Beef Production Quiz Questions
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
How many cattle are in the United States?
80 to 100 Million
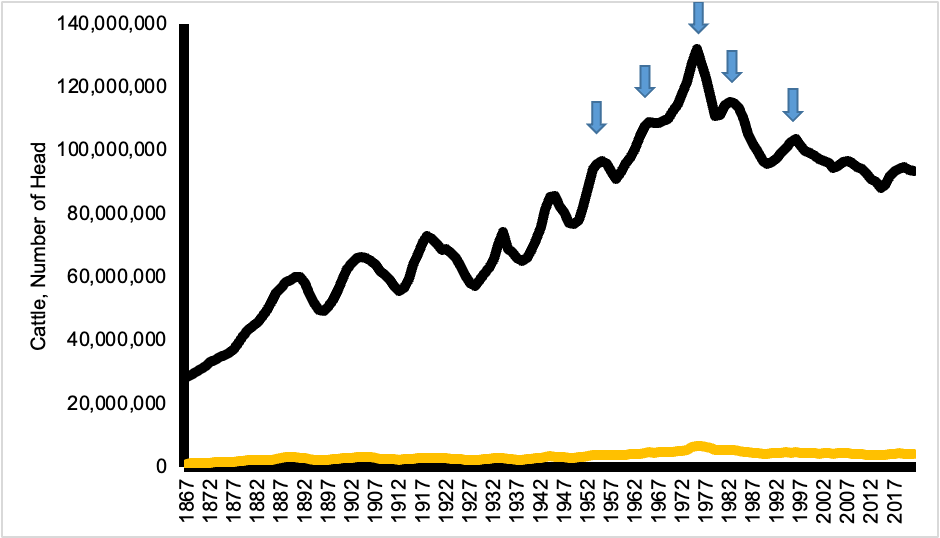
What phenomenon is depicted in the image below and why does it occur?
Known as the cattle cycle. Due to producers deciding to raise more cattle.
Across the past 45 years, beef production has consistently ranged between 23 to 29 billion pounds. During this same period of time, what has happened to total amounts of cattle in the United States (i.e. cattle inventory)?
It has decreased
Is the United States currently a net importer or exporter of beef?
The United States is a net exporter of beef, meaning it exports more beef than it imports.
What are the 2 primary countries from which beef is imported to the United States?
Mexico and Canada
Name 4 sources of cattle operations that provide cattle to feedlot operations.
Stockers, backgrounders, dairy producers, sale barns
Number of beef cows in Missouri
2 mil
Percent of US beef cows in Missouri
4.2%
Recommended age at first calf for Bos Taurus heifers
24 months
Gestation length of beef cattle
280 days
Recommended calving interval for beef cows
12 months
BIF weaning age
205 days
Days open and non-lactating for productive beef cows
0?
What do the US regions with high numbers of beef cows have in common?
can grow forage
poor row crop land
2 Benefits and 2 Disadvantages for the current structure (size of operations, distribution of operations) for the beef cow-calf industry.
Benefits: variation of genetics allows cattle to survive in many environments. Allows many people to partake in the industry.
Disadvantages: Variation in beef products; genetics, quality. Lost of $ spend on transportation
Compare and contrast size of operations and numbers of operations for beef cow-calf and feedlot operations in the US.
Many small cow-calf spread out throughout the country. Feedlots centrally located in NE, TX, KS, and usually large opertions
What is the main products marketed by cow-calf operations?
weaned calves
When would you expect beef cows to reach mature body weight?
5-7 years old
Draw the life of a beef cow
What is the primary advantage of storing silage in a bunker silo rather than bags or vertical silos
easier to pack down, and less loss due to oxygen exposure
How should hay be sampled from round bales?
Samples should be taken from multiple bales using a core sampler. Across the bale from the side to collect samples
Which is more accurate for hay analysis: wet chemistry or NIR?
Wet chemistry
Name 4 processes that beef cows that are already at their mature body weight partition nutrients to OTHER than maintenance.
Reproduction, lactation, thermoregulation and adipose storage
Give one pro and one con each for storing hay outside versus in a covered location
Pro for storing hay outside: cheaper option; Con: exposure to weather damages and nutrient run off. Covered: Pro: decreased nutrient loss; Con- expensive
Why are 2 and 3 year old cows at the most risk of being culled from the herd? What is a management choice we can make to help prevent this?
