Vaccines
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Influenza comes in what two type of vaccine(s)? What are the routes?
Live-attenutated (LAIV) → IN
Inactivated (IIV) → (IM/ID)
For the LAIV, what are the contraindications?
< 2 yrs or > 50 yrs
Immunocompromised
2-17 yrs with asthma or taking aspirin
Why is aspirin contraindicated in children/teenagers for certain viral vaccines (ie. influenza) or conditions?
Can lead to Reyes Syndrome (liver and brain swelling and damage)
What is the recommended vaccination age & timeline for influenza?
≥ 6 months, once annually
For the inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV), what are the contraindications?
< 6 months old
Egg allergy
Allergies to Flu vaccine or any of its components
Has or previously had Guillain-Barré Syndrome (immune system attacks nerves)
Why is asthma contraindicated in children/teenagers when taking the LAIV?
The live virus in the nasal spray can trigger respiratory distress, wheezing, and other issues
What are the two types of influenza vaccines? How many flu strains does each defend against, and which ones?
Trivalent: 3 strains → 2 A and 1 B strain
Quadrivalent: 2 strains → 2 A and 2 B strains
Manifestations of Influenza
Wheezing
Body aches
Myalgias (muscle pain)
Headache
Malaise
Inflammation → possible pneumonia (SOB, cough, clear/white sputum, ↓O2 sat)
Low-grade fever
Chills
Nasal Congestion
Cough
Manifestations of Pneumococcal disease?
Productive Cough
Colorful sputum (ie., blue, green, yellow, tan)
Difficulty breathing
Increased respiratory rate
Decreased O2 sat
Noise in lungs
Other: ear infection, sinus infection, pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis, death
What are the two pneumococcal vaccines? Through what routes are each administered? What do each contain?
Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23)
IM or SC
23 types of bacteria that cause pneumococcal disease
(PPSV23) Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)
IM
13 types of bacteria that cause pneumococcal disease
Who is recommended for the PPSV23?
Adults ≥ 65 yrs
Immunocompromised, ≥ 2 yrs
Who is recommended for the PCV13?
< 5 years → 4 series of doses
2 months
4 months
6 months
Between 12-15 months
≥ 65 yrs
≥ 6 years with certain chronic illnesses
The Hepatitis B vaccine is what type of vaccine? Through what route is it administered?
Recombinant subunit
IM
Who is recommended for the Hepatitis B vaccine?
All patients beginning at birth
At-risk infants
Those who share IV needles/injectable equipment
Men who have sex with men
Those with HBV-positive sexual partners
Those not in a monogamous relationship
How is HBV transmitted? Who is at risk?
Transmission: Blood (ie. transfusions, needles), bodily fluids (via sexual contact), and perinatal (mother → baby during birth)
At risk: IV drug abusers, HCPs, people with multiple sex partners, infants of infected mothers, men who have sex with men
Manifestations of Hepatitis B
Fever
Headache
Malaise
Anorexia
Arthralgia
Arthritis
Jaundice
Chronic infection → liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and death
When would infants receive hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG)?
If they’re at-risk for Hep B (mother is HBV+) → within 12 hours
Given along with Hep B vaccine
At-risk infants for HBV receive
HBIG and monovalent Hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours after birth
Infants not at risk for HBV receive
monovalent Hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours after birth
What type of vaccine is the tetanus vaccine? What are common names for it? through which route is it administered?
Type: Toxoid
Name: DTaP and Tdap (booster)
Route: IM
How can someone get infected with tetanus?
Environment: contaminated soil, rusty nail, manure
Clostridium tetani enters wound and produces toxins (ie. tetanospasmin) that interfere with nerve signaling
Manifestations of Tetanus
Muscle stiffness and rigidity in jaw, neck, and abdomen
Larynx spasticity: strained/tightened voice, voice breaks
Muscle spasms and tremors
Difficulty swallowing, speaking, and breathing
Fever
Broken bones
What are the age/dose recommendations for tetanus vaccine?
All children: 5-dose series
2 months
4 months
6 months
15-18 months
4-6 yrs
Booster every 10 yrs
All HCPs
TDaP and Tdap are for what age ranges? What is the difference between the two?
TDaP (active immunization): 6 wks to 6 yrs
Tdap (active booster): ≥10 yrs
Both contain the same Ags, but different amounts (concentration)
What are the recommendations for the tetanus vaccine if a person gets injured and has a contaminated, dirty wound?
If the patient received the tetanus vaccine
<5 yrs ago → assumed immunity
>5 yrs ago → booster (Tdap)
>10 yrs ago (regardless of injury) → booster (Tdap)
What type of vaccine is the Varicella (chickenpox) vaccine? Through what route is it administered?
Type: live-attenuated
Route: SC
Manifestations of Varicella (Chickenpox)
More severe in older children and adults, highly contagious and airborne:
Scarring
Blister-like rash
Redness
Pain
Fever
Respiratory Issues (later in life)
Complications: encephalitis, bacterial skin infections, pneumonia, Reye syndrome, and death
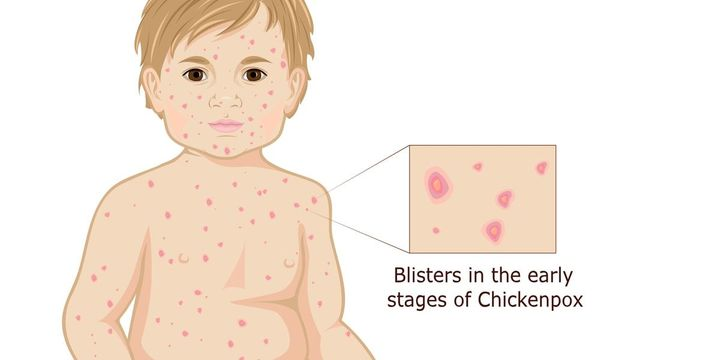
What are the age/dose recommendations for the varicella vaccine?
