- Involuntary
- Maintains balance/tone
4 Types of Reflexes
- Deep tendon (myotatic)
- Superficial
- Visceral (organic)
- Pathological (abnormal)
Spinal Nerves
Nerves that spread from the spinal cord and supply the rest of the body
Amount of Spinal Nerve Pairs
31
Amount of Spinal Nerve Pairs on the Cervix
8
Amount of Spinal Nerve Pairs on the Thoracic
12
Amount of Spinal Nerve Pairs on the Lumbar
5
Amount of Spinal Nerve Pairs on the Sacral
5
Amount of Spinal Nerve Pairs on the Coccygeal
1
Dermatome
A skin area that is supplied mainly from one spinal cord segment through a particular spinal nerve
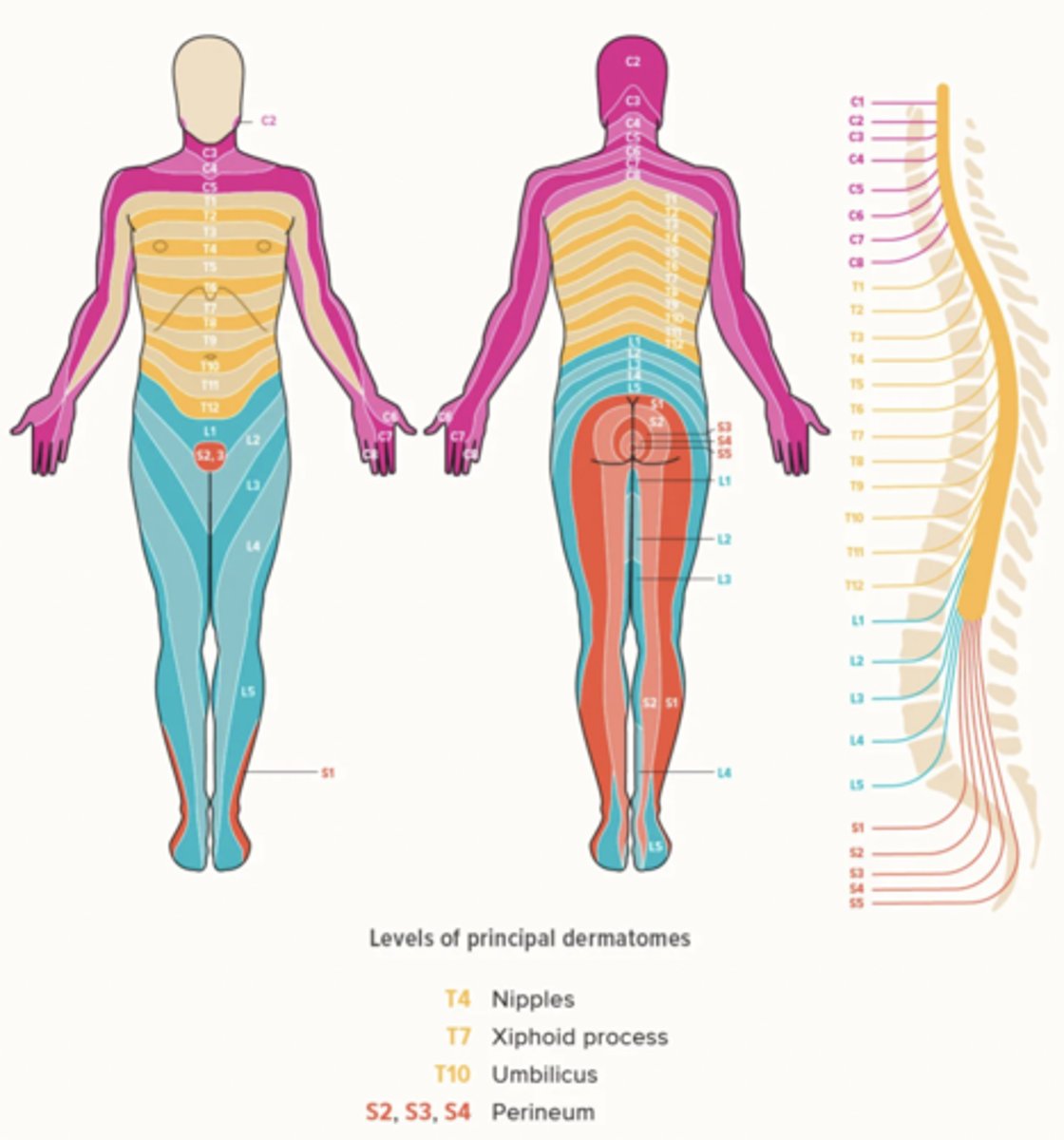
C6 Dermatome
Thumb
T1 Dermatome
Axilla
T10 Dermatome
Umbilicus
L1 Dermatome
Groin
L5/S1 Dermatome
Lower back
Subjective Data to Assess for the Neurological System
- Headache
- Head injury
- Dizziness/vertigo
- Seizures
- Tremors
- Weakness
- Incoordination
- Numbeness/tingling
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty speaking
- Significant history
- Environmental/occupational hazards
Equipments Needed for a Neurological Examination
- Penlight
- Tongue blade
- Cotton swab
- Cotton ball
- Tuning fork (128 Hz or 256 Hz)
- Percussion hammer
- (Possibly) familiar aromatic substances, such as peppermint, coffee, vanilla
Screening Neurological Examination
A neurological examination performed on seemingly healthy patients whose histories reveal no significant subjective findings
Complete Neurological Examination
A neurological examination performed on patients who have neurological concerns or have shown signs of neurological dysfunction
Neurological Recheck Examination
A neurological examination performed on patients who have neurological deficits that require periodic assessments
Objective Assessments for a Neurological Examination
1.) Mental status
2.) Cranial nerves
3.) Motor system
4.) Sensory system
5.) Reflexes
Motor System Assessments for a Screening Neurological Examination
- Gait/balance
- Knee flexion (hop or shallow knee bend)
Reflexes to Assess for a Screening Neurological Examination
- Biceps
- Triceps
- Patellar
- Achilles
Motor System Assessments for a Complete Neurological Examination
1.) Muscles
2.) Cerebellar function
3.) Coordinated and skilled movements
What to Assess for Muscles for a Complete Neurological Examination
- Size
- Strength
- Tone
- Involuntary movements
Muscle Tone
The normal degree of tension in voluntarily relaxed muscles
What to Assess for Cerebellar Function for a Complete Neurological Examination
- Gait
- Heel-to-heel
- Romberg test
- Foot hop
Romberg Test
A test that that assess a patient's coordination and equilibrium by making the stand straight for 20 seconds while their eyes are closed
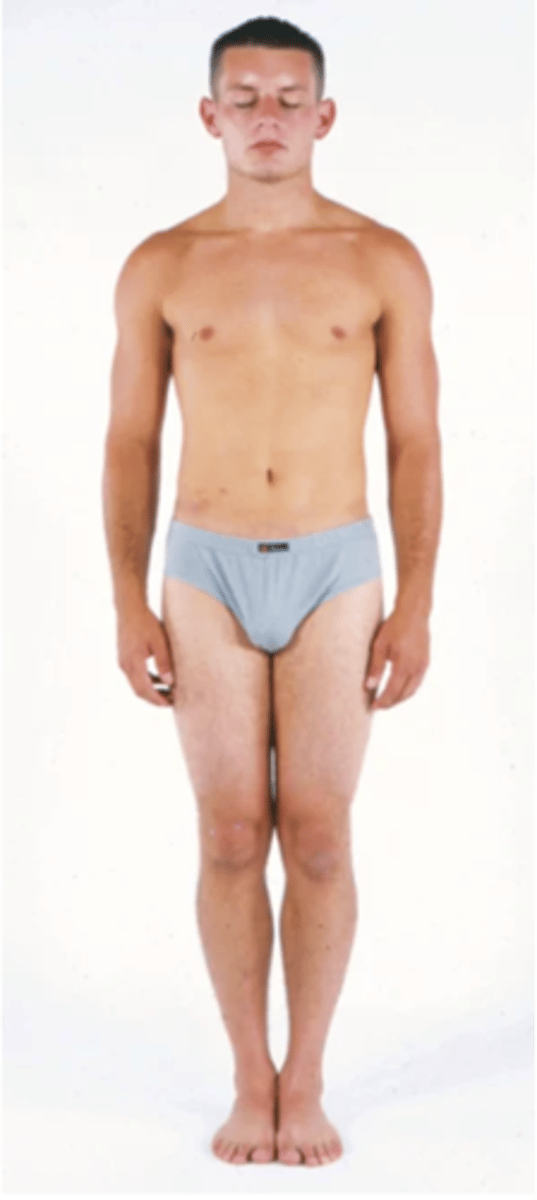
What to Assess for Coordinated Skilled Movements for a Complete Neurological Examination
- Rapid alternating movements
- Thumb-to-finger
- Finger-to-finger
- Finger-to-nose
- Heel-to-shin
(Often used to test intoxication levels)
Reflexes to Assess for a Complete Neurological Examination
- Deep tendon
- Superficial (cutaneous)
Deep Tendon Reflexes (DTR) that you Assess for a Complete Neurological Examination
- Biceps
- Triceps
- Brachioradialis
- Quadriceps/patellar ("knee jerk)
- Achilles ("ankle jerk")
- Clonus (optional)
5 Elements that DTRs Need to Function
- Intact afferent sensory nerve
- Functional synapse in the spinal cord
- Intact efferent motor nerve
- Neuromuscular junction
- Competent muscle
DTR Testing Guidelines
- Relax the limb and partially stretch the muscle.
