Module 9: Cell Division and Mitosis: Part: 2/2 (Combined 3 & 4): The Cellular Dynamic and it essential
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology
Biochemistry
A-Level Chemistry
AQA
Organic Chemistry
Module 9: Cell Division and Mitosis: Part: 2/2 (Combined 3 & 4): The Cellular Dynamic and it essential
Module 9: Cell Division and Mitosis: Part: 2/2: The Cellular Dynamic and it essential
Module 9
Module 9: Cell Division
Mitosis
Cell Division and Mitosis
The Cellular Dynamic and it essential
The Cellular Dynamic
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Phases
Spindle Apparatus and Chromosome Movement
Cell cycle
Mitosis Phase
Spindle Apparatus
Chromosome Movement
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
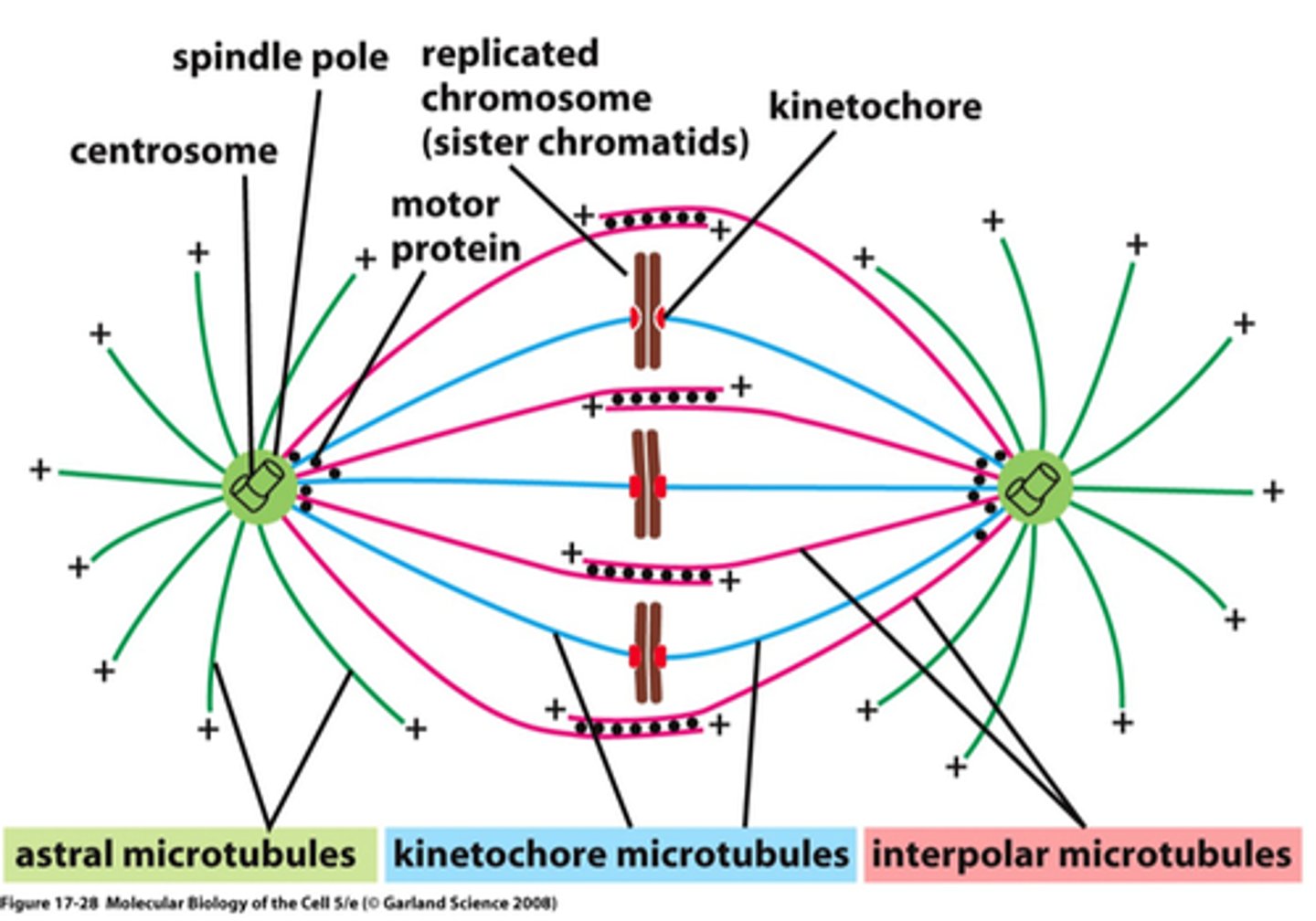
What is the mitotic spindle composed of?
