Practical 1 Wishlists
1/71
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
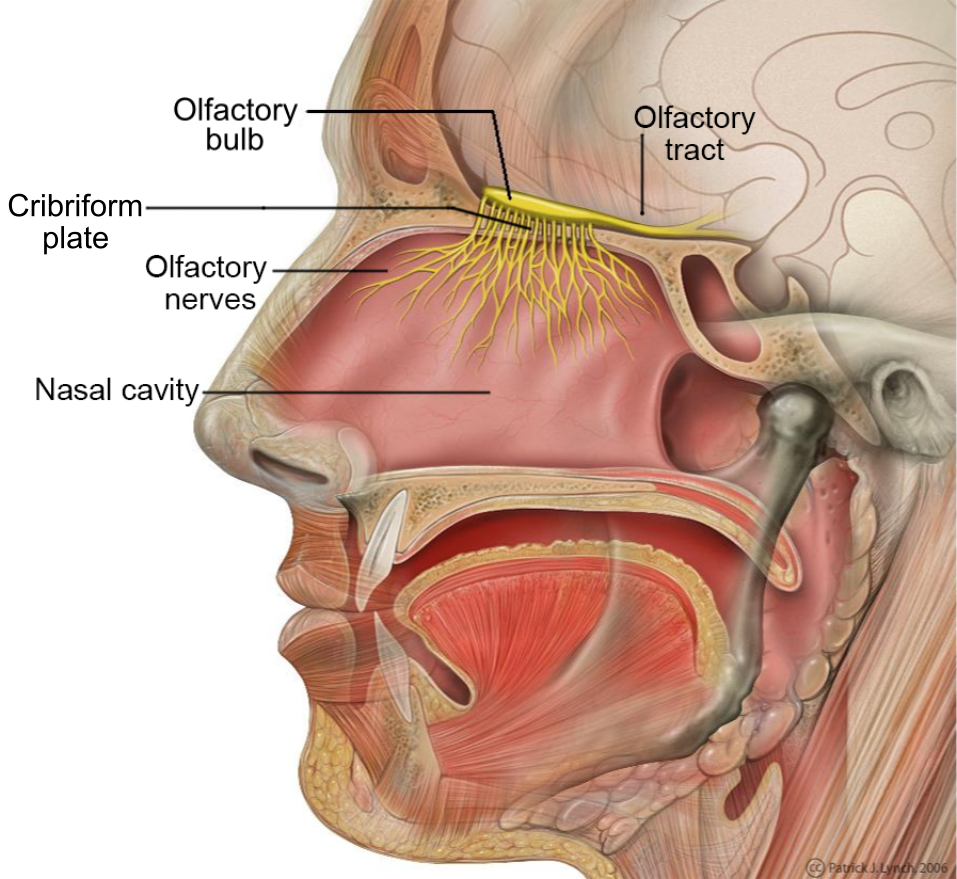
olfactory tract
a bundle of nerve fibers in the brain that transmits smell information from the olfactory bulb to higher brain regions; the neural pathway that carries signals from the olfactory bulb, allowing for the conscious perception and processing of odors and the triggering of memories associated with smells.
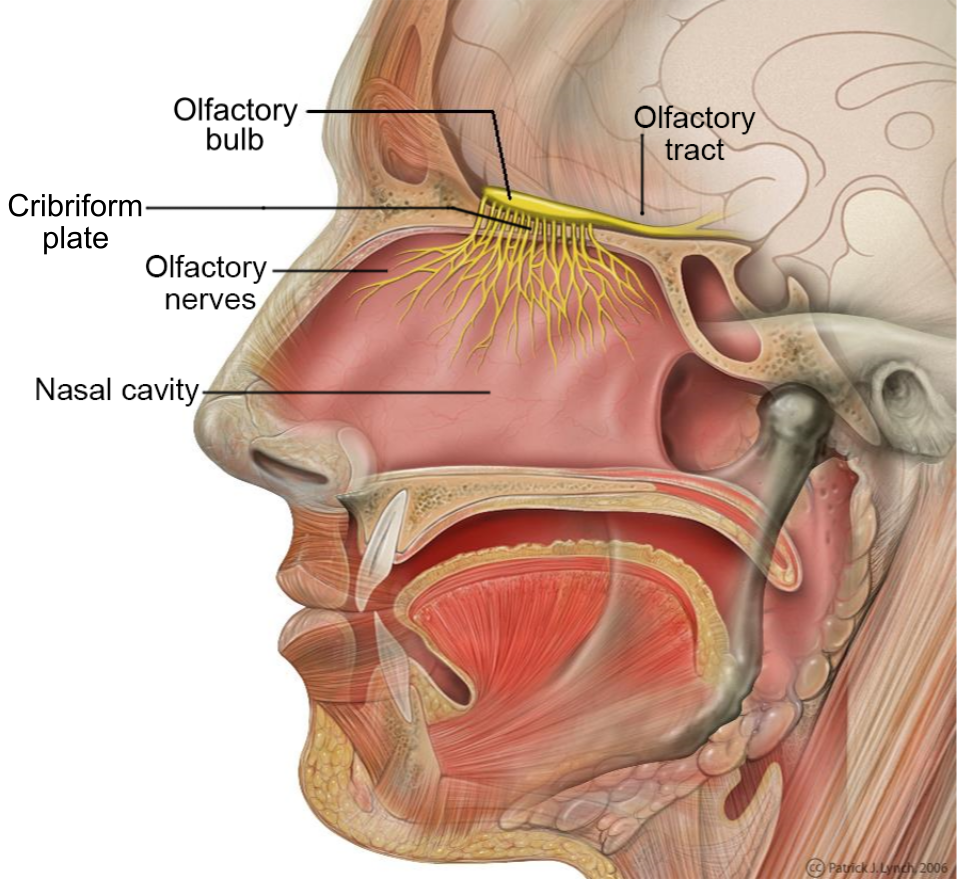
olfactory bulb
part of the brain located in the frontal love that processes smells by receiving signals from the olfactory epithelium int he nose; essential for olfactory transduction, where odor molecules detected in the nasal cavities are transformed into neural signals
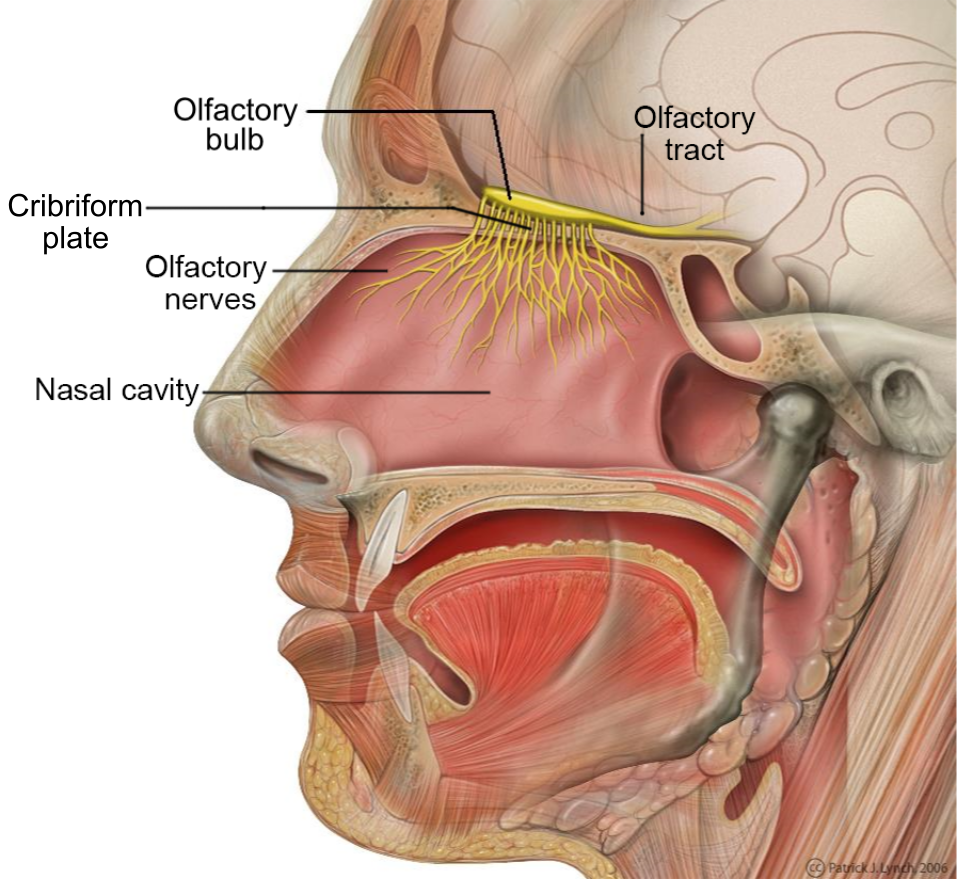
olfactory epithelium
a specialized sensory tissue in the upper nasal cavity that detects odors and is responsible for the sense of smell; neuroepithelium
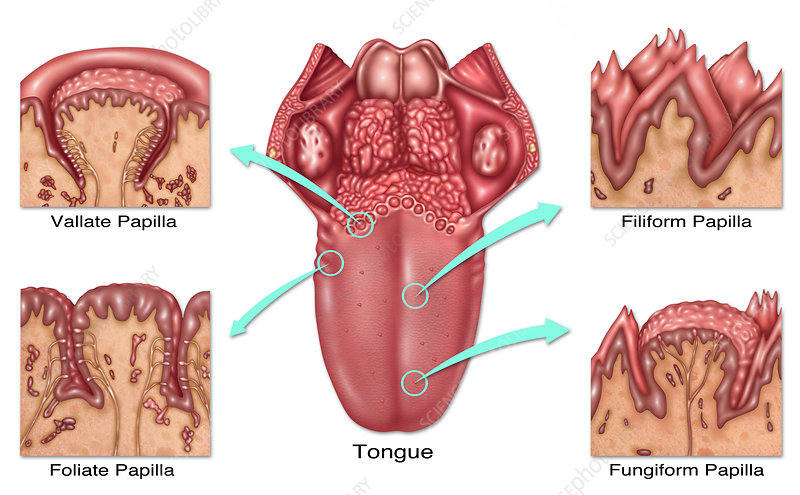
foliate papillae
leaf like, short vertical folds located on the sides of the back of the tongue
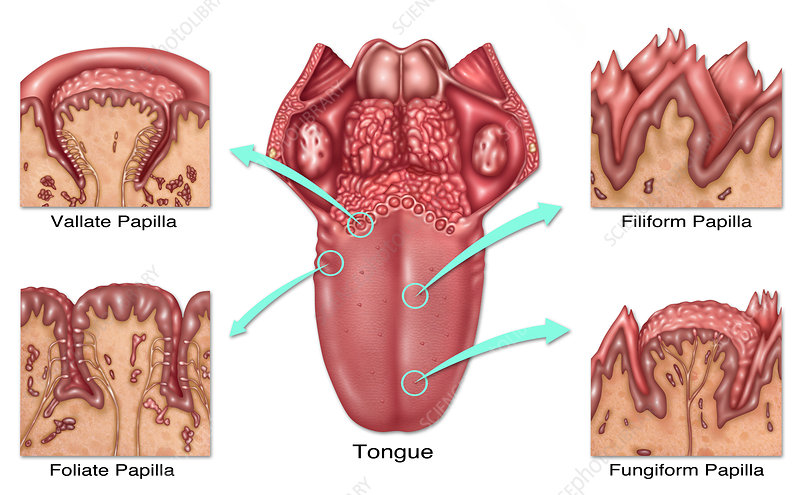
fungiform papillae
mushroom-shaped protrusions on the tongue’s surface that house taste buds, which detect flavors, temperature and touch
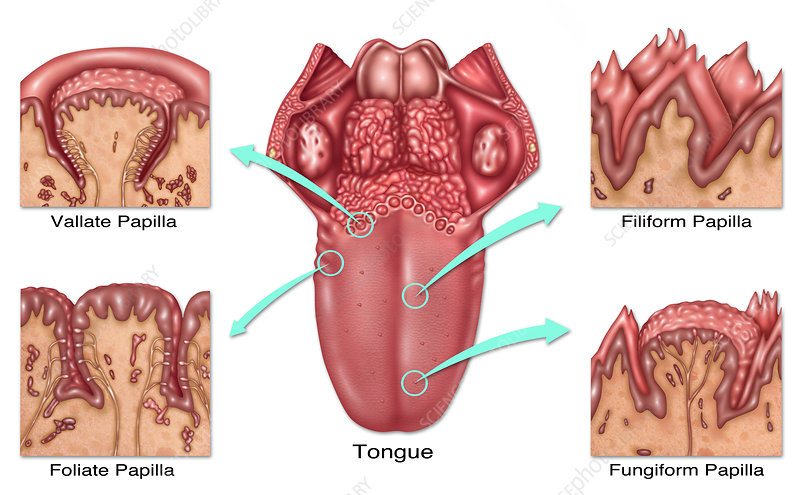
vallate papillae
large, prominent papillae on the back of the tongue that arranged in a v-shaped row
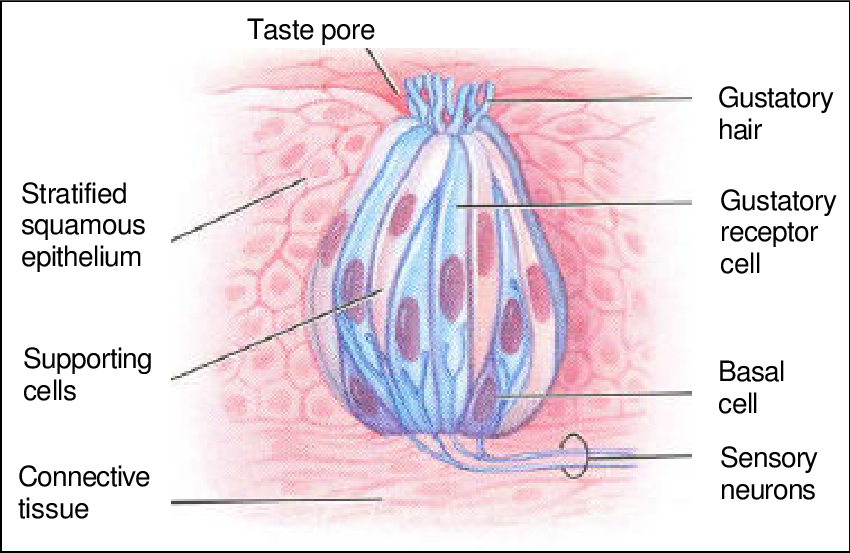
taste buds
sensory organs located on the tongue, soft palate, and throat; responsible for detecting and transmitting taste sensations to the brain
two point discrimination
a non-invasive test of tactile senses that measures the minimum distance at which two points can be perceived as separate; applied stimuli to the skin while the patients vision is blocked

equilibrium
the sense of balance and orientation maintained by the integration of input from the visual system, vestibular system and proprioception.