- Use the end of the hammer for smaller targets and the flat end for larger targets.
- Relax your hold on the hammer.
- Strike a short, snappy blow to the muscle's insertion tendon.
- Do no let the hammer rest on the tendon.
- Compare each side.
Things to do if a Person's Reflex doesn't Appear
- Encourage further relaxation
- Change the patient's position
- Increase the strength of your blows
- Have the patient do an isometric exercise on a muscle group that is somewhat away from the one being testes
Reflex Grading Scale

Grade 4+ Reflex
Very brisk, hyperactive with clonus, indicative of disease
Grade 3+ Reflex
Brisker than average, may indicate disease
Grade 2+ Reflex
Average, normal
Grade 1+ Reflex
Diminished, low normal
Grade 0 Reflex
No response
Superficial (Cutaneous) Reflexes to Asses for a Complete Neurological Examination
- Abdominal
- Cremasteric (only in men)
- Plantar
Objective Assessments for a Neurological Recheck Exam
- Vital signs
- Level of consciousness/orientation (PPT)
- Motor function
- Pupillary response
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
A scale used to assess the consciousness of a patient upon physical examination, typically in patients with neurological concerns or complaints
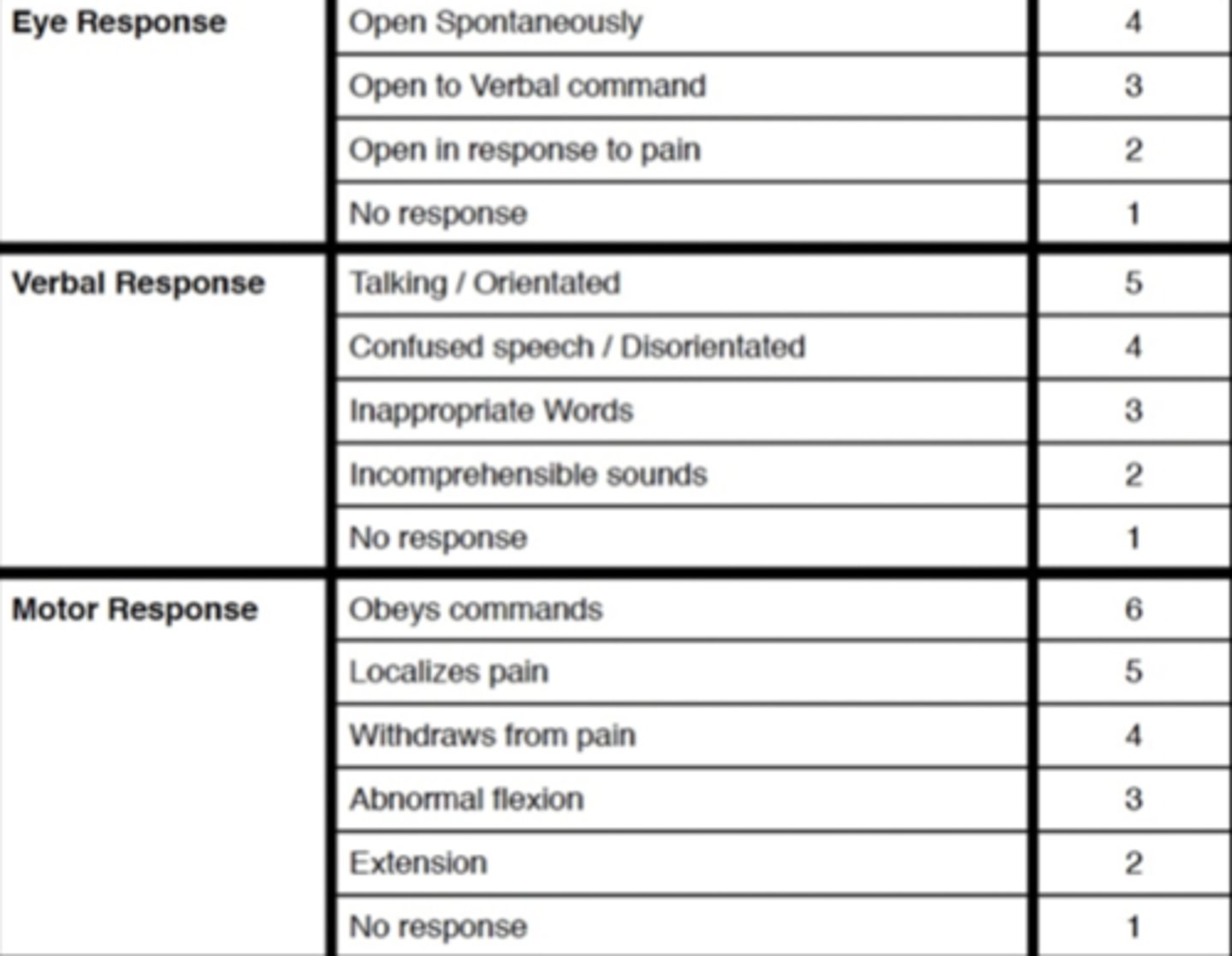
Abnormalities in Muscle Tone
- Flaccidity
- Spasticity
- Rigidity
- Cogwheel rigidity
Flaccidity
