Impact of Computing Innovations and Their Effects
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Computing Innovation
Includes a program as a core function.
Program
Collection of statements performing specific tasks.
Software
Another term for a computer program.
Physical Computing Innovation
Tangible innovations like self-driving cars.
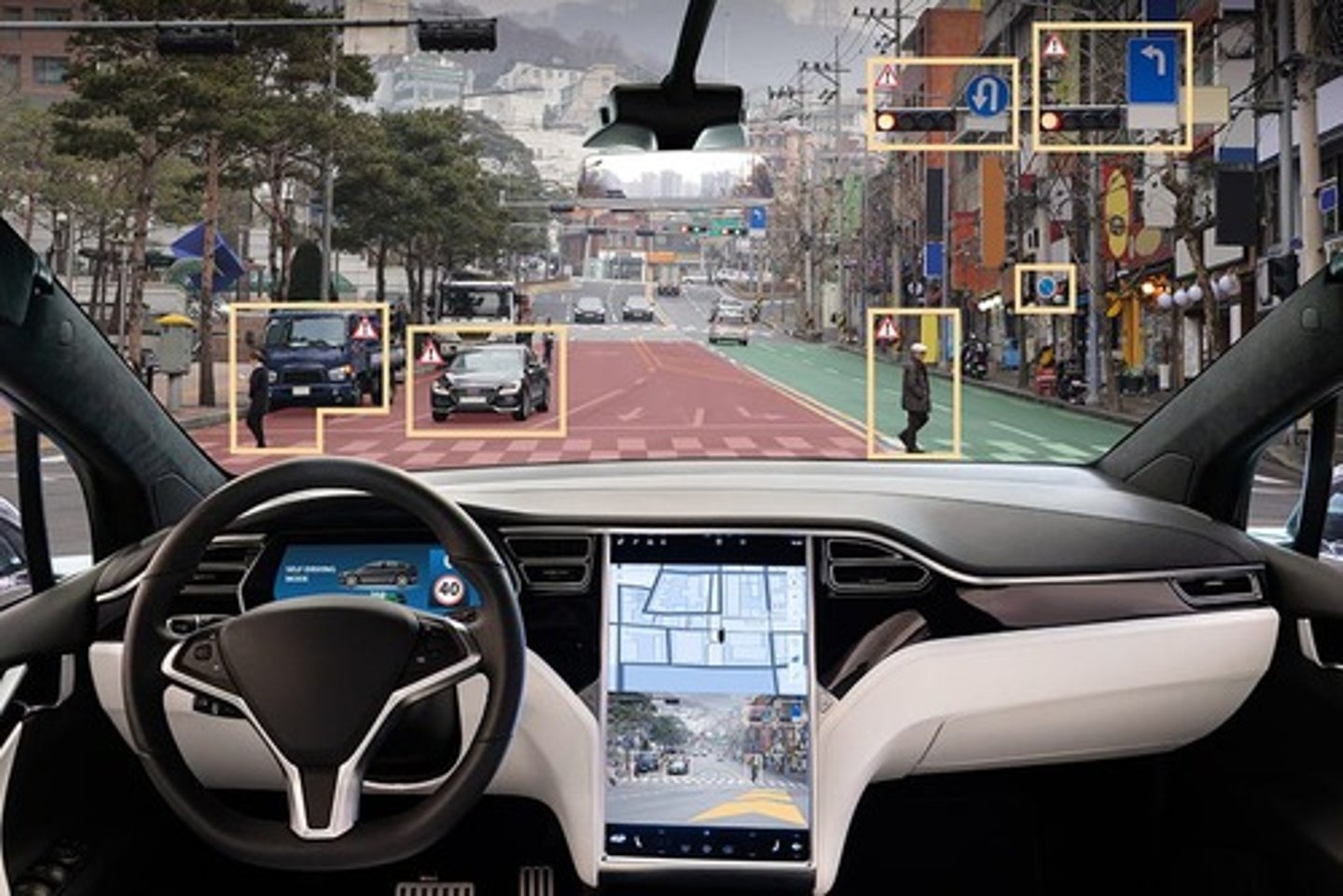

Nonphysical Computing Innovation
Intangible innovations like software or concepts.