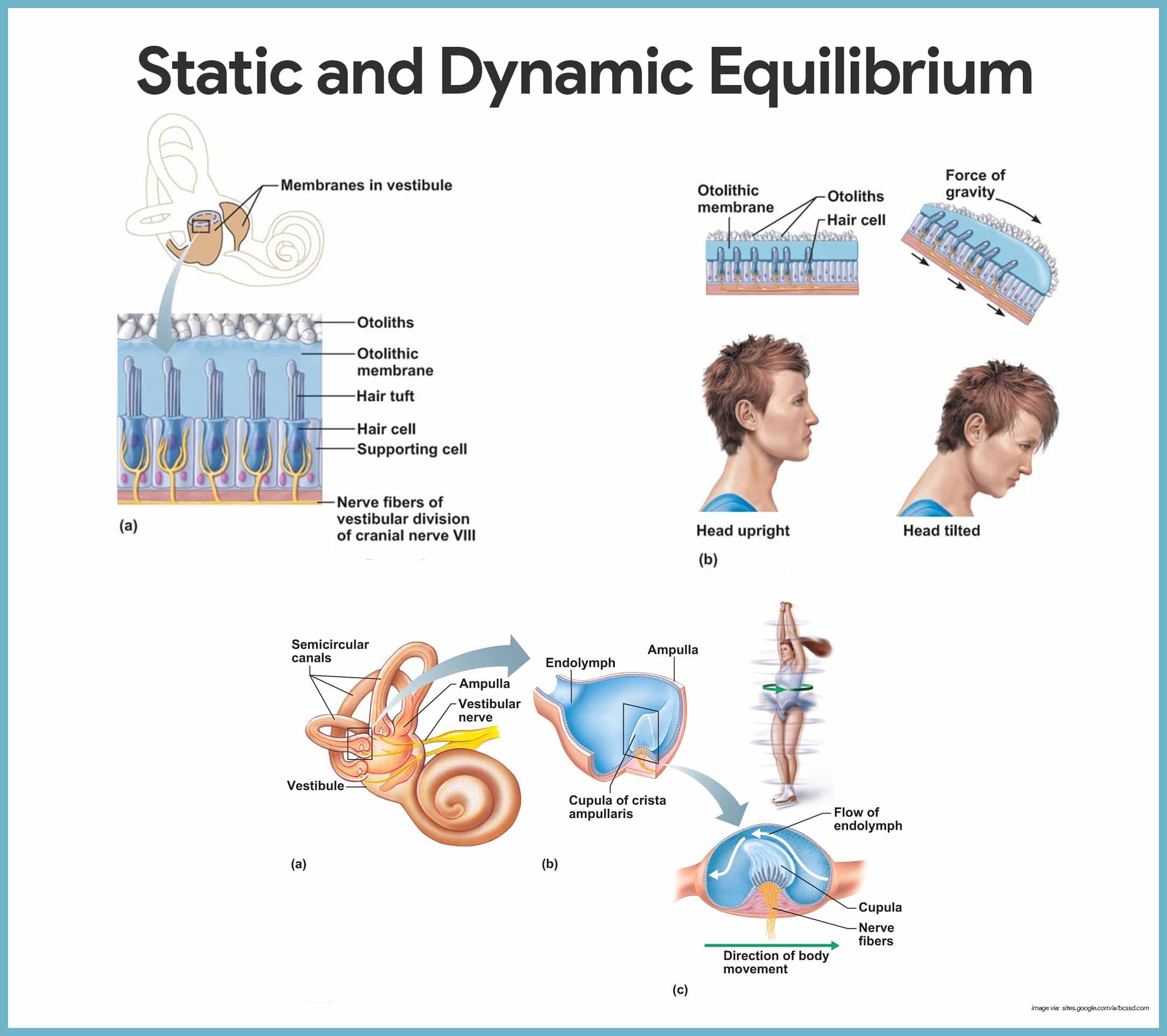
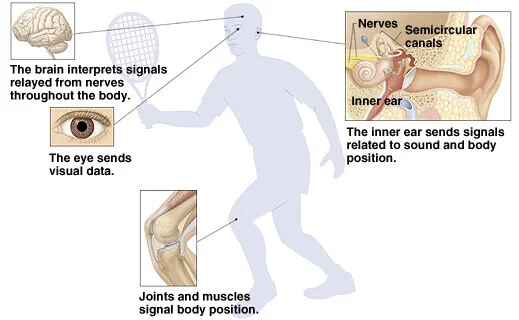
balance
reliance on the brain integrating sensory information from the vestibular system (detection of head motion and position), proprioception (information about posture & muscles & joints) and the visual system (spatial orientation relative to environment); integration used to generate motor outputs that adjust posture and eye movements to maintain stability
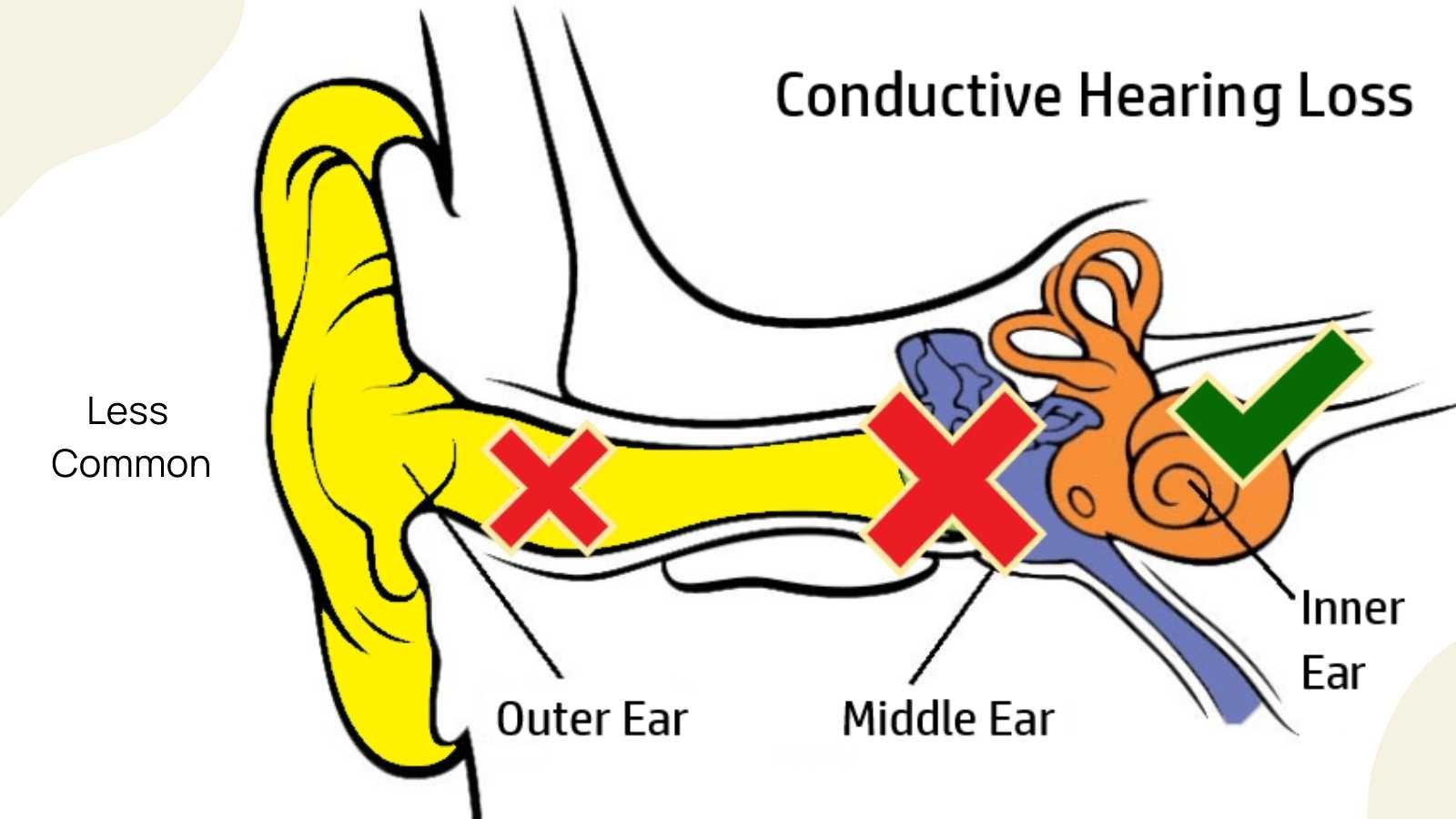
external ear
Composed of Auricle and External Auditory Meatus; the visible part of the ear that collects and directs sound waves towards the middle ear.
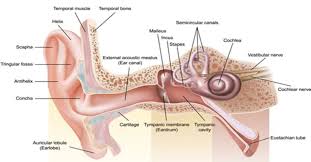
auricle
the visible outer part of the ear primarily made of cartilage and covered ins kin, including the earlobe.
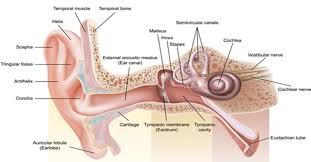
external auditory meatus
a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear
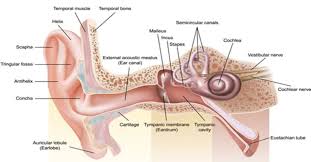
middle ear
composed of auditory tube and tympanic membrane; air-filled cavity located between the eardrum and the inner ear, has ossicles that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
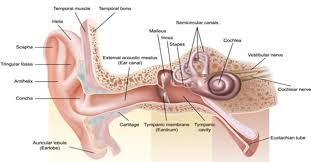
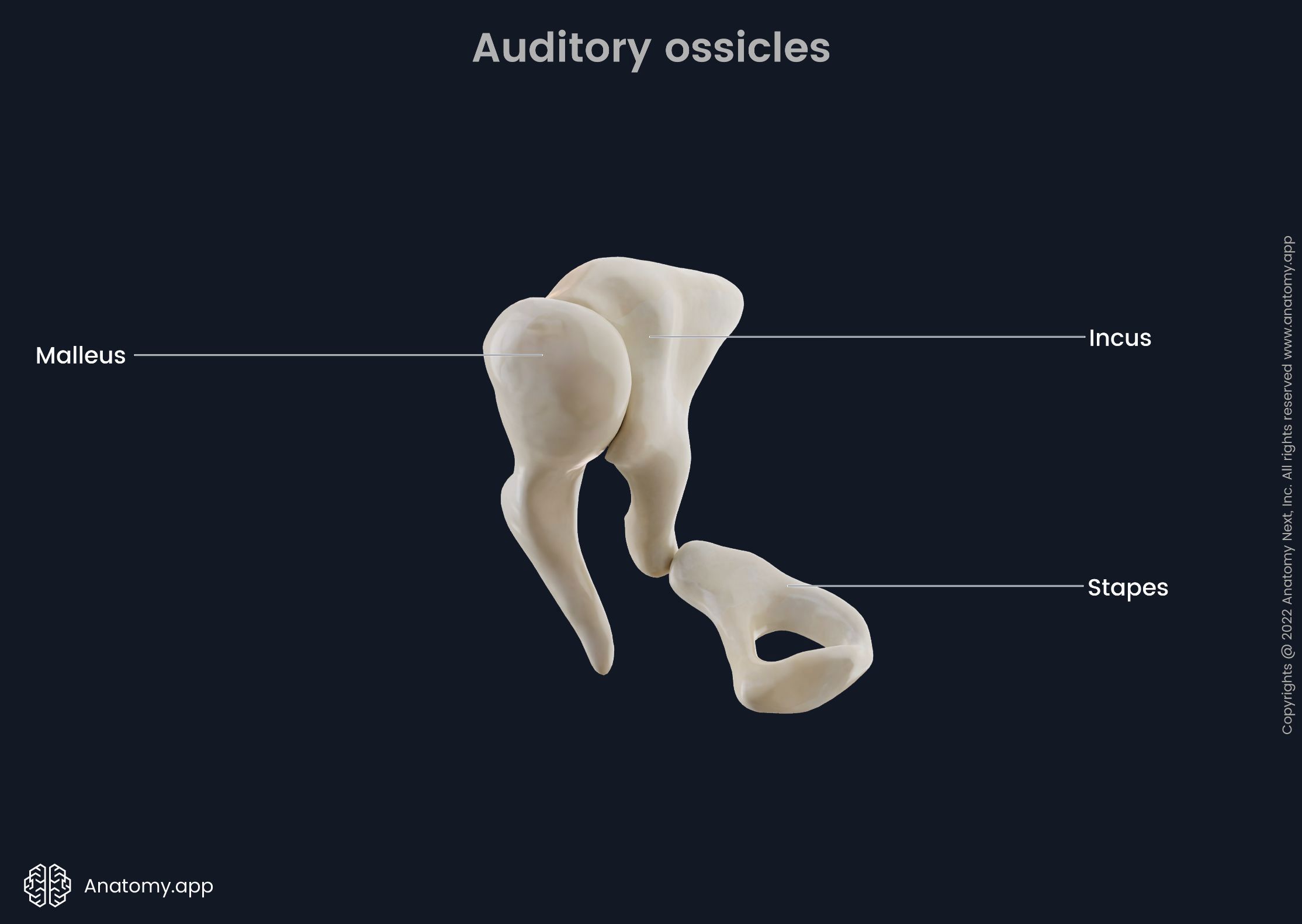
