Suppositories and displacement value calcs
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are the ways people can take suppositories?
Rectal, vaginal or urethral drug delivery
Systemically - far from contact (flagyl, indomectacin)
Locally - site of contact
What are the advantages of suppositories?
Bypass 1st pass metabolism
Faster onset (local)
Enhanced absorption (due to bypassing)
Higher bioavailability (due to bypassing)
Avoid taste issues (paeds)
Why are suppositories used rectally?
Solid unit dosage form suitably shaped for insertion
Melt when warmed to body temp
Dissolve when in contact with mucous secretions
Base can have a local action
Anusol, bisacodyl, protosedyl
How long can you keep suppositories?
3 months
What is the formulation of suppositories?
Nominal weight range for moulds
Infant - 1g
Child - 2g
Adult - 4g
Drug content from 0.1% - 40 %
Other excipients
Viscosity modifiers
Surface active agents
What are the 2 types of bases?
Fatty/oleaginous
Melt at body temp (oily)
Semi-synthetic fatty vehicles (adeps solidus)
Water soluble or miscible
Disperse in rectal cavity
Glycerinated gelatin and PEGs used
Mainly for laxative purposes
What are the properties for an ideal base?
Solid at room temp
Melt at body temp
Water soluble form of the drug dispersed in a fatty base
Release the drug
Non-toxic and non-irritant
Stable on storage
Compatible with drug
Capable of being moulded and easily removed
What is the difference between a high and low solubility base?
Very soluble base = low drug release
Low solubility base = drug deposits onto mucosal surface
What happens after the suspension has been inserted?
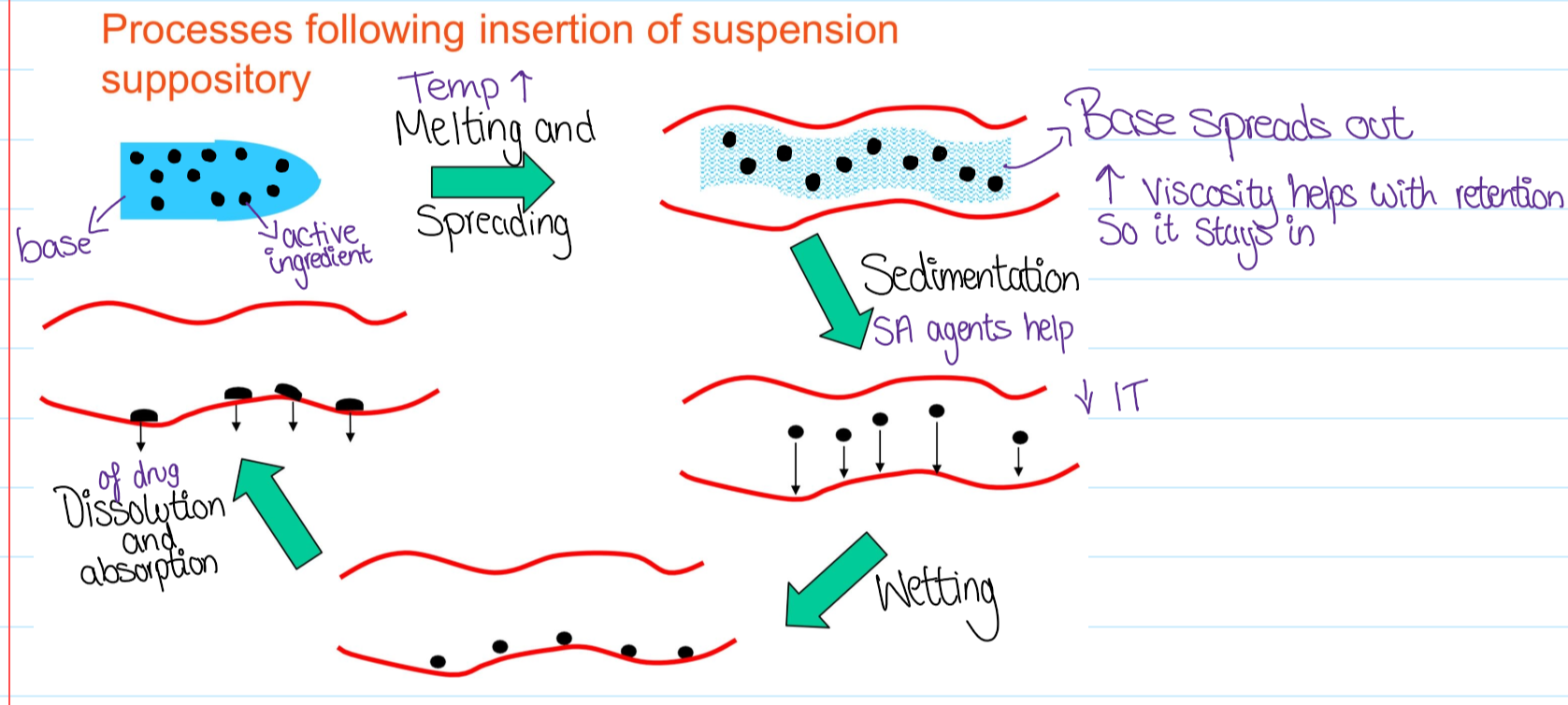
What are the 2 ways suppositories prepared?
Moulding from a molten mass (most common)
The base is melted and the drug added
Poured into moulds and allowed to cool
Suppositories removed and wrapped
Cold compression (less uniform)
Ingredients combined by thorough mixing into a paste
Then forced into moulds
What is the displacement value?
