HS 346: exam 1 study guide (lecture 4-the AAMA project, Nepal MSNP, Micronutrient Interventions, UNICEF Child Malnutrition)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is exclusive breastfeeding and who is it recommended for?
Infants (AGED 0-6 MONTHS) only receive breast milk, no other food or drinks.
What is colostrum and why is it important?
"First milk", rich in antibodies and nutrients for newborn immunity.

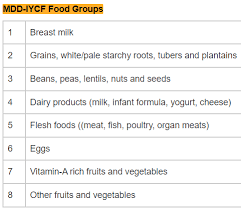
What are the key goals in complementary feeding?
introduce family foods at 6 months
dietary diversity > 4 food groups
age-appropriate meals per day
diverse/frequent diet
When and where was the AAMA (action against malnutrition) project implemented?
Nepal in (2016?)
What was the context in which the intervention was developed?
High childhood malnutrition
What were the 2 core components of the AAMA project?
BEHAVIOR CHANGE COMMUNICATION (moms with a little bit of land and had young kids needed to farm more often, and farm more dietarily diverse foods)
COMMUNITY MOBILIZATION (female community health workers to hold meetings with mothers monthly to check up on them).
Who did the AAMA project target and why?
Mothers of young children with a bit of land because they could implement the behavior changes and they have control over their land and therefore, some aspects of their health.
What is an FCHV
Female Community Health Volunteers.
The AMMA project utilized this kind of workers because they serve the communities that they are from.
They are trusted sources of information and service, and can provide important, basic services like immunizations and vitamin supplication.
What is formative research?
research conducted at the beginning of the planning process, or during the implementation of a plan, to understand BEHAVIORS and BARRIERS before designing interventions.
What are the 8 determinants of action in AAMA's barrier analysis?
perceived susceptibility
perceived severity
perceived benefits
perceived barriers
cues to action
self-efficacy
social norms
positive/negative reinforcement
What behavior change theories informed AAMA?
Health belief model
Theory of planned behavior.
What methods were used in AAMA's impact evaluation?
Mixed methods:
surveys
interviews
focus groups
Key finds of AAMA and how did Suaahara build on it?
Improved feeding practices.
Suaahara scaled up with broader multi-sectoral strategies.
Trends in infants <5 and neonatal mortality in Nepal over 30 years?
Significant decline due to improved health interventions
Trends in stunting, wasting, and underweight
stunting declined
wasting and underweight remain challenges.
When did Nepal develop its first multi-sectoral nutrition plan? How has it evolved over time?
It was launched in 2013, expanded to MSNP-III with broader sectors and targets
Nutrition specific interventions
Direct (ex: supplementation)
Nutrition sensitive interventions
Indirect (ex: agriculture, education)
Examples of MSNP-III nutrition specific interventions
Vitamin A
iron-folic acids
Examples of MSNP-III nutrition sensitive interventions
school meals
sanitation programs
What are some other categories for strategic intervention in MSNP III?
sustainable food systems
resilience to crisis
GENDER EQUALITY
Maternal and child nutrition targets being measured as part of the MSNP III
reduce STUNTING, anemia, and improve dietary diversity
Out of the estimated USD 1.5 billion required to implement MSNP-III, what percentage is paid for by the government of Nepal?
~15%
What is hidden hunger
micronutrient deficiencies without visible signs
What are the 5 approaches to address micronutrient deficiencies
supplementation
fortification
dietary diversification
biofortification
public health measures
What is supplementation?
addition of nutrients to the diet through pills (think of a vitamin A supplement, like a GUMMY, individual)
Supplementation vs point-of-use fortification?
Supplementation: Pills or syrups. Point-of-use: nutrient powders added to food
What is fortification?
Adding extra nutrients to foods that wouldn't have them naturally in a MASSIVE way like in agriculture. For the GENERAL POPULATION, targeted for vulnerable groups, as its commercially driven by markets.
When is fortification appropriate (or not)?
Appropriate when infrastructure for it exists (like tech and factories), not when access is limited.
What is dietary diversification?
expand production, processing, marketing, and consumption of a wide variety of foods
What is biofortification?
The development of crops with enhanced nutritional profiles to combat nutrient deficiencies.
What are public health measures?
Measures that contribute most to people being healthier today than they were a century ago :
Sanitation
Better nutrition
occupational safety
What is the triple burden of child malnutrition?
Undernutrition (stunting/wasting)
micronutrient deficient
overweight/obesity
How does UNICEF assess children's diets?
Using MDD (minimum dietary diversity); compares to recall-based methods
UNICEF framework determinants of malnutrition
Immediate
inadequate diet
disease
Underlying:
food insecurity
care practices
Enabling:
policies
systems
Primary outcomes UNICEF aims to influence?
Improved maternal and child malnutrition
reduced stunting and wasting
Perceived susceptibility in AAMA
mothers recognized that poor feeding could lead to weakness/illness in their kids → helped motivate early breastfeeding and interest in dietary diversity to prevent malnutrition
Perceived severity in AAMA
Focus groups revealed awareness that undernutrition could stunt growth and affect future success → reinforced urgency to adopt recommended feeding practices
Perceived benefits in AAMA
Mothers believed that breast milk made children strong and healthy → supported promotion of exclusive breastfeeding and colostrum feeding
Perceived barriers in AAMA
Many moms feared that they couldn’t produce enough milk due to poor diets, some discarded colostrum due to cultural beliefs → informed messaging to reassure moms abt milk adequacy and educate on colostrum’s value
Cues to action AAMA project
Flip charts, crop calendars, and home visits by trained volunteers served as visual and interpersonal prompts → triggered behavioral change by linking nutrition messages to agriculture and daily routine
Self efficacy in AAMA
mothers lacked confidence in preparing diverse meals or feeding animal-source foods → AAMA provided hands-on training in homestead food production and cooking demos to build skills
Social norms in AAMA
Grandmothers were often primary caregivers and influenced feeding decisions, some discouraged colostrum → strategy targeted influential family members with tailored education and group discussions
Positive/negative reinforcement in AAMA
Mothers saw visible improvements in child health when feeding practices improved, group leaders praised progress → reinforced continued adoption of behaviors like timely breastfeeding and diverse complementary feeding