- Decreased muscle tone
- Associated with lower motor neuron injury
Spasticity
- Increased tone (hypertonia)
- Associated with upper motor neuron injury to corticospinal motor tract
Rigidity
- Resistance to passive movement in any direction (dystonia)
- Associated with an injury to the extrapyramidal motor tracts
Cogwheel Rigidity
- A type of rigidity that lessens by degrees during passive ROM
- Associated with parkinsonism
Characteristics of Abnormal Upper Motor Neuron Findings
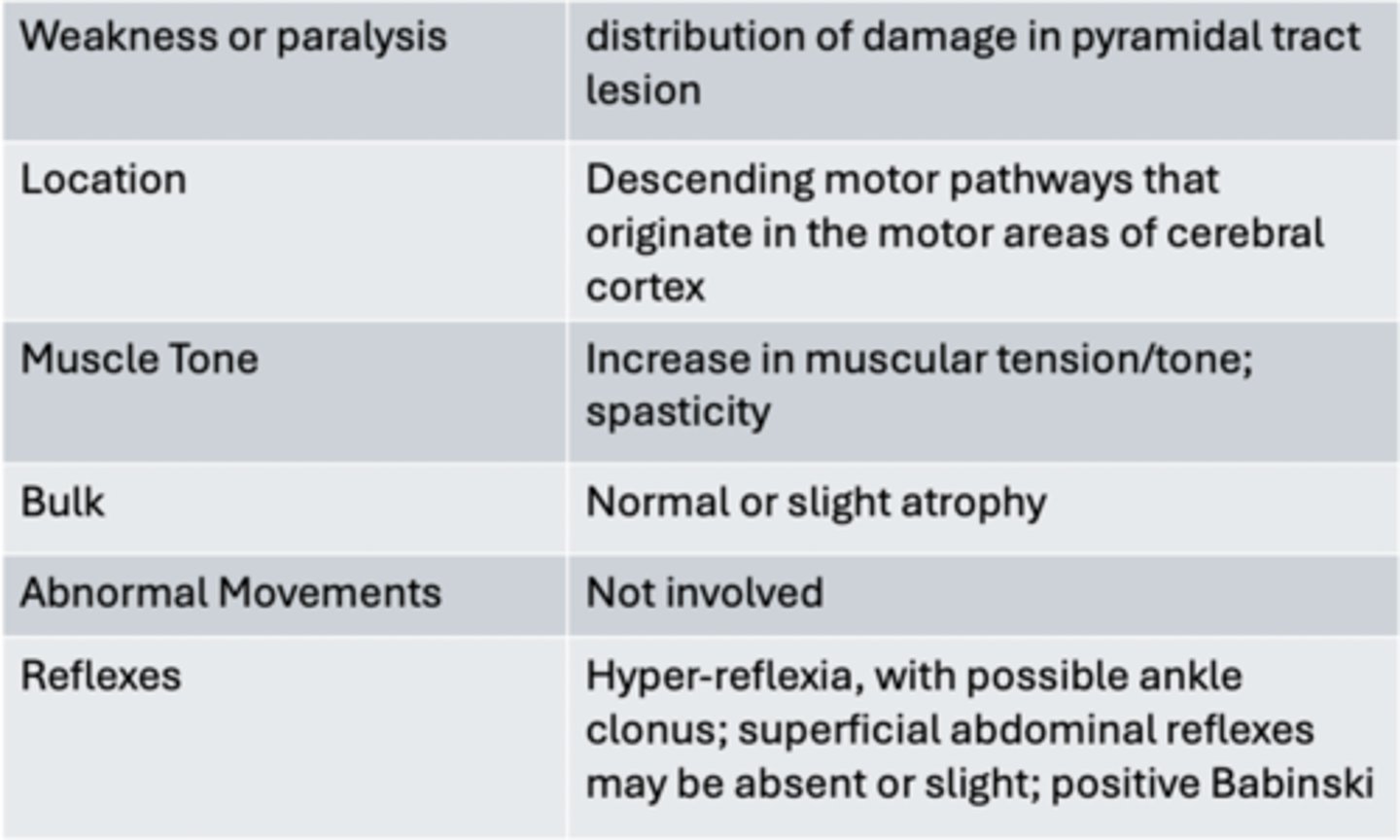
Characteristics of Abnormal Lower Motor Neuron Findings
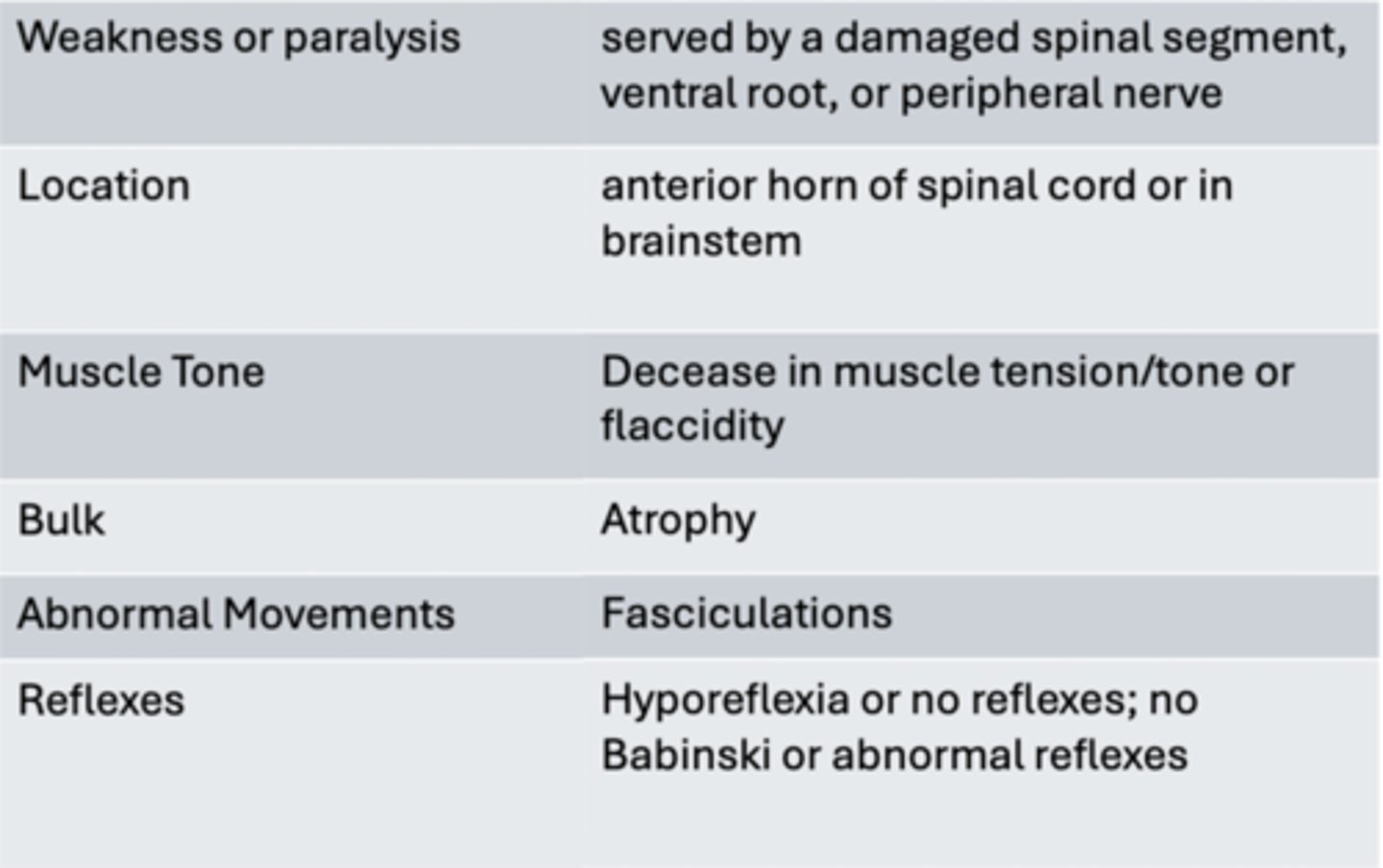
Paralysis
Muscle weakness (paresis) or loss of power - hemi/para/quadriplegia