The number of parts by weight of the drug which displace one part by weight of theobroma oil

b. no paracetamol
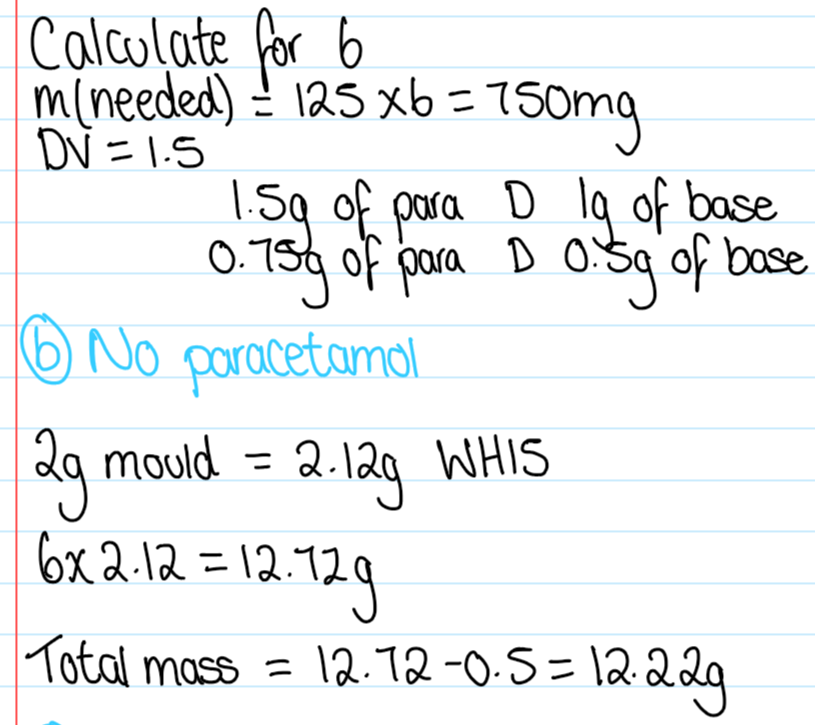

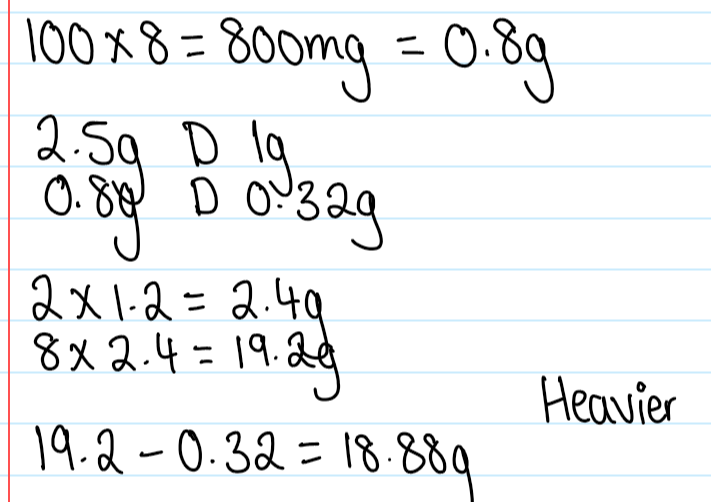

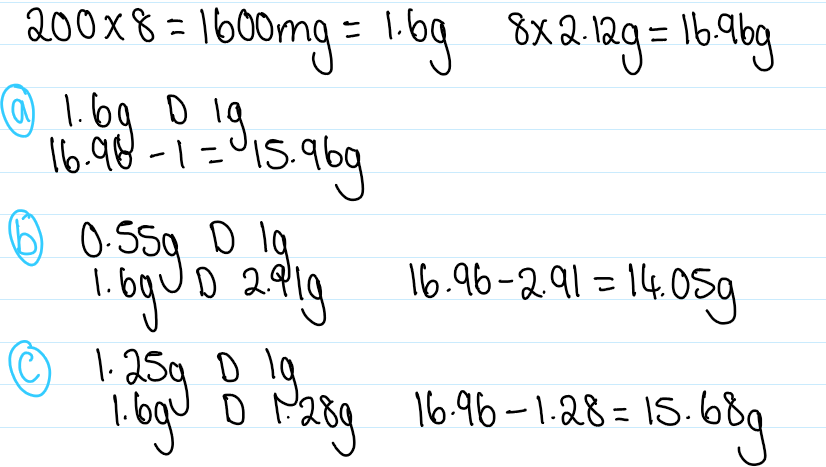
What are semi-solids?
Dermatological vehicles for topical application and transdermal delivery
What does the skkin do?
Regulates heat and water loss
Acts as a barrier to noxious chemicals and MOs
3 layers
Hypodermis
Dermis
Epidermis layers
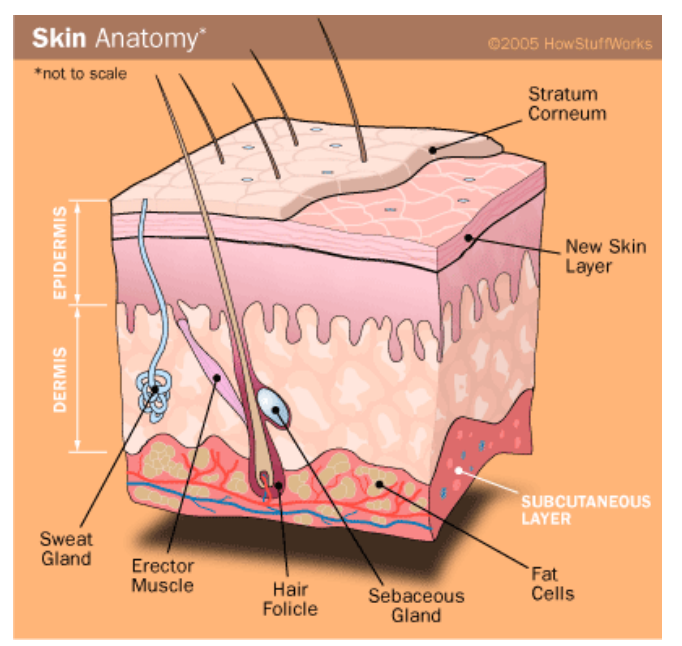
Describe the hypodermis
Subcutaneous fat layer
Insulates the body
Protects against shock
Source of energy
Contains blood vessels and nerves
Describe the dermis
3-5 mm thick
For support (collagen) and elasticity (elastin)
Extensive vasculature
Regulates temp
Delivers oxygen and nutrients around the body
Removes toxins and waste
Describe the epidermis layers
0.1-0.2 mm thick
Protection
Cell renewal after 4 week lifespan
Avascular
No blood vessels
What are the main advantages and disadvantages of transdermal deliver?