All children: 2-dose series
12-15 months
4-6 yrs
What are the contraindications for the varicella vaccine?
Immunocompromised
Pregnancy or possibility of pregnancy within 1 month
Previous anaphylaxis to vaccine or any of its components
Aspirin or other salicylates
Other: active, untreated TB infection, moderate-to-severe acute illness
What are some common side effects and possible adverse effects of the varicella vaccine?
Side Effects
Localized/confined redness and soreness around injection site
Fever
Adverse Effects
Anaphylaxis
Encephalitis
Brain inflammation
Thorombocytopenia
Low platelet count→ bruising/bleeding risks
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)
Flu-like symptoms, painful blister-like rashes, and outer skin layer detachment
Reyes Syndrome (possible with aspirin)
Varicella requires what type of precautions?
Standard (gloves)
Contact (gown + gloves)
Airborne (N95 mask + negative pressure room)
What are the two types of Herpes zoster vaccines? Through which routes are they administered? What are the names? Which one was discontinued? How many doses does each require?
Live-attenuated: Zostavax (SC) → discontinued
1 doses
Recombinant subunit: Shingrix (IM)
2-dose series
Manifestation of Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
Unilateral, local red, painful blister-like rash
Chronic severe pain post blister (postherpetic neuralgia)
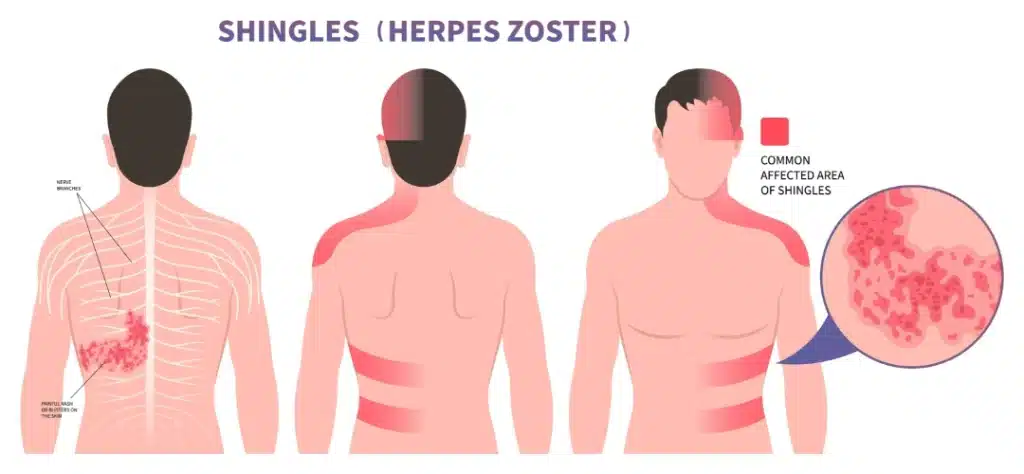
What is the recommended age and dosing for the current Herpes zoster vaccine (Shingrix)?
Recombinant subunit (Shingrix), IM
≥ 50 years
2nd dose: 2-6 months after 1st dose
≥ 19 yrs who are or will be immunocompromised or immunosuppressed
2nd dose: 1-2 months after 1st dose
Herpes Zosta, commonly known as 1)_________ is the reactivation of the 2)_______________, which lays dormant in the body after causing 3)__________.
When reactivated, it travels along a 4)______ that doesn’t cross the body’s ________, leading to ________ manifestations on the skin. The 5)______ in the ________ is highly contagious. The patient is no longer contagious when it is drained out, and the wound 6) ______ over.
Shingles
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Varicella (Chickenpox)
nerve; midline; unilateral
fluid; blisters
scabs
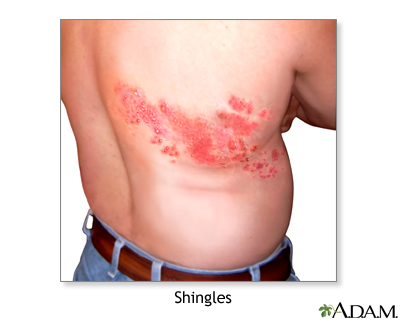
What are contraindications for the herpes zoster vaccine?
Previous anaphylaxis or current allergies to herpes zoster vaccine or any of its components
Pregancy
Moderate-to-severe acute illness
What are some brand names for the COVID-19 vaccine? What type of vaccine is it? Through what route is it administered?
Names: Pfizer, Moderna, Novavax
Type: Nucleic Acid (mRNA)
Route: IM
Manifestations of COVID-19
Fever
Muscle aches
Headache
Cold symptoms
Nausea/vomiting/diarrhea
Loss of taste and smell
Conjunctivitis (red eyes)
What are the age and dosing recommendations for the COVID-19 vaccine brands?
Moderna (2-dose series)
Dose: 28 days apart
Age: ≥ 6 months
Pfizer (2-dose series)
Dose: 21 days apart
Age: ≥ 6 months
Novavax (3-dose series)
Dose: 21 days, 6 months
Age: ≥ 12 yrs
What are the contraindications for the COVID-19 vaccine?
Previous anaphylaxis or current allergies to COVID-19 vaccine or any of its components