Fibers made of microtubules and associated proteins.
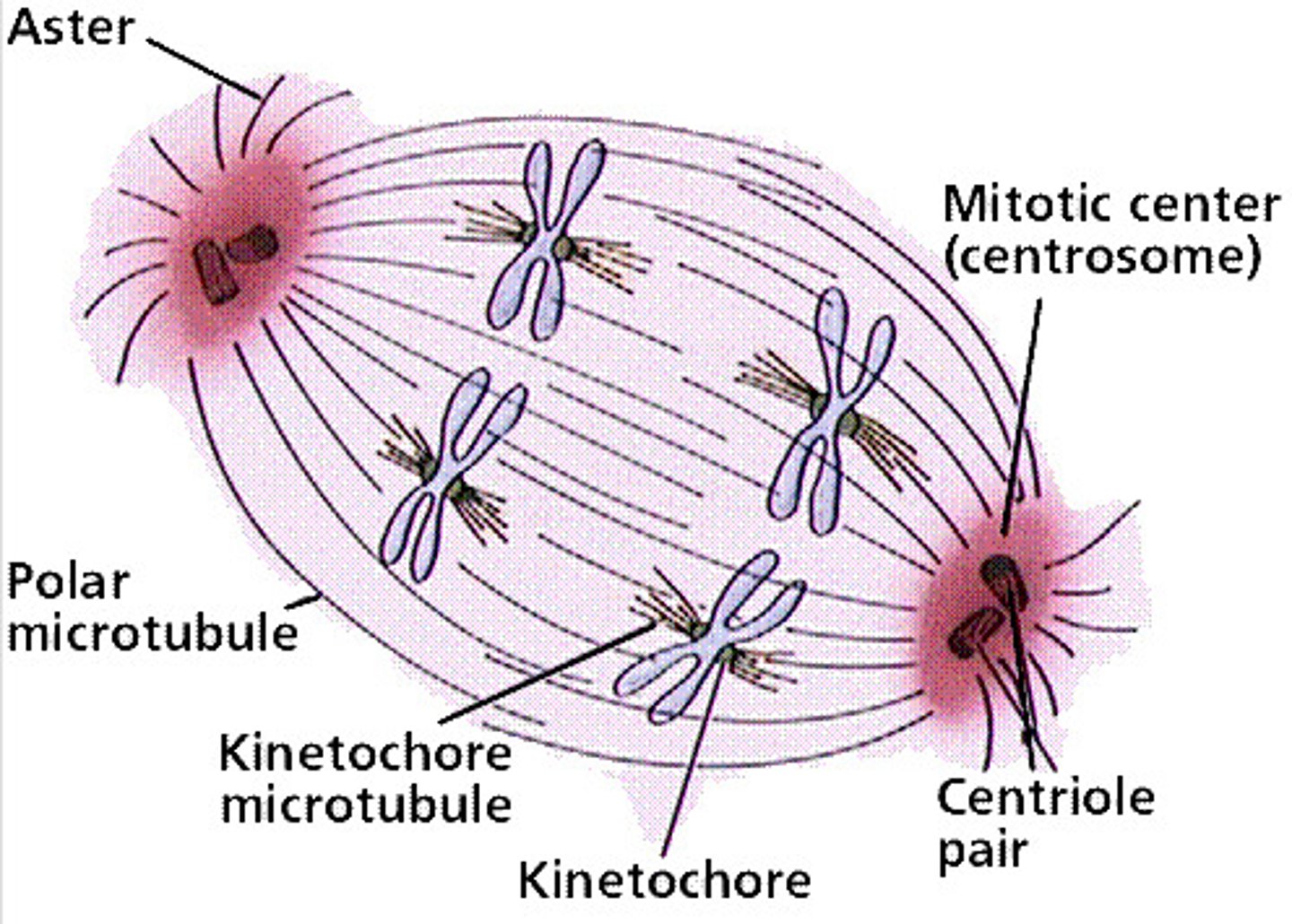
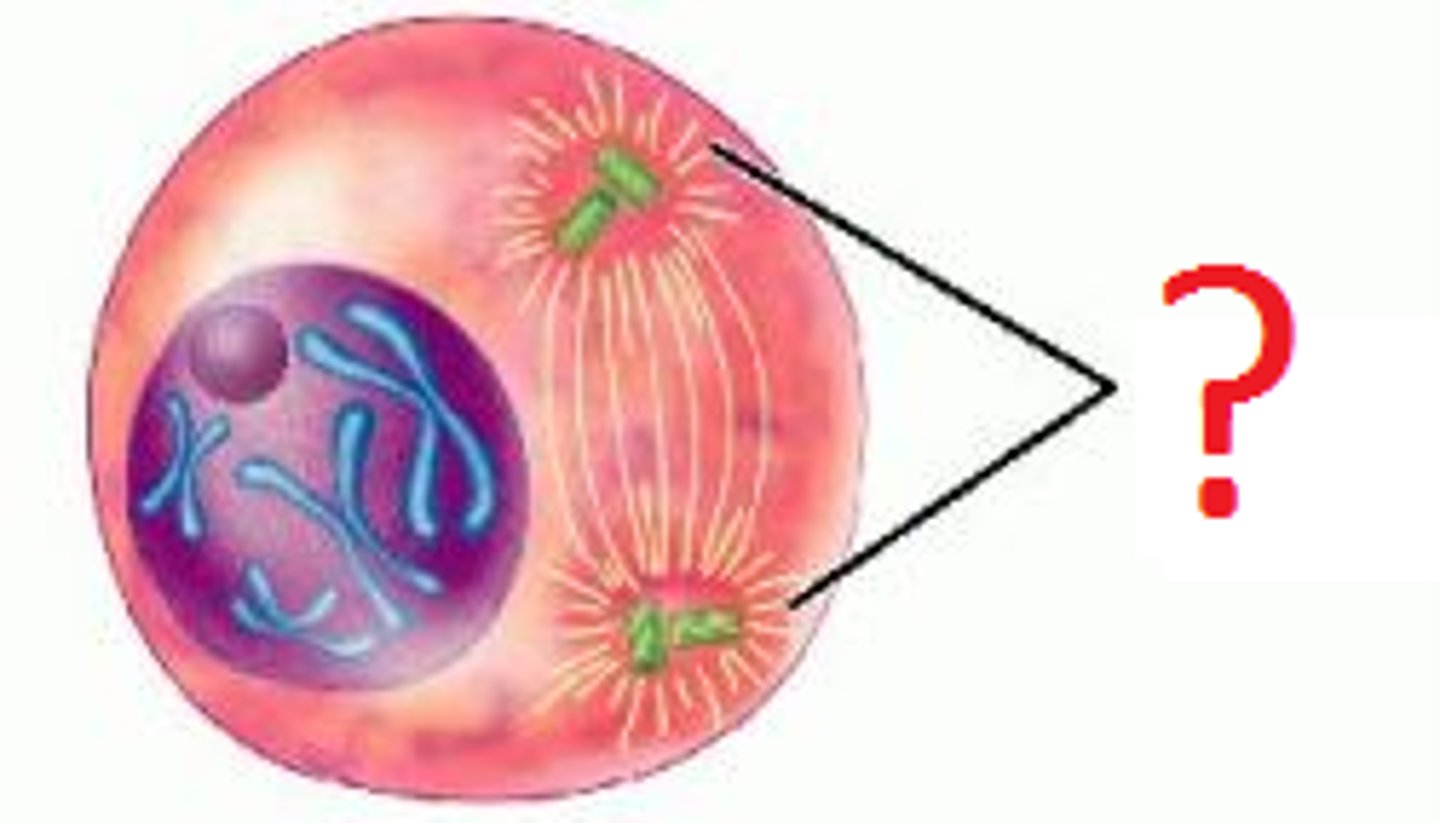
Where does the assembly of the spindle fibers begin?
In the centrosome, or microtubule-organizing center.