Advantages:
Simple removal of dose
Avoids the GI tract and liver (first pass) metabolism
Lower dose needed
Avoids multi dosing as the drug action lasts longer
Disadvantages:
Skin barrier limits absorption
Not for all types of drugs
Irritation and sensitisation
Different for all races, ages and environments
Why do drugs target the skin surface?
To generate a protective layer/attack bacteria and fungi
Protective films/sunscreens to avoid moisture loss
Topical antibiotics, antiseptics and deodorants to kill MOs
Why do drugs target the stratum corneum?
To improve emollience by raising water content
Stimulates sloughing
Removing dead cells
Why do drugs target the viable epidermis and dermis?
Can treat diseases
Steroid
Non- steroidal anti-inflammatory agents
Anaesthetic drugs to relieve pain (mainly local effect)
Anti-histamines to alleviate itches
Why do drugs target the skin appendages?
Hair follicles and sweat glands
Shunt routes that bypass stratum corneum
High permeability
Low surface area (0.1% of total)
Antiperspirant to reduce hyperhidrosis of sweat glands
Barium sulphides as depilatories (hair removal creams)
Why do drugs target systemically?
Low delivery efficiency so limited
Patches decrease pill usage but only 10mg a day so less drug
Hyoscine for travel sickness
Clonidine for hypertension
Nicotine for smoking
Fentanyl for pain
What are the 3 different routes of absorption?
1 - Transepidermal (most common)
Intercellular