ossicles
composed of Malleus, incus and stapes; three irregular bones in the middle ear that move sound vibrations from eardrum to cochlea
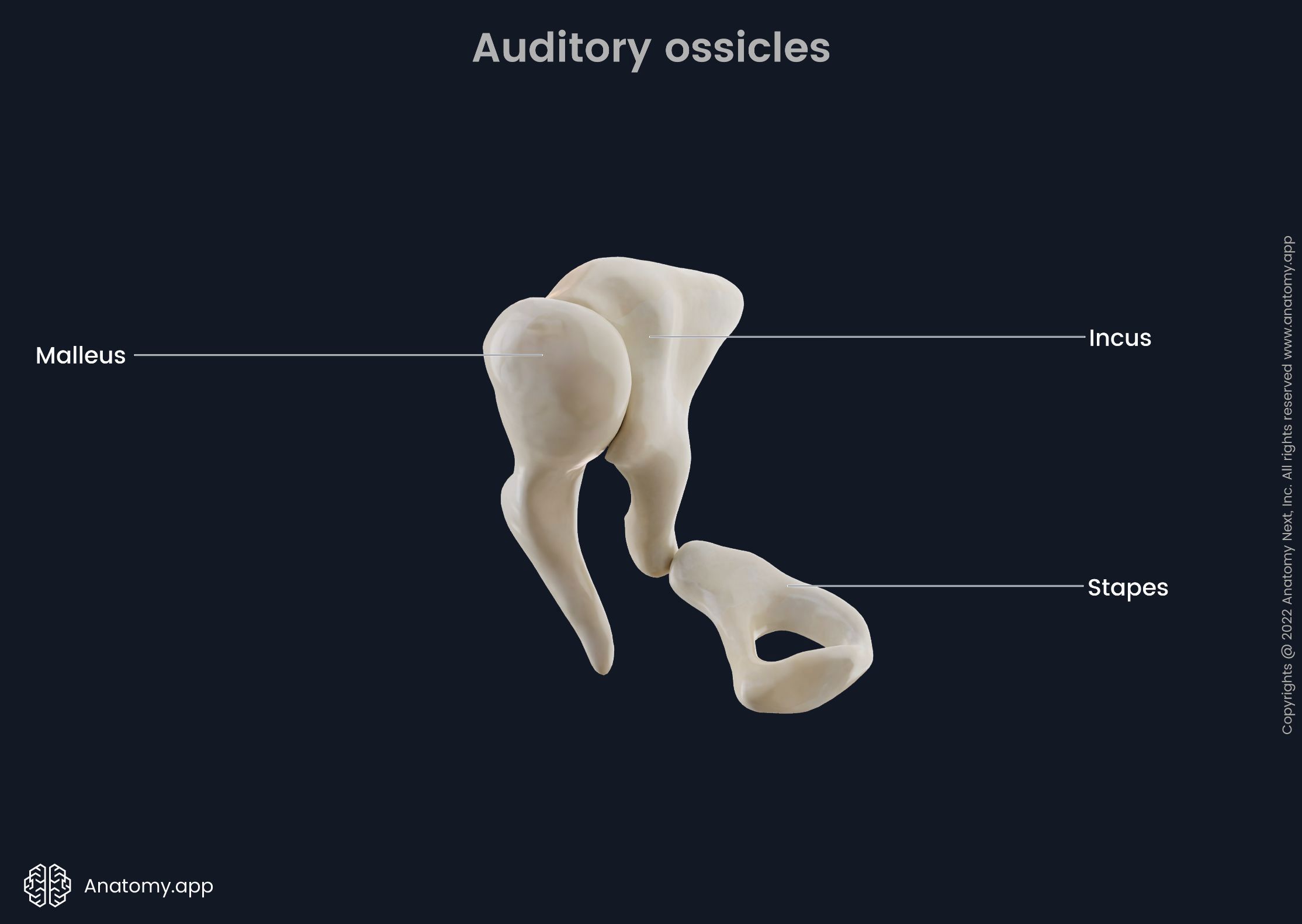
stapes
a small stirrup-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations from the incus to the inner ear; third in the order of the ossicles (M.I.S)
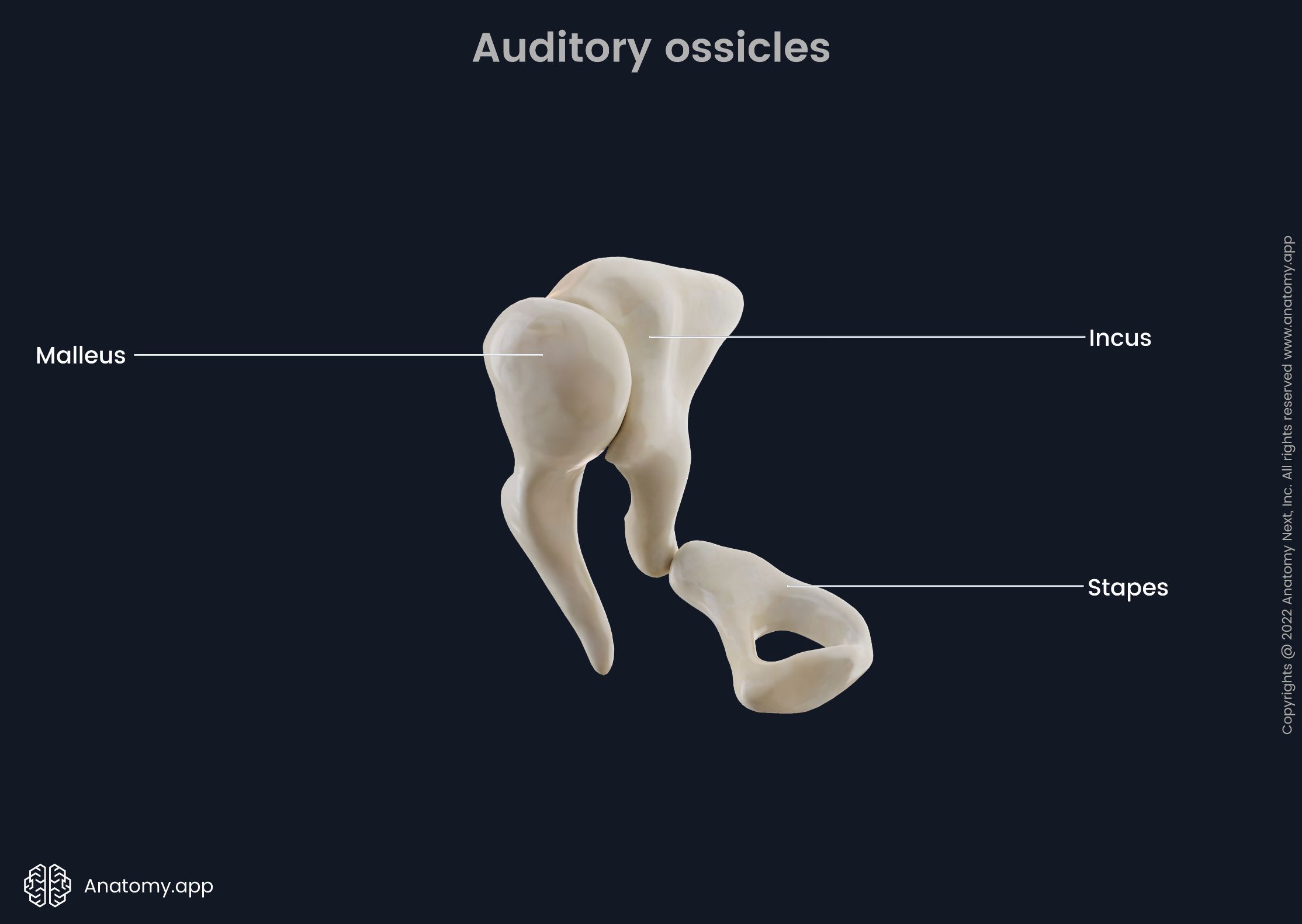
incus
anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear that transmits sound vibrations to the inner ear; second in the order of the ossicles (M.I.S.)
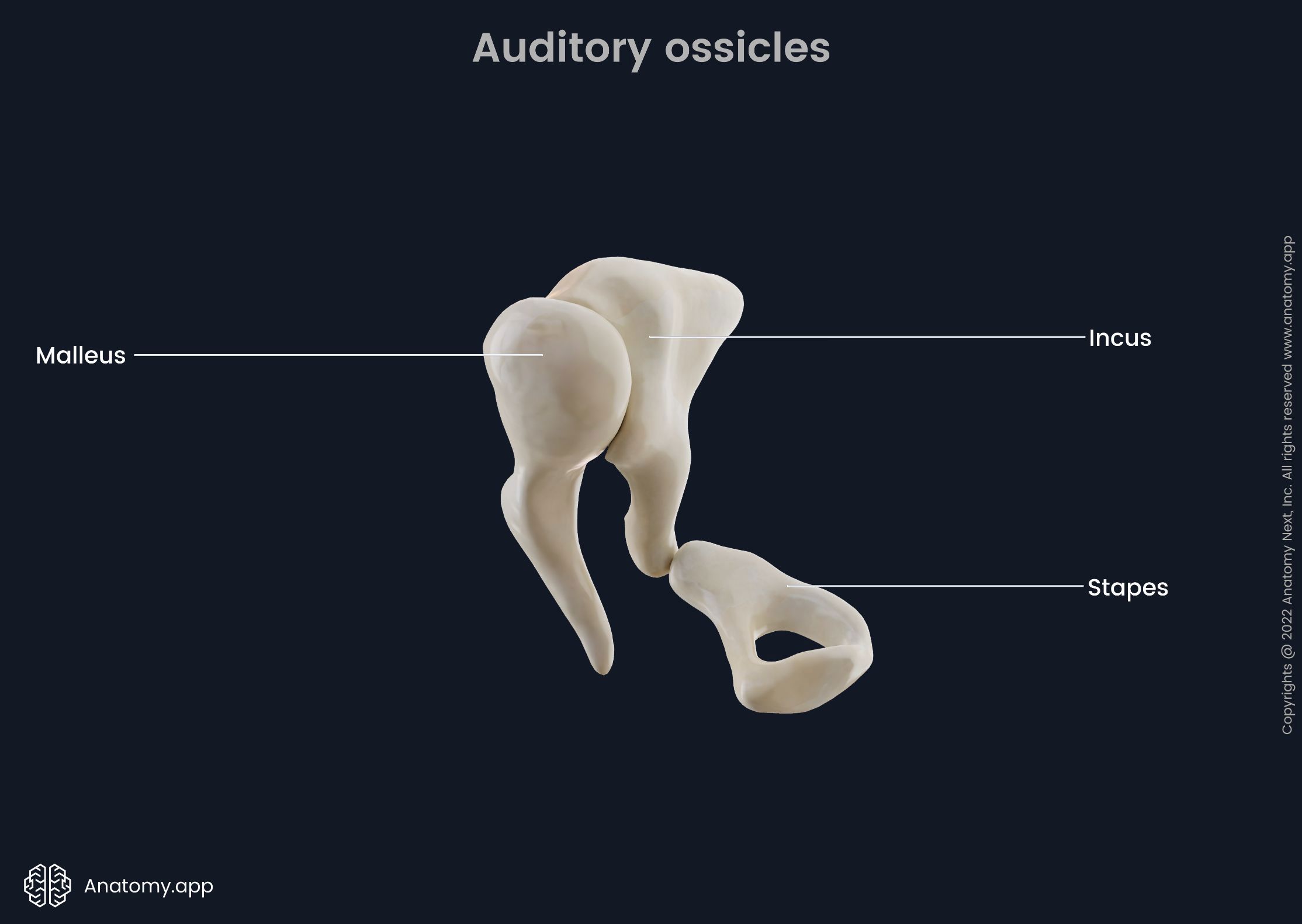
malleus
a small bone in the middle ear which transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus; hammer shaped; first in the order of the three ossicles (m.i.s)
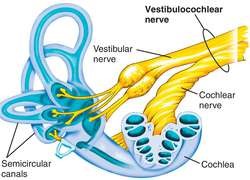
inner ear
composed of oval and round windows; innermost part of the hearing system and home to the vestibular system as well as the cochlea.
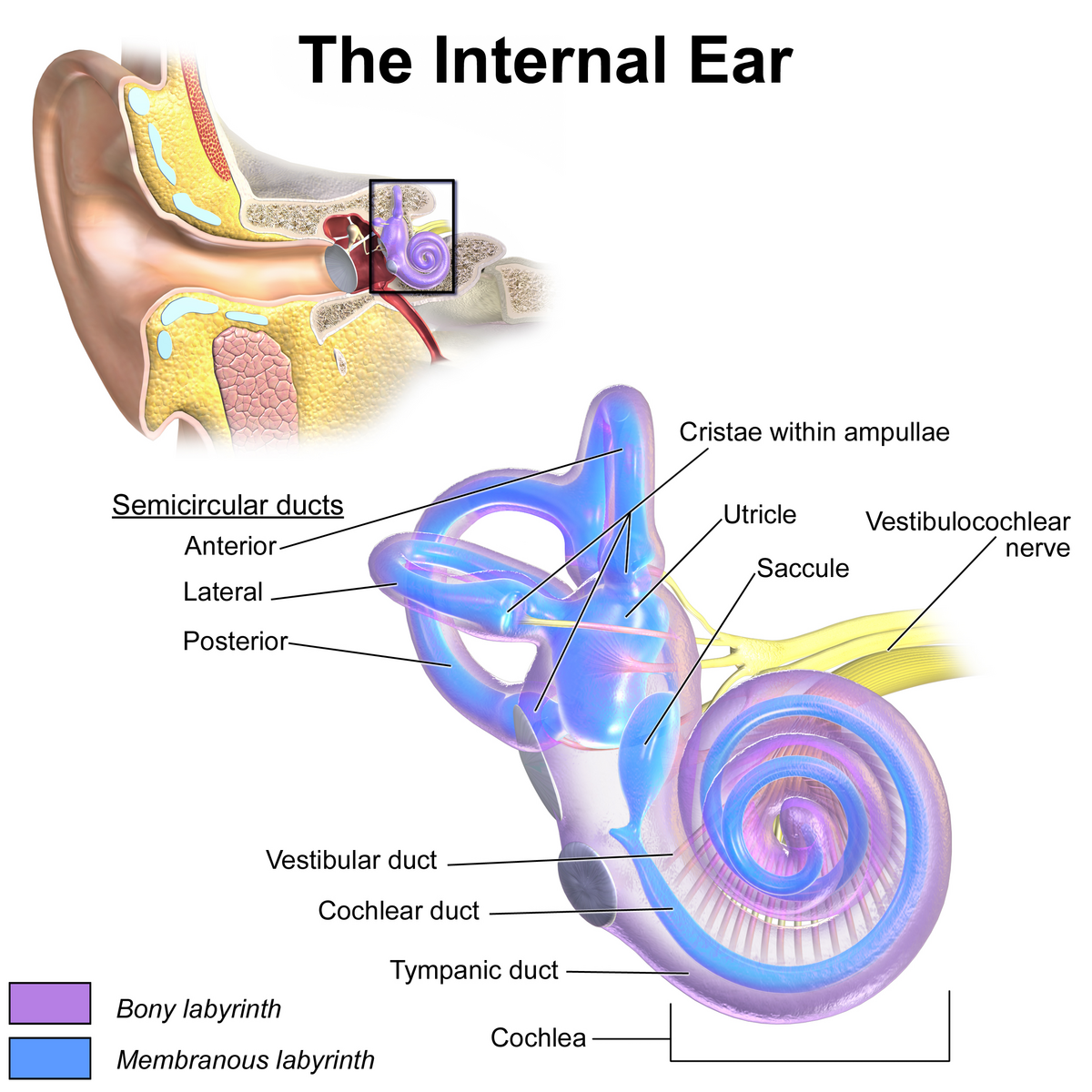
vestibule
the central egg-shaped cavity of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear, located between the cochlea and semicircular canals; two fluid-filled sacs (utricle and saccule) which are crucial components dealing with equilibrium/balance.