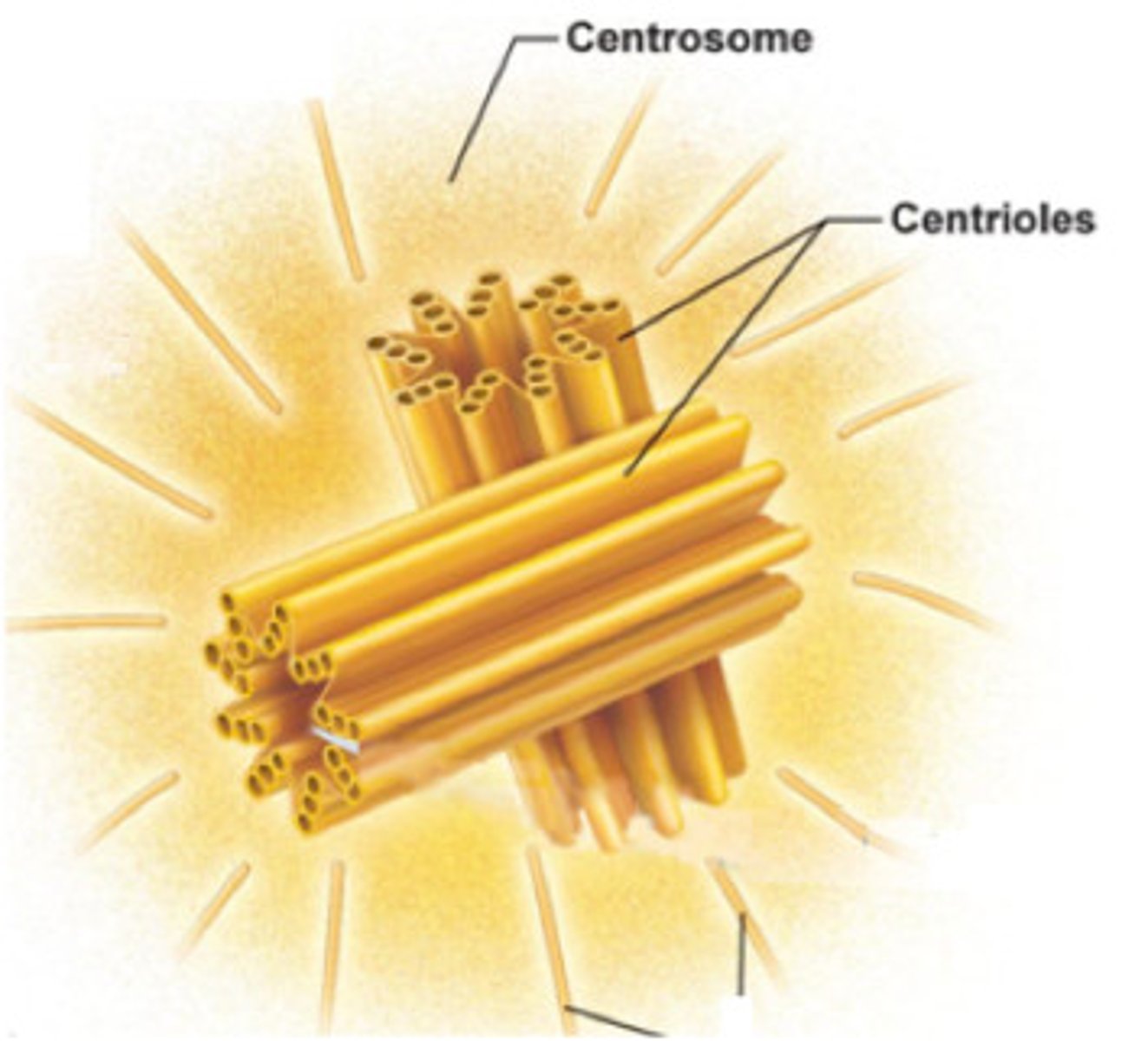
What happens to the centrosome during interphase?
It replicates to form two centrosomes.

What is an aster?
A radial array of short microtubules extending from each centrosome.
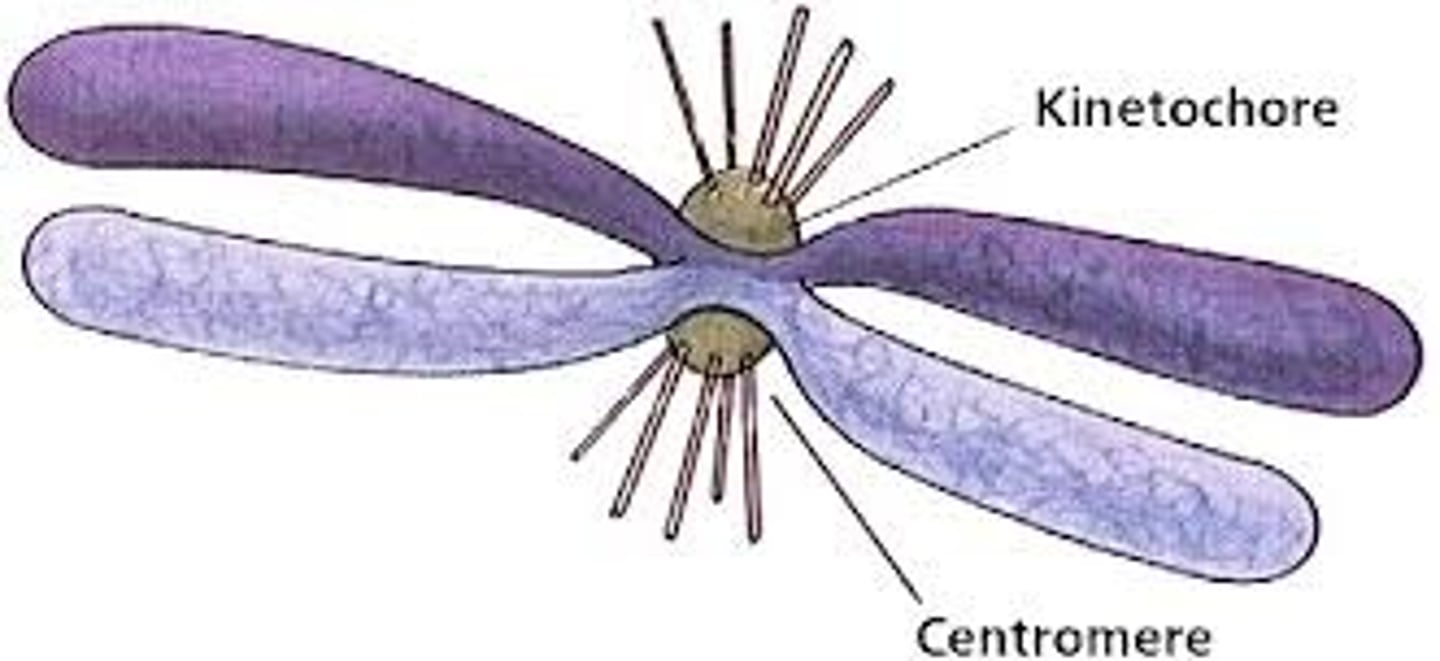
What are kinetochores?
