343 Chapter 10 Testing and Quality Assurance
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
activities designed to measure and improve quality in a product and process
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
activities designed to validate and verify the quality of the product through detecting faults and “fixing” the defects
What is Quality Control (QC)?
They are similar
Are QA and QC similar?
good techniques, process, tools, and team
What do you need for testing?
What is the traditional definition of Quality?
Conforms to requirements
Fit to use
What is Verification?
checking the software conforms to its requirements (did the software evolve from the requirements properly; does the software “work”?)
What is Validation?
checking software meets user requirements (fit to use)
What are some Error Detection Techniques (finding errors)?
Testing
Inspections and Reviews
Formal methods (proving software correct)
Static Analysis detects “error-prone conditions”
What is testing?
executing program in a controlled environment and “verifying/validating” output
What is an Error?
a mistake made by a programmer or software engineer that caused the fault, which in turn may cause a failure
What is a Fault (defect, bug)?
condition that may cause a failure in the system
What is a Failure (problem)?
inability of system to perform a function according to its spec due to some fault
What is Fault or failure/problem severity base on?
Consequences
What is Fault or failure/problem priority base on?
importance of developing a fix, which is in turn based on severity
Why do we do testing?
Evaluating product quality
Improving products by identifying defects and having them fixed prior to software release
Dynamic (running-program) verification-
of program’s behavior on a finite set of test cases selected from execution domain
Testing can NOT prove product works 100%,-
even though we use testing to demonstrate that parts of the software works
Who tests
Programmers
Testers/Req. Analyst
Users
What is tested?
Unit code testing
Functional code testing
Integration/system testing
User interface testing
Why Test?
Acceptance (customer)
Conformance (std, laws, etc)
Configuration (user vs. dev.)
Performance, stress, security, etc.
How to test (test cases designed)?
Intuition
Specification based (black box)
Code based (white box)
Existing cases (regression)
What is Black-box testing?
A testing methodology where the test cases are mostly derived from the requirements statements without consideration of the actual code content
What is White-box testing?
A testing methodology where the test cases are mostly derived from examining the code and the detailed design.
What is regression?
It executes some (or all) test cases available for a previous version of the system on a new version.
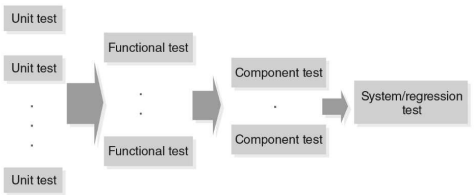
What is this?
Progression of Testing
What is Equivalence-Class Partitioning?
It is based on dividing the input into several classes that are deemed equivalent for the purposes of finding errors.
Why do Equivalence-Class Partitioning?
Lessen Duplication
Complete Coverage
Past experiences show that “boundaries” are what?
error-prone
The “basic” boundary value testing for a value would include what?
At the “minimum” boundary
Immediately above minimum
Between minimum and maximum (nominal)
Immediately below maximum
At the “maximum” boundary
Boundary Value Analysis is what technique?
A Black Box Technique
Path Analysis is what technique?
A White Box Technique
What are the task of Path Analysis?
Analyze number of paths in program
Decide which ones to test
What is the decreasing coverage of Path Analysis?
Logical paths
Independent paths
Branch coverage
Statement coverage
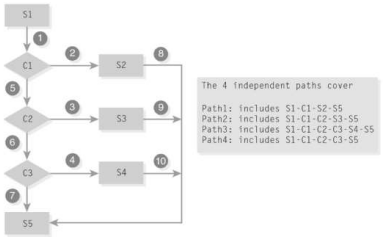
What is this?
A “CASE” Structure
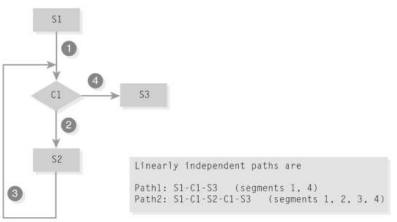
What is this?
A Simple Loop Structure
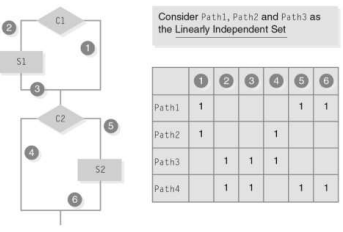
What is this?
Linearly Independent Set of Paths
What is Combinations of Conditions for?
Functions of Several related variables
How do we fully test?
we need all possible combinations (of equivalence classes).
How to reduce testing?
Coverage analysis
Assess “important” (e.g., main functionalities) cases
Test all pairs of relations (but not all combinations)
What is Unit Testing?
test each individual unit
Who usually does Unit Testing?
the programmer
Test each unit as-
it is developed (small chunks)
What should we keep test cases/results around?
Allows for regression testing
Facilitates refactoring
Tests become documentation!!
What are Test-Driven Development
Write unit-test cases BEFORE the code
Test cases “are”/”becomes” requirements
Forces Development in small steps
What are the steps of Test-Driven Development?
Write test case and code
Verify (it fails or runs)
Modify code so it succeeds
Rerun test case, previous tests
Refactor until (success and satisfaction)
When to stop testing (simple)?
All planned test cases are executed
All those problems that are found are fixed
Other techniques to stop testing are?
Stop when you are not finding any more errors
Defect seeding: test until all (or % of )the seeded bugs found
Running out of time means
poor planning
What is a Review?
any process involving human testers reading and understanding a document and then analyzing it with the purpose of detecting errors
What is a Walkthrough?
author explaining document to team of people
What is a Software Inspection?
detailed reviews of work in progress, following Fagan’s method
What are the steps of Software Inspections?
Planning
Overview
Preparation
Inspection
Rework
Follow-up
What is Software Inspections focused on?
Finding Defects
What does Software Inspections output?
List of defects
What does the team of Software Inspections look like?
3-6 people
Author included
People working on related efforts
Moderator, reader, scribe
What makes testing different from inspections?
Finds errors cheaper, but correcting them is expensive
Can only be applied to code
Catches defects late (after implementation)
Necessary to gauge quality
What makes inspections different from testing?
Partially cost-effective
Can be applied to intermediate artifacts
Catches defects early
Helps disseminate knowledge about project and best practices
What techniques do formal methods use?
Mathematical techniques used to prove that a program works
What are formal methods used for?
Used for requirements/design/algorithm specification
What do formal methods prove?
that implementation conforms to spec
Formal methods have what conditions?
Pre- and post-conditions
What are the problems of Formal Methods?
Require math training
Not applicable to all programs
Only verification, not validation
Not applicable to all aspects of program (e.g., UI or maintainability)
What is Static Analysis?
Examination of static structures of design/code for detecting error-prone conditions (cohesion—coupling)
Automatic program tools are more what?
Useful
What can Static Analysis be applied to?
Intermediate documents (but in formal model)
Source code
Executable files
Who Checks Static Analysis output?
by the programmer