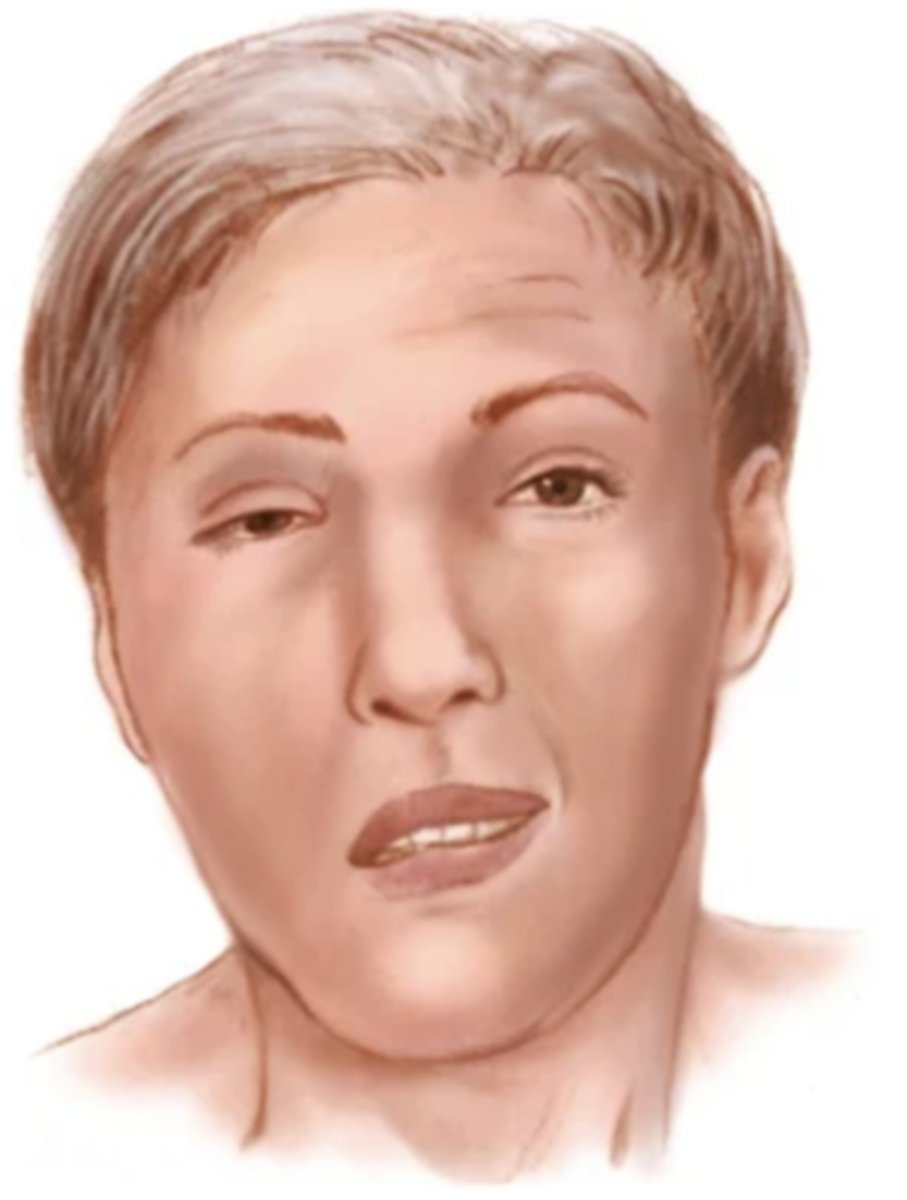
Fasciculation
When a resting muscle twitches
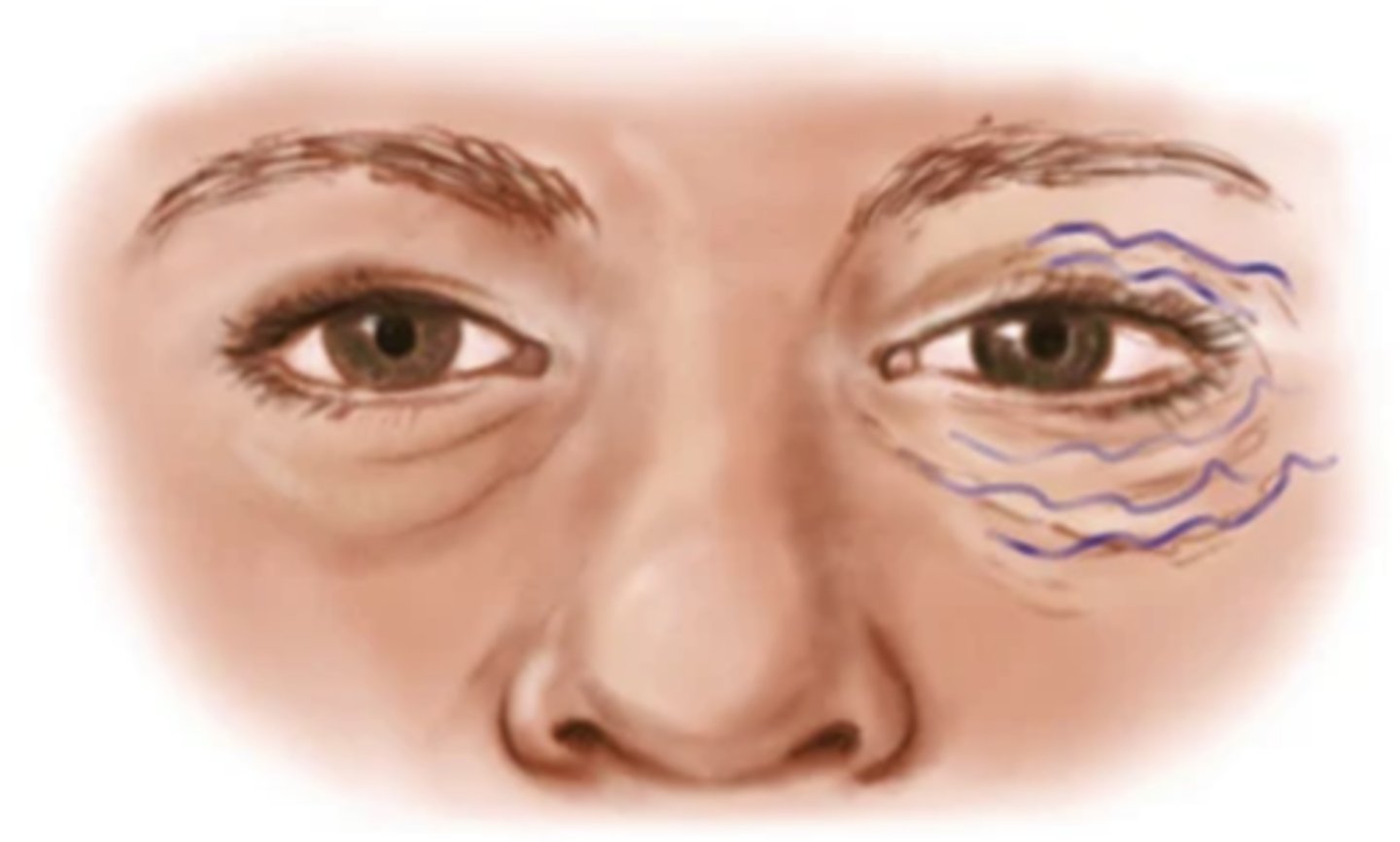
Tic
Twitch that is repetitive; occurs often in relation to a neurological disorder
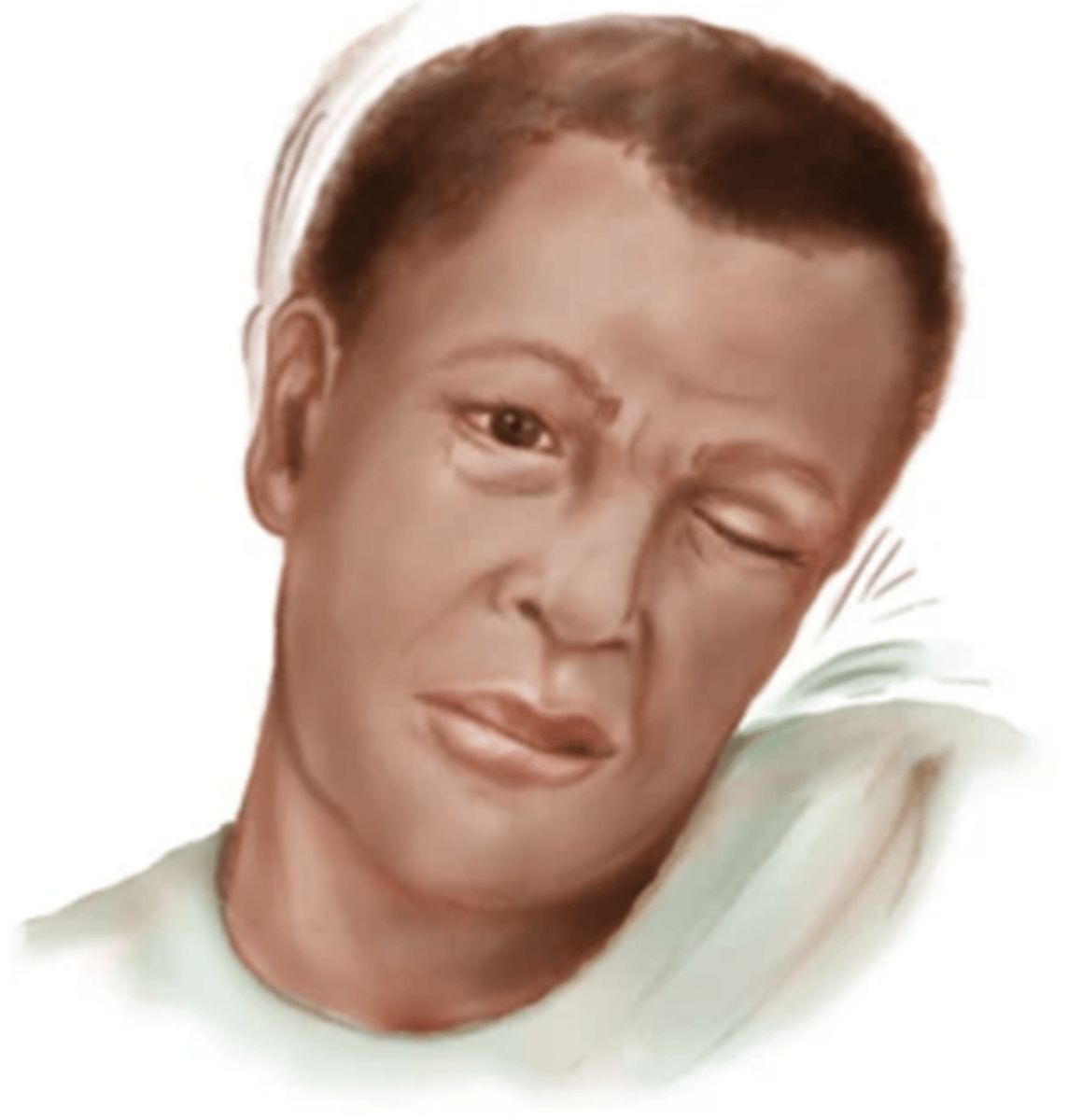
Myoclonus (Hiccup)
Sudden rapid jerk when falling asleep
Tremor
Contraction of muscles around a joint; dissapears in sleep
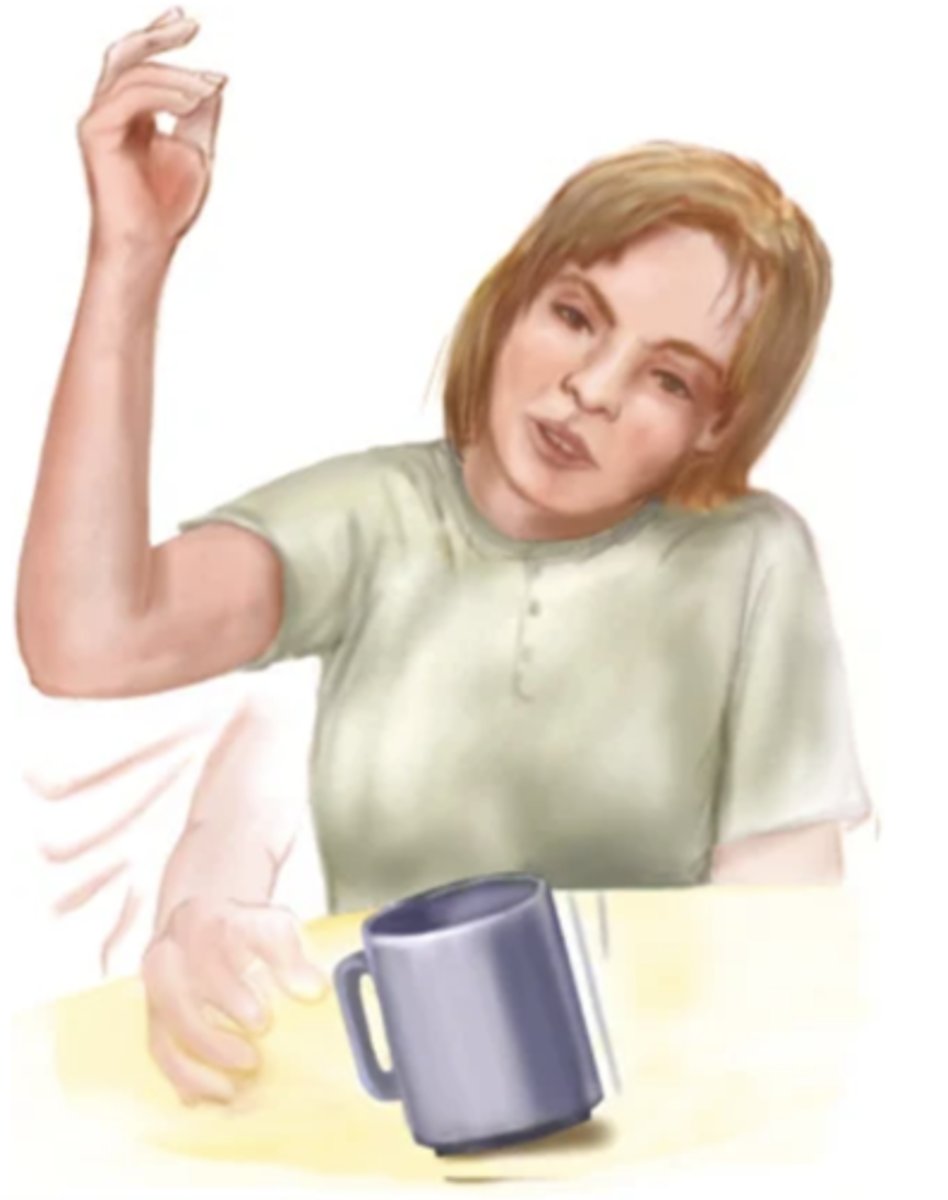
Rest Tremor
Tremor that disappears with voluntary movement

Intention Tremor
Tremor that appears with voluntary movements; medications can calm it
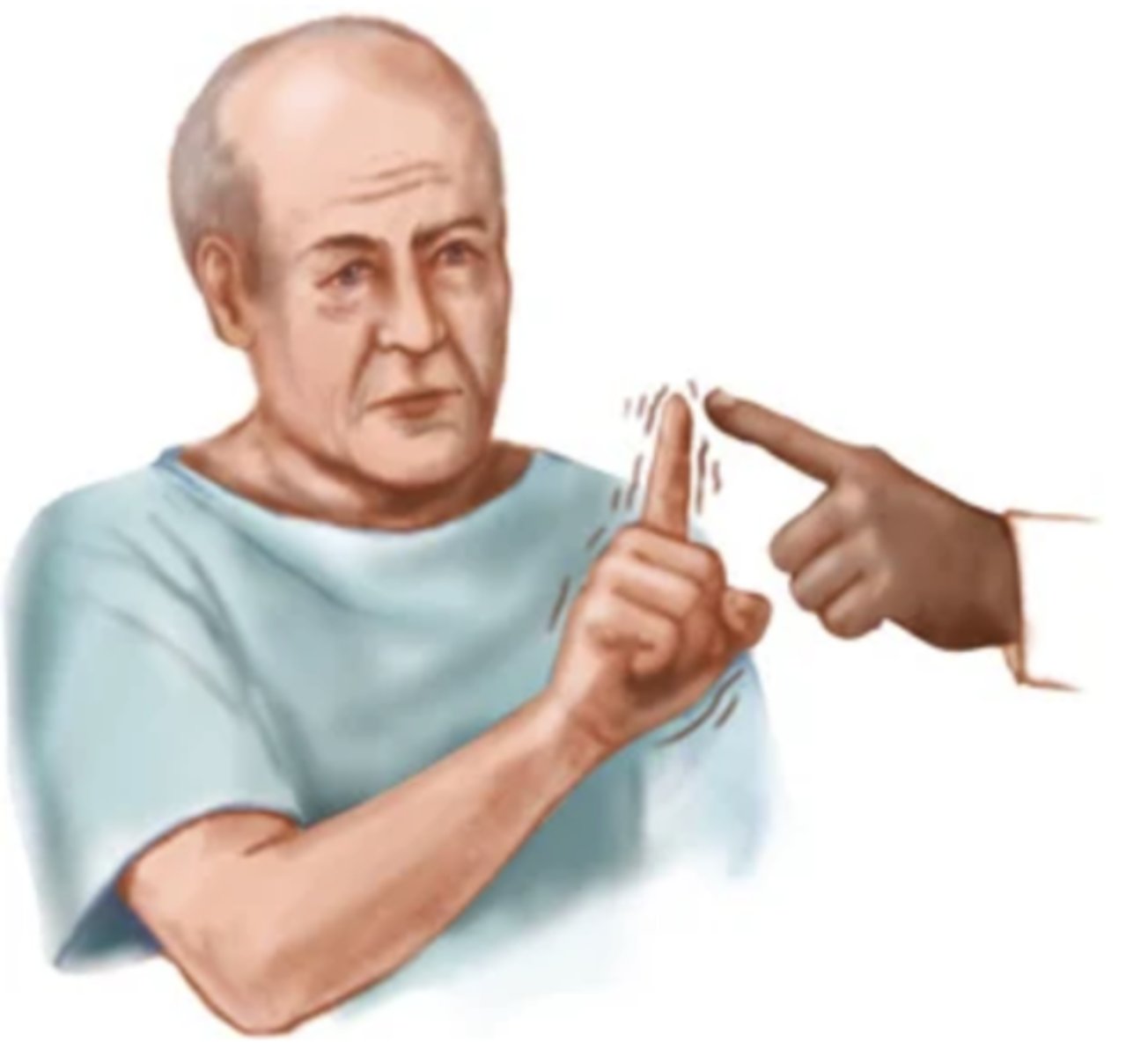
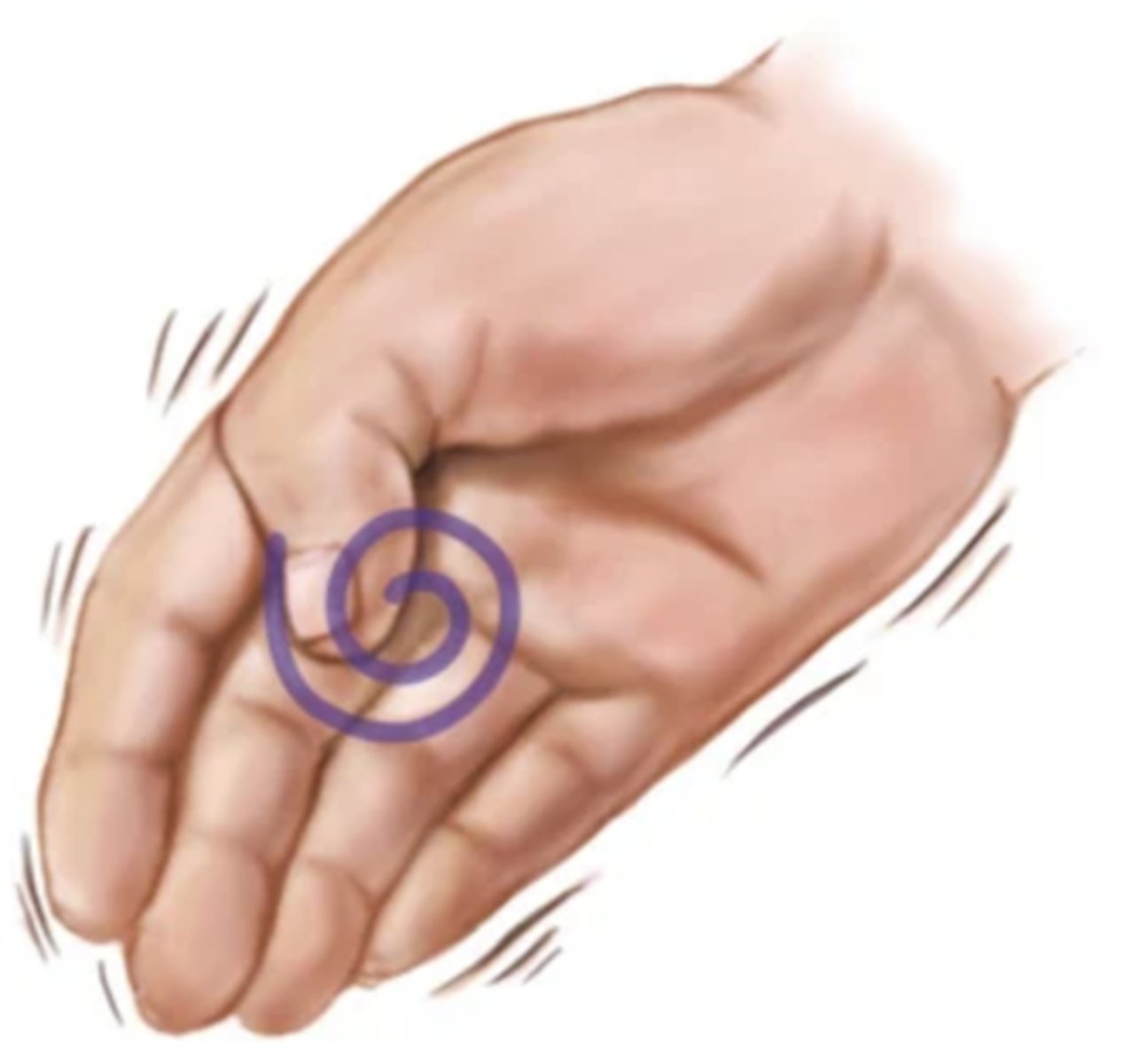
Chorea