Protein structures on sister chromatids that attach to spindle microtubules.
What occurs during prometaphase regarding spindle microtubules?
Some spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores.
What are the phases of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle consists of the mitotic (M) phase and interphase.
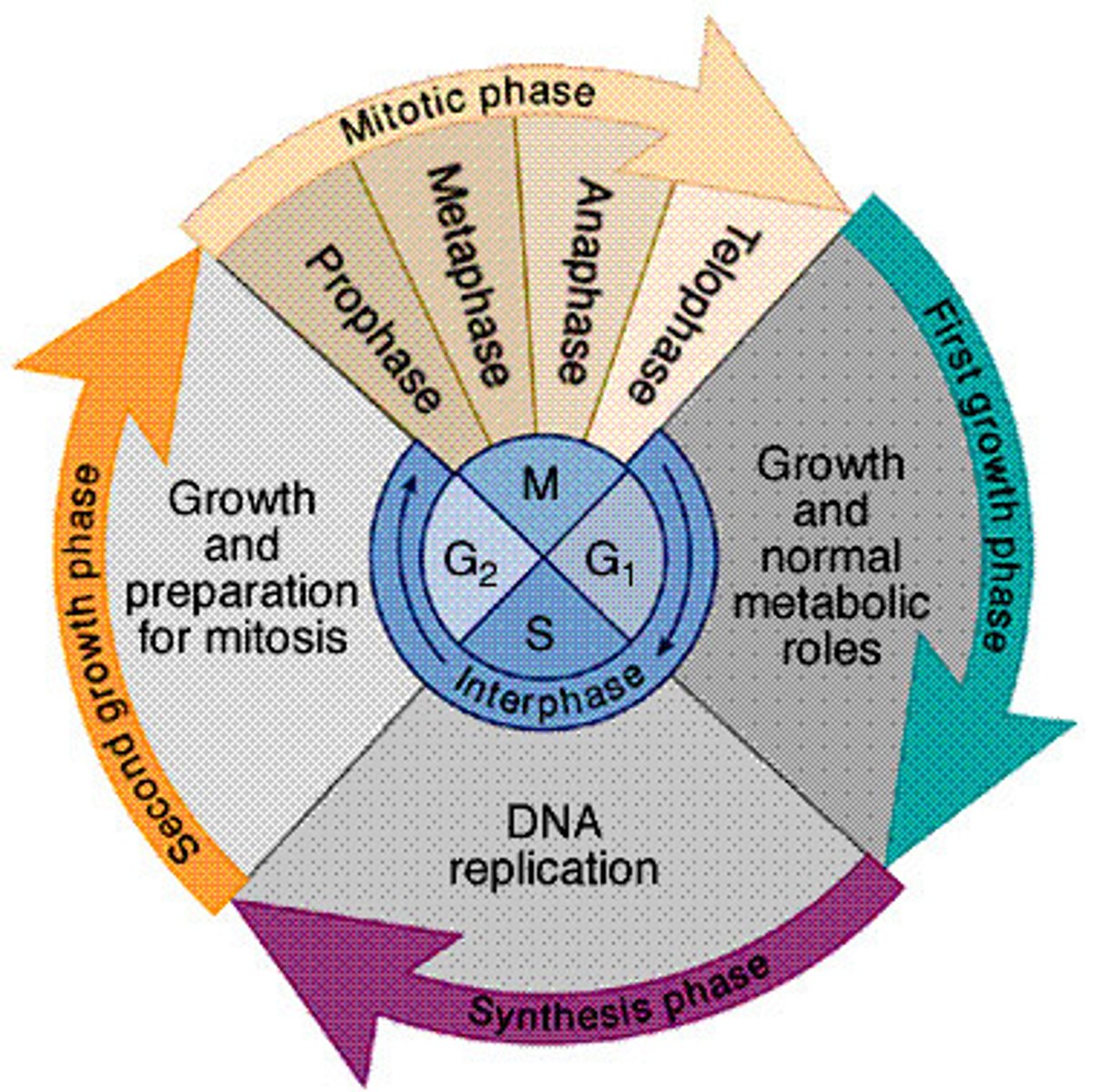
What percentage of the cell cycle does interphase account for?
About 90%.
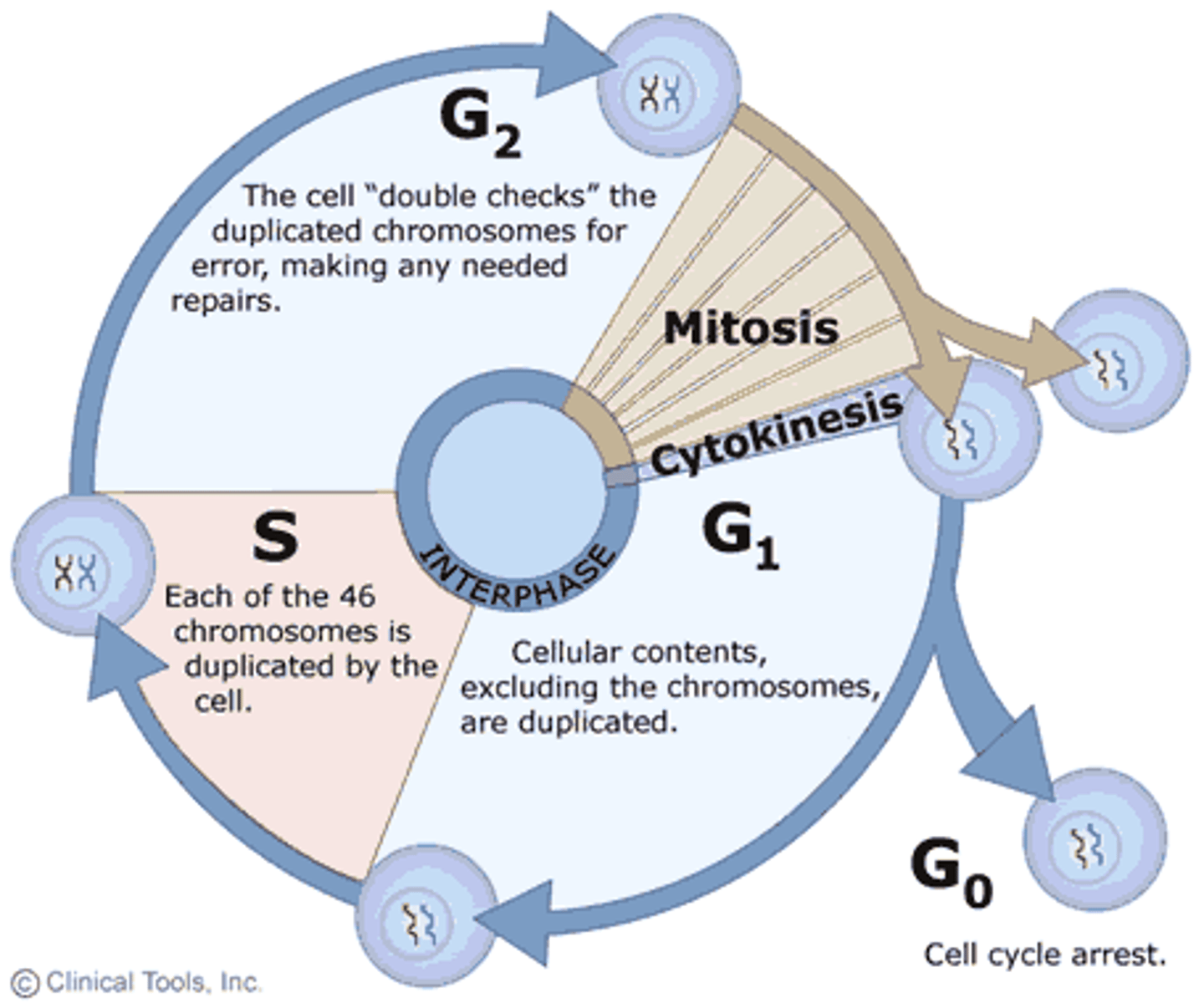
What are the three subphases of interphase?