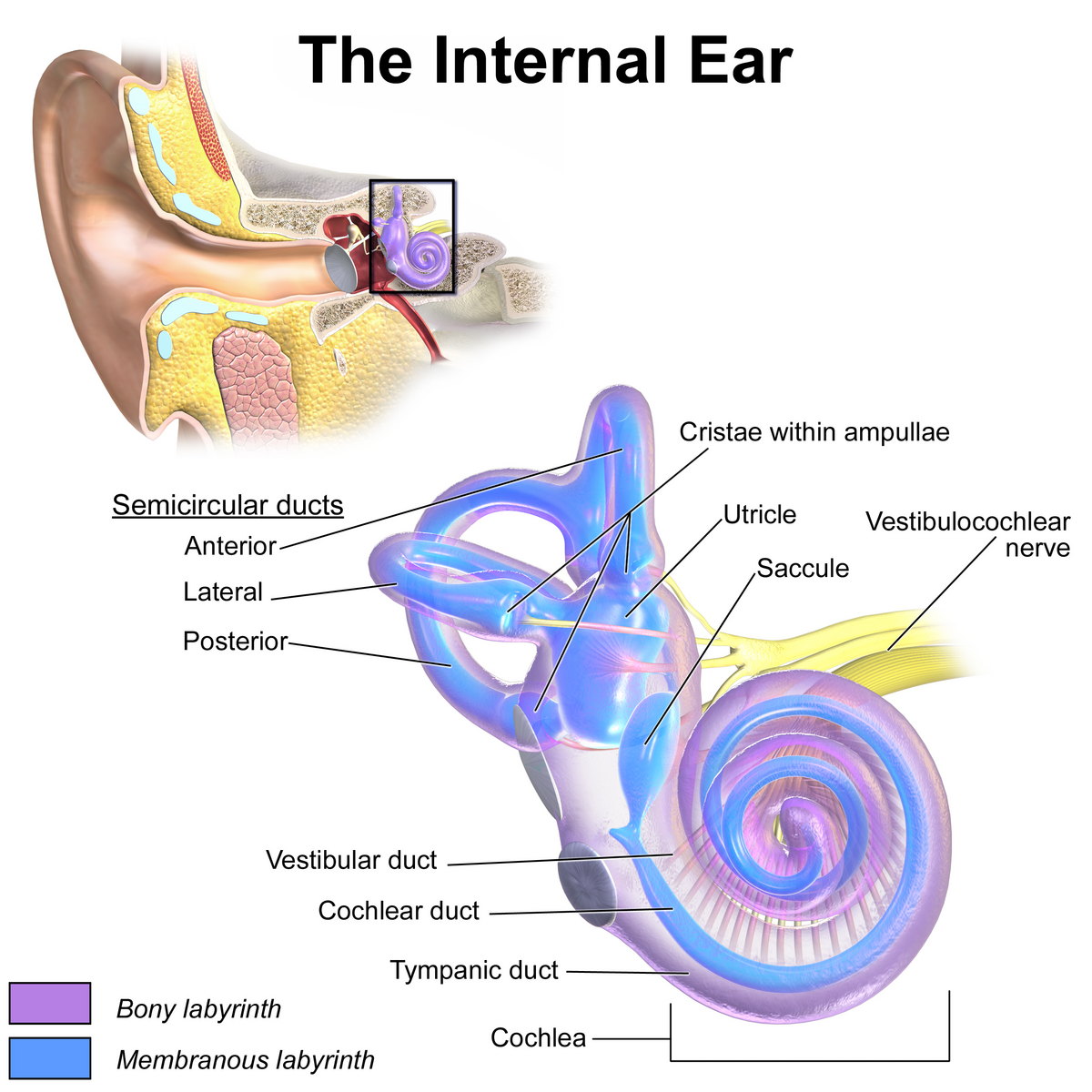
utricle
a small, oval-shaped sensory organ located in the inner ear, specifically in the vestibule; filled with fluid and contains a specialized sensory epithelium (macula — has hair cells that are sensitive to linear acceleration and head tilt); superior to saccule.
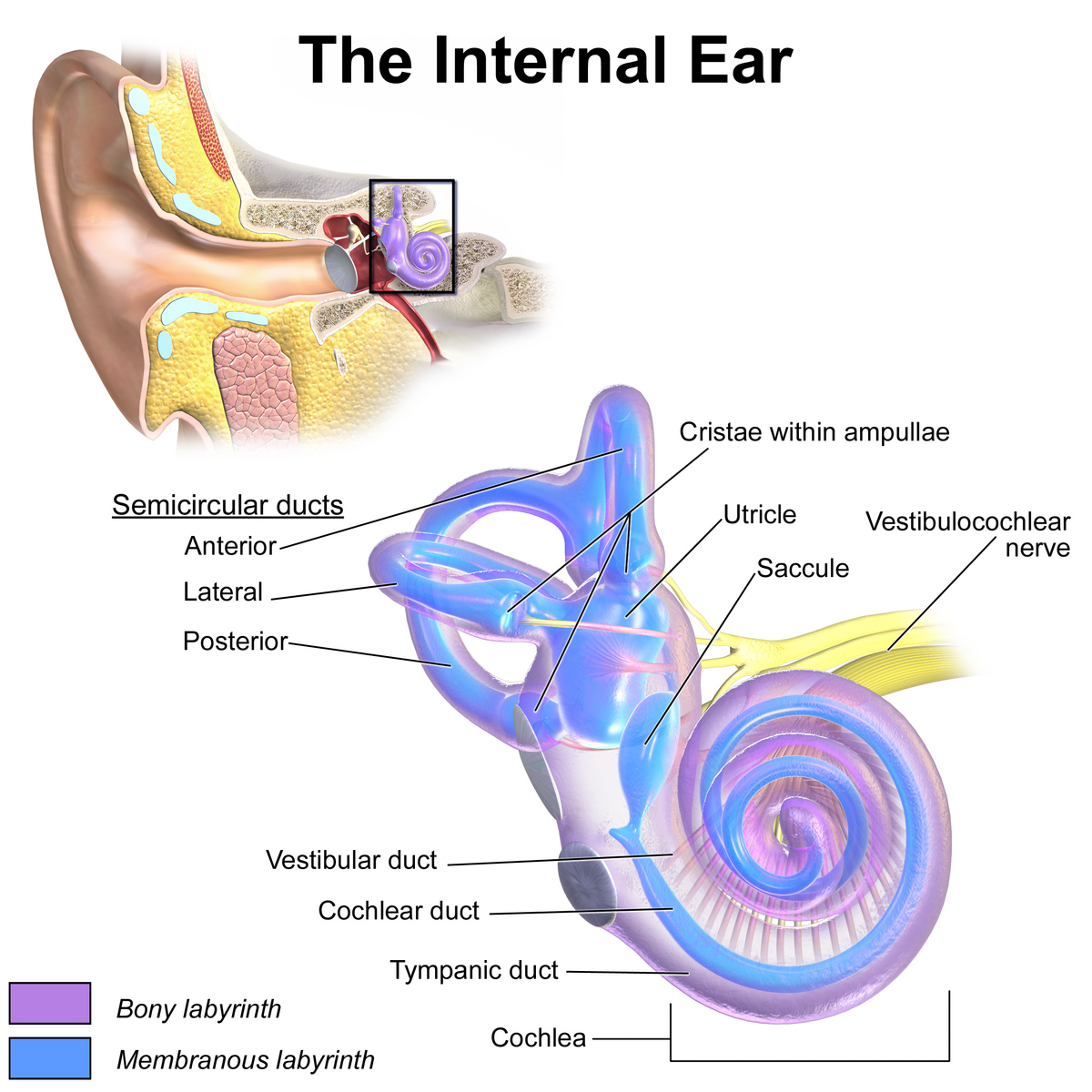
saccule
a small membranous sac, paired with utricle, within the vestibule of the inner ear; part of the membranous labyrinth and plays an important role in vertical tilt; inferior to semicircular canals and utricle.
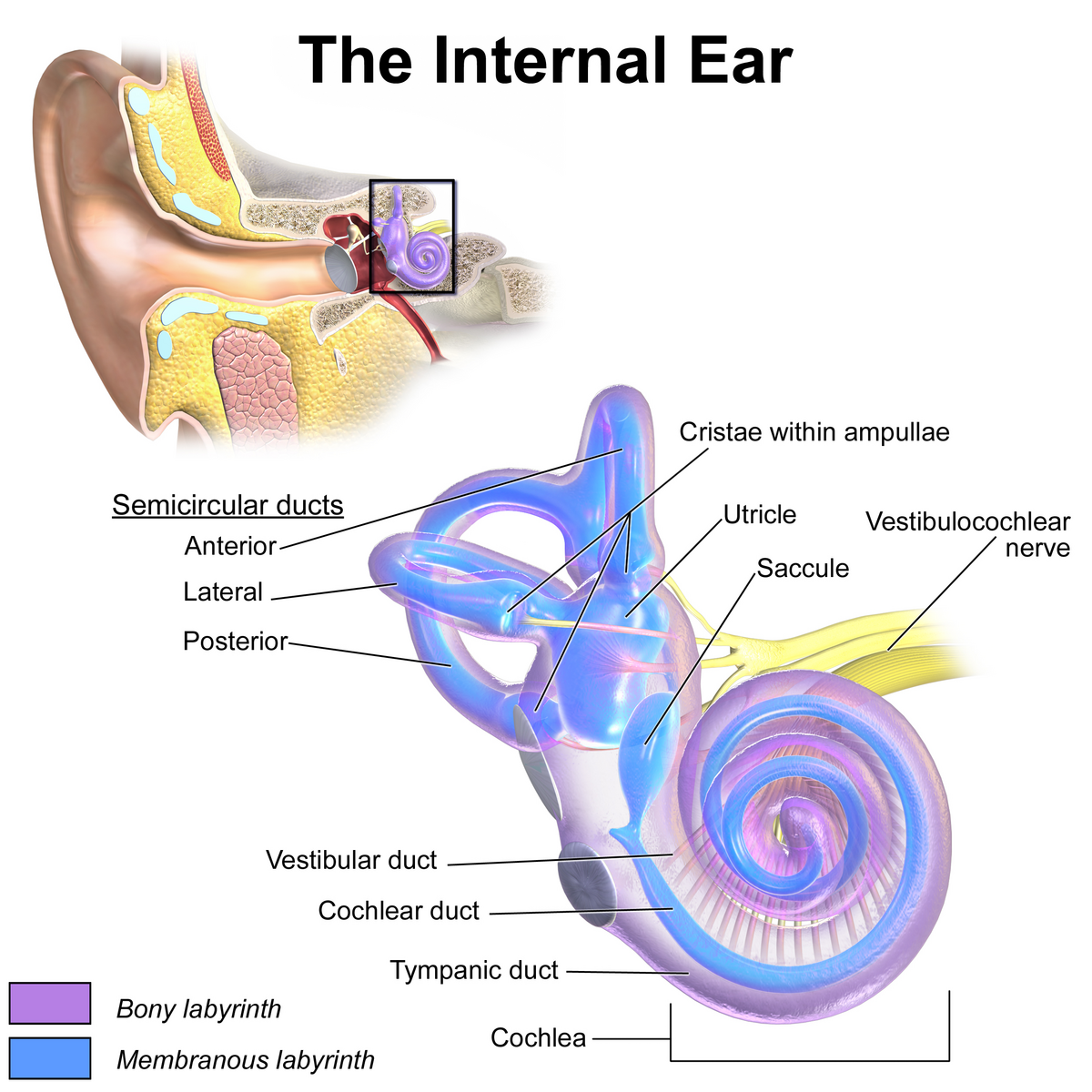
semicircular canals
three fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that, along with the saccule and utricle, form part of the vestibular system; detect rotational movements of the head (nodding/shaking)
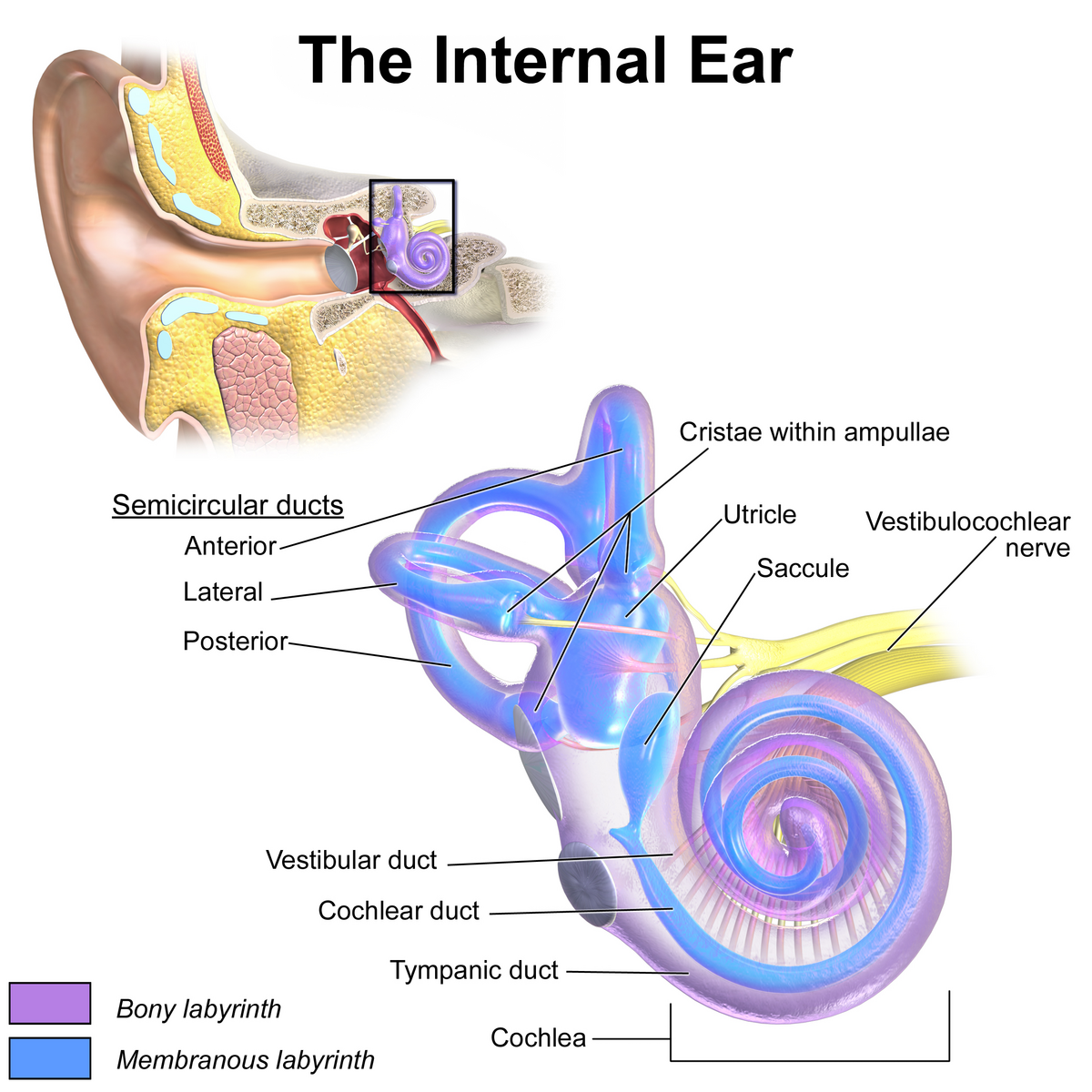
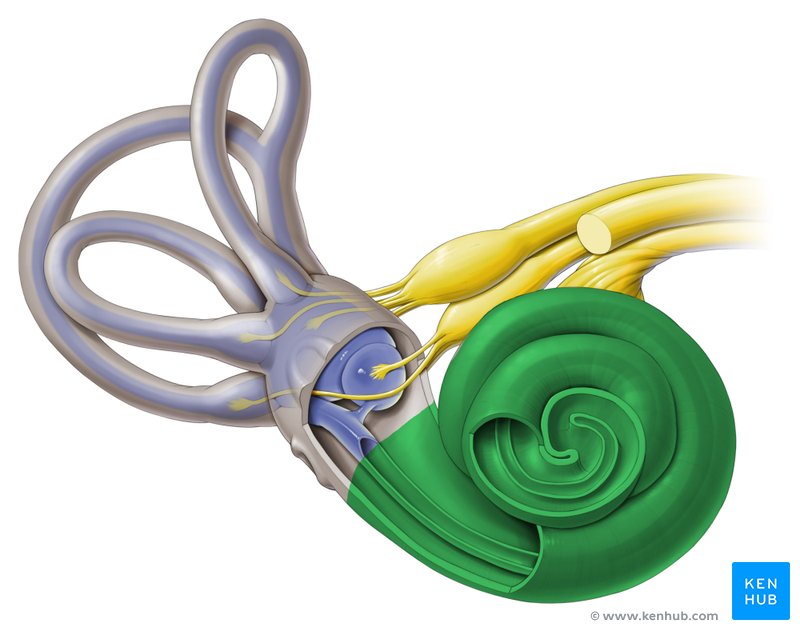
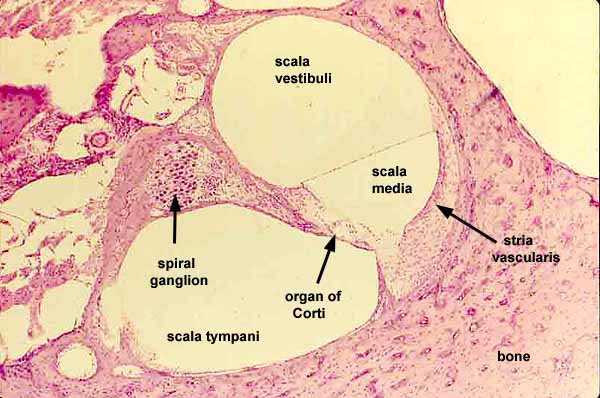
cochlea
spiral cavity of the inner ear containing the organ of corti, involved in hearing
vestibulocochlear nerve
CN VIII, conveys sensory impulses from the organs of hearing and balance in the inner ear to the brain; composed of two branches — vestibular and cochlear
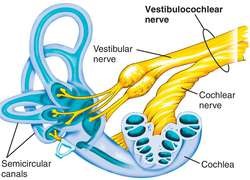
internal cochlear structures
vestibular duct, cochlear duct, tympanic duct, organ of corti, basilar membrane, tectorial membrane, hair cells, cochlear nerve and spiral ganglion cells;
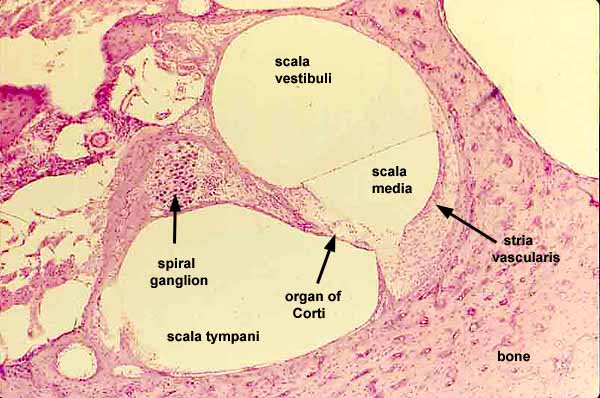
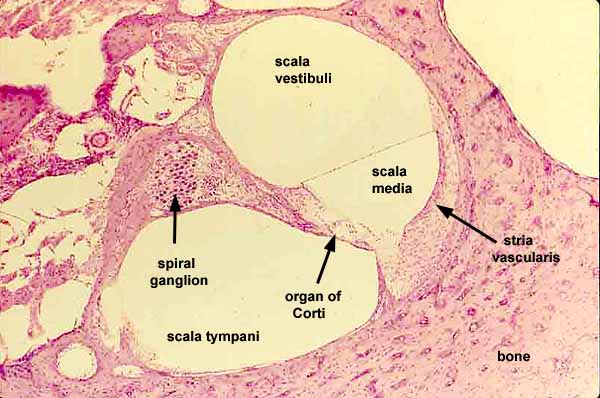
vestibular duct
part of the cochlea that conducts sound; filled with perilymph; referred to as the Scala vestibuli
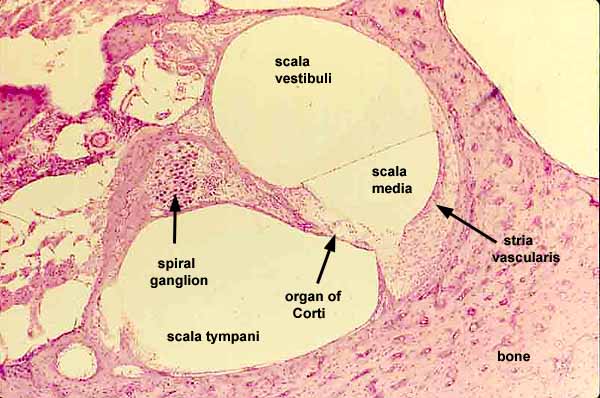
cochlear duct
contains the organ of corti and hearing sensory receptors; between the vestibular and tympanic ducts separated by Reissner’s membrane and basilar membrane; referred to as the Scala media and contains endolymph
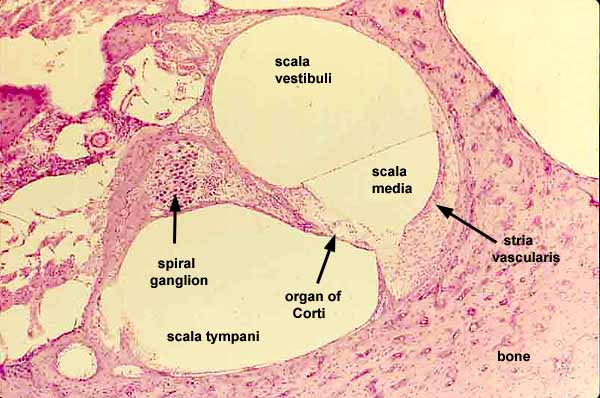
tympanic duct
located beneath the organ of corti and filled with perilymph; receives vibrations from the oval window and transmits them via the basilar membrane to the organ of corti where they are converted into neural signals that the brain interprets as sound; referred to as the Scala tympani