Purposeless movements; jerky, sudden, and increases with voluntary movements; disappears with sleep

Acthetosis
Twisting continuous movement; slow and usually involves a distal limb
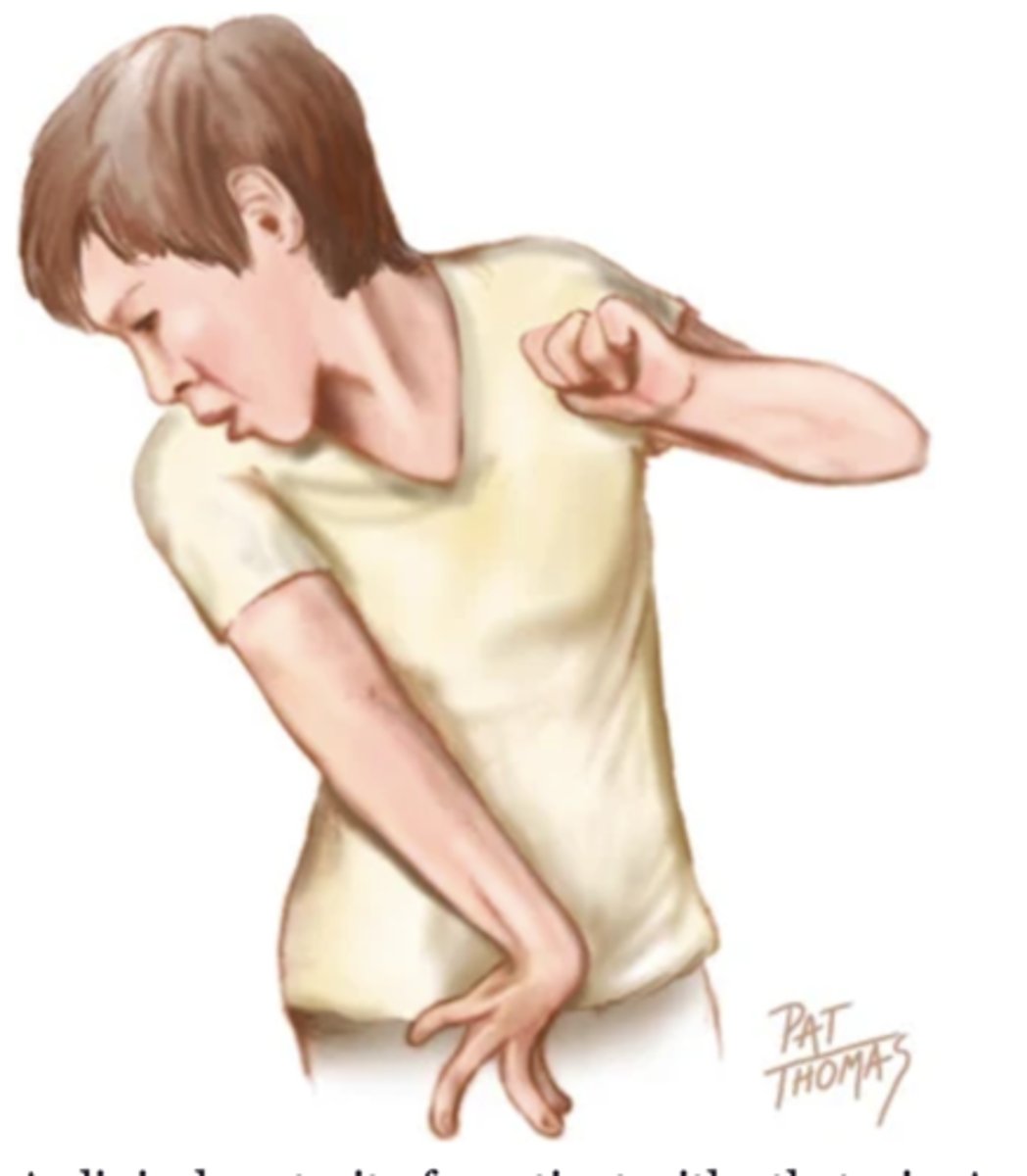
Abnormal Gaits
- Spastic hemiparesis
- Cerebellar ataxia
- Parkinsonian (festinating)
- Scissors
- Steppage/footdrop
- Waddling
- Short leg
Spastic Hemiparesis
- An abnormal gait in which one side of the body is paralyzed
- Can be caused by a head trauma
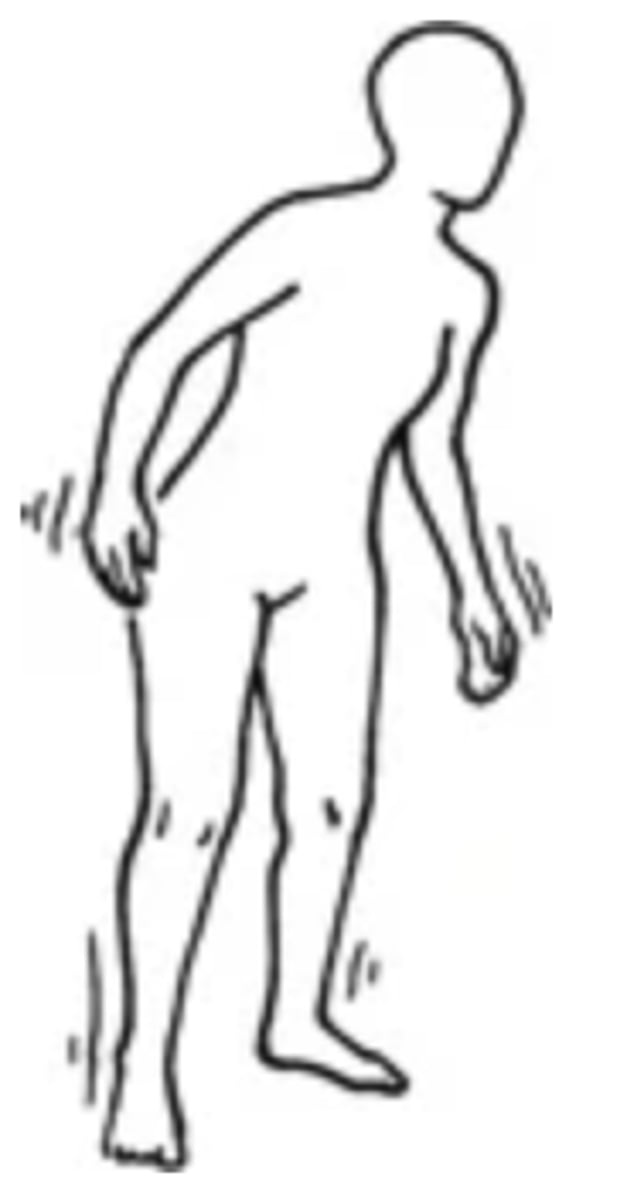
Cerebellar Ataxia
- An abnormal gait in which the person has staggering, wide-based gait; difficulty with turns; uncoordinated movement
- Can be caused by alcohol, cerebellar tumour, or MS