Purpose of Computing Innovations
To solve problems or express creativity.
Unanticipated Effects
Consequences not foreseen by innovators.
Harmful Effects
Negative impacts like shortened attention spans.
Beneficial Effects
Positive impacts like increased creativity.
World Wide Web
Originally for scientific information exchange.
Targeted Advertising
Used for business but risks privacy misuse.
Machine Learning
Enables innovation but can perpetuate discrimination.
Data Mining
Extracting patterns from large data sets.
Digital Divide
Gap in access to technology and information.
Socioeconomic Factors
Influence access to computing technology.
Geographic Factors
Location affects technology access and usage.
Demographic Factors
Population characteristics influencing technology access.
Equity Issues
Concerns about fair access to technology.
Computing Bias
Reflects human biases in algorithms and data.
Facial Recognition Bias
Underrepresentation of women and minorities in data.
Algorithm Bias
Biases embedded in software development processes.
Crowdsourcing
Using public data to identify and solve problems.
Crowdsourcing
Sourcing model using a large group online.
Idea Competitions
Contests for generating innovative ideas.
Innovation Contests
Competitions to develop new products or solutions.
Microtasks
Small tasks performed by many individuals simultaneously.
Amazon Mechanical Turk
Marketplace for outsourcing tasks to distributed workers.
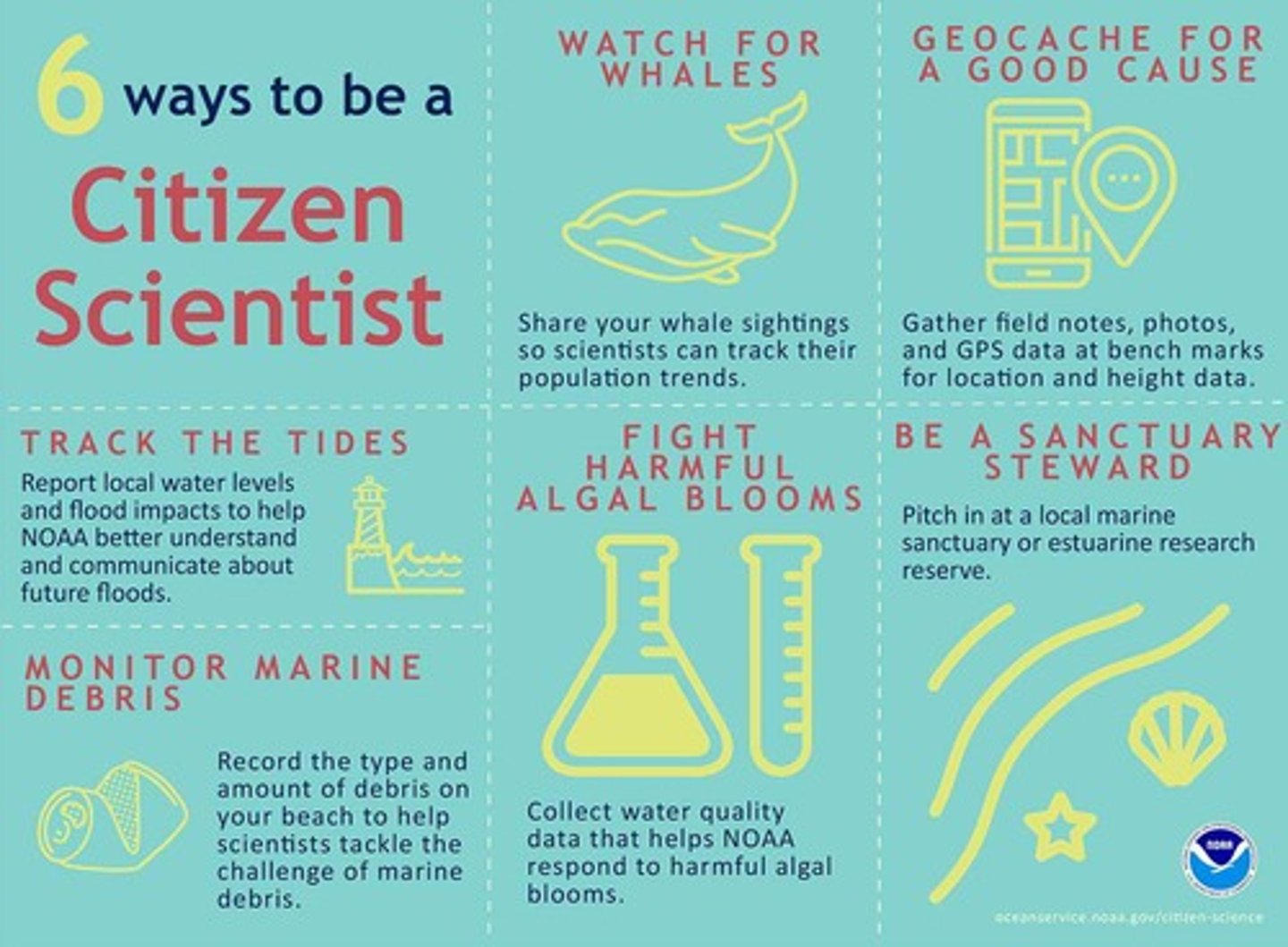
Citizen Science
Public participation in scientific research projects.
Folding@home
Distributed computing project for protein folding research.
Galaxy Zoo
Platform for classifying galaxies using public contributions.
ImageNet
Database using crowdsourced image labeling for algorithms.
CAPTCHA
Test to differentiate humans from bots online.
reCAPTCHA
CAPTCHA variant aiding book digitization efforts.
Intellectual Property
Legal rights to creations of the mind.
Plagiarism
Using someone else's work without proper citation.
Creative Commons
License allowing free distribution of copyrighted works.
Open Access
Free online access to research outputs.
Open Source
Software available for modification and redistribution.