Between cells
Predominant route
Transcellular
Across membranes
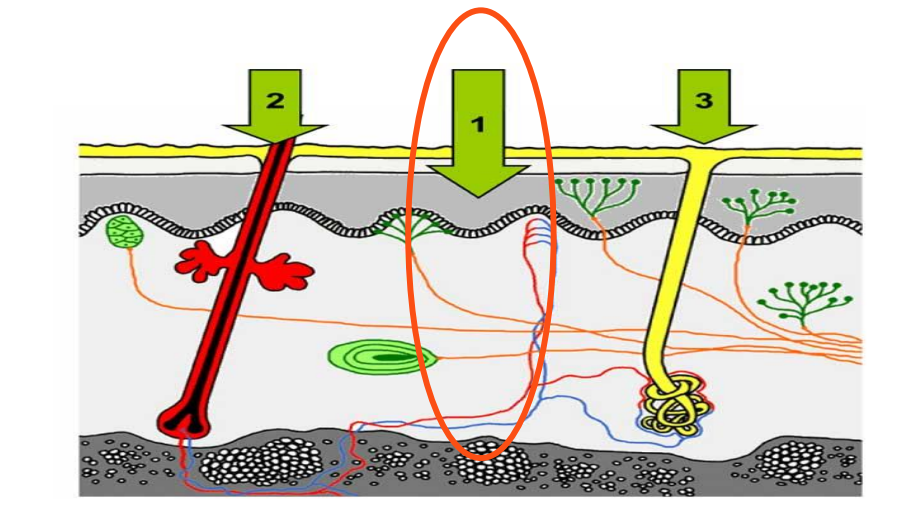
What are the optimal drug characteristics?
Small MW ( <500 daltons)
Lipophilic (logP ~ 2)
Low melting point (good solubility)
Hydrogen bonds interact with lipid polar head groups in skin
pKa in unionised form
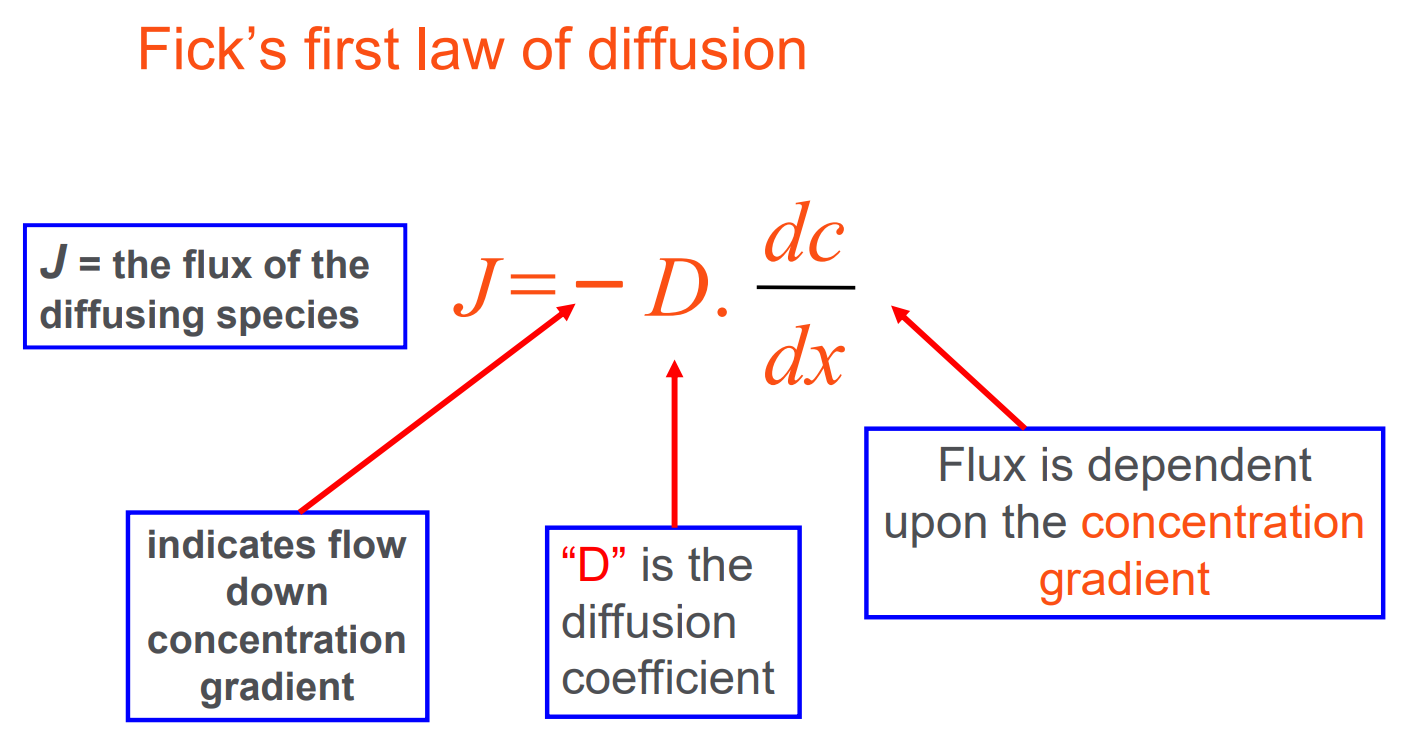
Ficks first law of diffusion
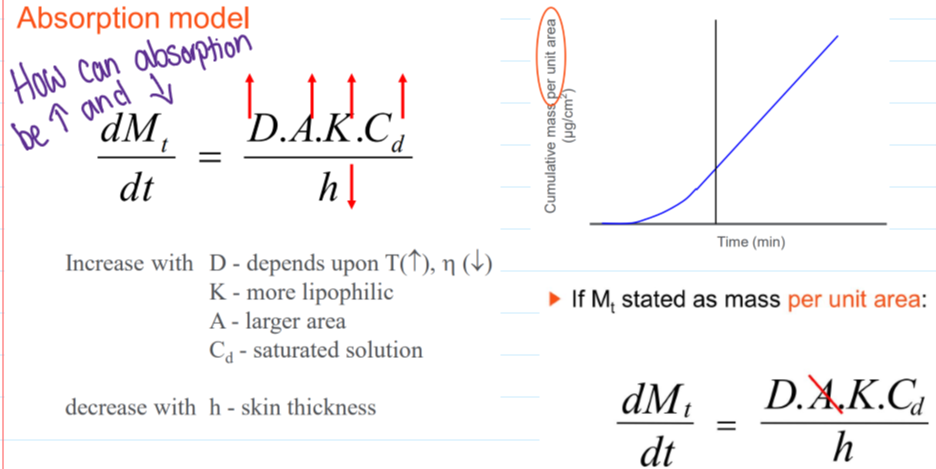
Absorption model
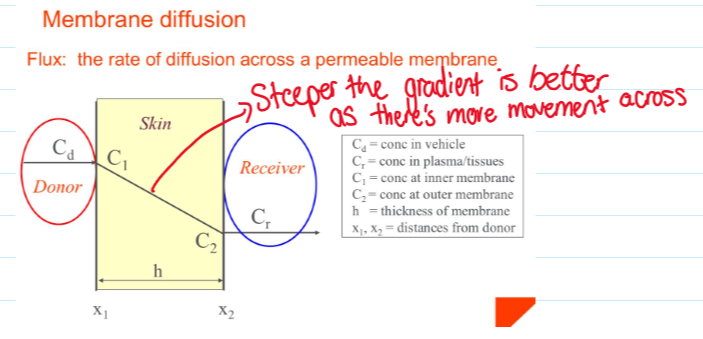
Membrane diffusion
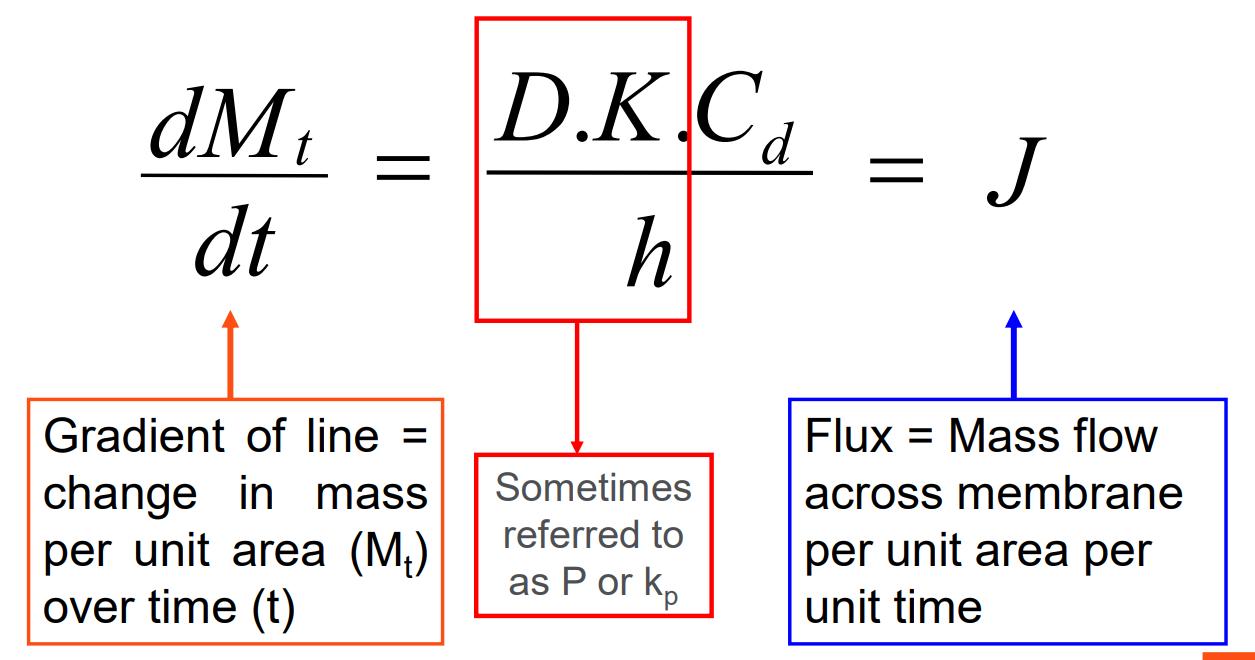

Octanol-water partition coefficient
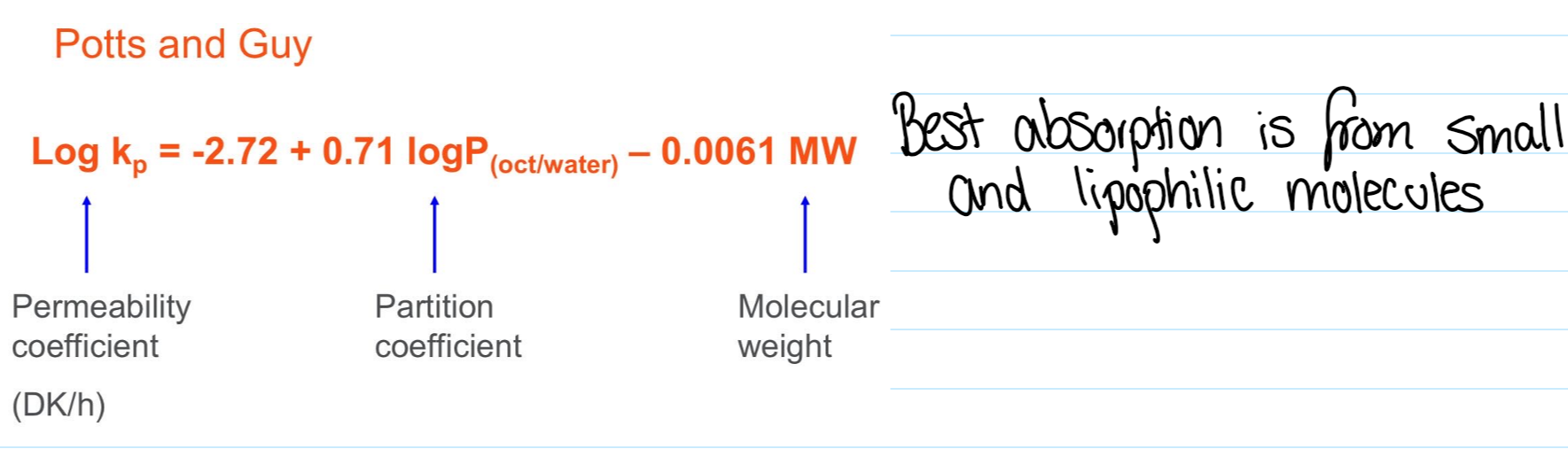
Potts and Guy
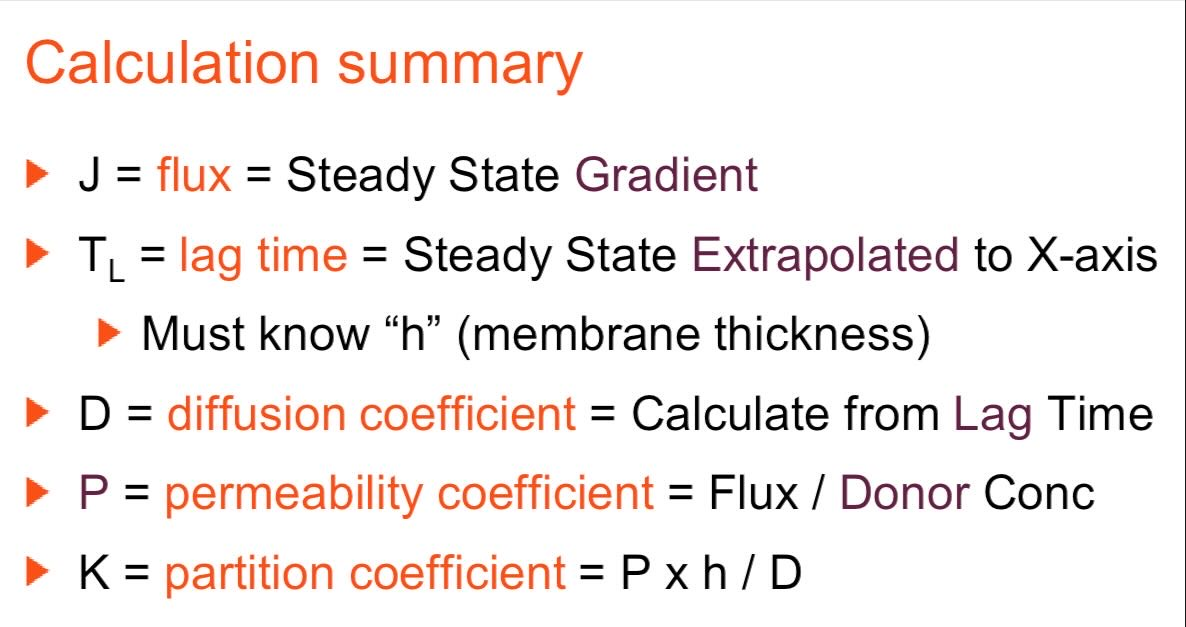
Calculation summary
What is the pH partition hypothesis?