Many changes: growth, reproducing, lactating. We are asking them to do a lot. One way to help is by separating them into one group and monitoring BCS and supplementing if necessary.
What is the most nutrient demanding time of a beef cow’s year?
Peak lactation
Approximately how much of a beef cow-calf operation’s total yearly costs are made up by feed?
72%
What is one way that energy needs associated with cold stress can be decreased for beef cows?
Providing wind breaks
Which form of castration often has greater negative perception?
Surgical castration as compared to banding because you are pulling the testes out
What is the BCS scale used in beef cattle. What BCS should cow be at calving?
Body condition scoring (BCS) of cattle allows producers to assess the fat reserves of cows during various production phase. 5.5-6 is ideal at calving
3 options for how to supplement energy and protein?
Feeding grain, forages (hay/silage), lick tubs (liquid or molasses)
Steps to determine how much energy and supplementation is needed for beef cows
Identify DMI, CP and Mcal Needed
Use feed sample analysis to calculate CP and Mcal of the baseline forage
Find the difference between needed and supplied
Find a supplement that will fill the difference
Why are the major caving seasons selected from a nutritional standpoint?
Peak lactation is occurring in season of high quality forage and volume
Main goals of heifer development?
Attain puberty
Grow
Get pregnant
One option for a strategy of gain during heifer development. What is target body weight at breeding?
Steady growth strategy. Slow, steady and continuous growth.
55-65%
3 Heat detection options
KMAR patch, Estrotech Patch, heat watch electronic system
What is the main event of each stage of parturtion?
Stage 1: waterbag loss
Stage 2: calf explusion
Stage 3: placenta explusion
Why is colostrum important for a neonatal calf? When should it be consumed for maximal effect?
Immunoglobulins and high in nutrients, first 8-15 hours
1 pro and 1 con for each modified live and killed vaccines?
Modified Live: pro- one dose/year at lease, con- needed to be done 30 days prior to breeding due to potential inflammation
Killed: pro- less concern with temperature/element exposure, con- needs additional booster shots; especially naive animals (2-5 weeks after initial dose)
2 important time points for vaccinating cows?
Pre-breeding and pregnancy diagnosis
2 time points for vaccinating pre-weaning calves?
Calf processing- 60-90 days after birth
At weaning
When should you watch for scours vs. respiratory disease in pre-weaning calves?
Scours- first weeks of life
Respiratory disease- few weeks to 120 days
What are 4 negative potential consequences for pre-weaning calves from poor late gestational nutrition of their dams?
Less vigor
Smaller calves
More susceptible to heat/cold stress
Higher disease risk
What is the USDA thickness scores and how do they relate to feeder calf pricing?
1-4 indicate the amount of muscling. Thicker calves (1) are more valuable because thickness relates to finished body weight
What is the ‘slide’ and why does it occur?
Price break system that protects buyers and sellers in feedlot sector. Calves delivered at lighter weights than agreed get a slide increase in price. Calves delivered at heavier weight get slide decrease in prices. Occurs to protect both buyers and sellers.
4 factors that influence feeder calf pricing
Horns, sex, thickness score, frame score
Why are feeder heifers less than feeder steers
Heifers finish at a lighter weight. Less weight to gain and make money on.
Mott curves
What disease complex does a 5way or 7way provide immunity against?
BRD
What percentage of cattle in stocker, backgrounding or feedlot operations are impacted by subclinical and clinical respiratory disease?
53%
What impact does rapid weight gain during the stocker/backgrounder phase have on hot carcass weight
decrease it?
What is the principle role of stocker/backgrounders?
The stocker sector provides basic production value for the cattle industry. Matches beef with demand rather than following the calving graph. Stocker production also helps balance forage and feed grain values.
What is value of gain?
Value of gain (VOG) in the beef industry refers to the amount the market is willing to pay for each pound of weight a cattle animal gains. It's calculated by subtracting the purchase price from the sale price, then dividing the result by the pounds gained. Understanding VOG is crucial because it helps producers determine if it's profitable to retain and fatten cattle, rather than selling them at a lighter weigh