ANSC220 - Sensory (Exam #2)
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Nictitating Membrane
Third eyelid that helps clean out and protect eye
Granula Iridica
Reduces glare and increases visual clarity
Tapetum Lacidum
Green reflective material in the back of the eye; Found in cats
Retina
Rod and cone cells; Where light information is collected and sent
Choriod
Collection of blood cells in the eye
Vitreous Humor
Gel-like substance in vitreous chamber of eye
Cornea
First area of eye that light travels through
Iris
Smooth muscle that allows eye to change size pupil
Lens
Reflects light onto back of retina; Changes shape to accomodate distance of light
Ciliary Body
Smooth muscle connected to lens by suspensory ligaments that changes shape of lens
Pupillary Constriction
Parasympathetic circular muscle
Pupillary dilation
Sympathetic radial muscle
Rod cells
Provide light vision based on intensity, not color
Cone cells
Provide color vision
Rhodopsin photopigment
Absorbs all wavelengths of light
Scotopsin Photopigment
Detects red, green, and blue wavelengths
Semicircular Canals
Detect changes in head position and acceleration of head
Ampulla
Flaring out ends of semicircular canals
Cupula
Tissue that sticks up in ampulla that contains hair cells
Otolith organs
Detect changes in head position and linear acceleration
Otoliths
Provide weight to fluid overlaying hair cells
2 Otolith organs
Utricle and Saccule
Tympanic Membrane
Vibrates in response to sound waves; Provides sound intensity and pitch information
Intensity
Loudness of sound; Depends on sound wave amplitude (height)
Pitch
Tone of sound; Depends on sound wave frequency
Ossicles
Three small bones in mammals that transfer vibrations from tympanic membrane to cochlea oval window
Columella