organ of corti
a structure in the cochlea of the inner ear which produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations; composed of hair cells, nerve fibers, and supporting structures
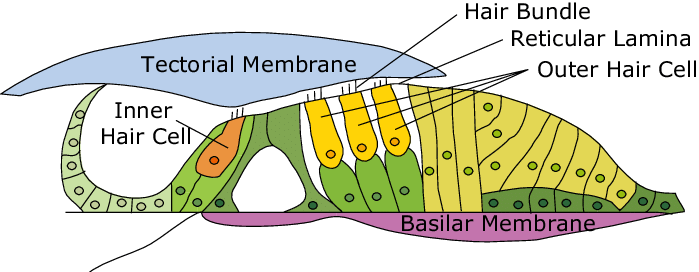
basilar membrane
a flexible membrane in the inner ear’s cochlea that vibrates in response to sound waves, acting as a frequency analyzer to separate different sound frequencies; supports organ of corti.
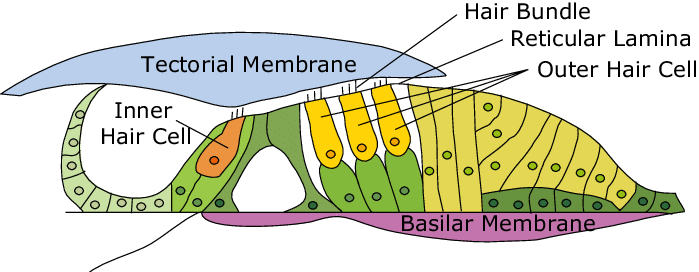
tectorial membrane
a gelatinous, protein-rich extra cellular matrix that sits over the organ of corti and is essential fro auditory processing and hearing
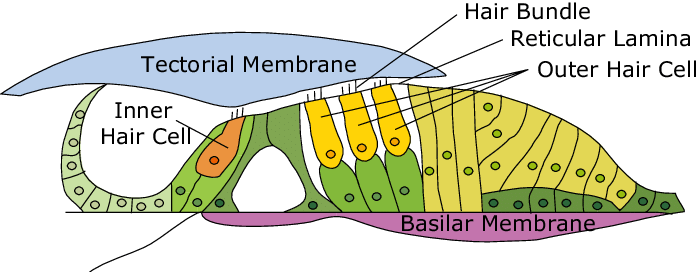
hair cells
sensory receptors for hearing, converting sound vibrations into electrochemical signals that the brain interprets as sound; have hairlike structures that bend due to sound waves; inner and outer components
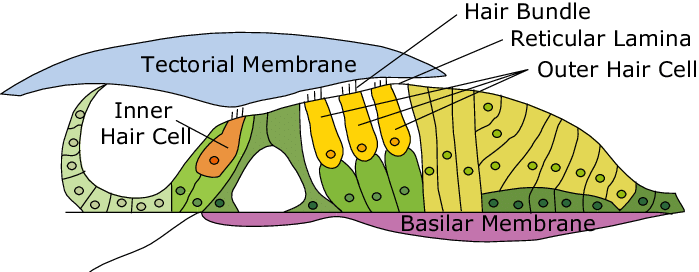
cochlear nerve
½ of CN VIII, a sensory nerve that plays a crucial role in hearing, connected to the cochlea, can be seen in the histology of the cochlea
spiral ganglion cells
specialized neurons in the cochlea of the inner ear that transmit auditory information from hair cells to the brain
conductive deafness
a type of hearing loss caused by problems with the outer or middle ear that precent sound from reaching the inner ear
sensorineural deafness
a type of hearing loss that affects the inner ear and the nerve that carries sound signals to the brain
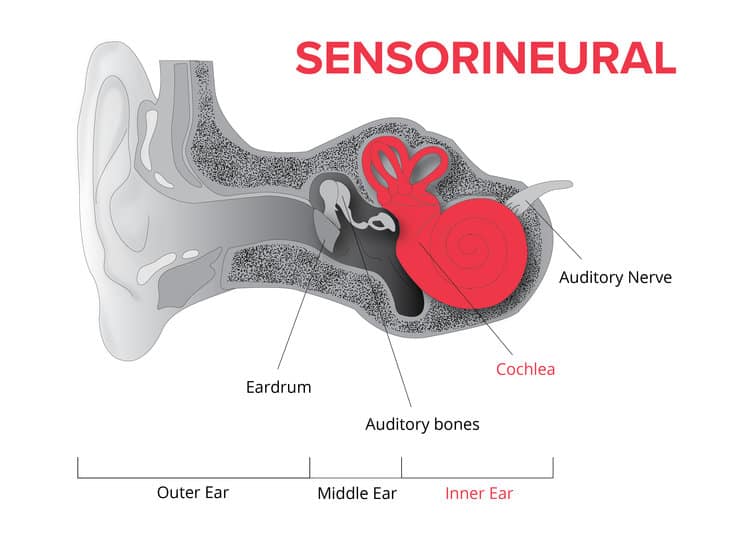
Rinne test
used to evaluate hearing loss in 1 ear; done by striking a tuning fork against a hard surface and placing the base of the tuning fork on the mastoid process of the ear being tested, better for testing for conductive deafness
Weber test
used to evaluate for sensorineural hearing loss; done by striking a tuning fork against a hard surface and placing it on top of the patients head and seeing where the patient best hears sound.