Unionised partition into lipid membranes
Transdermal absorption of weak electrolytes favours the unionised form
Examples of semi solids
Liquid Preparations
Gels (Jellies)
Powders
Ointments
Hydrocarbon, fats and fixed oils, silicones, absorption, emulsifying, water soluble
Creams (emulsions for topical administration)
Water-in-oil, Oil-in-water
Pastes
Features of creams
Prone to MO contamination
Aqueous cream BP
Dimethicone cream BP
Describe cream o/w emulsions
As continuous phase evaporates the conc of water soluble drug increases
Deposits liquid and moisturisers onto skin
Needs mixed emulsifiers - surfactants and fatty acids

Describe cream w/o emulsions

Describe ointments
Dispersion/dissolution of a medicament into an ointment base
The base depends on:
Size of application (occlusion)
Rate of drug release (solubility and diffusion)
Drug stability (hydrolysis reduced in hydrophobic base)
Rheology (effect of drug inclusion)
Describe HC bases
Hard, soft liquid paraffin
Diff consistencies depending on temps
Bad solvents
Properties:
Form thick, occlusive films
Sticky feel
Describe silicone bases
Dimethicone and dimethyl polysiloxanes
Water repellent if ST is ↓
Protects against water soluble irritants
Nappy rash, bedsore, colostomy discharge
Describe absorption bases
Less occlusive that HCs (weaker barrier for water loss)
Not emulsified so water has to be absorbed with low HLB surfactants to form w/o
Wool alcohol ointment BP
W/O absorb more water (hydrous wool fat BP)
Describe emulsifying bases
Anhydrous bases containing o/w emulsifying agents
Water miscible
Washable
Self emulsifying

Describe water soluble bases
Mixtures of high and low MW polyethylene glycols (macrogols carbowaxes)
Non greasy, soften and melts into skin
Doesn’t incorporate large volumes of aq solutions
Reduces the anti microbial activity of methyl and propyl p
What is the difference in stability between creams and ointments?
Ointments have a longer shelf life (3 months vs 28 days)
Ointments are less prone to hydrolysis
No susceptible to microbial contamination
Little to no water phase
More thermodynamically stable
More homogeneous and stable
As they’re hydrophobic
Less phase separation or drying out
Creams are aq so they have less chemical stability so need a preservative
Water promotes hydrolysis and oxidation (degradation of active ingredients)
What are pastes?
Up to 50% of powder is dispersed into ointment base (Zn, talc, starch)
Localises the action of irritants (dithranol) or staining materials (coal tar)
Forms opaque films (sun block)
What are gels?
Semi solid system where there an interaction between colloidal particles in a liquid, type 1 and type 2
Can be based on:
Dispersed solids
Hydrophilic polymers
What are hydrogels?
Type 1 gels
Covalent interactions mediated by cross-linkers
Doesn’t flow when there’s stress
Able absorb lot of water
Wound dressings and sustained release implants
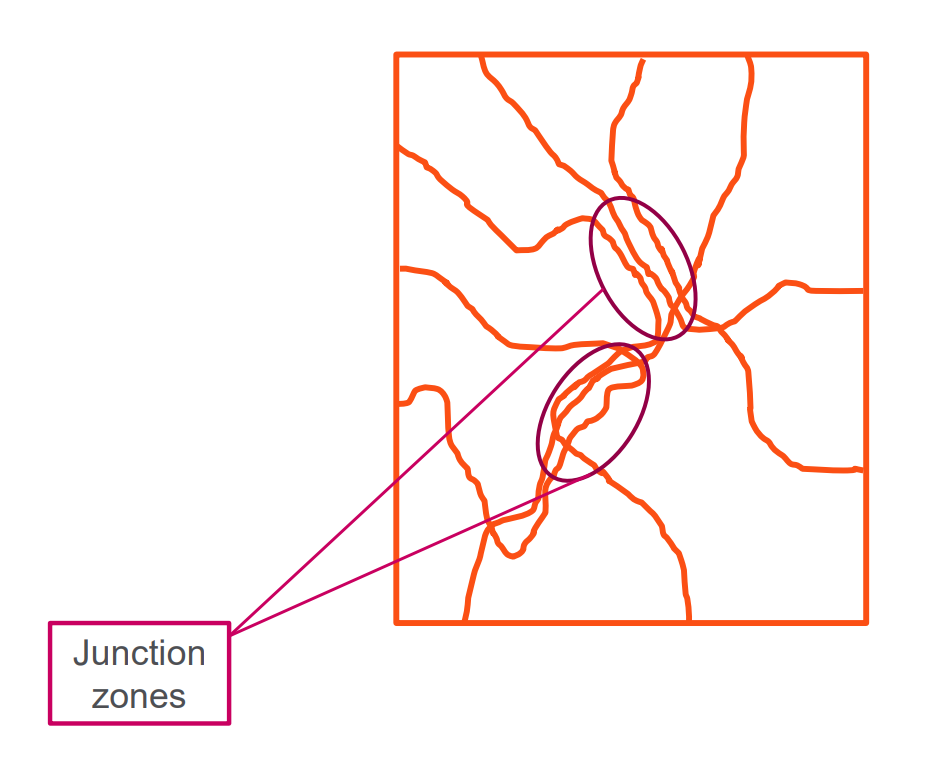
Describe type 2 gels
Most common gel type
Weak bonds
Stress leads to junction zones (reversible destruction)
Pseudoplastics
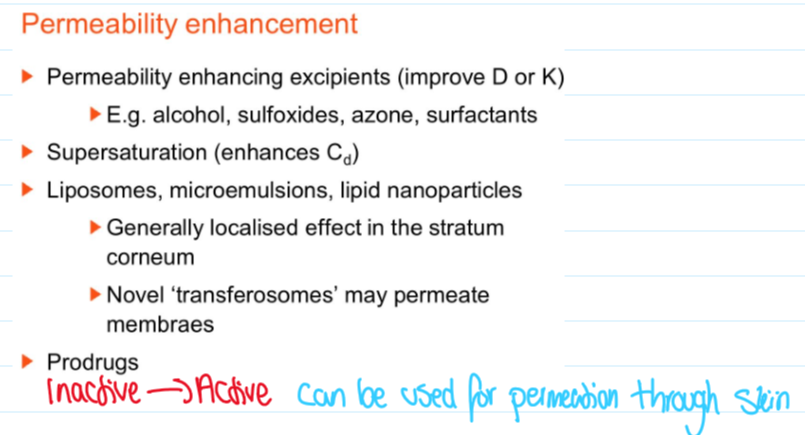
What are excipient and physical types of permeability enhancements?