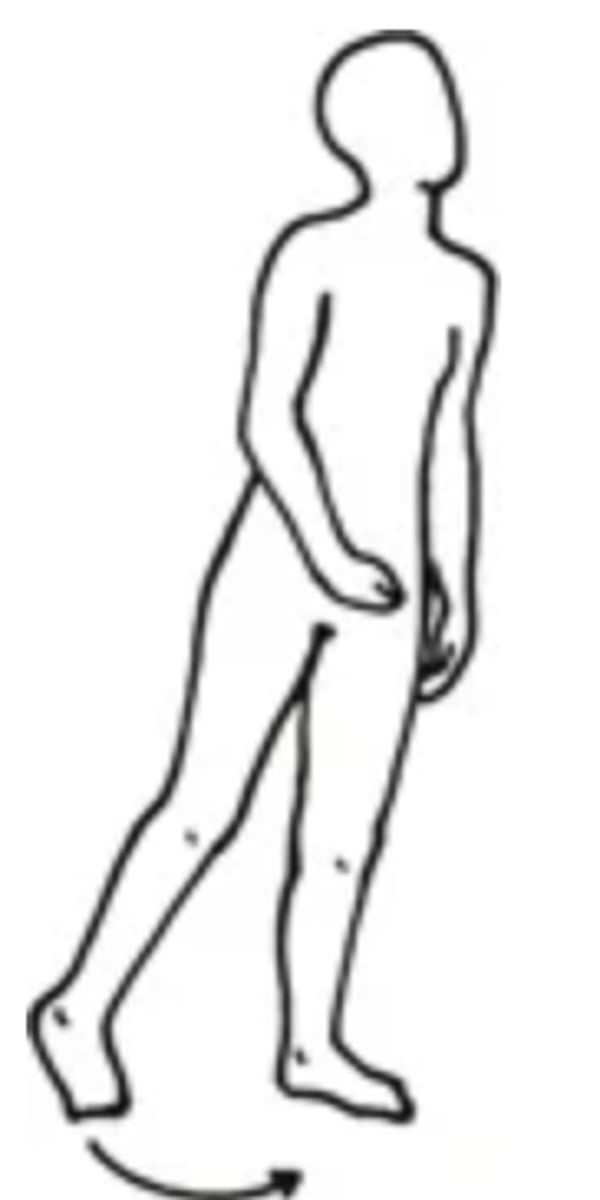
Parkinsonian (Festinating)
- An abnormal gait in which the person hesitates to walk and has difficulty stopping suddenly
- Can be caused by parkinsonism
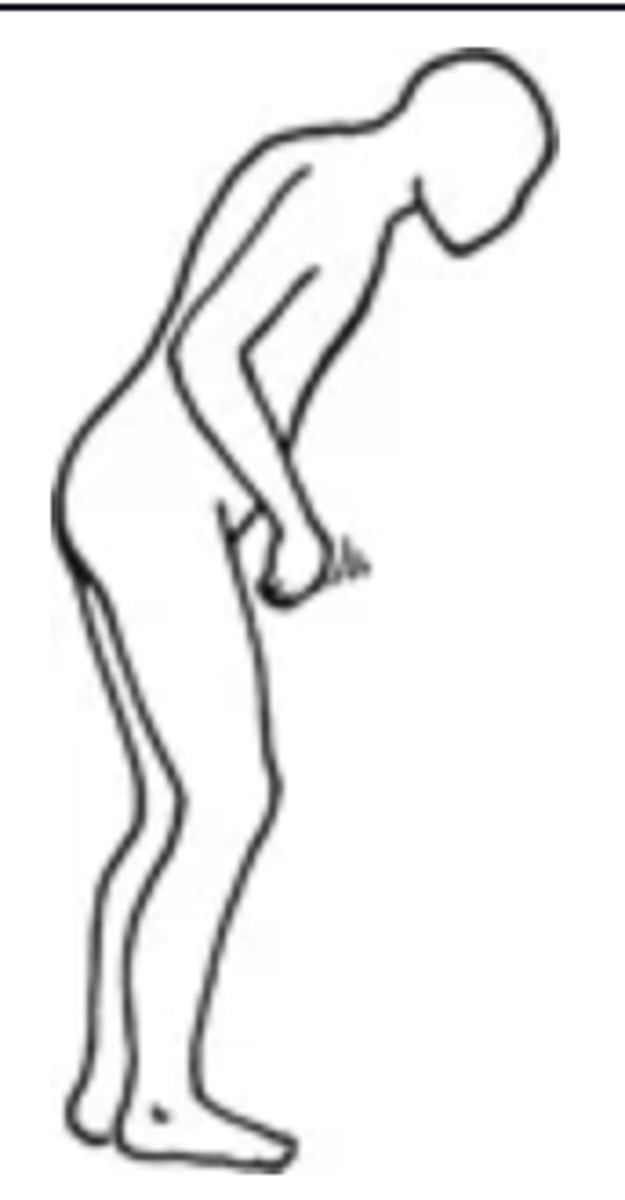
Scissors
- An abnormal gait in which the person's knees cross or are in contact, like holding an orange between the thighs
- Can be caused by MS
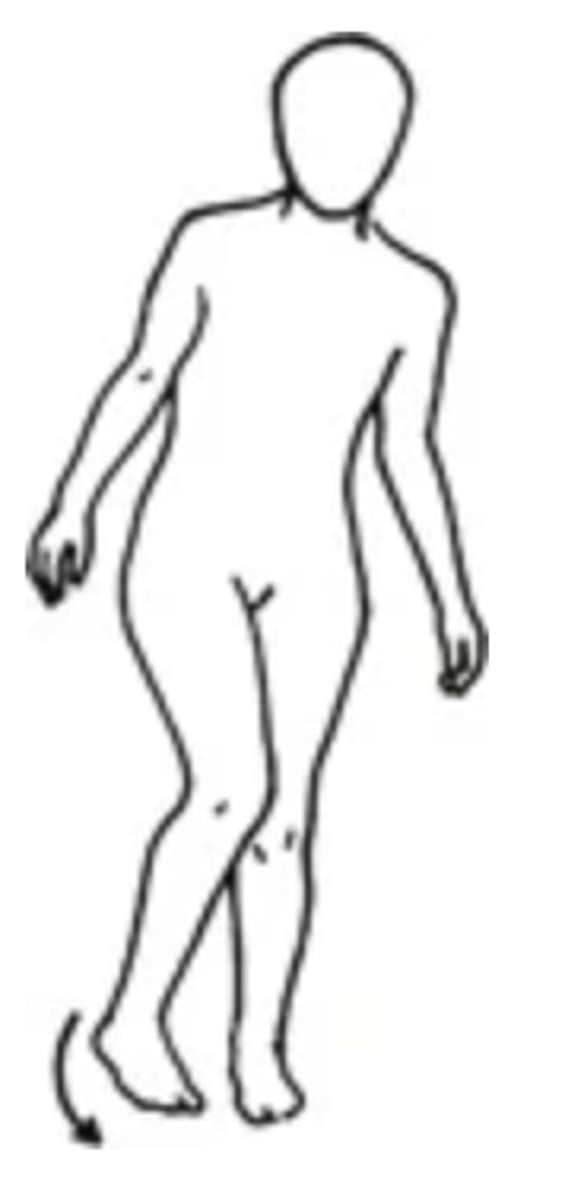
Steppage/Footdrop
- An abnormal gait in which the person lifts knee and foot high and slaps it down hard and flat to compensate for footdrop when walking up stairs
- Can be caused by weakness of tibial muscles
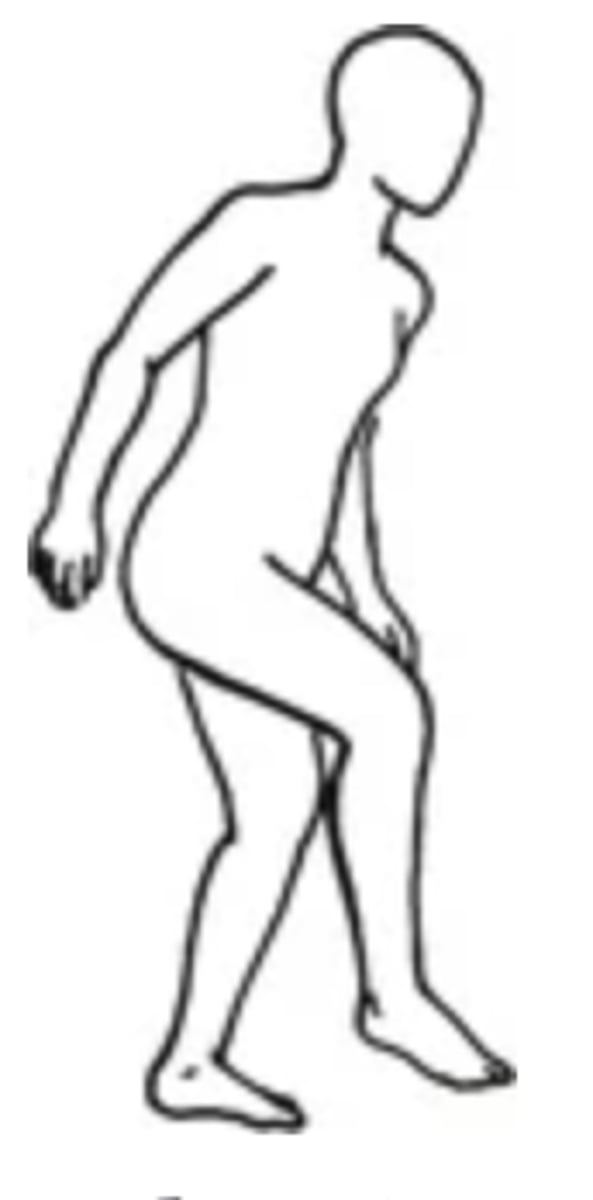
Waddling