One bone in reptiles/amphibians/birds that transfers vibrations from tympanic membrane to cochlea oval window
Order of Ossicles
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
Cochlea
Coiled tubular system with three fluid-filled compartments
Scala Vestibuili
Upper compartment of cochlea
Scala media/Cochlear duct
Middle compartment of cochlea
Scala tympani
Lower compartment of cochlea
Organ of Corti
On top of basilar membrane in cochlear duct; Provides sense of hearing by transforming vibrations into action potentials
Gustatory cells
Chemoreceptors found in tongue
How many cells per taste bud?
50
Olfactory neurons
Chemoreceptor; Only type of neuron in mammals to undergo cell division during adult life
Olfactory Glomeruli
Mitral cells where olfactory neurons synapse
Olfactory neuron action potentials increase/decrease with concentration of odor molecule.
Increase
Vomeronasal Organ (VMO)
Additional sense organ in mammals and reptiles; Causes reproductive/social behaviors by reception of pheromones
Flehming Response
Opening the nasal passages so that pheromones stimulate VMO
Suspensory Ligament
A
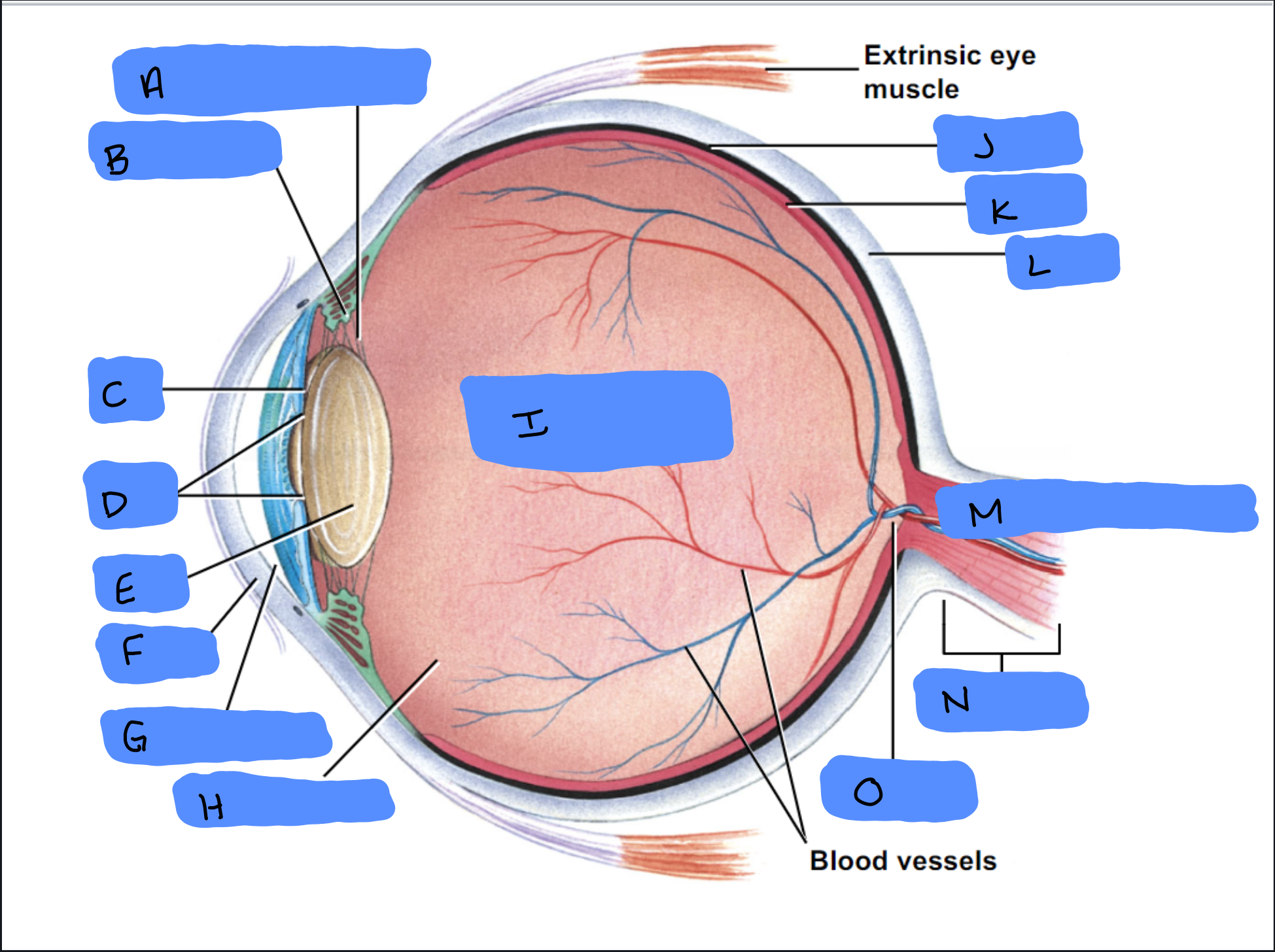
Ciliary Body
B
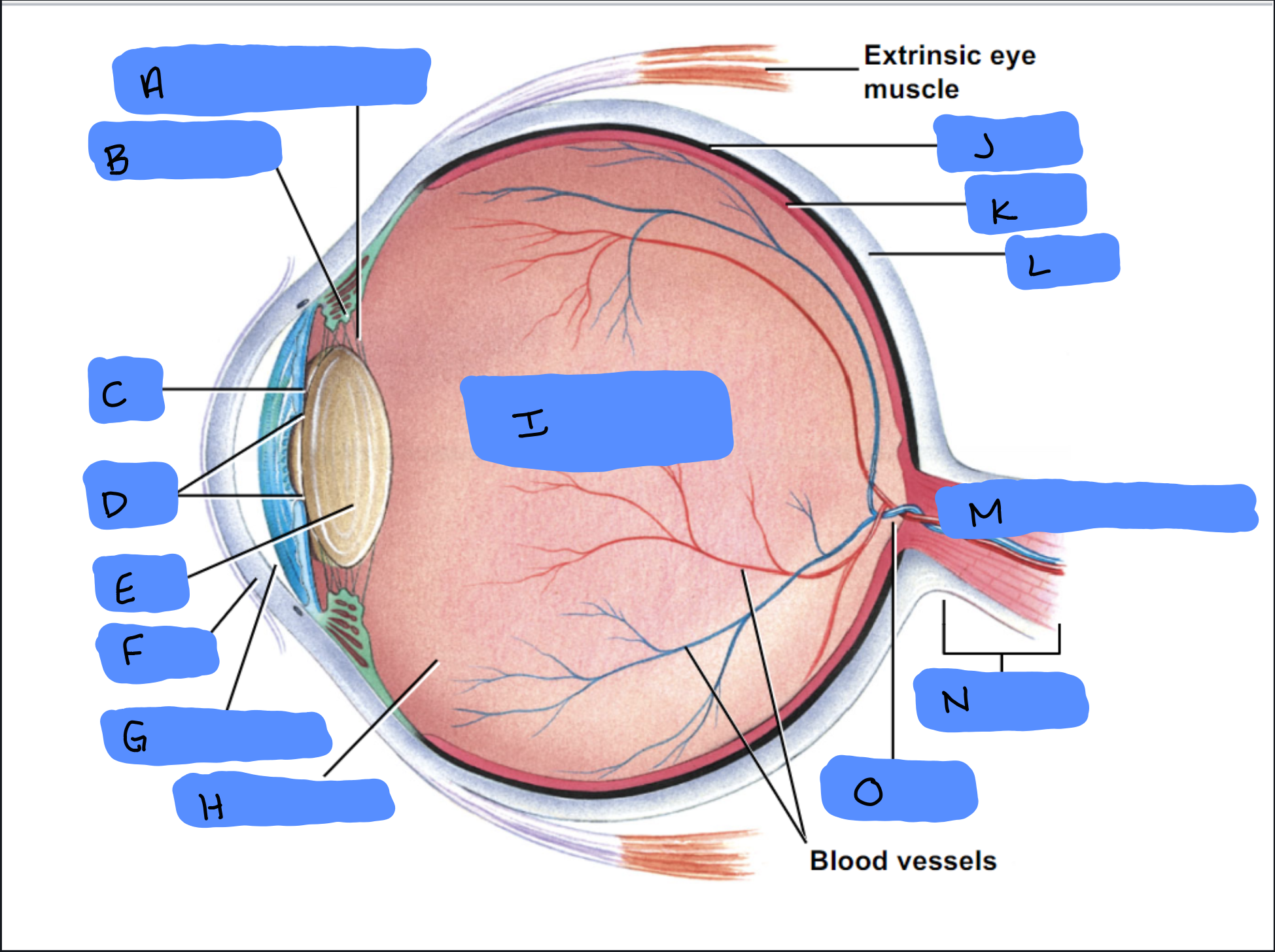