Excipients:
Alcohol
Sulfoxides
Azone
Surfactants (improves diffusion and K)
Physicals:
Needles
Disadvantages:
Pain
Physiological fear
Infection risk
What are the minimally invasive methods for enhancing permeability?
Tape stripping
Suction ablation
Iontophoresis
Electroporation
Sonophoresis
High velocity particles
Laser assisted delivery
Microneedles
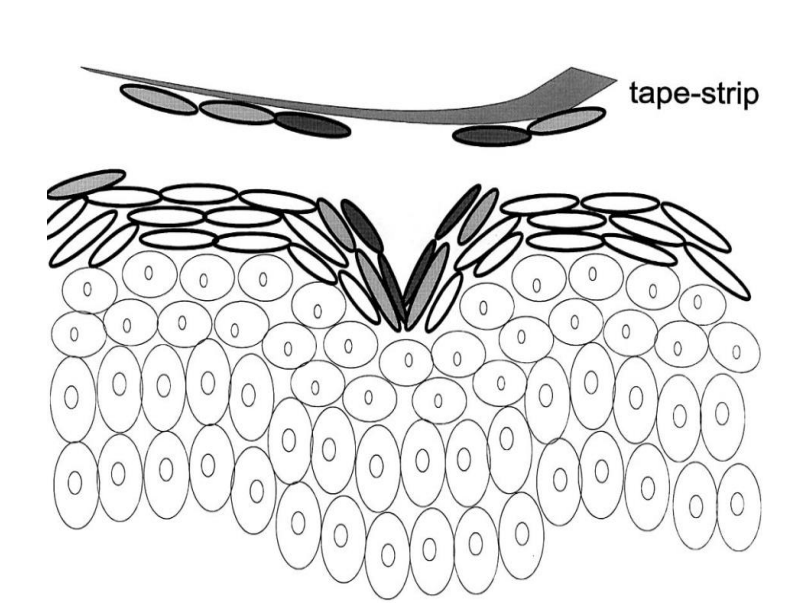
What is tape stripping?
The adhesive removes layers of stratum corneum
Uncontrolled but hydration helps
What is suction ablation?
Removal of stratum corneum by suction blister formation
Vacuum is applied to selected area
Drug delivery can happen straight to stratum lucidum
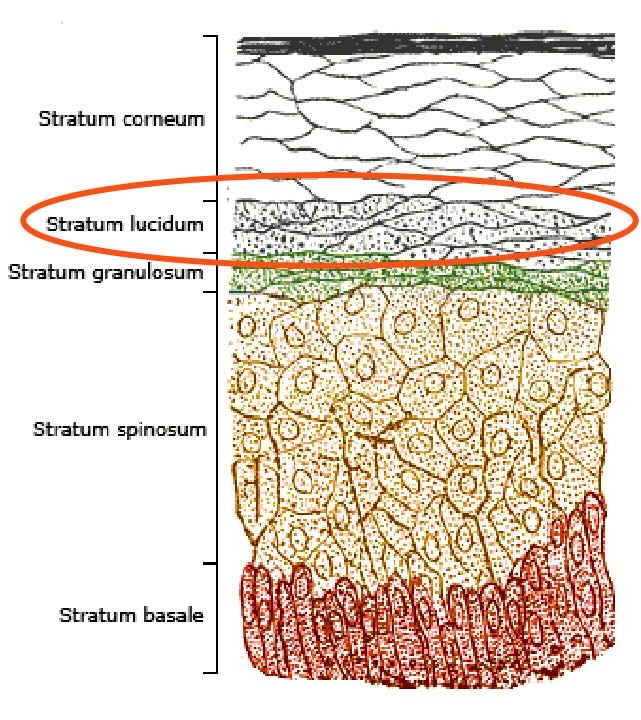
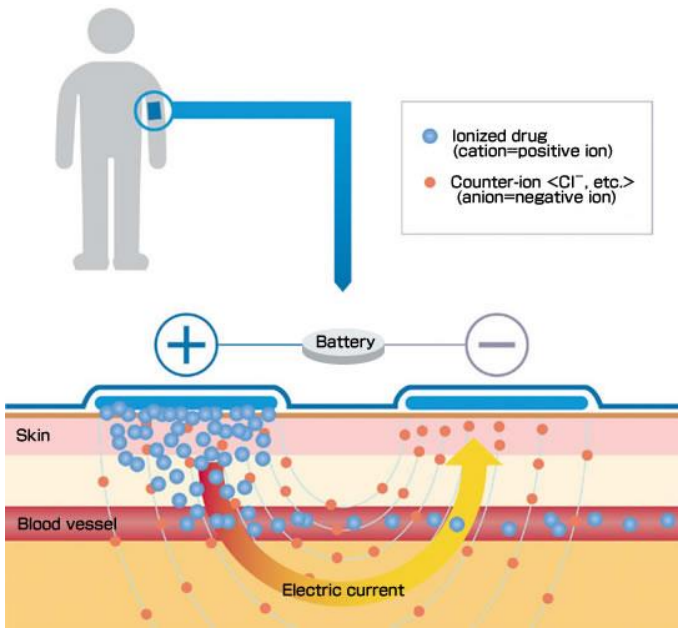
What is iontophoresis?