Legal Concerns
Issues arising from digital information ownership.
Ethical Concerns
Moral implications of technology use and access.
Privacy
Concerns regarding personal data security and usage.
Digital Media Piracy
Illegal downloading or streaming of copyrighted content.
Algorithmic Bias
Prejudice in algorithms affecting decision-making.
Computational Systems
Systems designed for processing and analyzing data.
Social Issues
Challenges arising from technology's impact on society.
Privacy
Rights to control personal information usage.
Security
Protection of personal information from unauthorized access.
PII
Personally identifiable information that identifies an individual.
Cookies
Data files tracking user browsing habits.
Targeted Advertising
Ads tailored to individual user preferences.
Social Engineering
Tricking individuals to reveal confidential information.
Phishing Attacks
Fraudulent emails impersonating legitimate entities.
Rogue Access Point
Unauthorized wireless access point to secure networks.
Keylogging
Recording keystrokes to access confidential information.
Geo-location
Tracking user's physical location data.
Browsing History
Record of websites visited by a user.
Information Aggregation
Combining data from various sources to profile individuals.
Email Forwarding
Sharing emails that may expose private information.
Retweeting
Sharing tweets that can reach unintended audiences.
Search Engine History
Record of user searches for targeted suggestions.
Data Interception
Unauthorized access to data during transmission.
Identity Theft
Using PII to impersonate someone else.
Biometric Data
Unique physical characteristics used for identification.
Public Networks
Open networks susceptible to data interception.
Email Indicators
Signs of phishing, like misspellings or strange links.
Information Exploitation
Using personal data for malicious purposes.
Harmful Impact
Negative consequences of sharing information online.
Search Suggestion
Recommendations based on search history.
Security
Ensuring authorized access to systems and data.
Authentication
Process to verify user identity and access rights.
Multifactor Authentication
Access control requiring multiple evidence types.