Iris
C
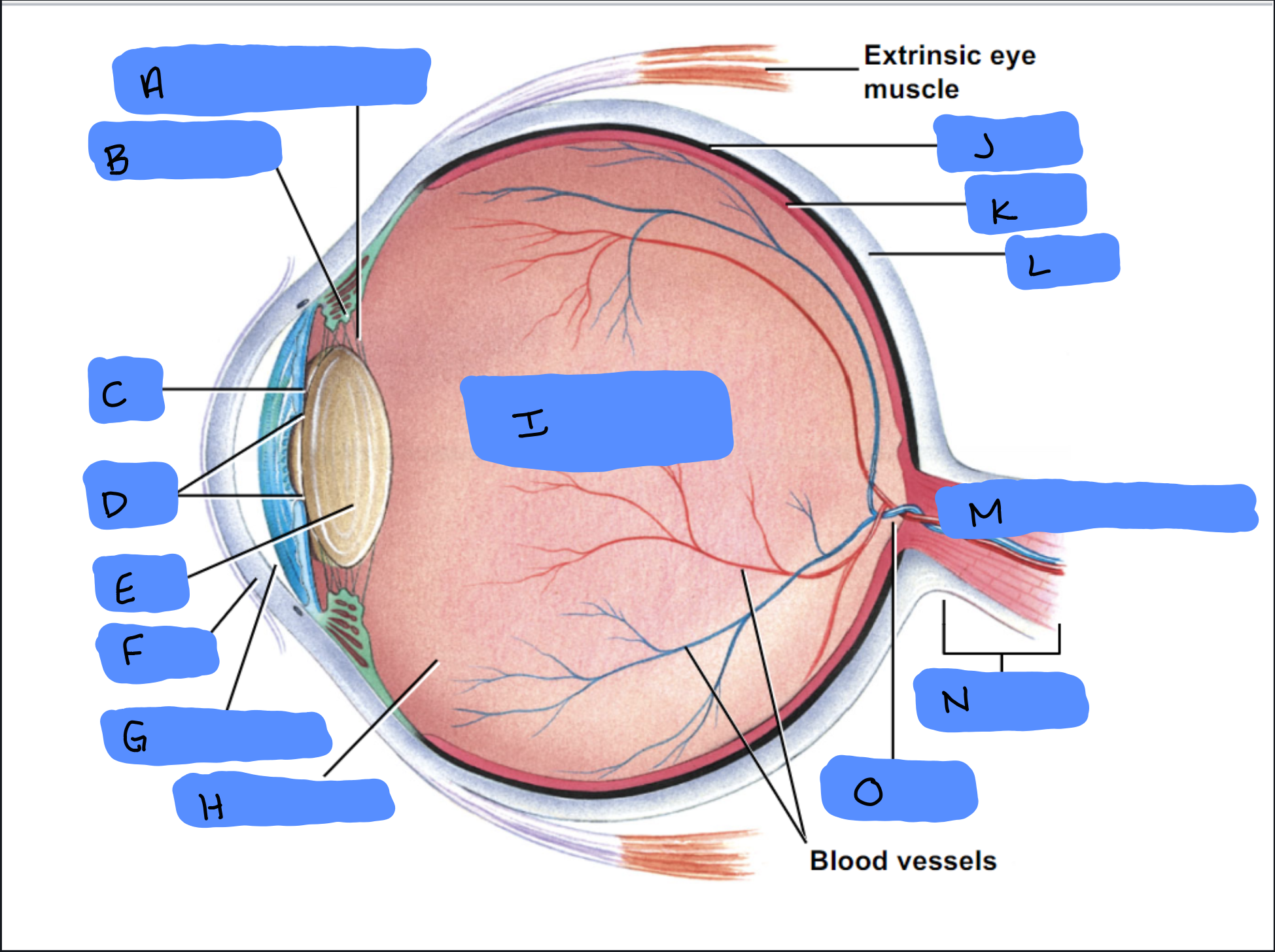
Pupil
D
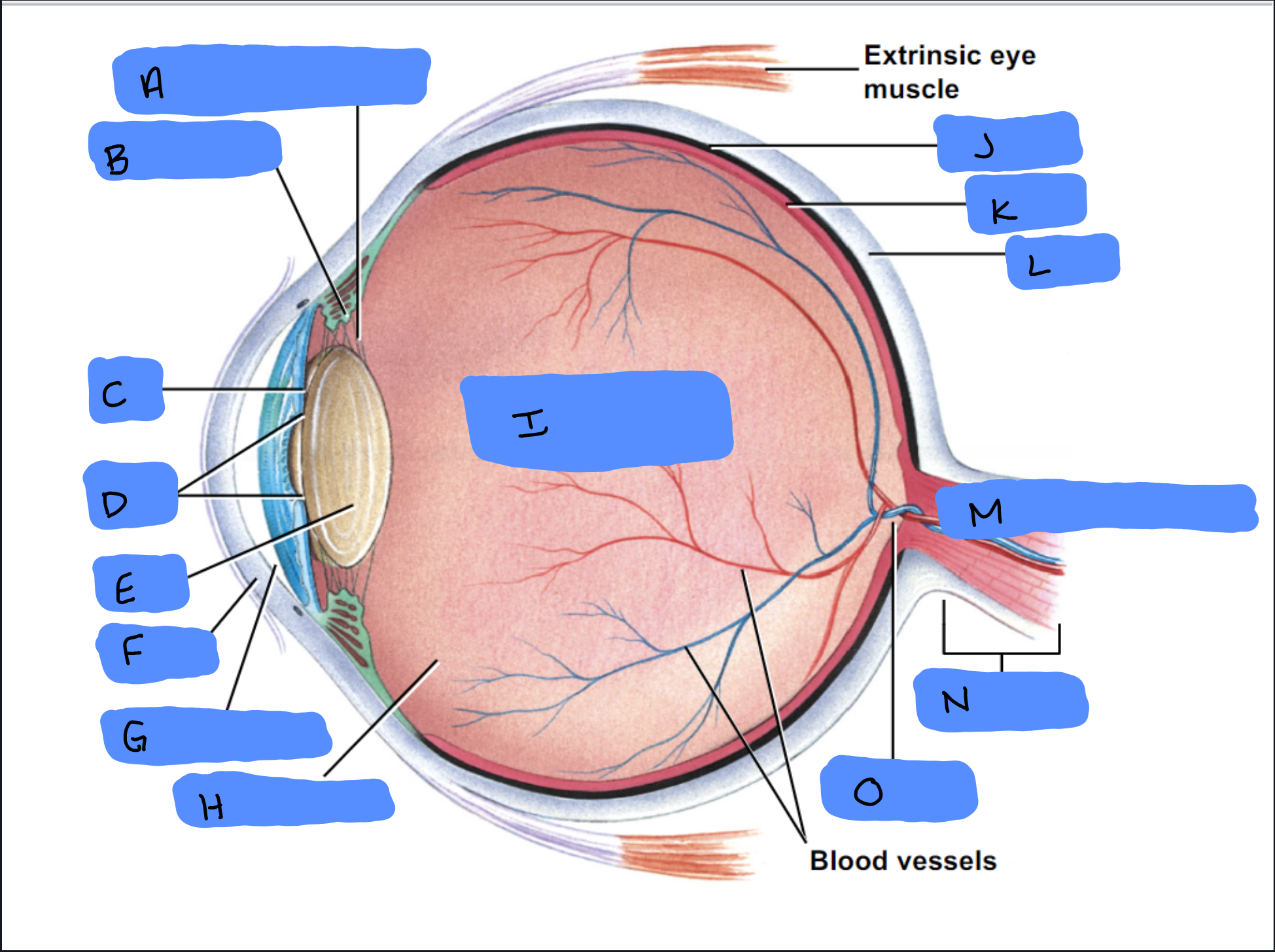
Lens
E
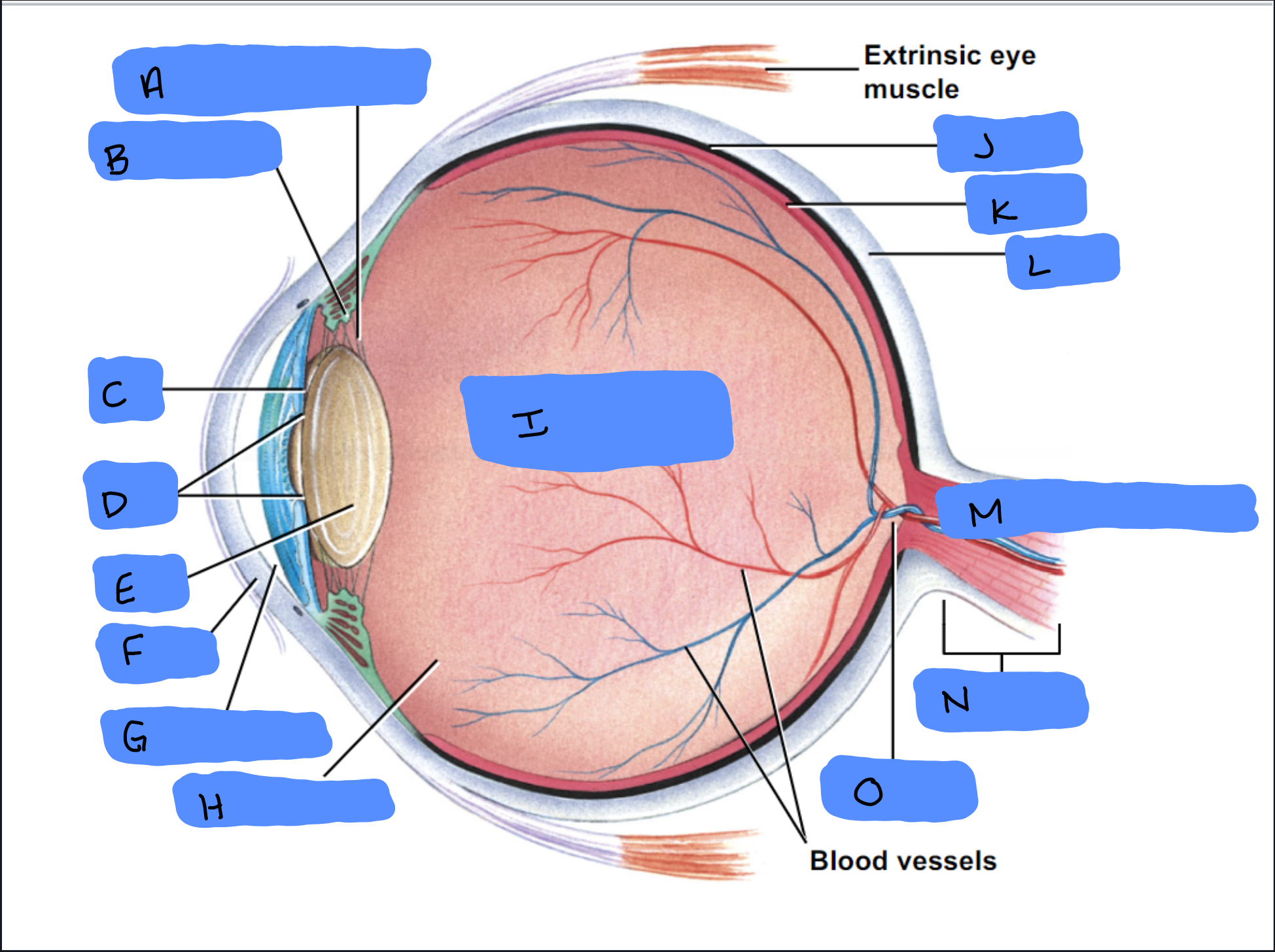
Cornea
F
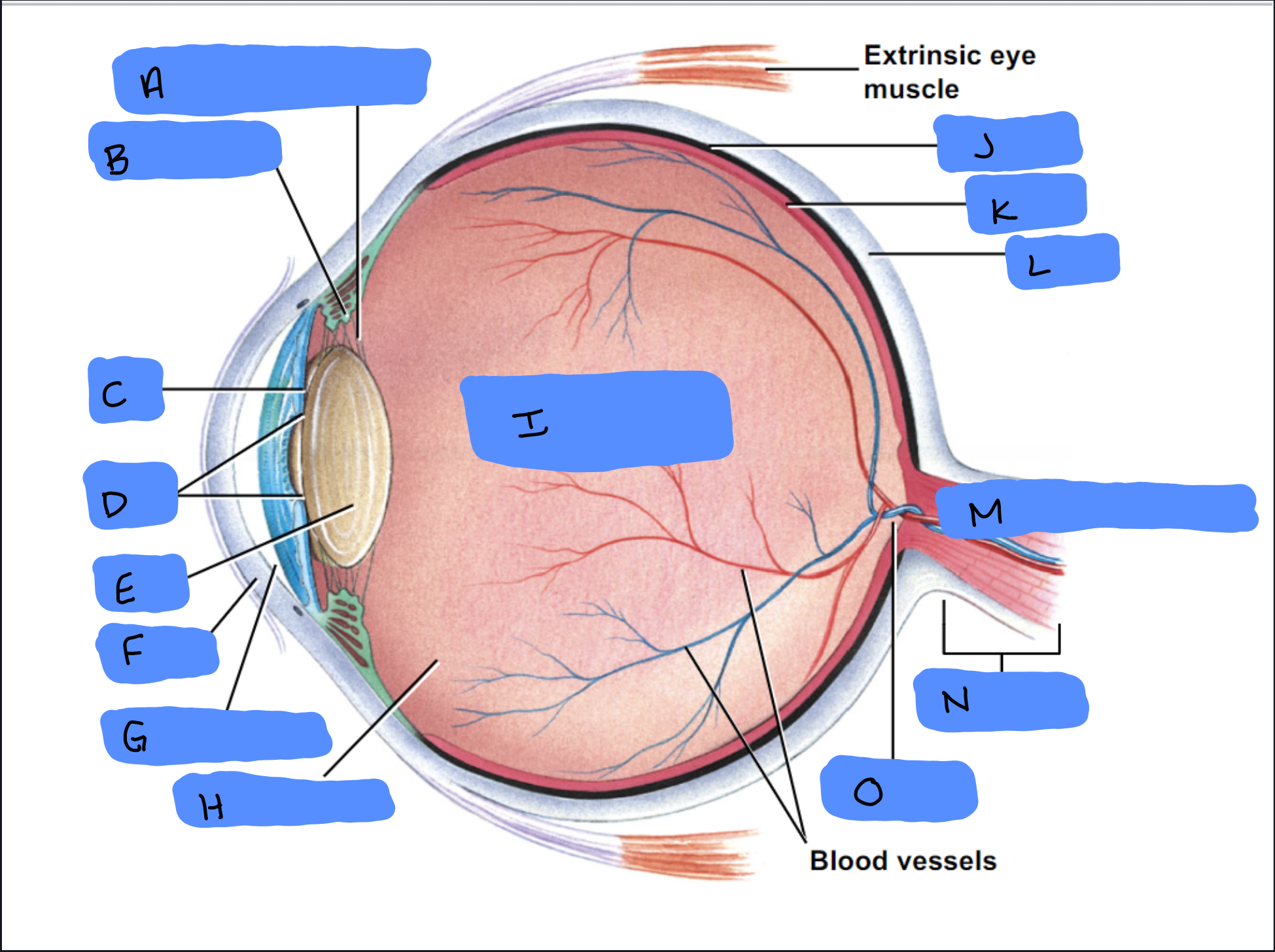
Aqueous Humor
G
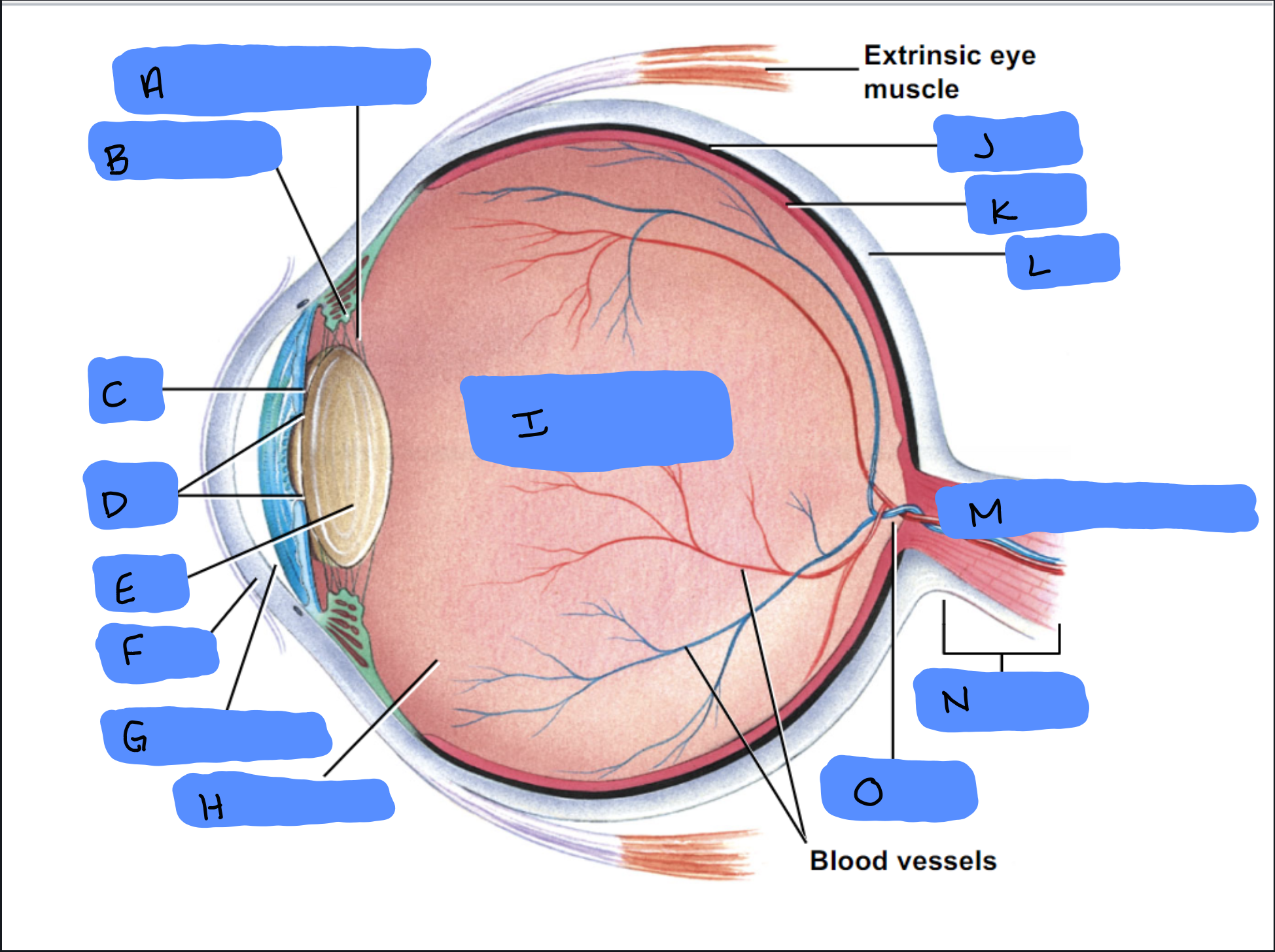
Vitreous Humor
H
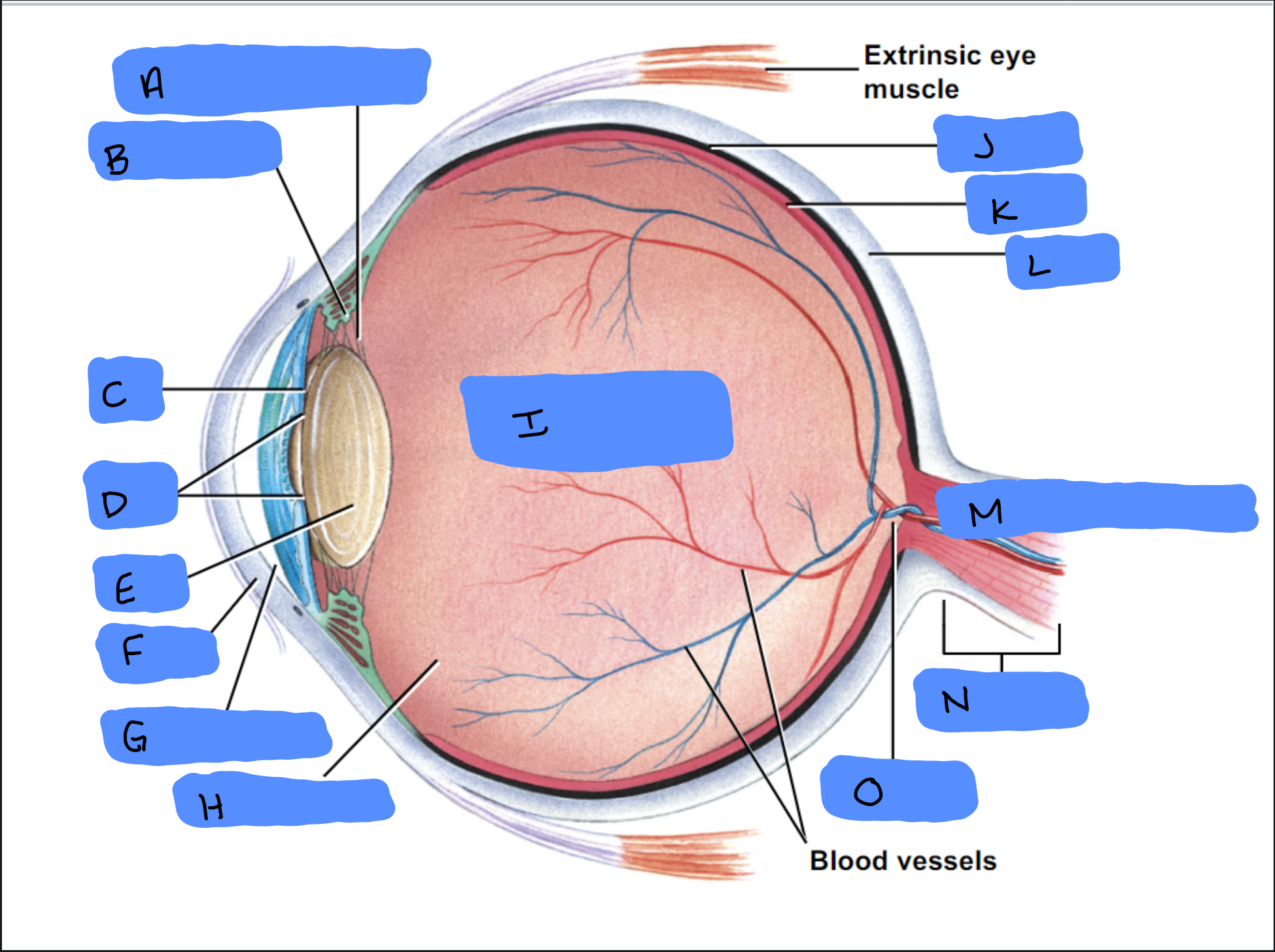
Vitreous Chamber and Body
I
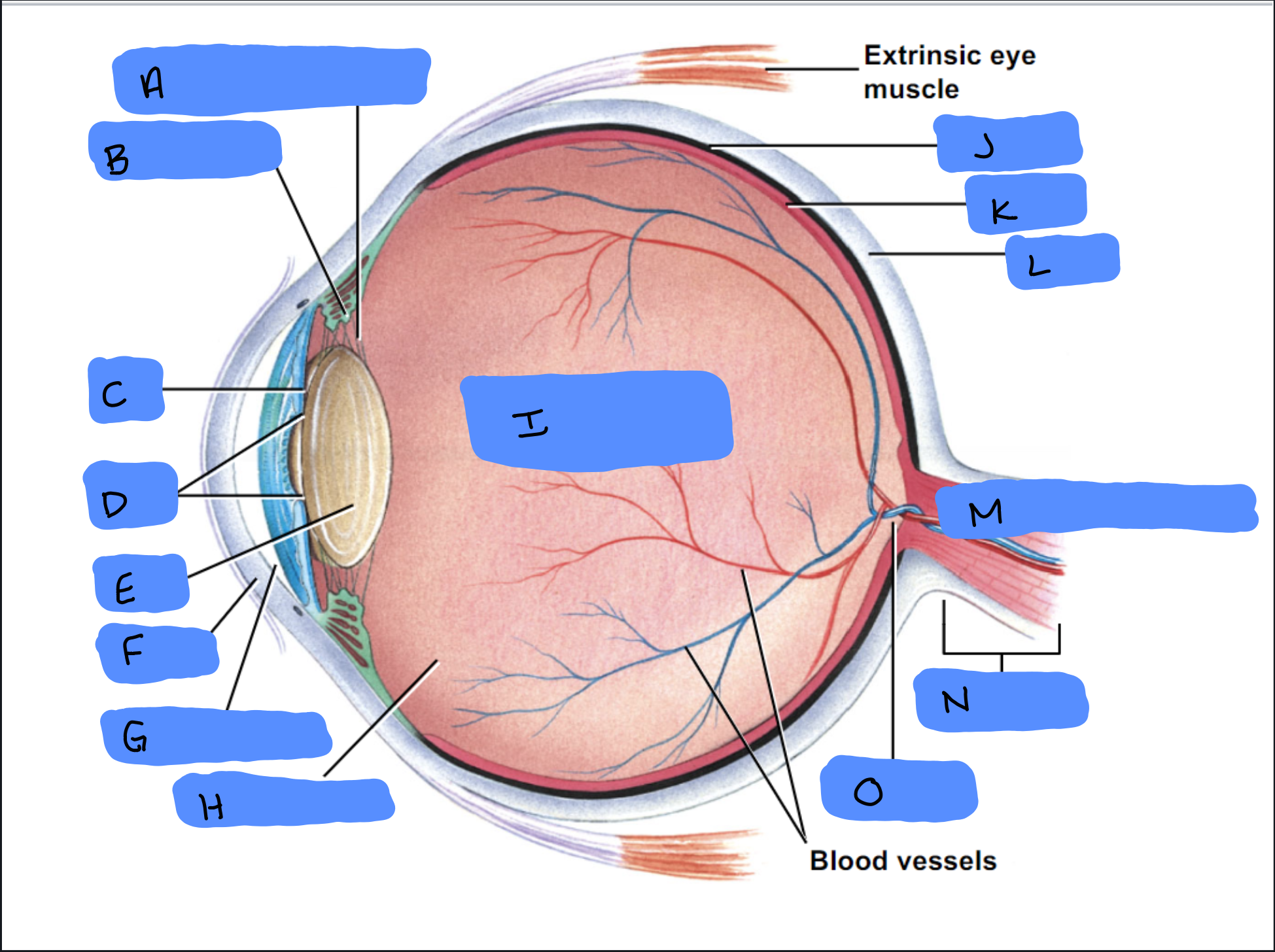
Choroid
J
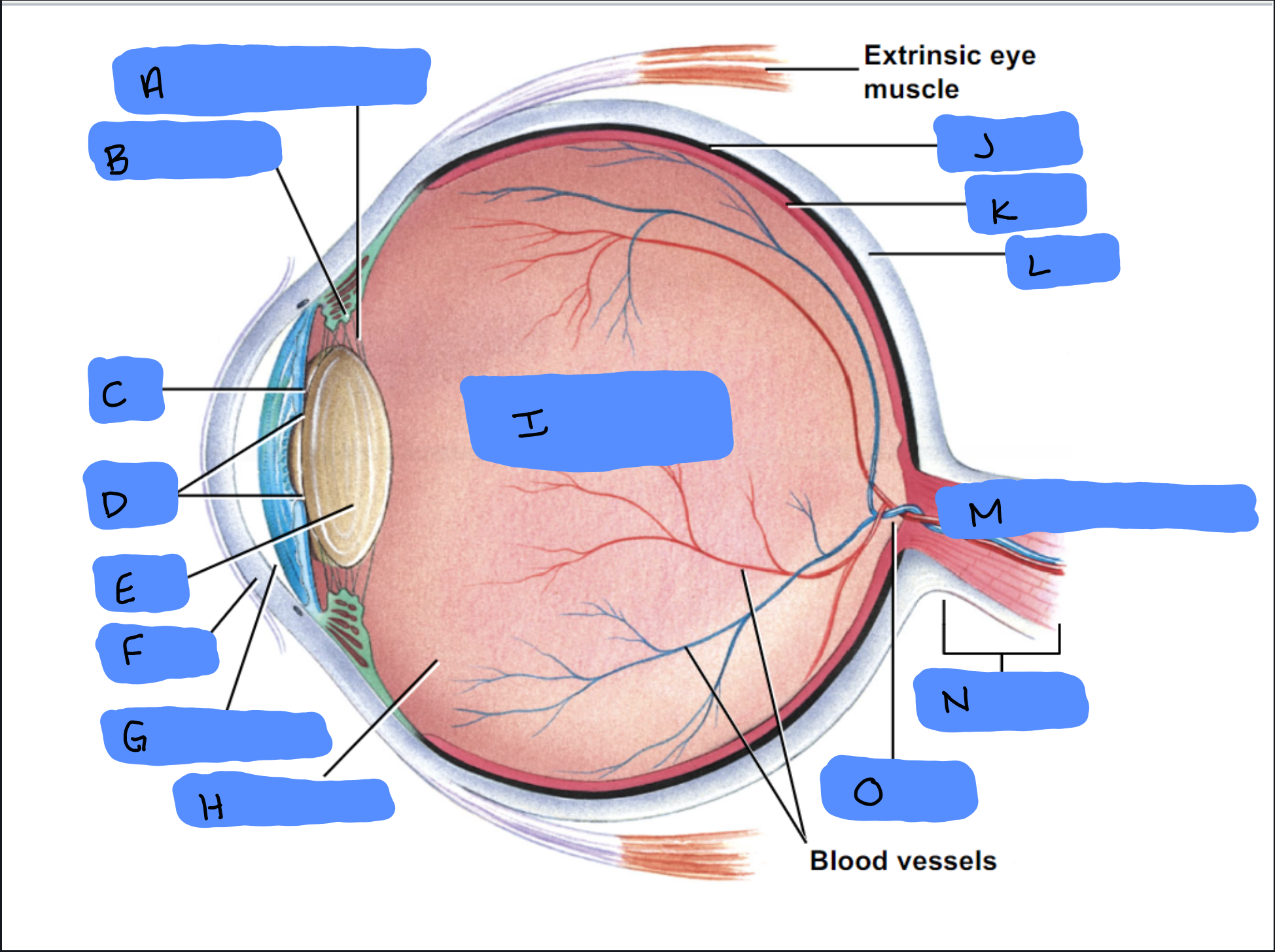
Retina
K
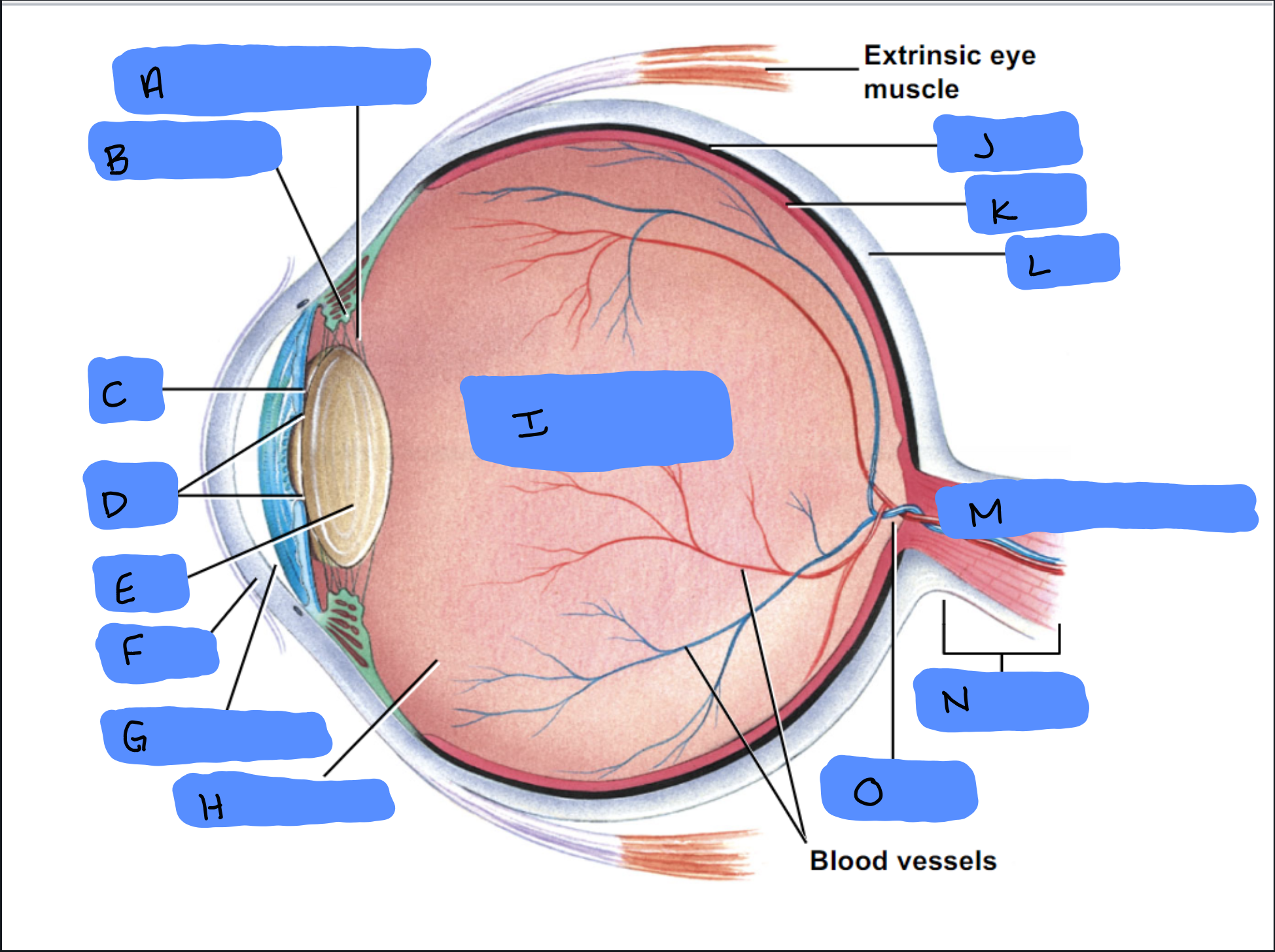
Sclera
L
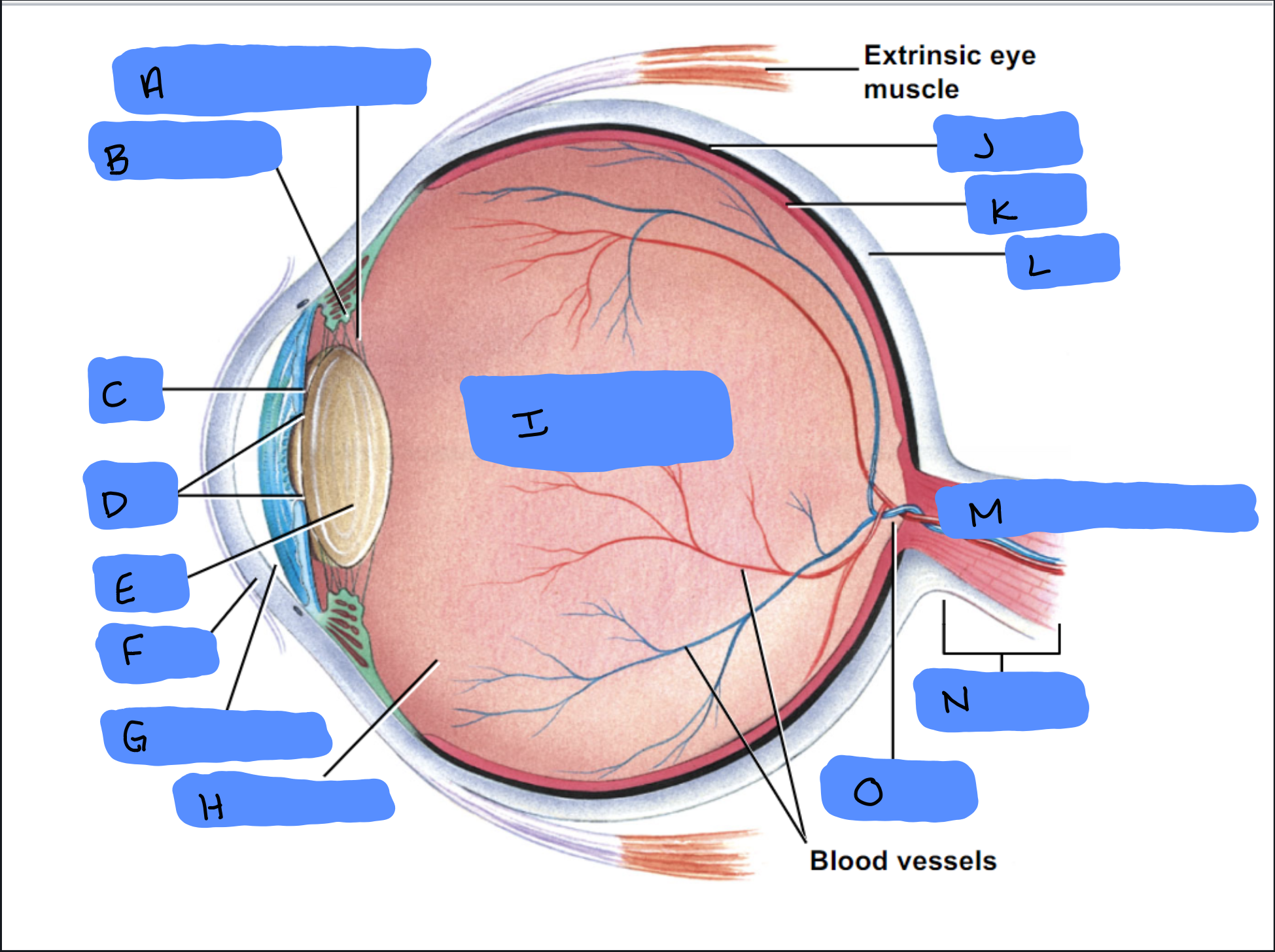
Optic Disc (“Bind spot”)
M
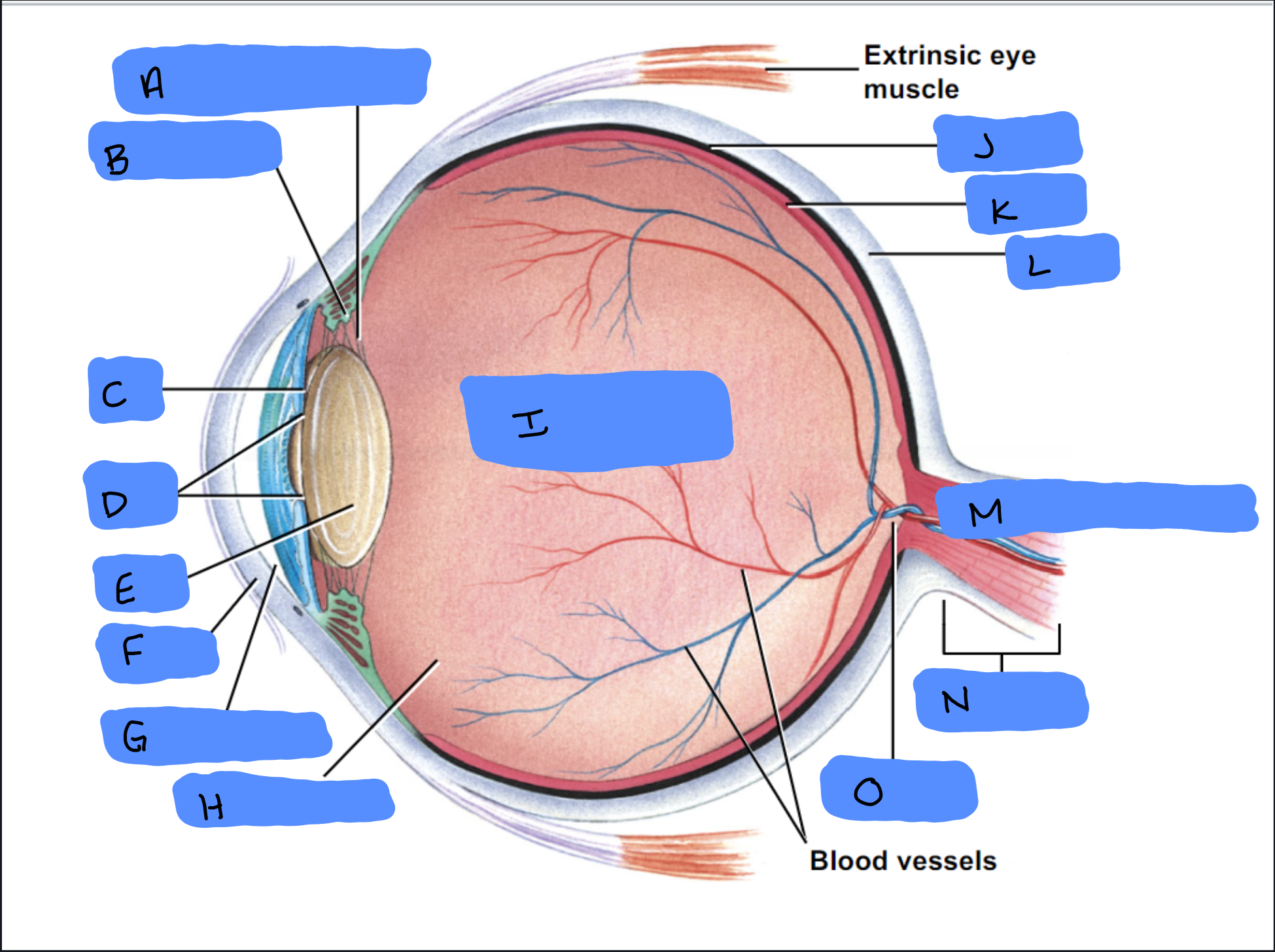