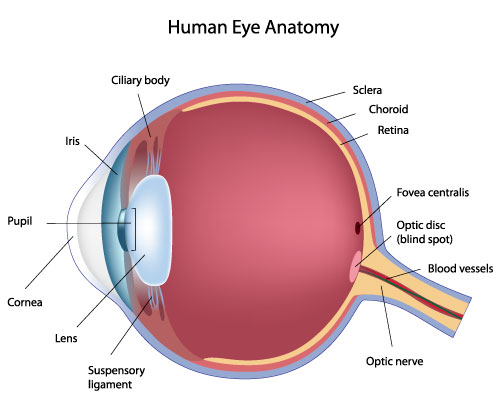
Palpebrae
eyelid; layers structure containing skin, orbicularis oculi muscle, tarsal plates, a vascular layer, eyelashes, meibomian glands and the conjunctiva.
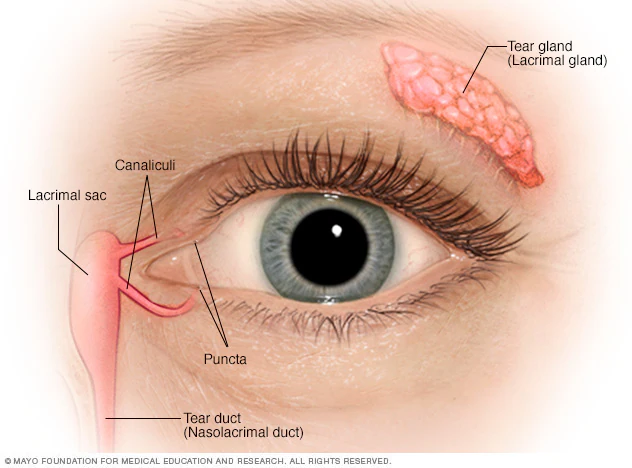
lacrimal gland
tear-shaped gland located above each eye that produces the aqueous portion of the tear film.
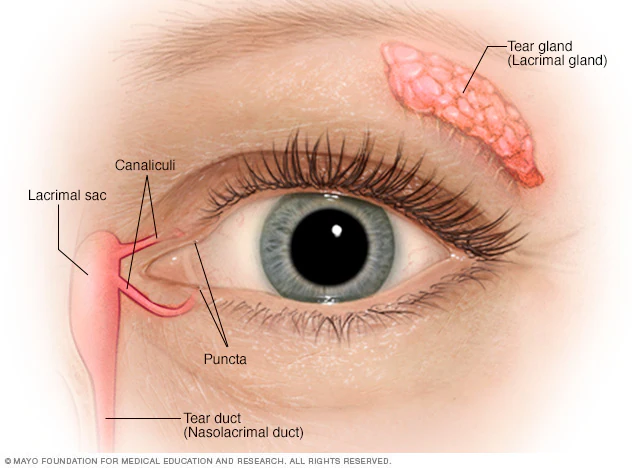
lacrimal gland duct
a system of tubes that transport tears from the lacrimal gland to the eye surface
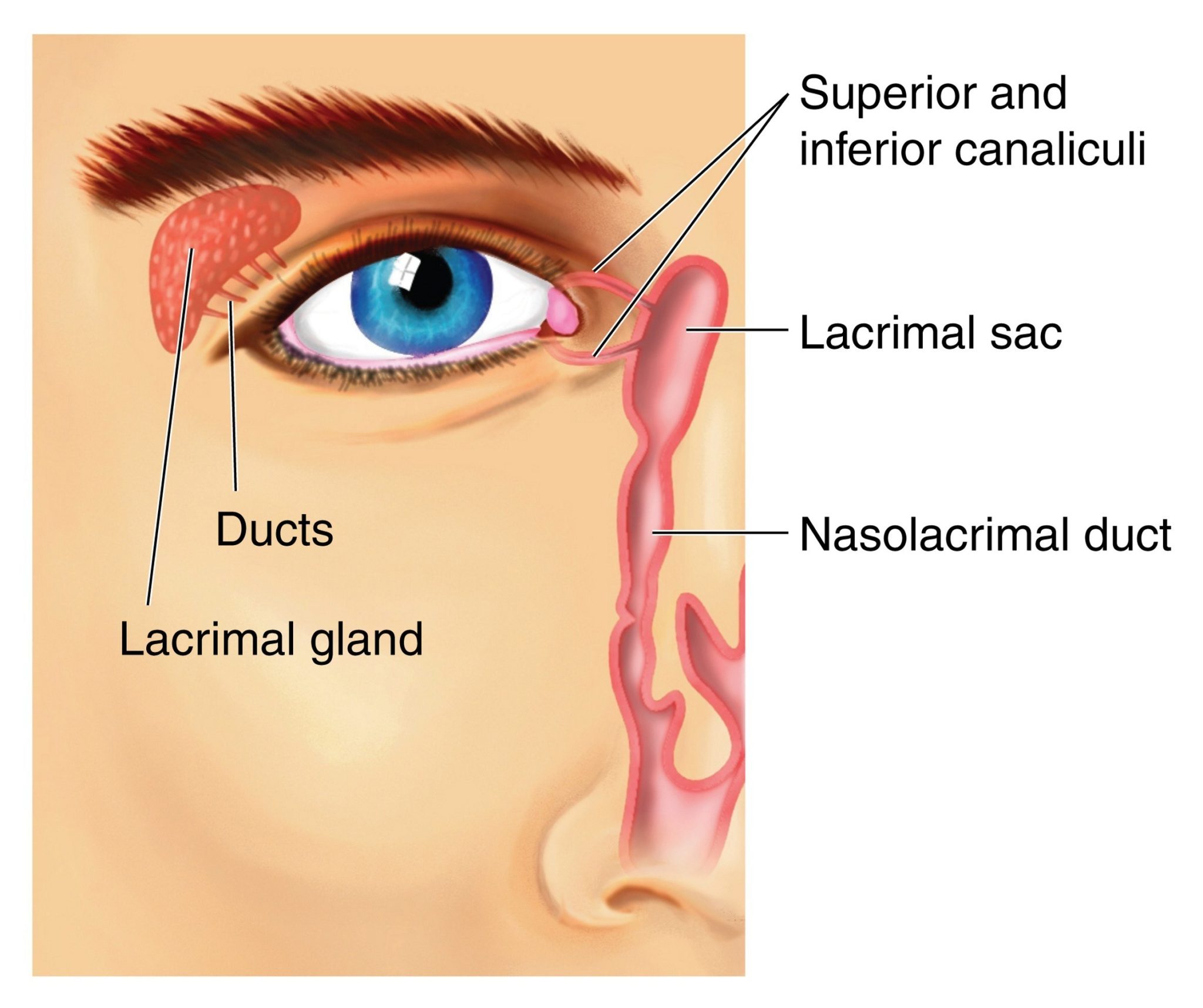
lacrimal sac
a small, dilated structure in the inside corner of the eyes tear duct system that collects tears after they have drained from the eye’s surface through the puncta and canaliculi.
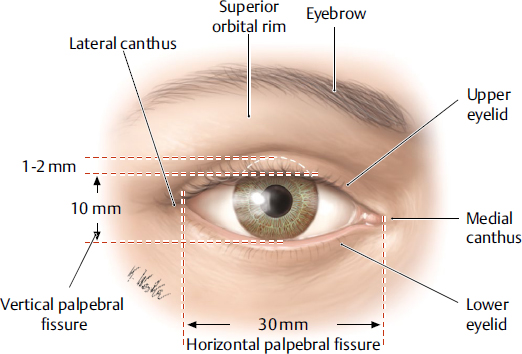
medial canthus
the medial corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet; collects tears and form the entry point into the lacrimal drainage system.
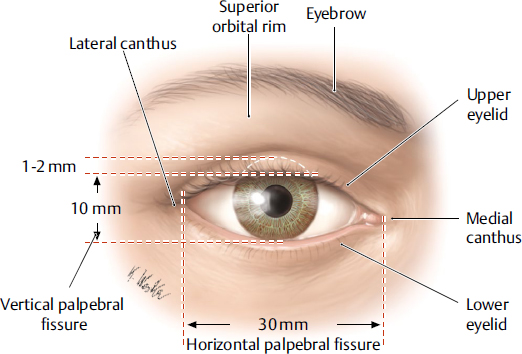
lateral canthus
the lateral corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet; provides structural support for the lower eyelid, preventing its displacement and contributing to the overall contour and health of the eye.
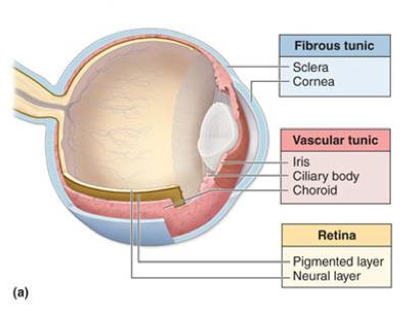
fibrous tunic
the eye’s tough, outermost layer; composed of the cornea and the sclera.
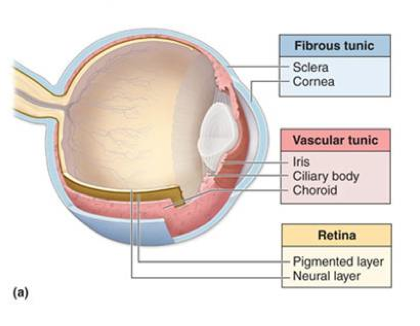
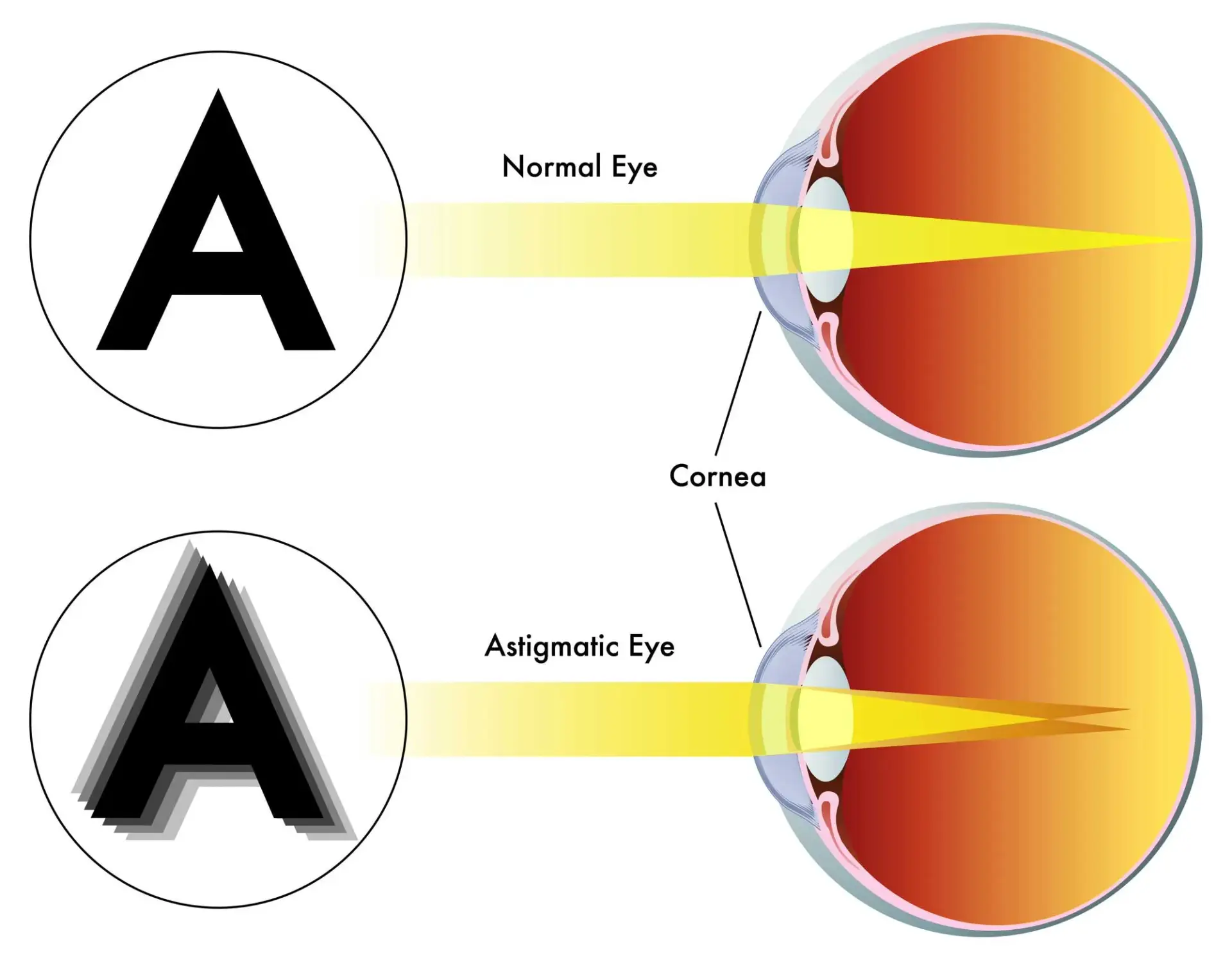
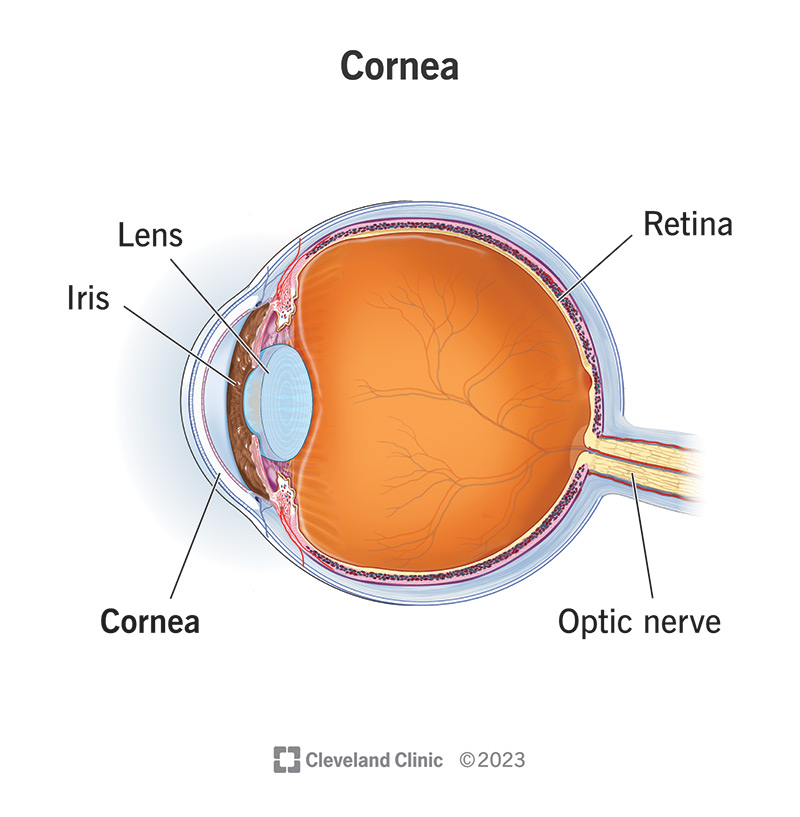
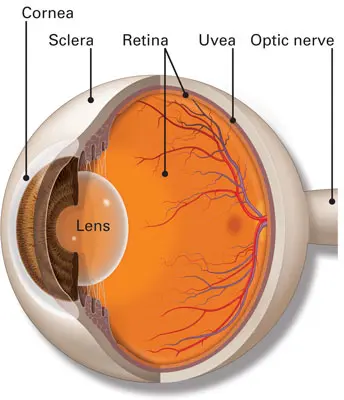
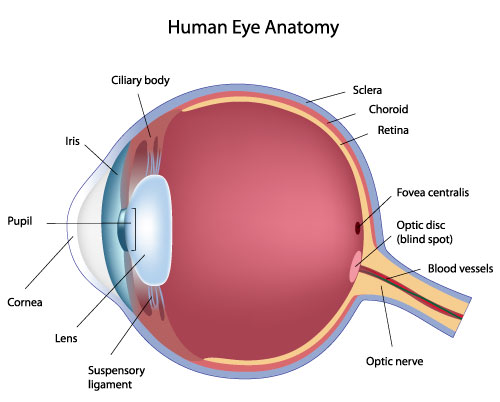
cornea
transparent, dome-shaped front layer of the eye that protects and focuses light into the retina; parting of the fibrous tunic
sclera
the white outer layer of the eyeball; at the front of the eye it is continuous with the cornea; part of the fibrous tunic
vascular tunic
the middle layer of the eye; composed of the choroid, the ciliary body and the iris; plays a crucial role in providing blood supply to the eye, supporting the retina, and regulating light entry.