G1 phase (first gap), S phase (synthesis), and G2 phase (second gap).
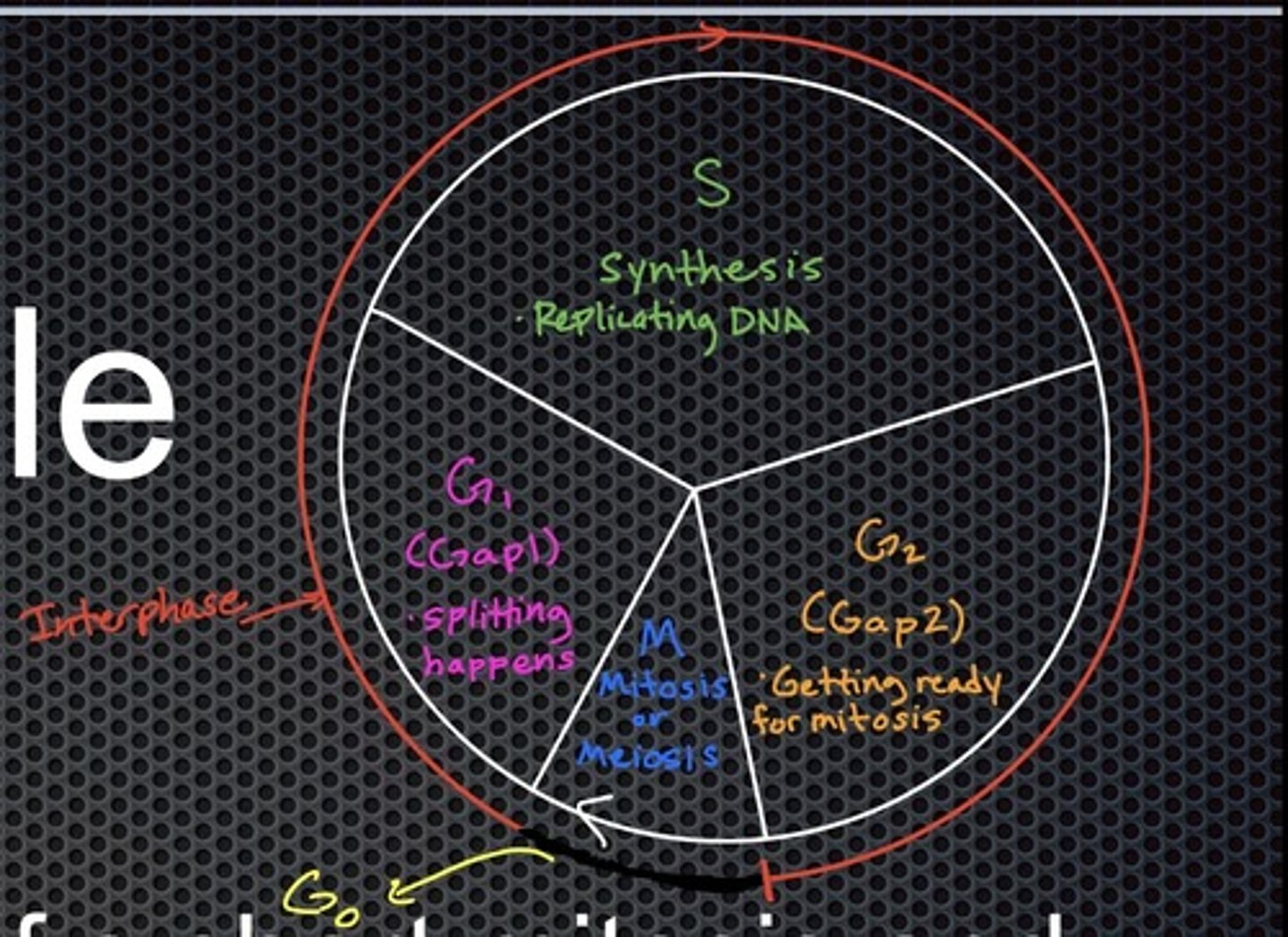
During which phase are chromosomes duplicated?