Optic Nerve
N
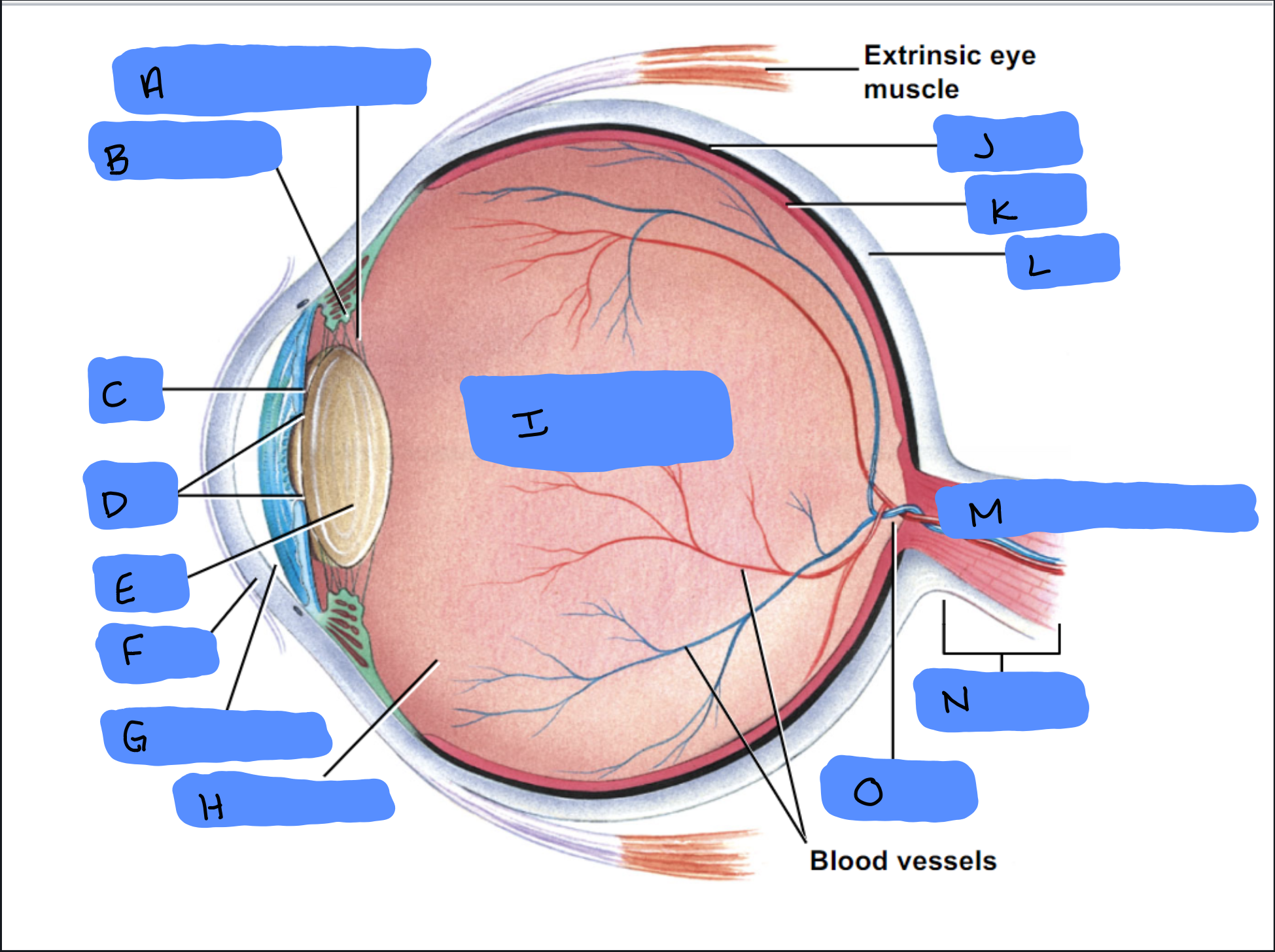
Optic Disc
O
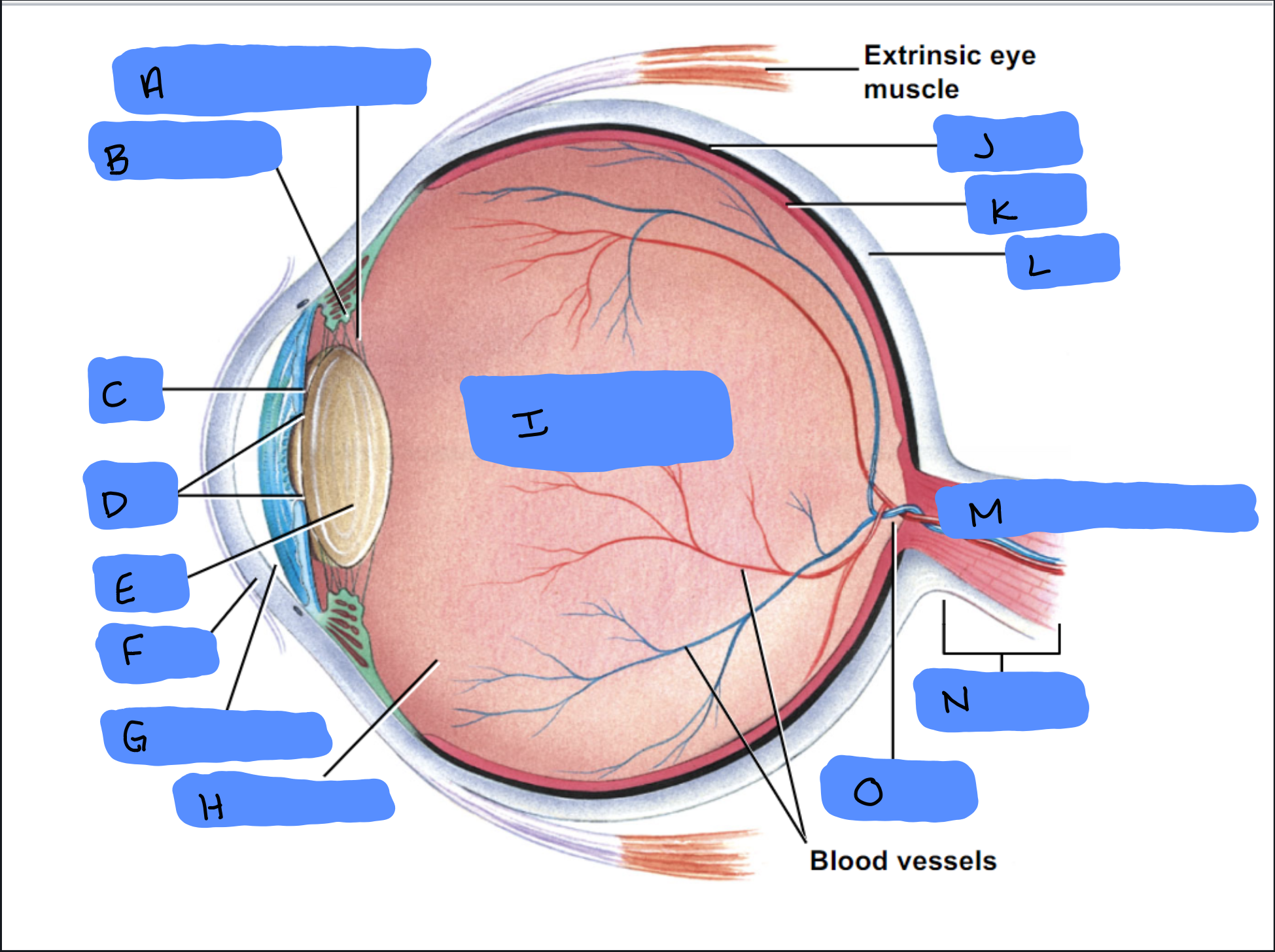
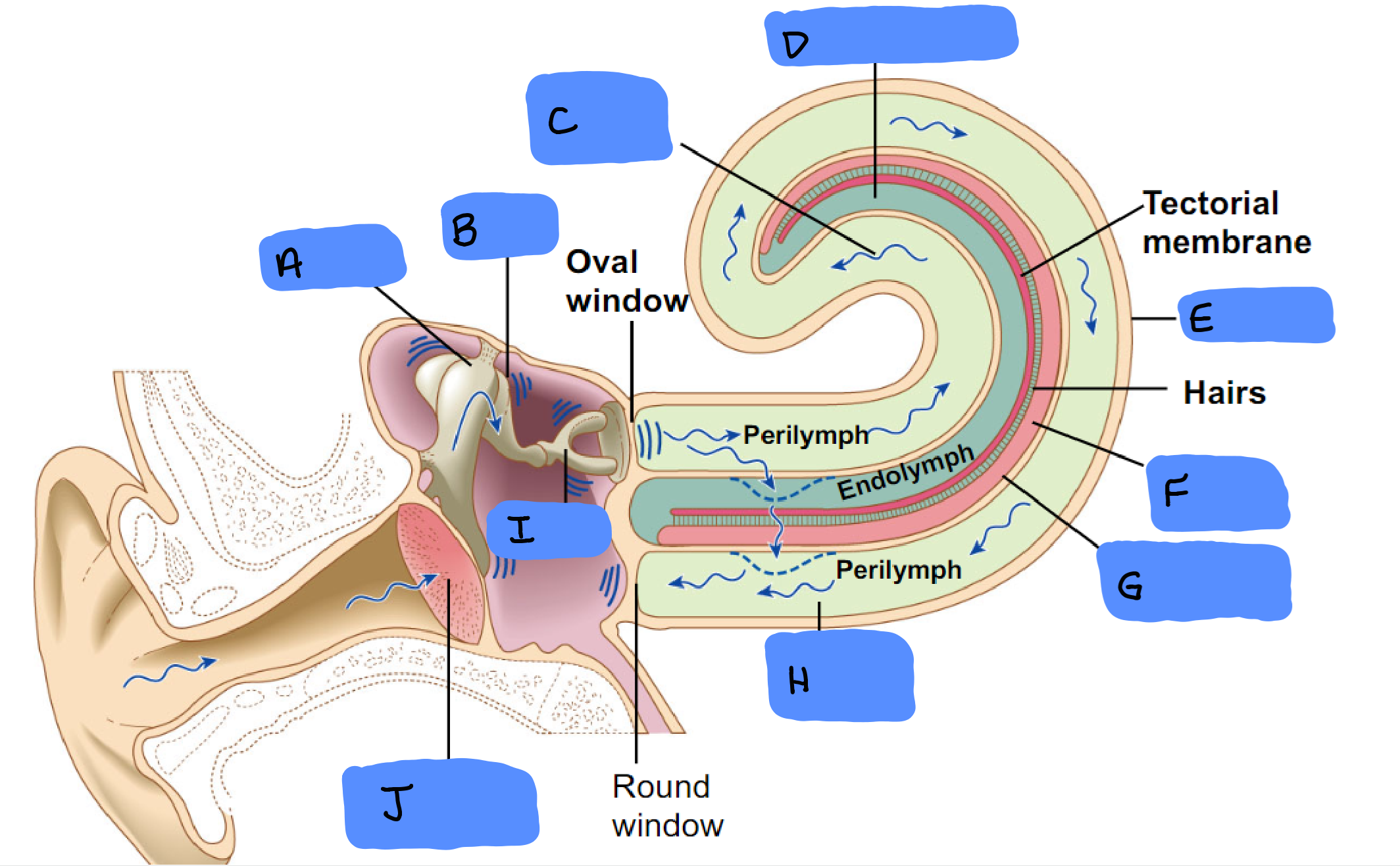
Malleus
A
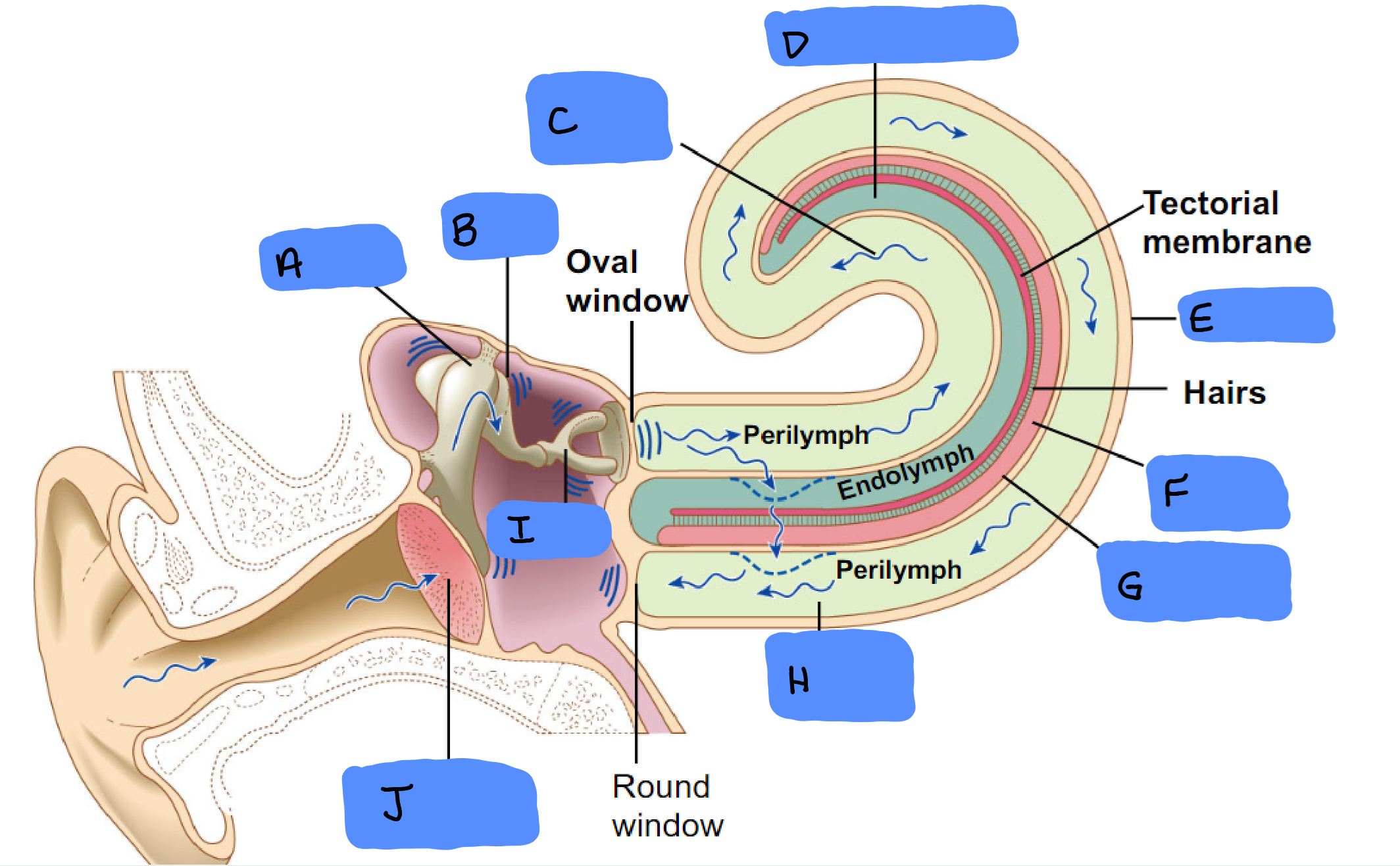
Incus
B
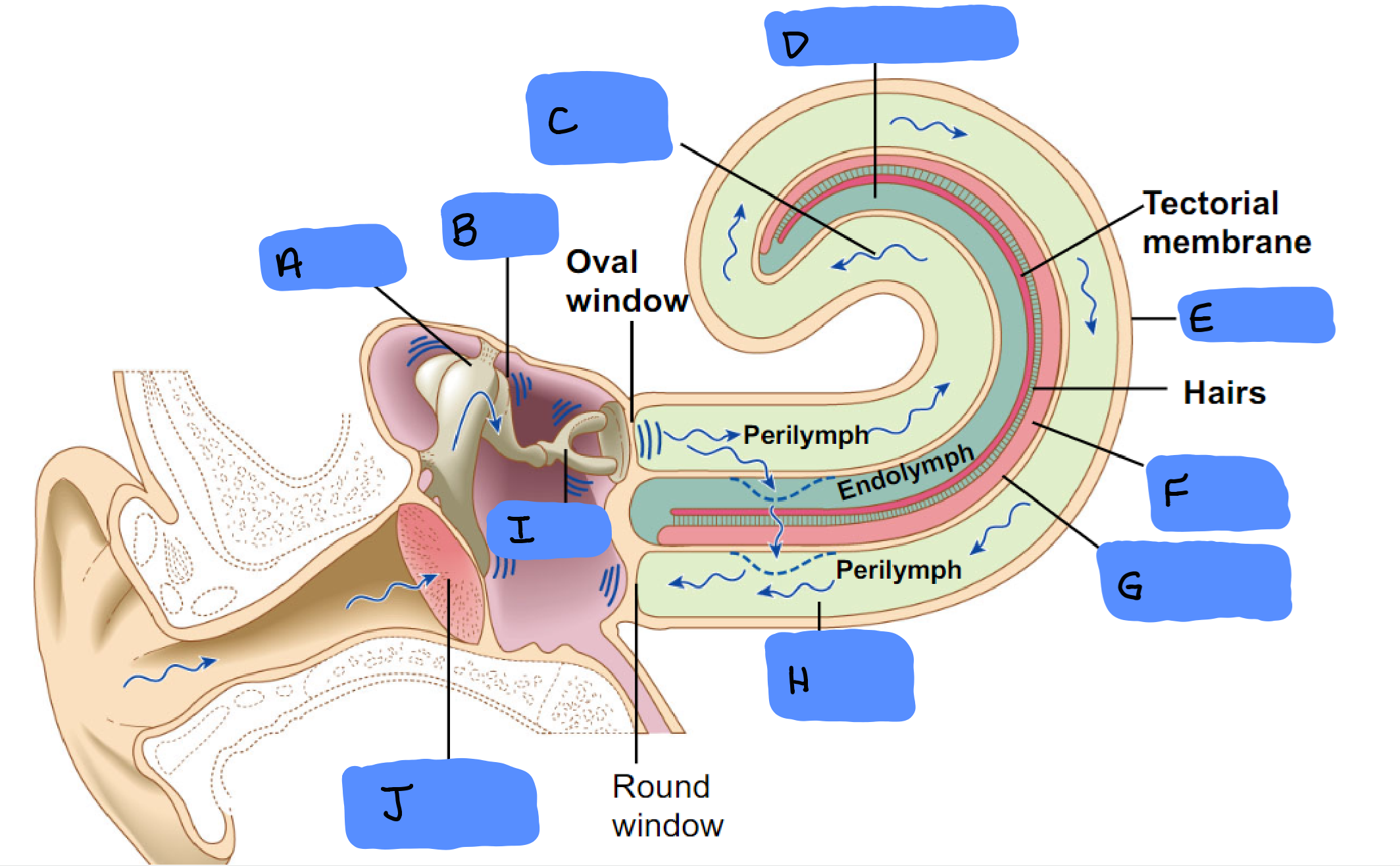
Scala Vestibuli
C
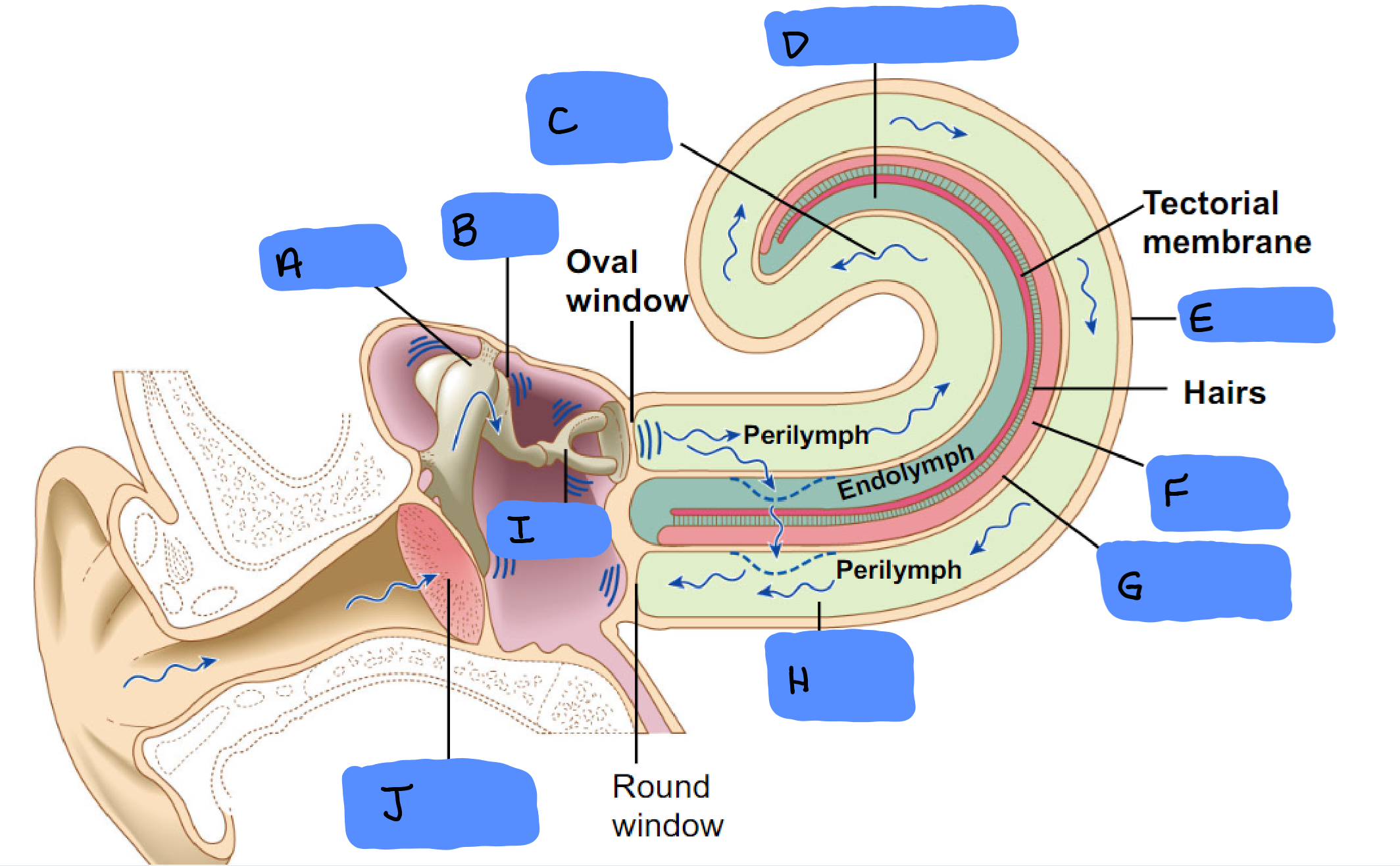
Cochlear Duct
D
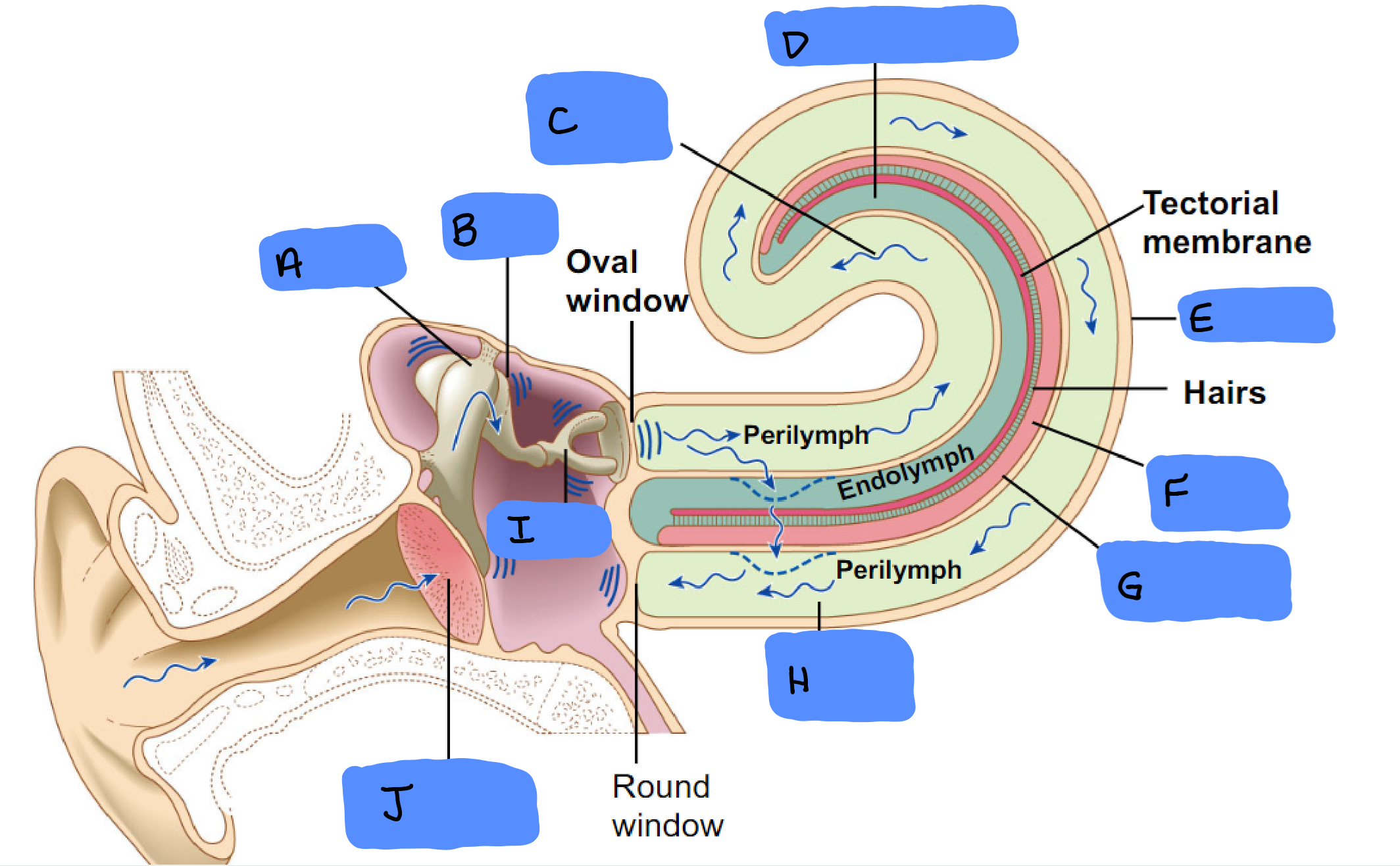
Cochlea
E
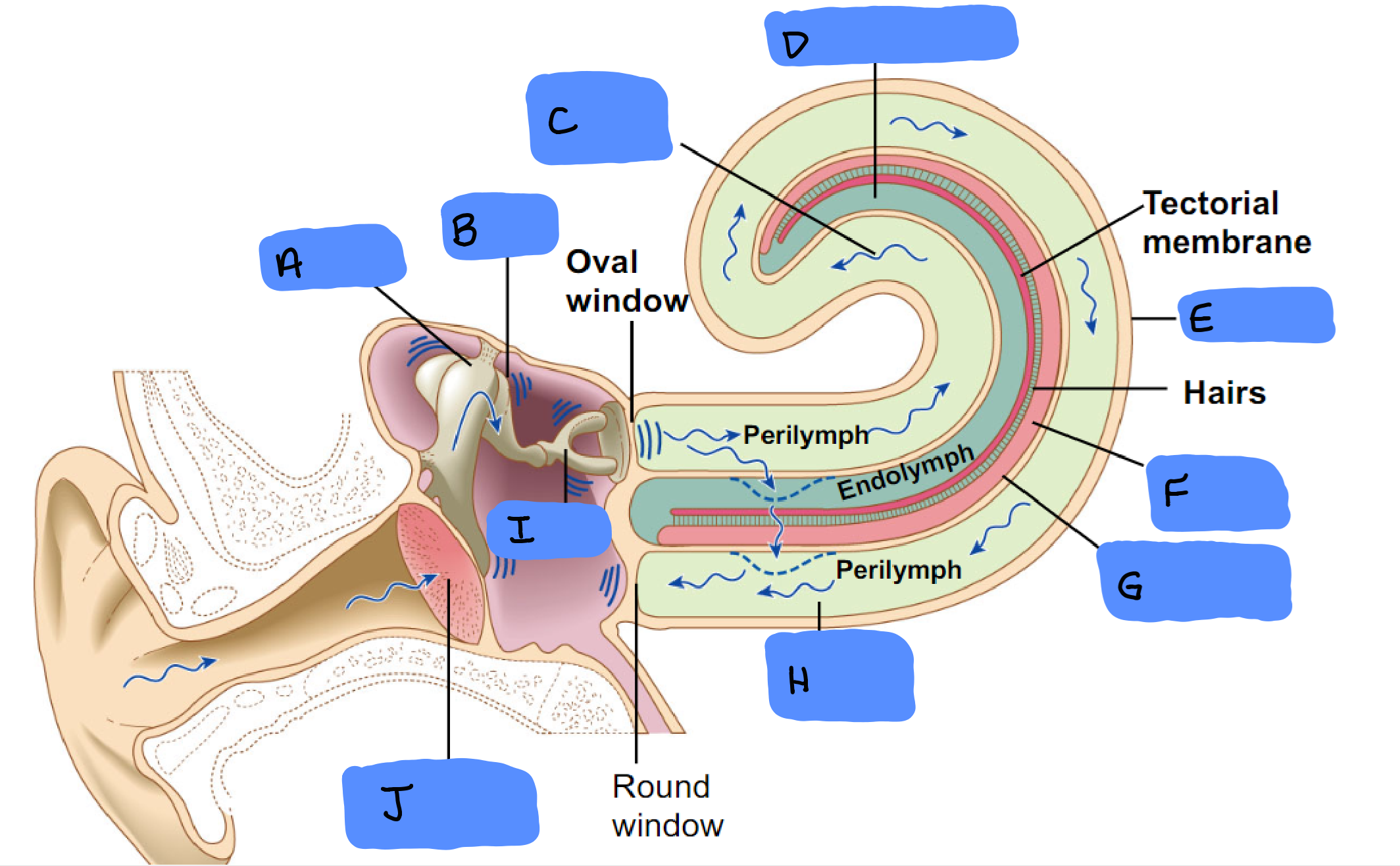
Organ of Corti
F
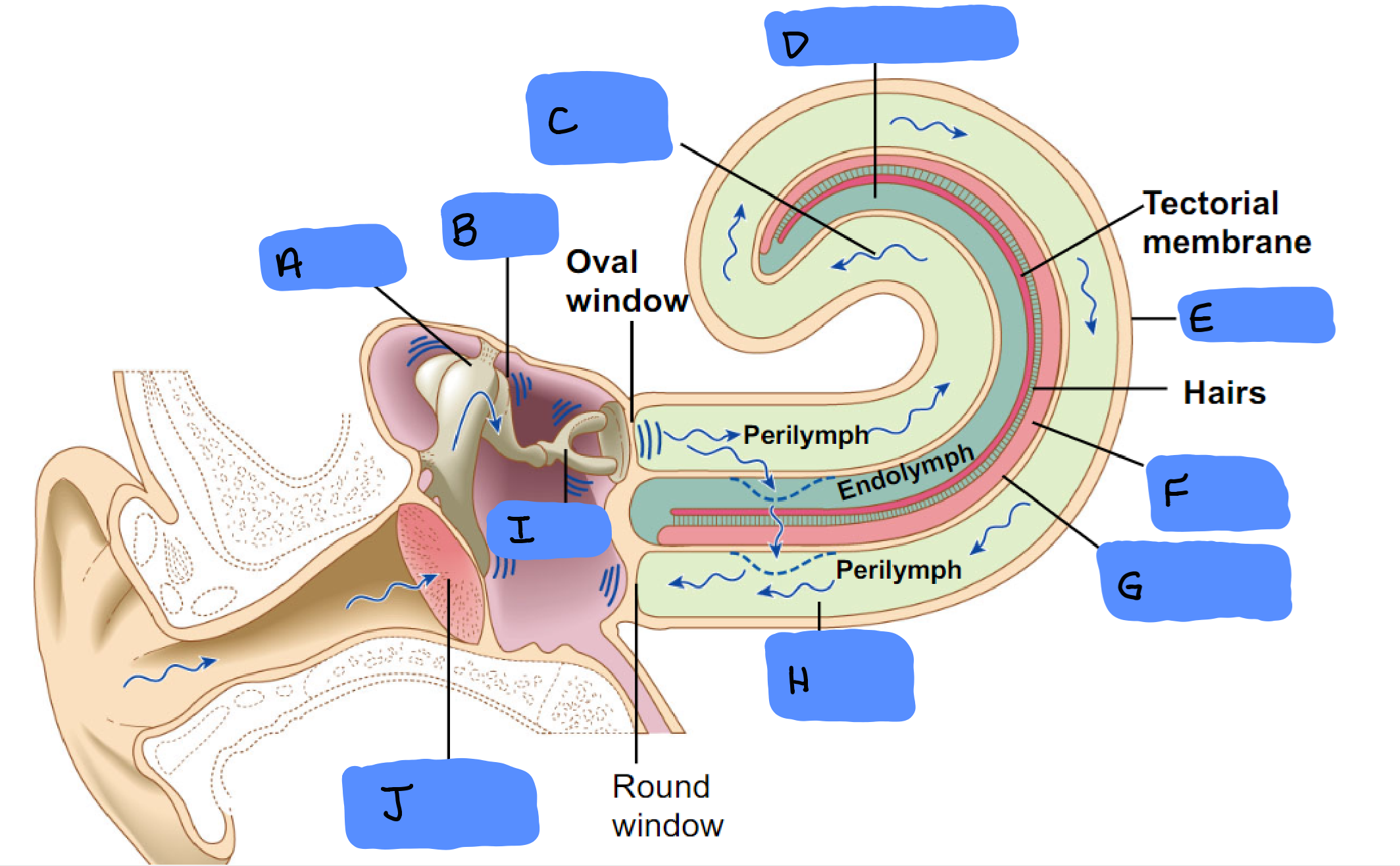
Basilar Membrane
G
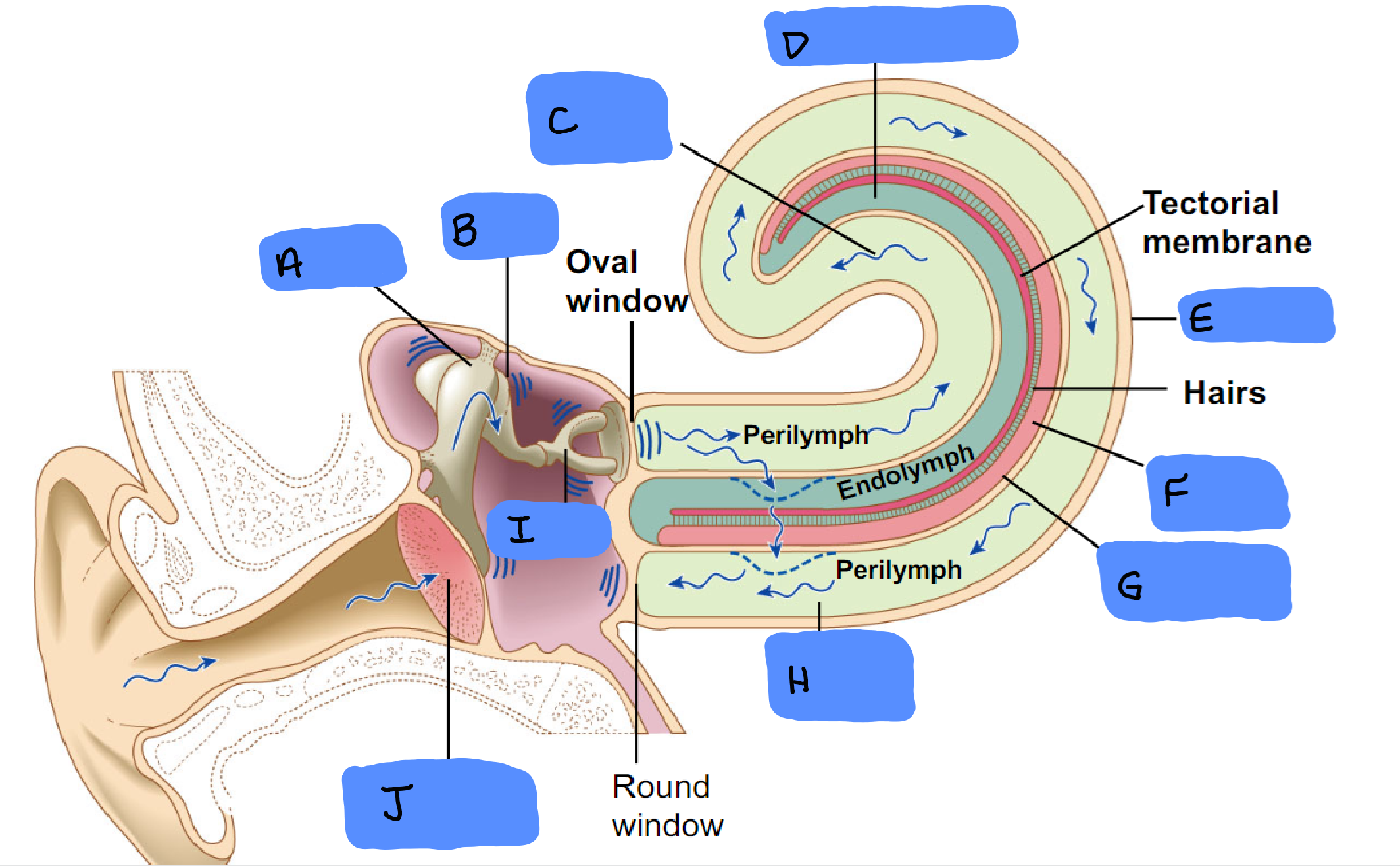
Scala Tympani
H
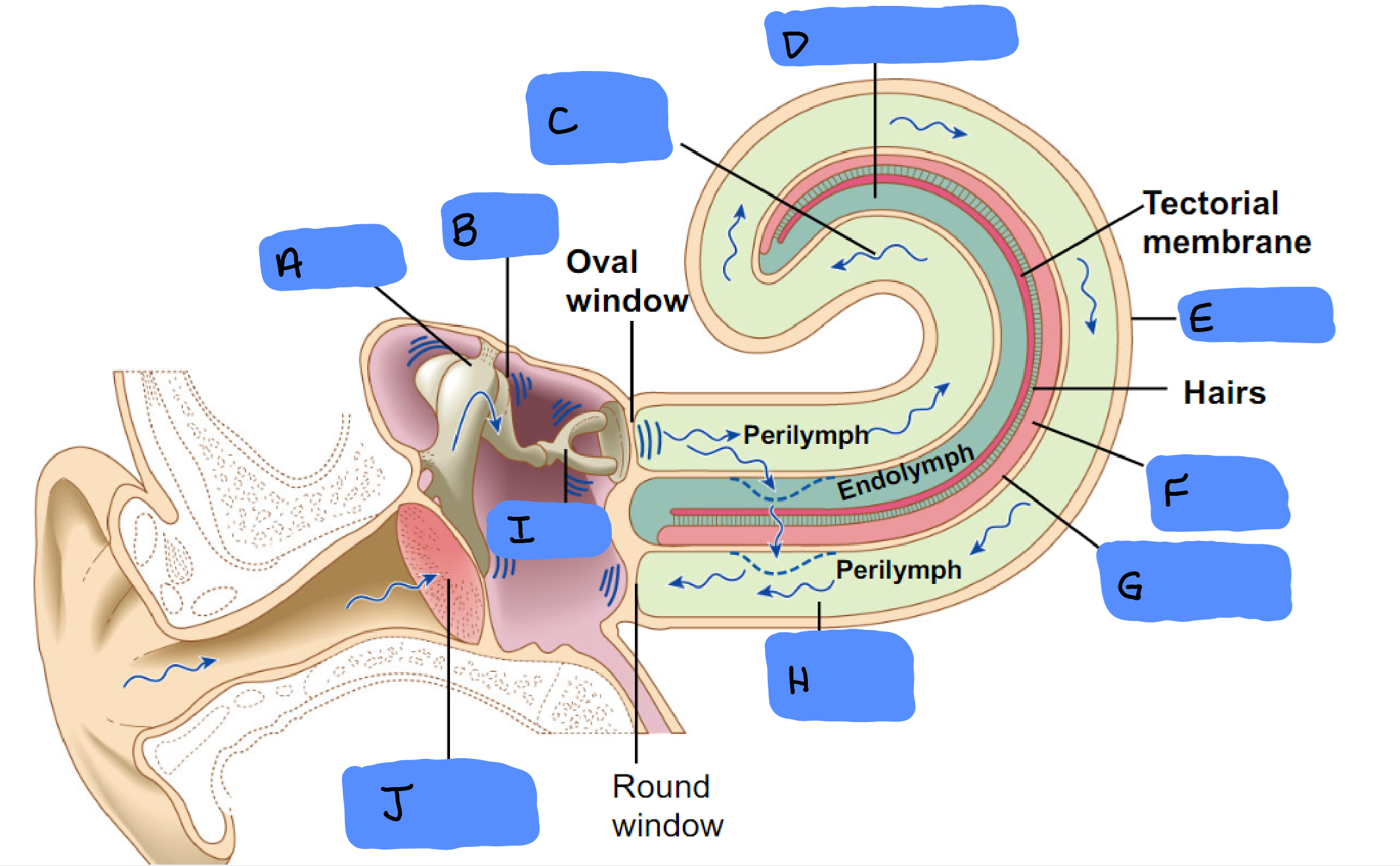