choroid
the pigmented vascular layer of the eyeball between the retina and sclera; part of the vascular tunic
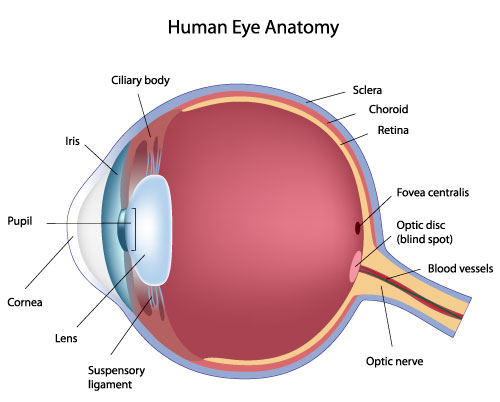
ciliary body
a ring- shaped structure located in the eye, behind the iris; maintains the shape of the lens and producing aqueous humor; part of the vascular tunic
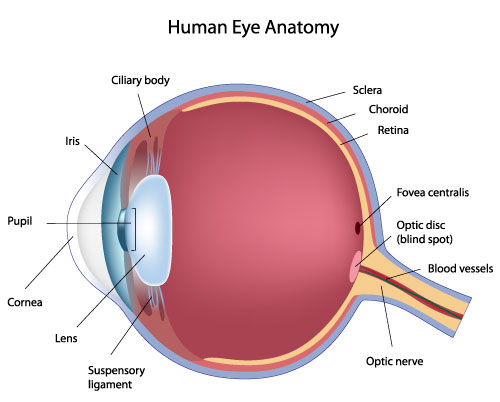
suspensory ligament
zone of zinc; a ring of fibrous strands connecting the ciliary body to the eyes crystalline lens, holding it in place and adjusting its shape for focusing; can also be Lockwood’s ligament — hammock-like structure of tenon’s capsule that supports the eyeball in the orbit and prevents it from sagging.
lens
a transparent, curved structure located posterior to the pupil that focuses light onto the retina to create a clear image.
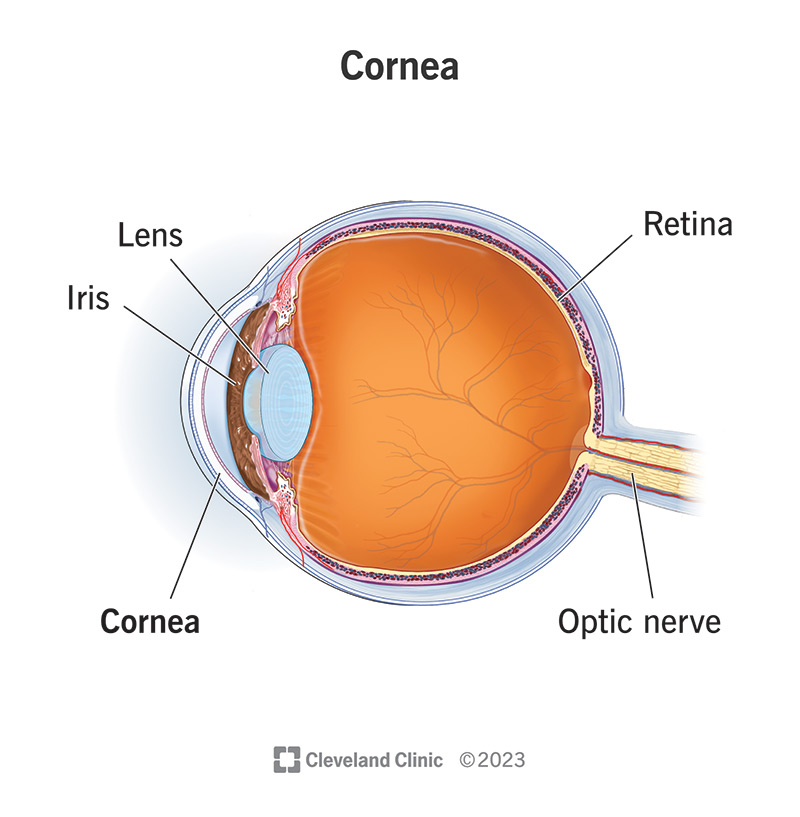
iris
the colored, muscular part of the eye that controls the side of the pupil, regulating the amount of light entering the eye to allow for clear vision in various light conditions; between the cornea and the lens
aqueous humor
a clear, watery fluid that fills the front part of the eye; provides nutrients to avascular structures like the lens and cornea, maintains the eye’s shape and regulates intraocular pressure.
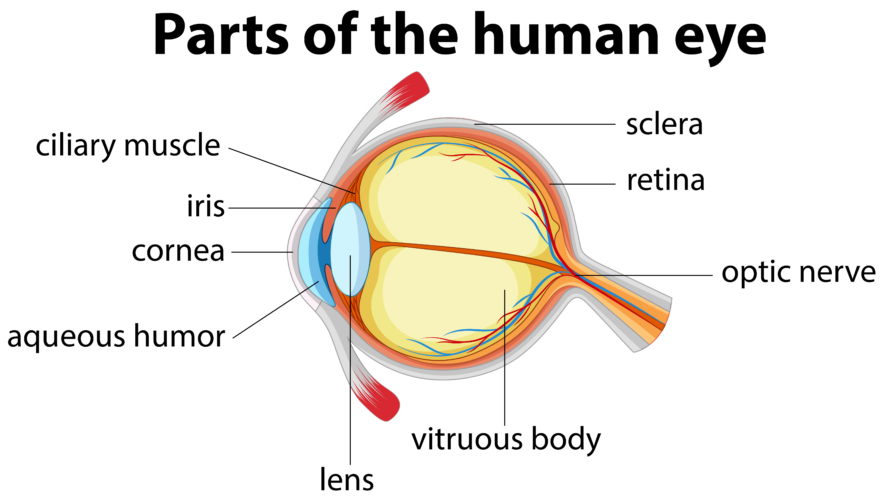
vitreous humor
a clear, gel-like substance that fills the center of the eyeball; fills the space between the lens and the retina.
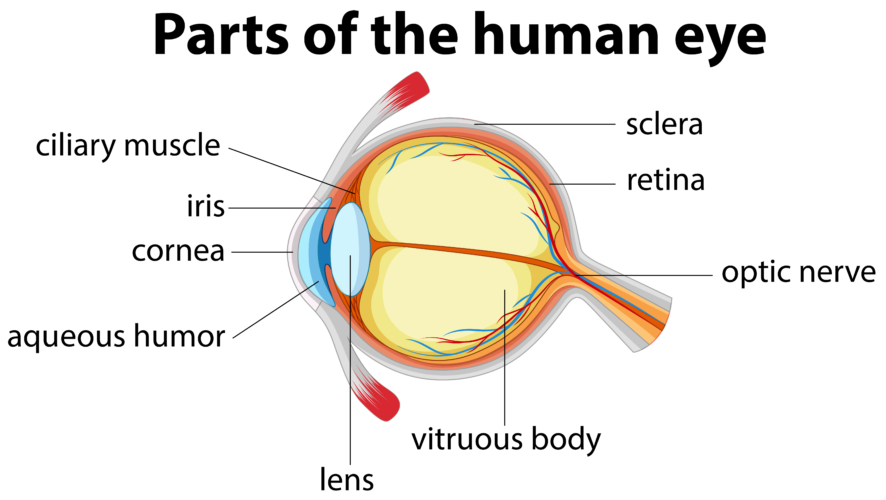
pupil
the black, circular opening in the center of the iris; regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
neural tunic
the innermost layer of the eye; known as the retina; contains several layers.
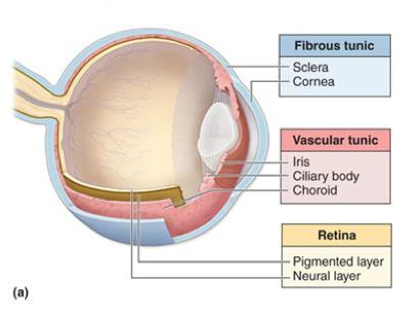
pigmented layer
a layer in the retina; between the choroid and the photoreceptor layer that contains rods and cones.
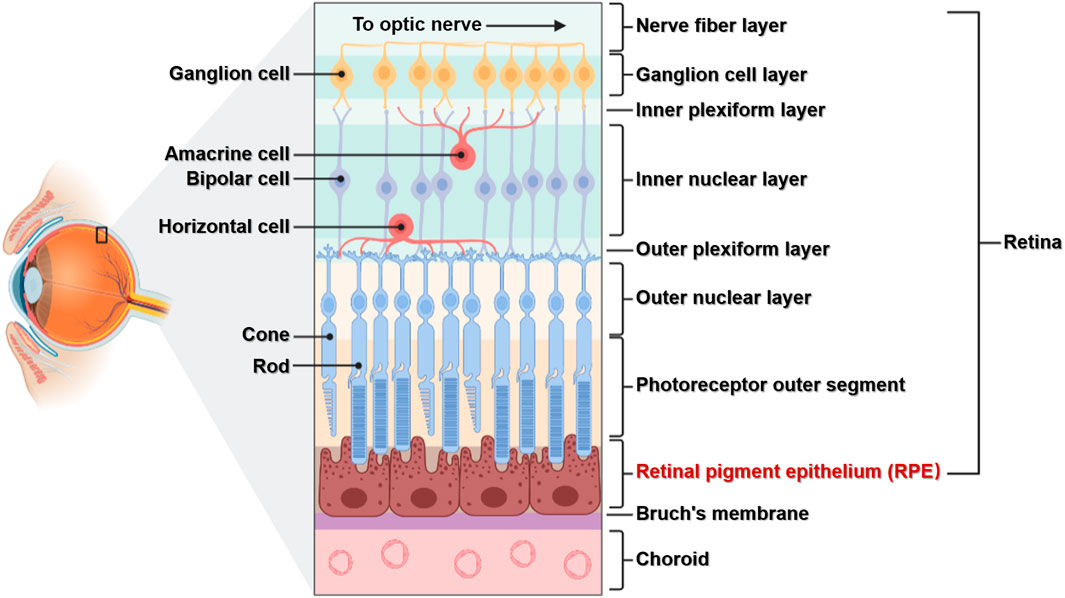
photoreceptor layer
a layer in the retina; contains rods and cones which are responsible for processing light; between the pigmented layer and the bipolar/cell layer
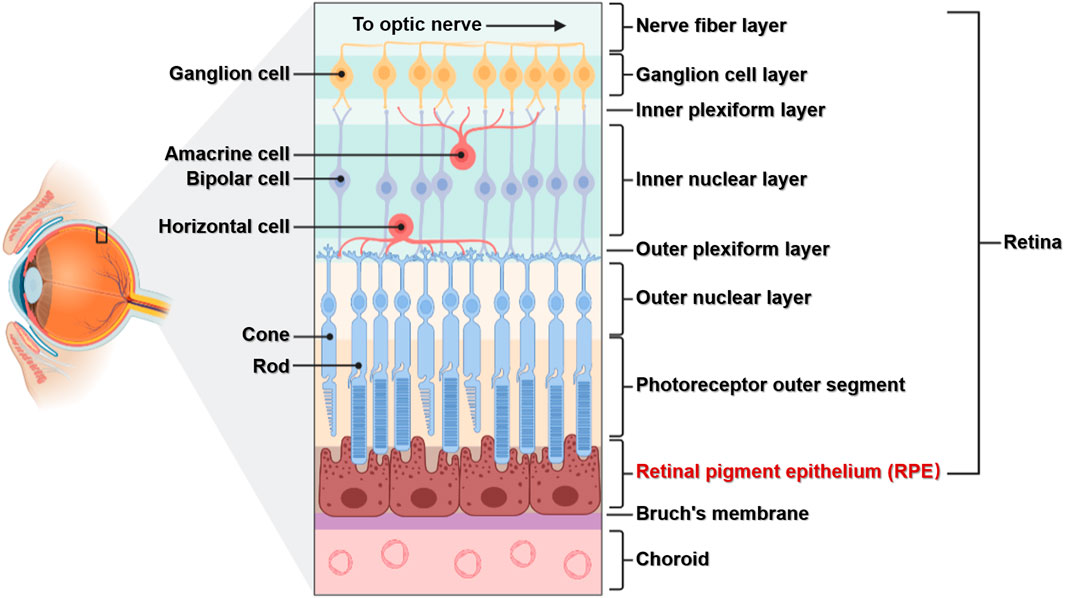
rods
part of the photoreceptor layer in the retina; processes black/white in vision; looks like tunnels
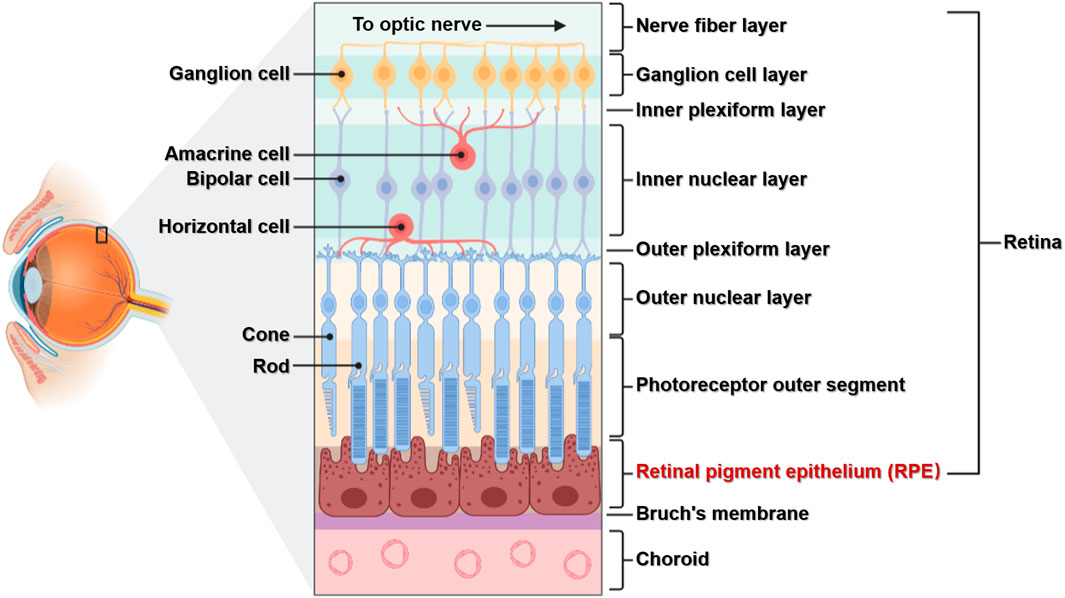
cones
part of the photoreceptor layer in the retina; processes color in vision; looks like serrations in a butter knife.