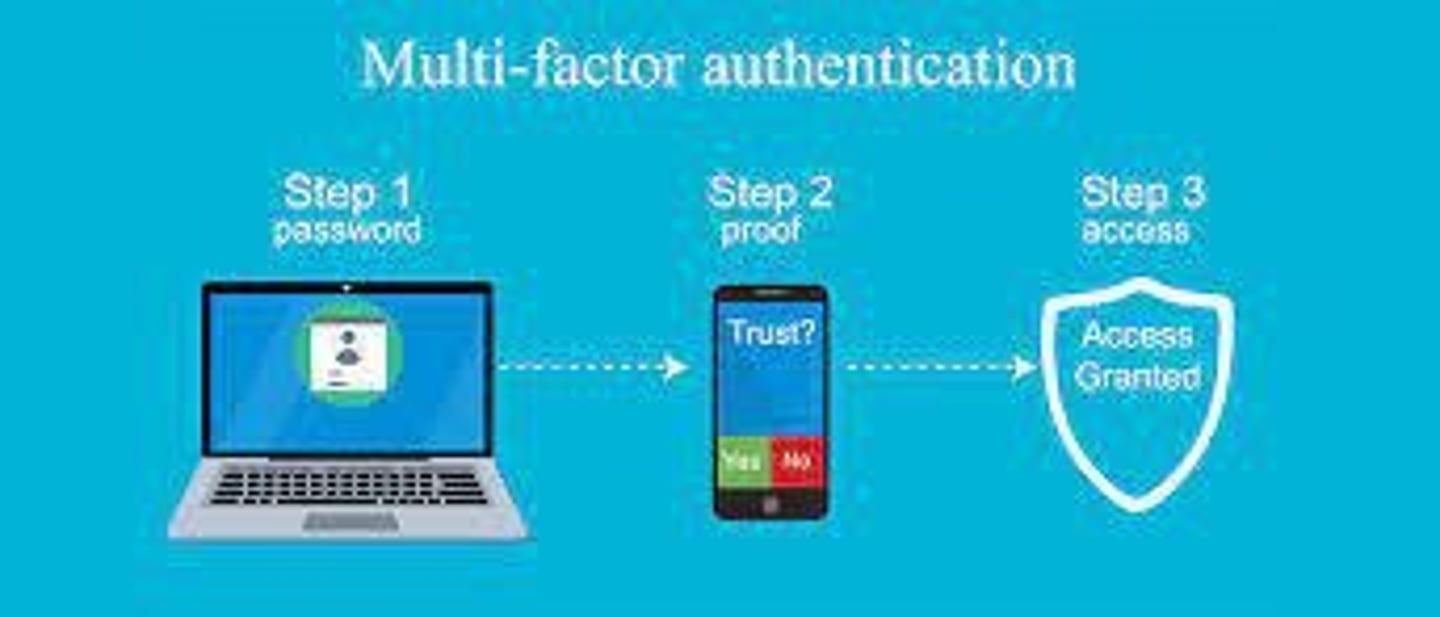
Knowledge-based Authentication
Access using secret knowledge like passwords.
Possession-based Authentication
Access using a physical token like a key.
Inherence-based Authentication
Access using biometric traits like fingerprints.

Strong Passwords
Complex passwords that resist guessing and brute force.
Brute Force Attack
Attempting all possible password combinations to gain access.
Lockout Mechanism
Prevents access after a set number of failed attempts.
Biometric Authenticators
Devices that use physical traits for user verification.
Deterministic Methods
Consistent output from a given input for access.
Probabilistic Methods
Variable output from the same input for access.
White Hat Hackers
Ethical hackers assessing security for vulnerabilities.
Black Hat Hackers
Malicious hackers exploiting systems for personal gain.
Malware
Malicious software designed to harm or exploit systems.
Trojan Horse
Malware disguised as harmless software or files.
Spyware
Malware that steals confidential information without consent.
Keylogger
Records keystrokes to capture sensitive information.
Ransomware
Malware that encrypts data and demands payment for access.
Virus
Malware that attaches to files and disrupts systems.
Hacktivists
Hackers promoting political or social causes through hacking.
Cybercriminals
Individuals committing crimes via computer networks.
Access Control
Regulating who can view or use resources in a computing environment.