Tympanic Membrane
J
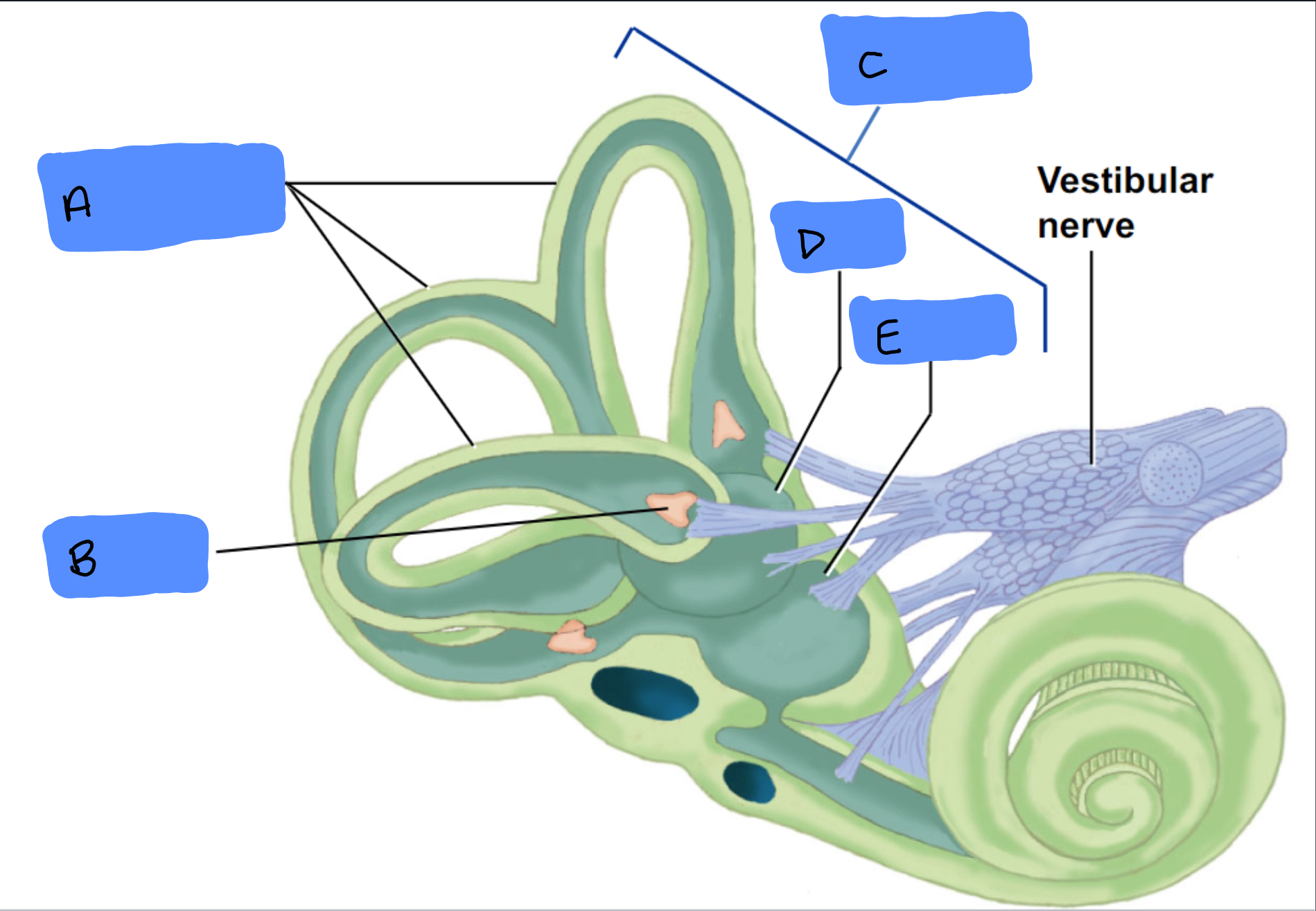
Semicircular Canals
A
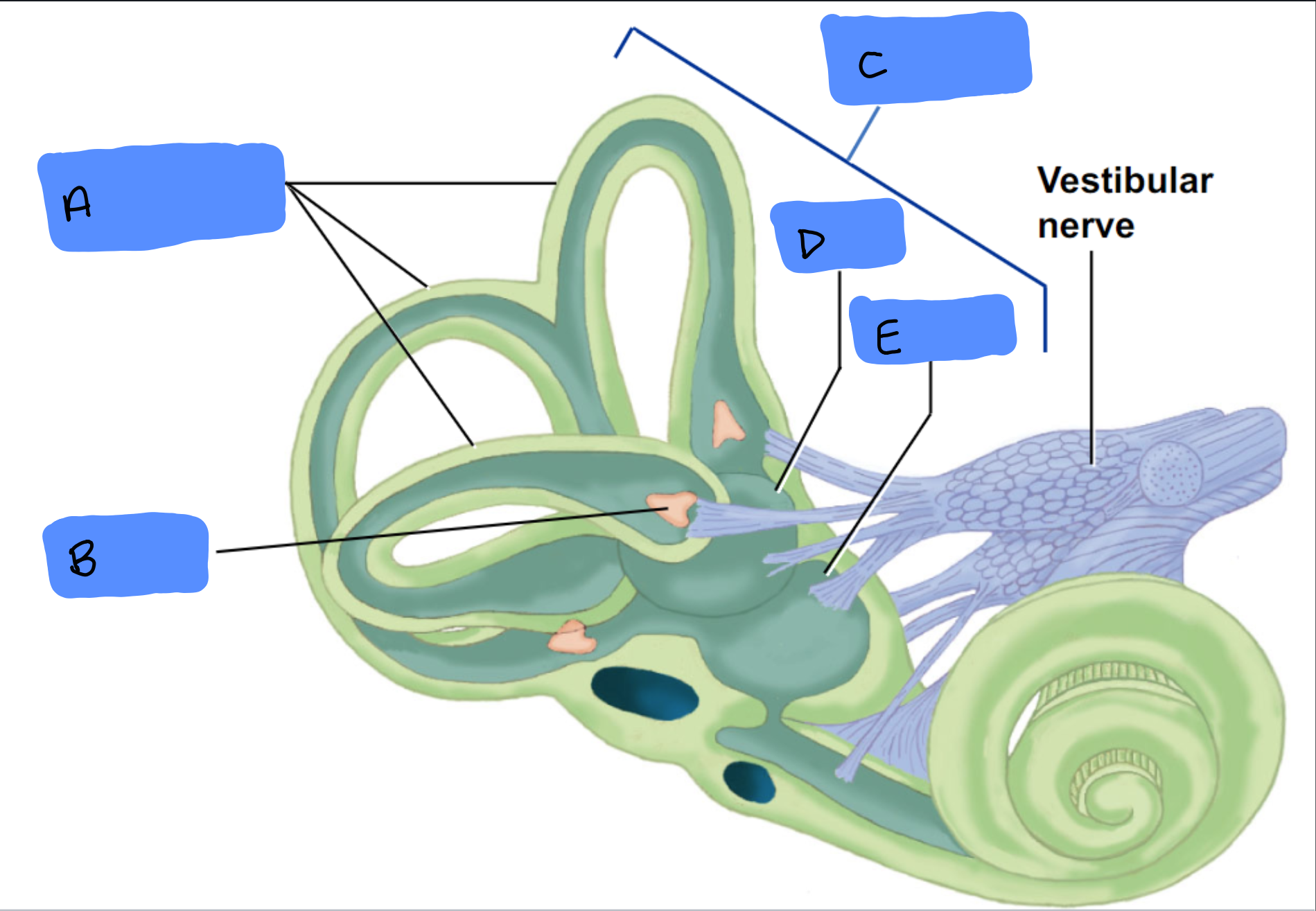
Ampulla
B
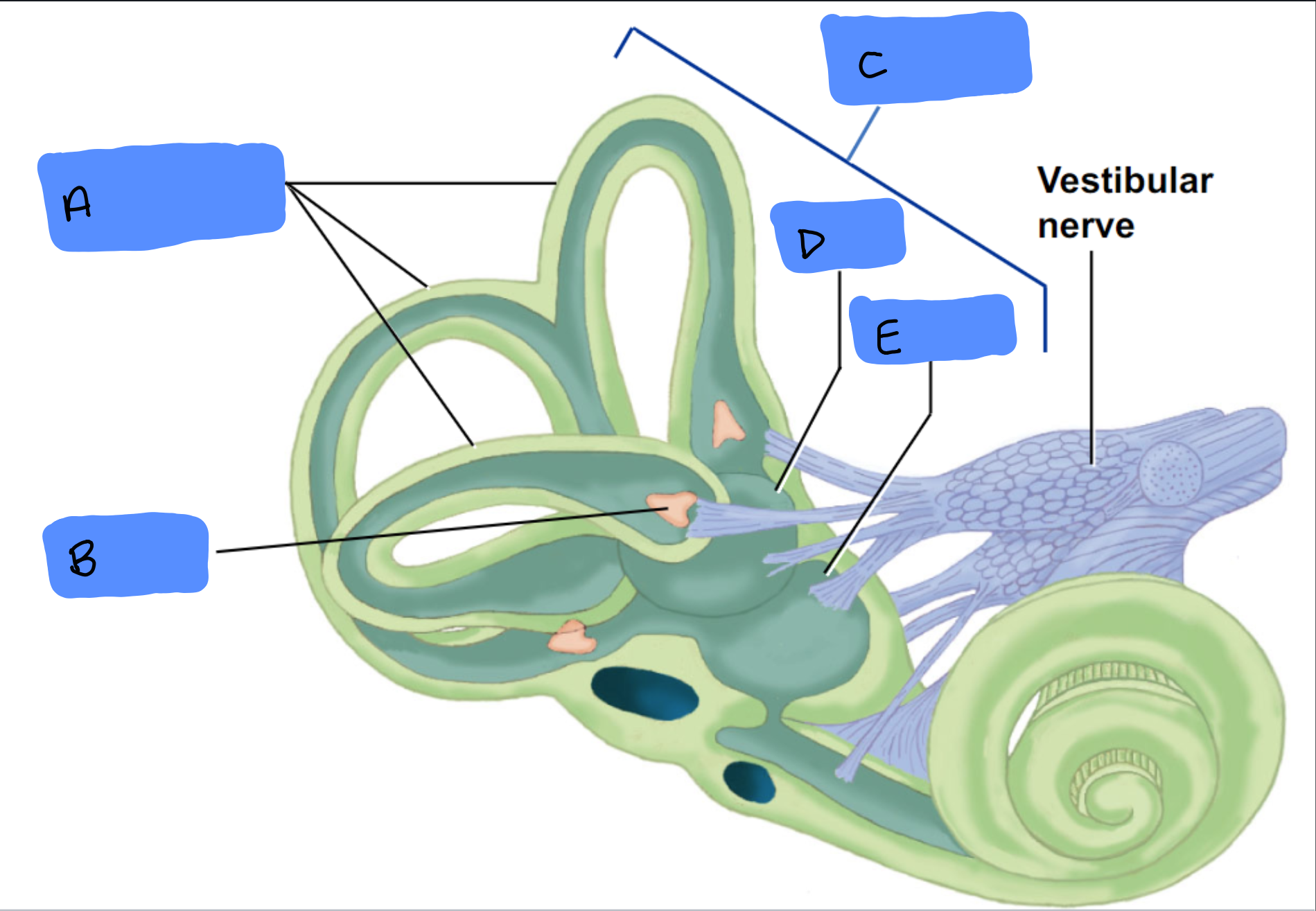
Vestibular Apparatus
C
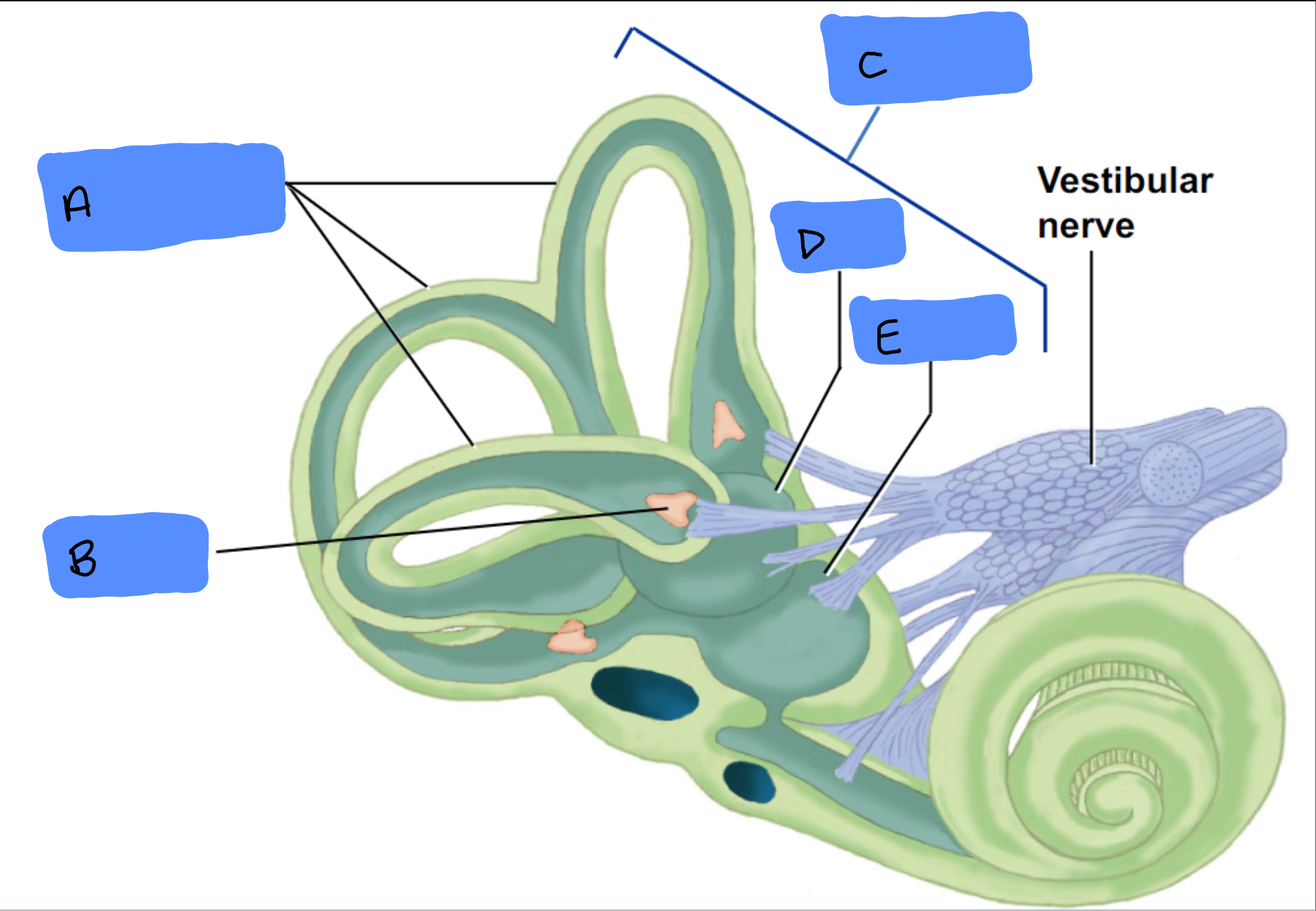
Utricle
D
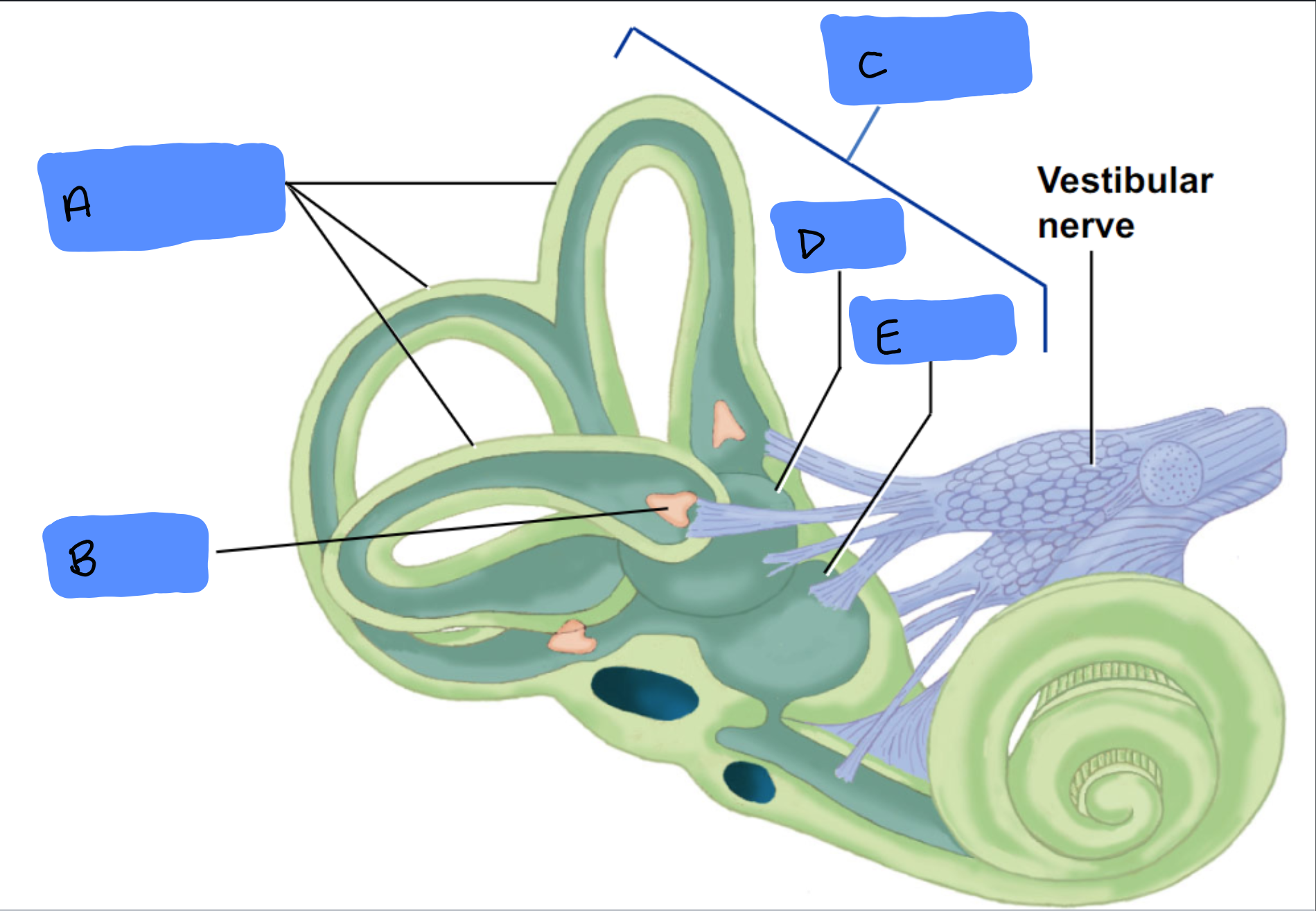
Saccule
E
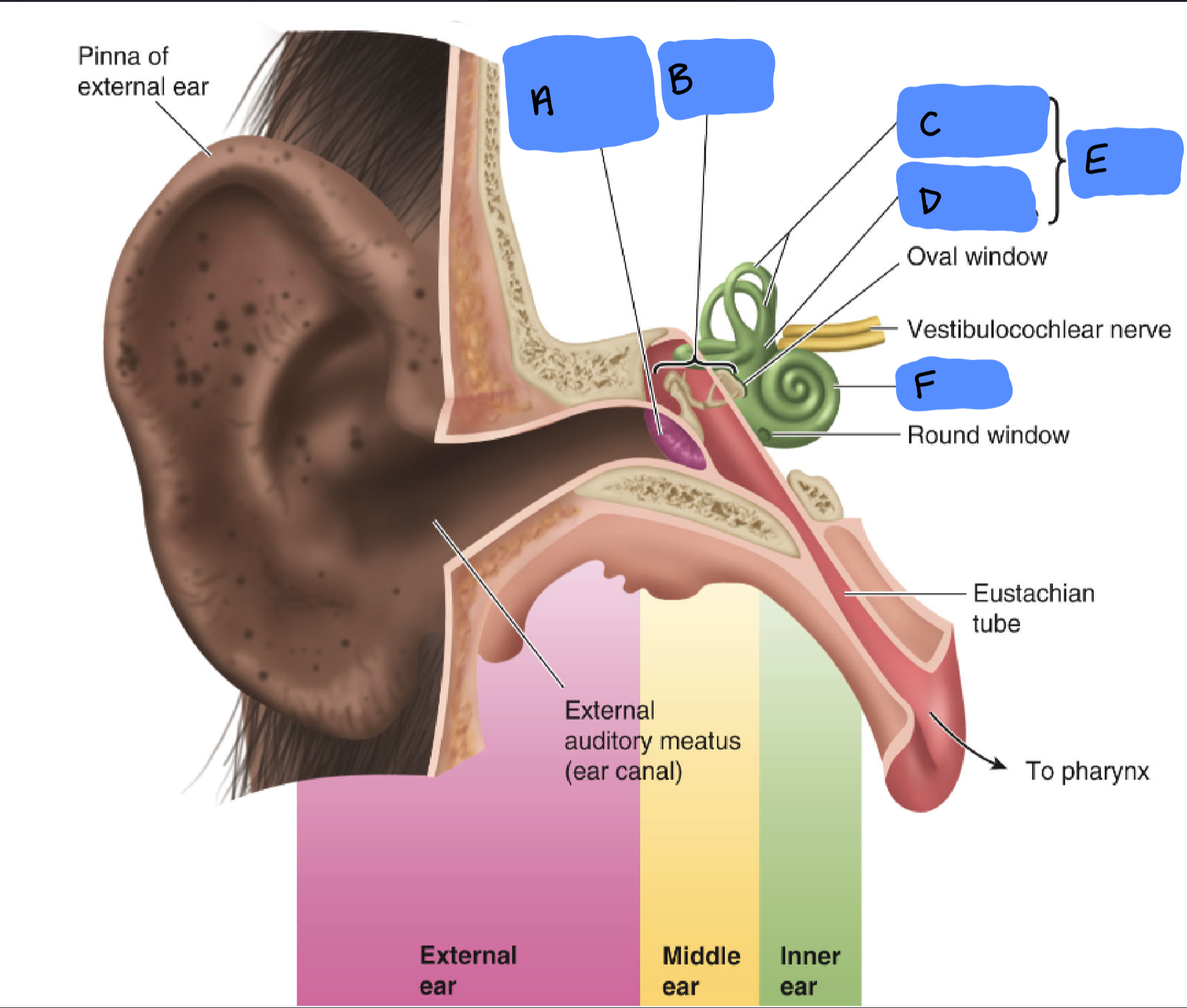
Tympanic Membrane
A
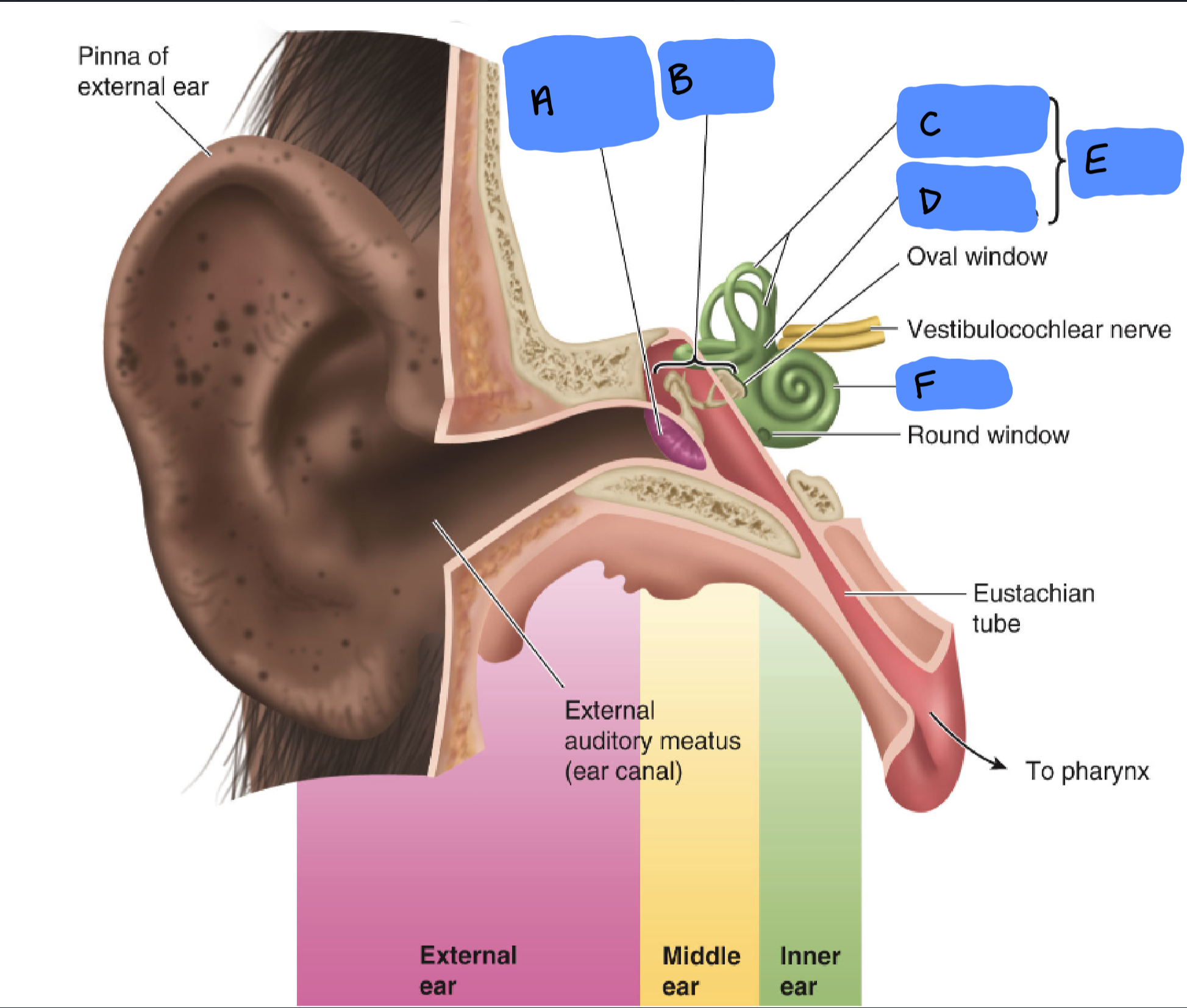
Ossicles
B
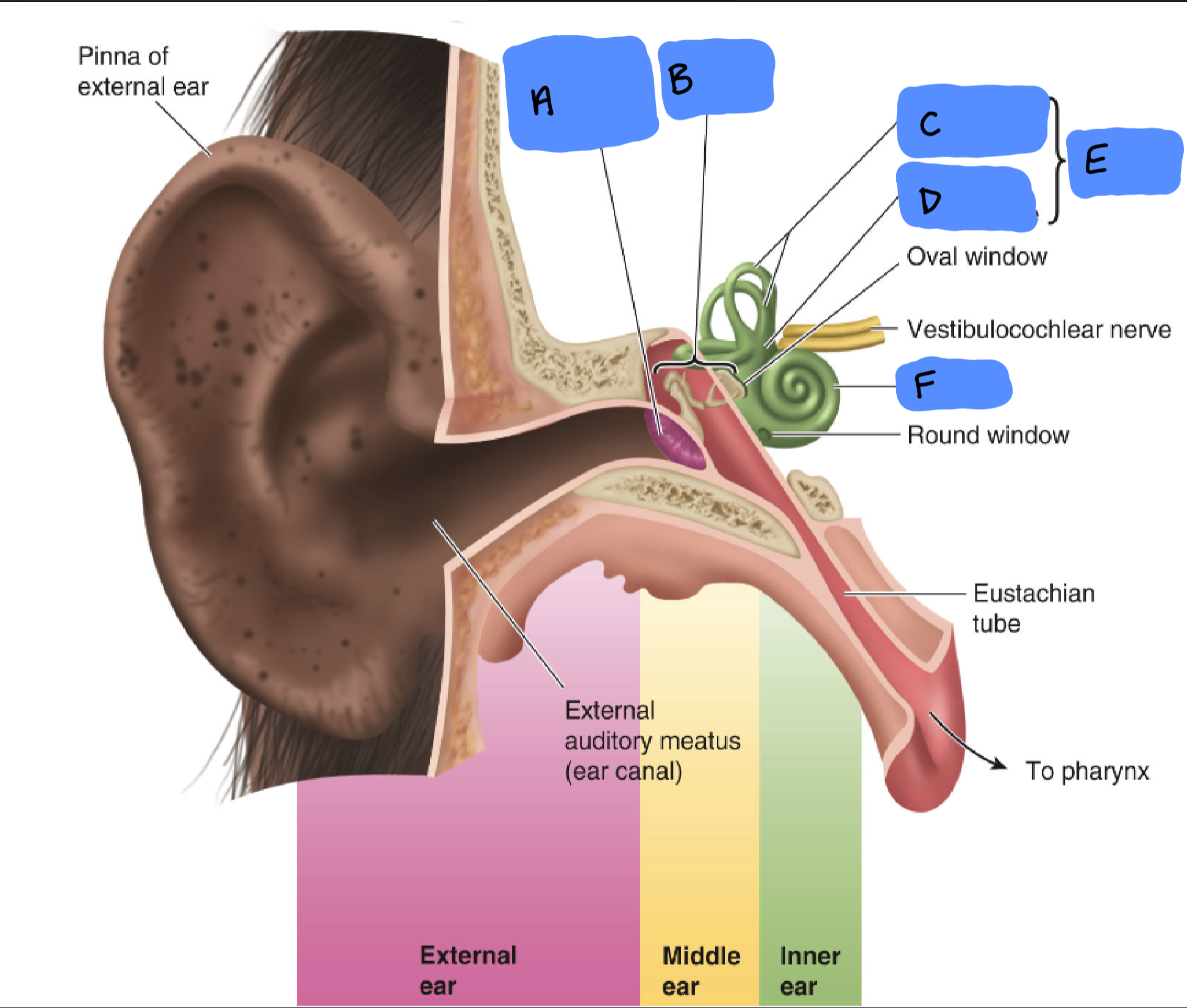
Semicircular Canals
C
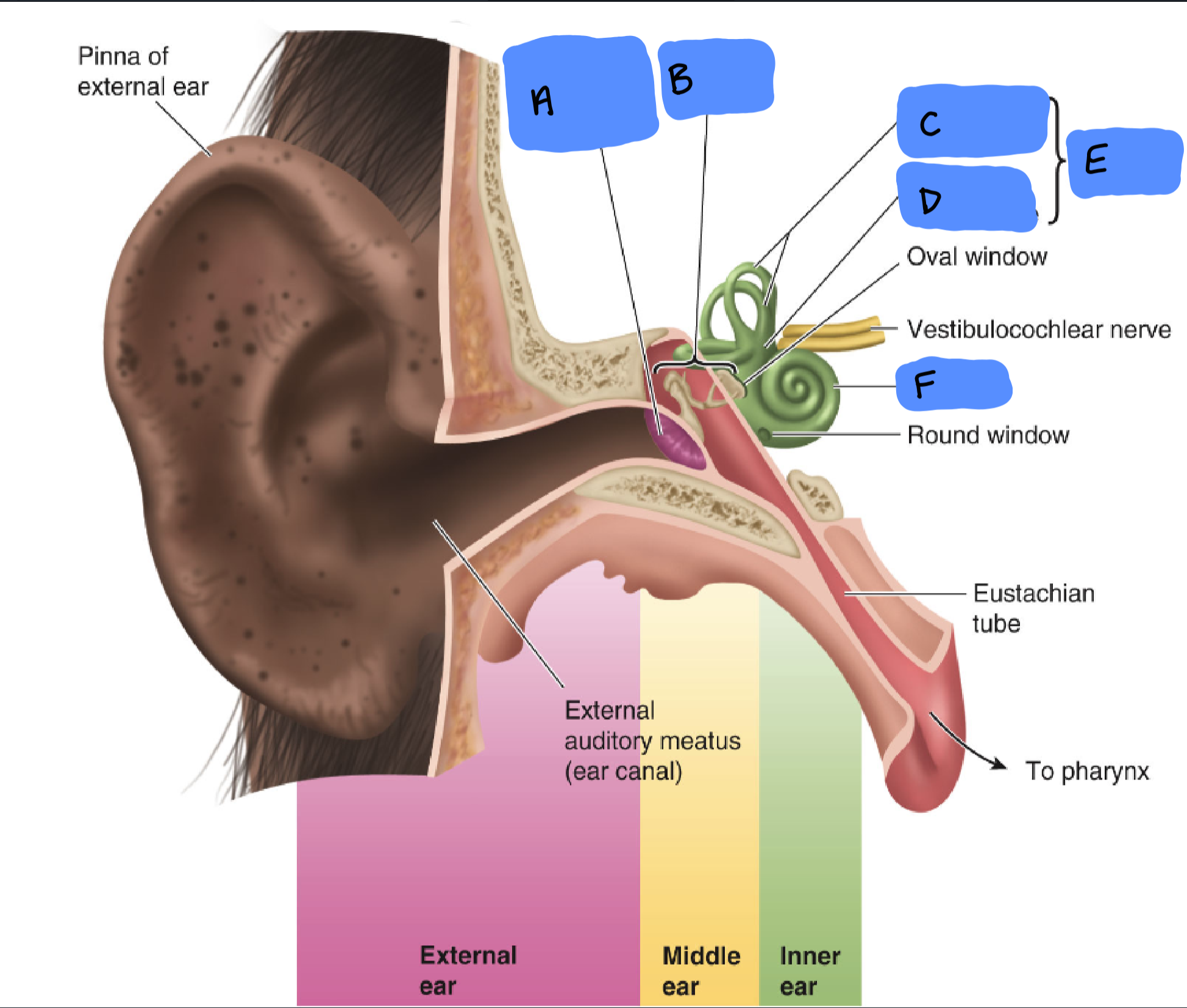
Utricle and Saccule
D
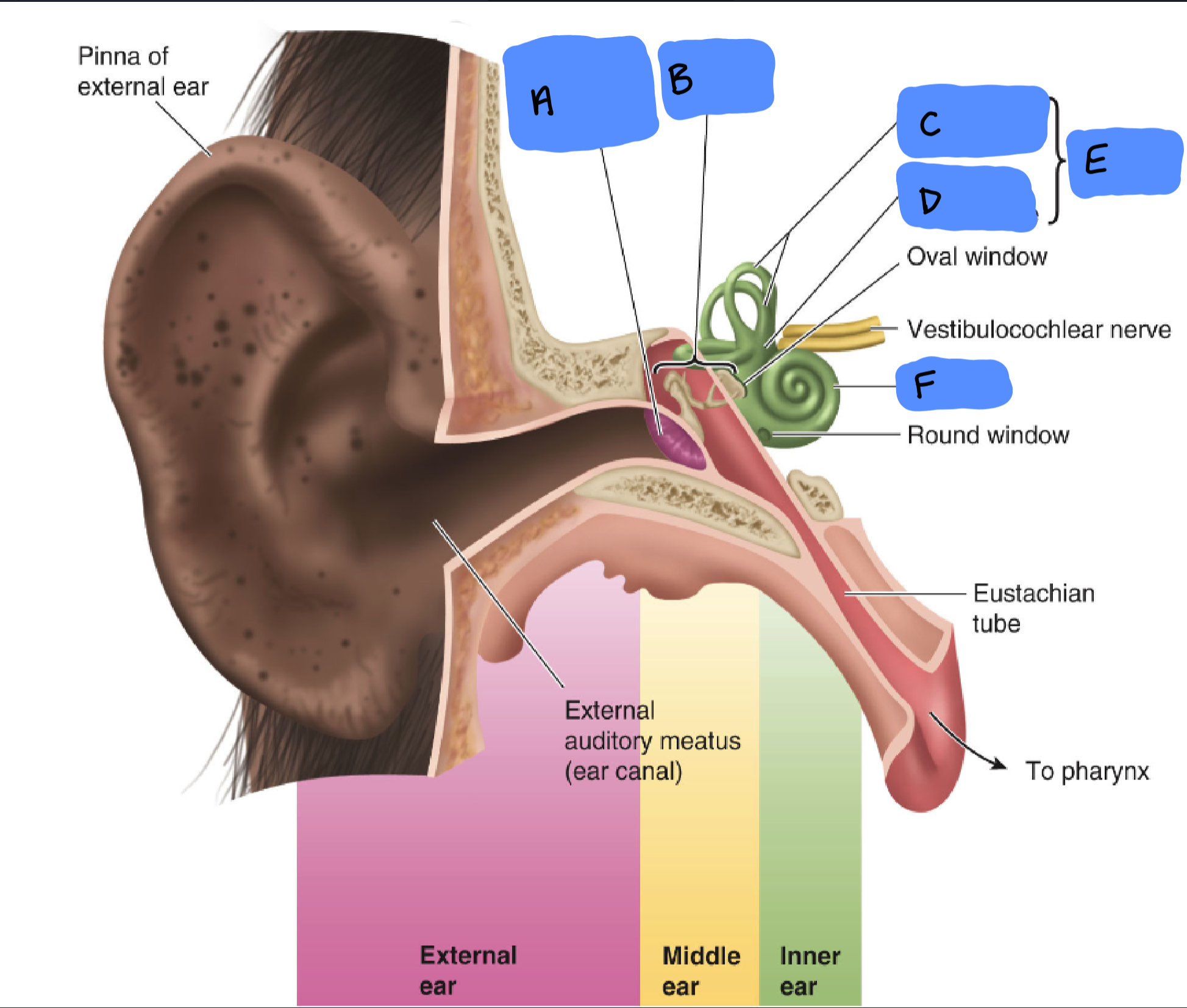
Vestibular Apparatus
E