- An abnormal gait in which the person's pelvis moves up and down with walking
- Can be caused by weak hips
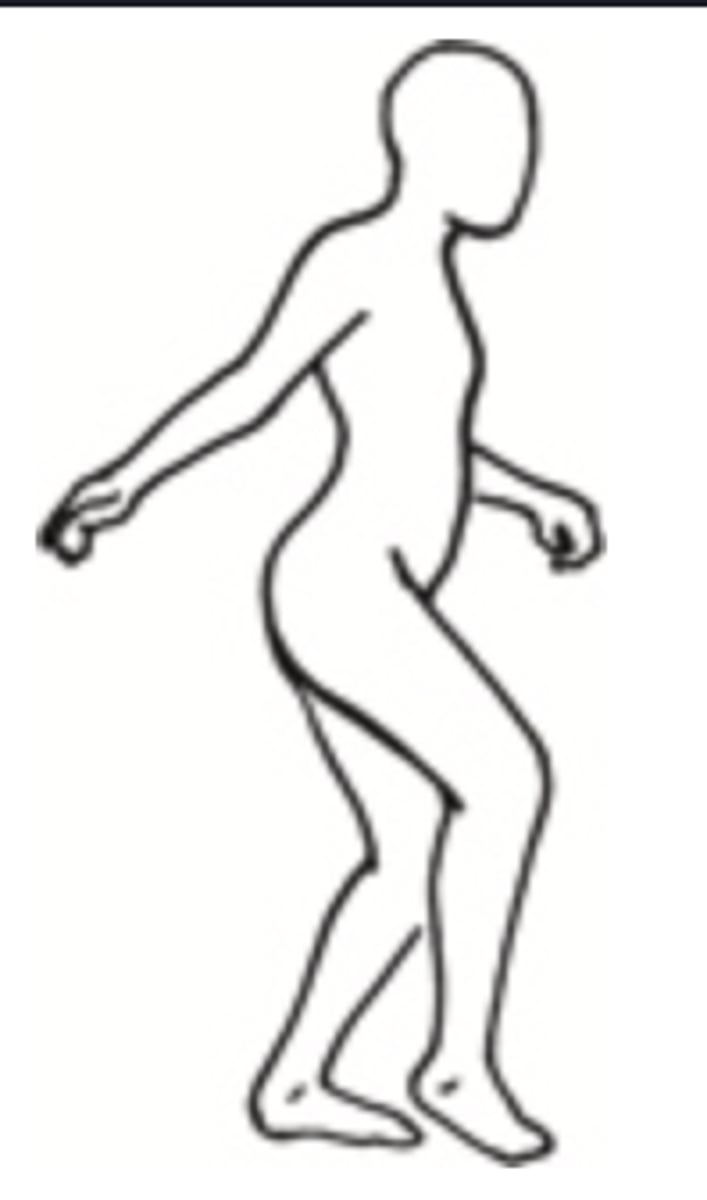
Short Leg
- An abnormal gait in which a person has a leg length discrepancy >2.5cm
- Can be caused by a congenital dislocated hip
Cerebral Palsy
Mixed group of paralytic neuromotor disorders of infancy and childhood
Muscular Dystrophy
Chronic, progressive wasting of skeletal musculature
Hemiplegia
Paralysis of one side of the body
Parkinsonism
A defect of the extrapyramidal tracts, causing tremor, rigidity, and akinesia (inability to initiate movement)
Cerebellar
A lesion in one hemisphere produces motor abnormalities on the ipsilateral side