Transfer of charged substances using an electric field
Enlarges range of drug candidates (polar and charged)
More drug candidates as it acts in molecules themselves
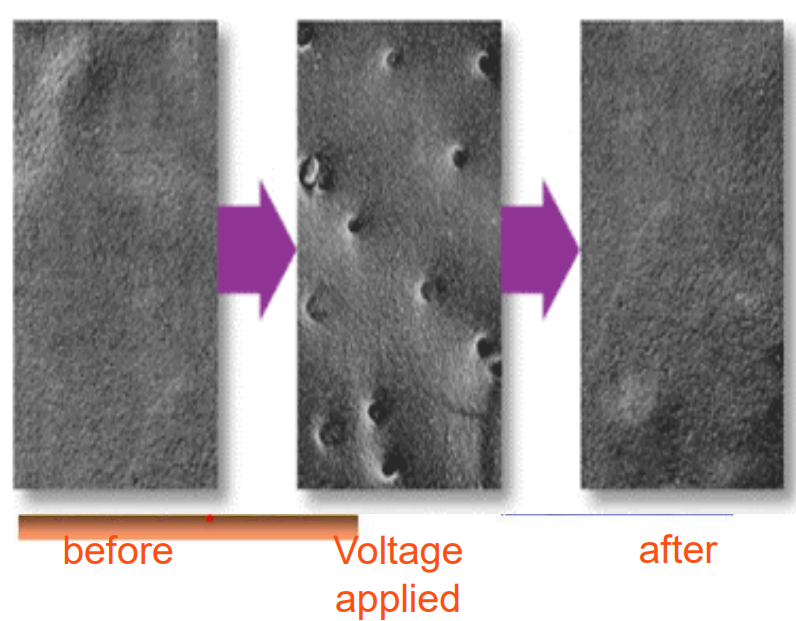
What is electroporation?
Large voltage treatment to make transient hydrophilic pores
Pores aren't permanent
Allows things to get through when needed
10us - 100ms lasting
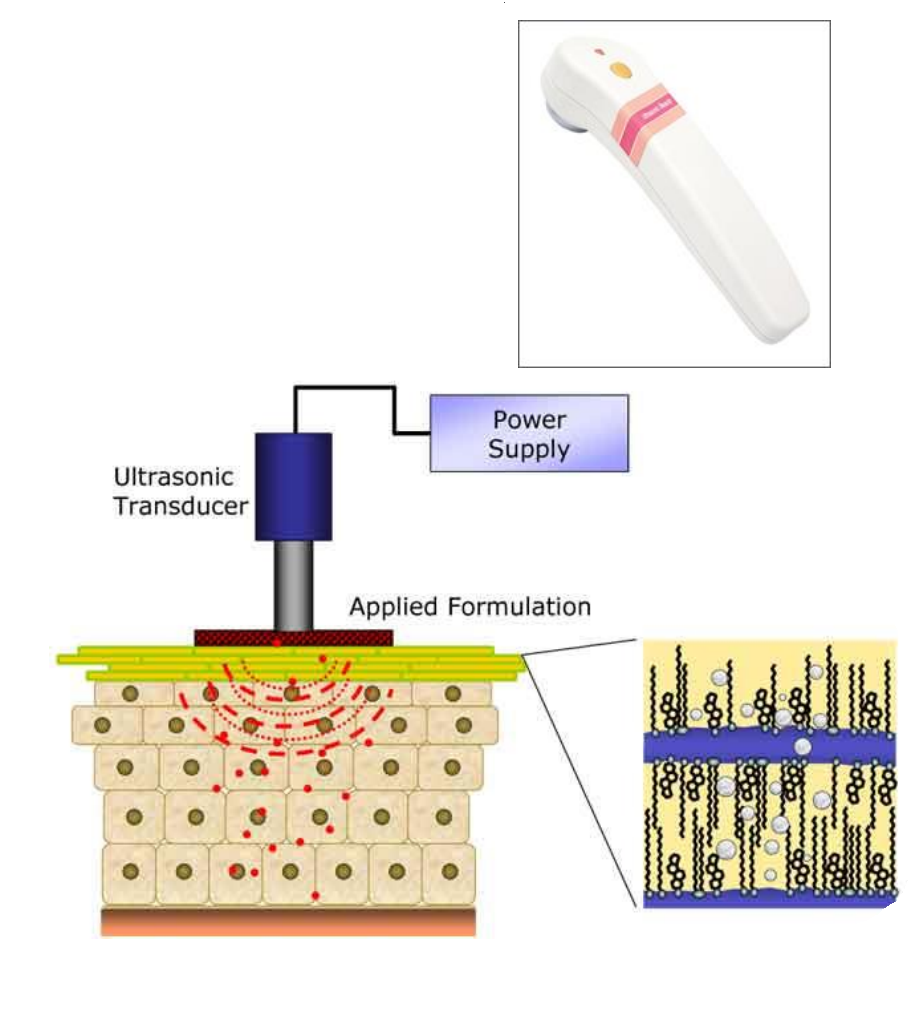
What is sonophoresis?
Formation and collapse (cavitation) of gas bubbles
Uses ultrasonic energy
Temp elevation
What are high velocity particles?
Compressed gas shoots fine particles through the skin
Used for macromolecules (vaccines)
Drug can be coated in particles
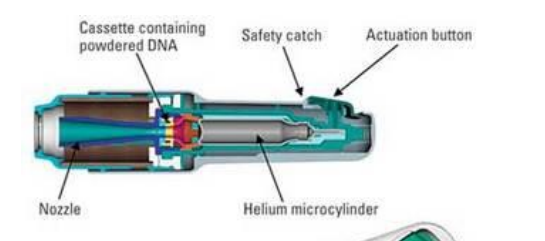
Describe laser assisted delivery
Ablative - high energy forms pores
Optoacoustic - stress wave transiently increases permeability
Well controlled
Hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs
What are microneedles used for?
Piercing upper epidermis
Can be hollow or solid
What are coated and polymeric microneedles?
Coated microneedles – usually stainless steel arrays coated with a formulation containing drug
Polymeric microneedles – higher resilience, can provide improved drug-release pattern because of the polymer's degradation and dissolving capabilities