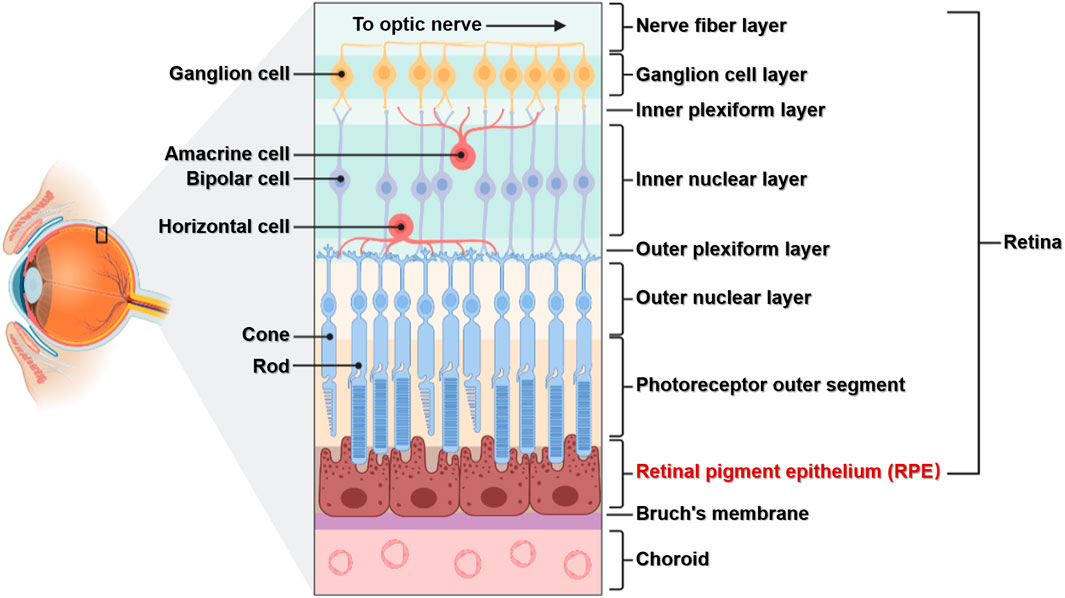
bipolar layer
part of the retina; between the ganglionic layer and the photoreceptor layer; home to bipolar cells which act as the primary conduit for transmitting visual signals from the photoreceptor cells to retinal ganglionic cells.
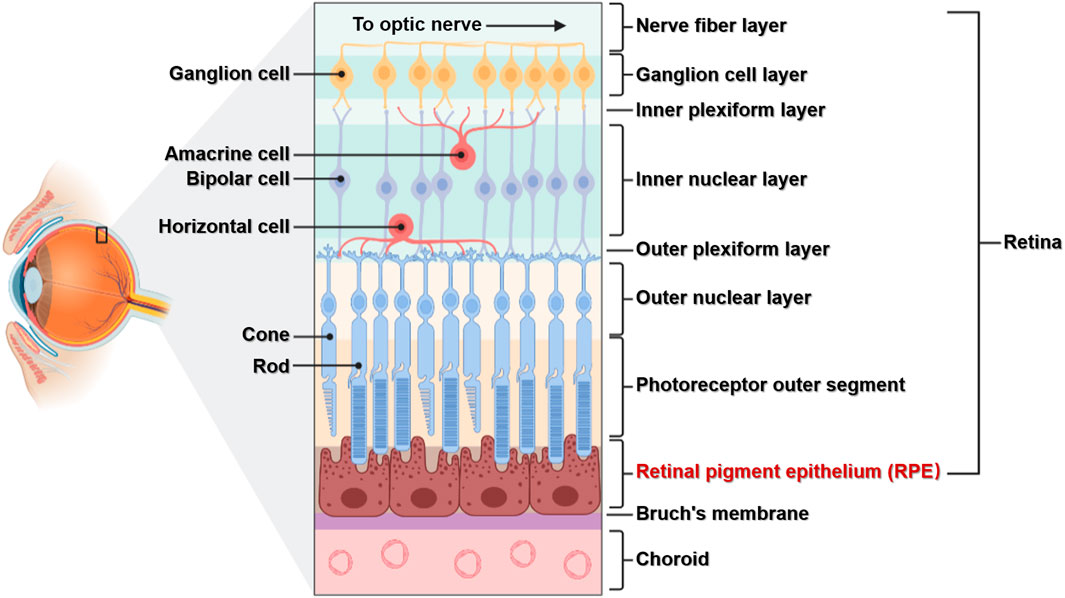
ganglion layer
part of the retina; above the bipolar layer of the retina; a thin layer of neurons located near the inner surface of the retina; receives and processes signals from photoreceptor cells.
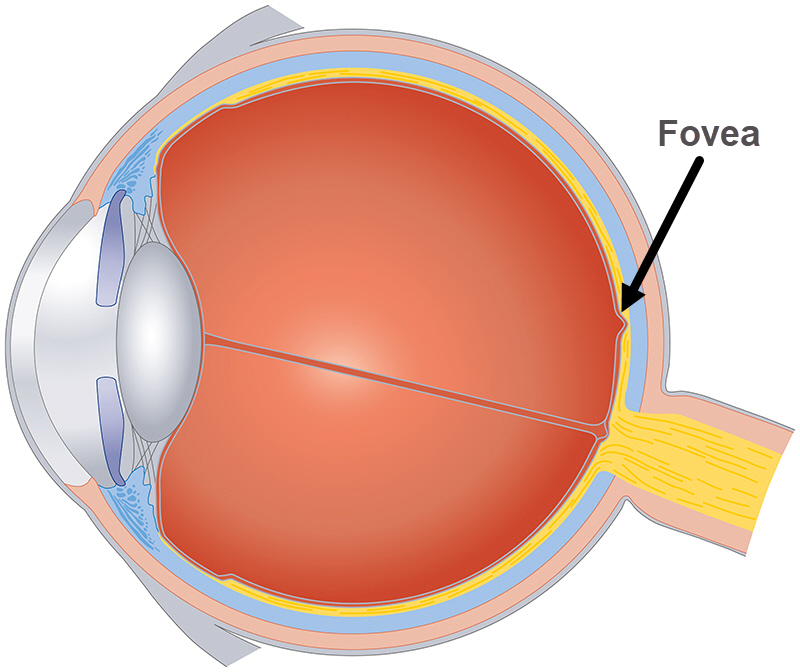
fovea
a small, highly specialized area of the retina located in the center of the macula, a small pin dot on models relatively near the optic nerve/disc.
optic disc
the beginning of the optic nerve and its point where the axons of the retinal ganglion cells come together.
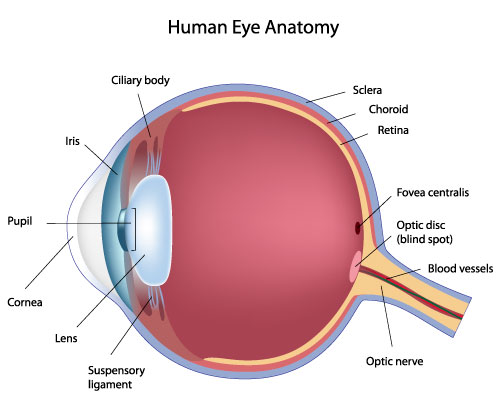
optic nerve
CN II, carries visual information from the retina in the eye to the brain
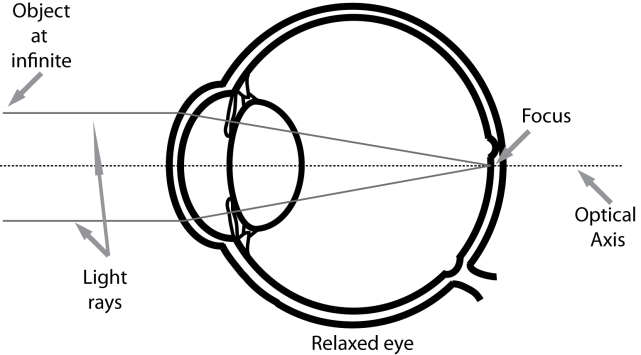
Emmetropic eye
normal, clear vision that occurs when the eye’s optical components are properly aligned and focused
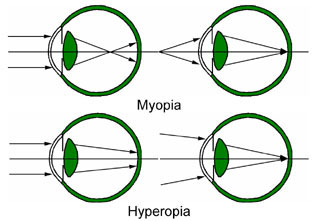
hyperopia
farsightedness, a refractive error where the eye’s focal point is located behind the retina instead of on it.
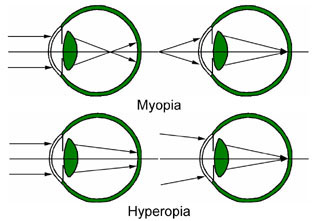
myopia
nearsightedness, a common condition where distant objects appear blurry while close objects remain clear.
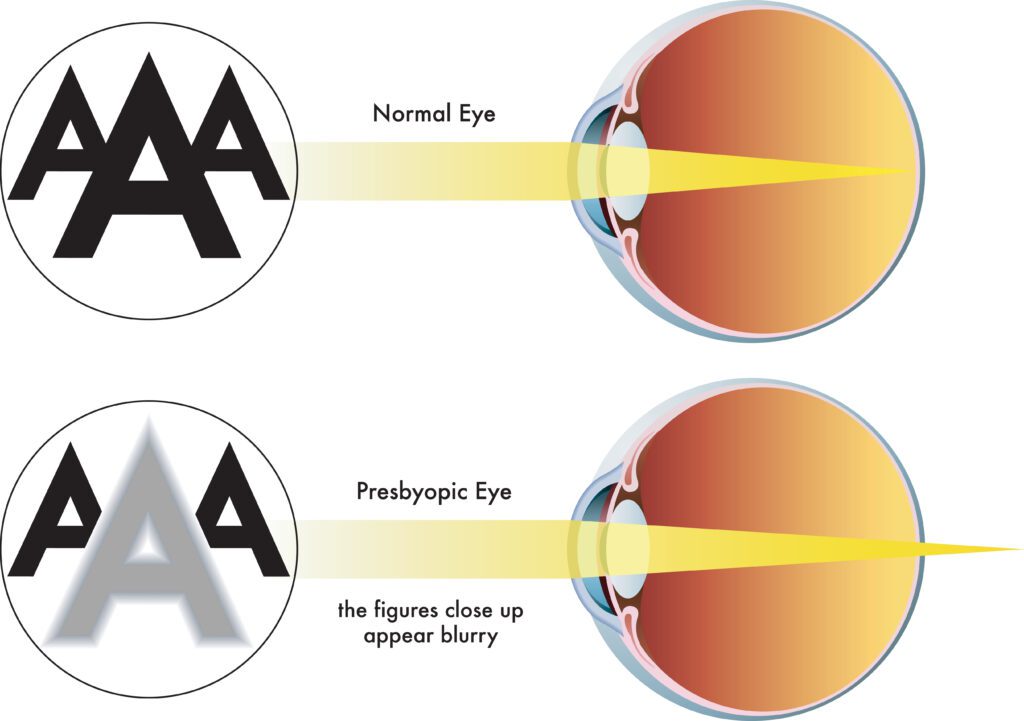
presbyopia
a common age related condition that affects the eye’s ability to focus on near objects; why older people hold phones far away from themselves
astigmatism
a common eye condition where the cornea, the clear front part of the eye is not perfectly curved; results in uneven light focus on the retina, resulting in blurred or distorted vision.