During the S phase of interphase.
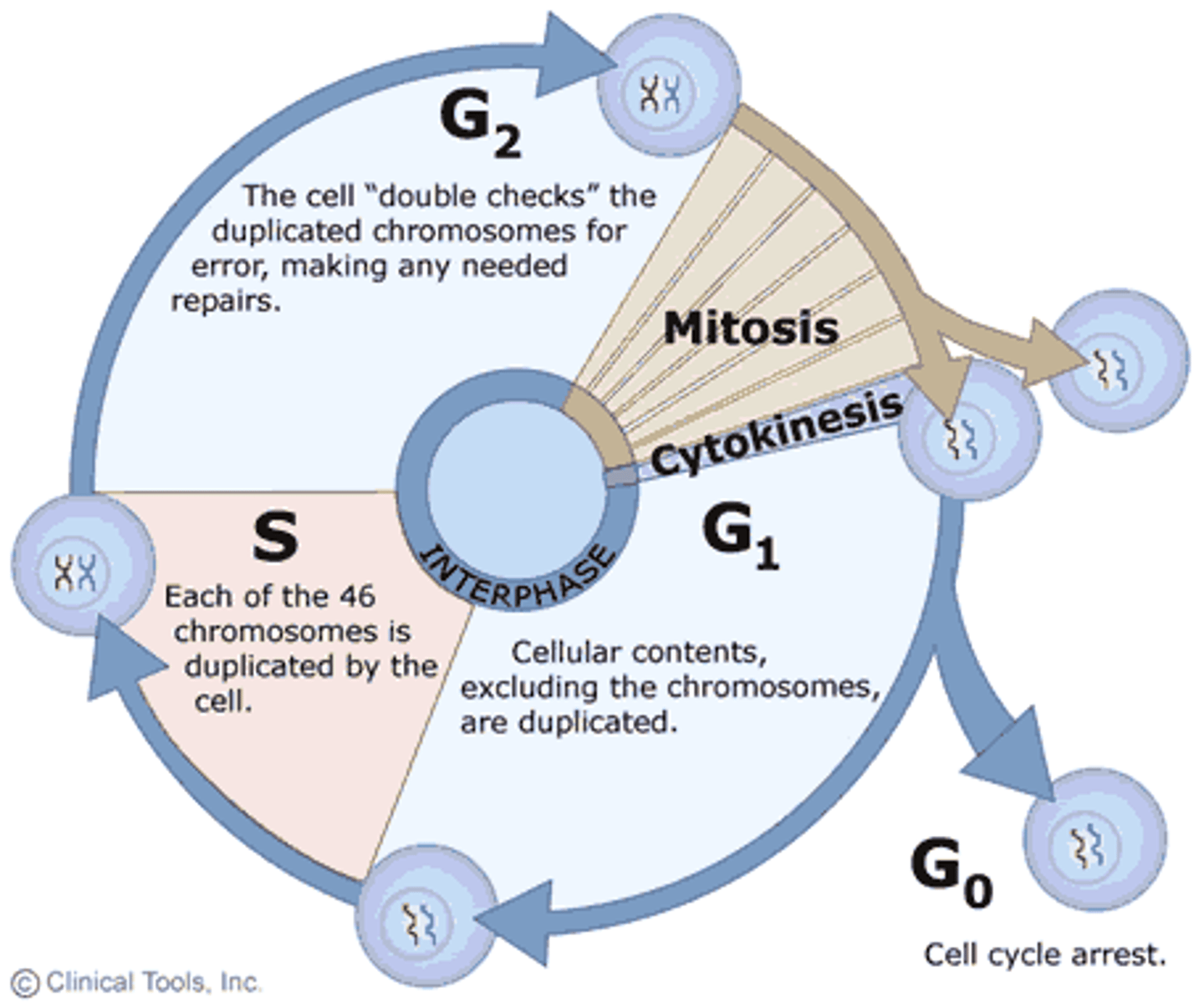
How long does the M phase typically last in a human cell cycle?
Less than an hour.
What is the typical duration of the S phase in a human cell cycle?
10-12 hours, or about half the cycle.
What are the five subphases of mitosis?
Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
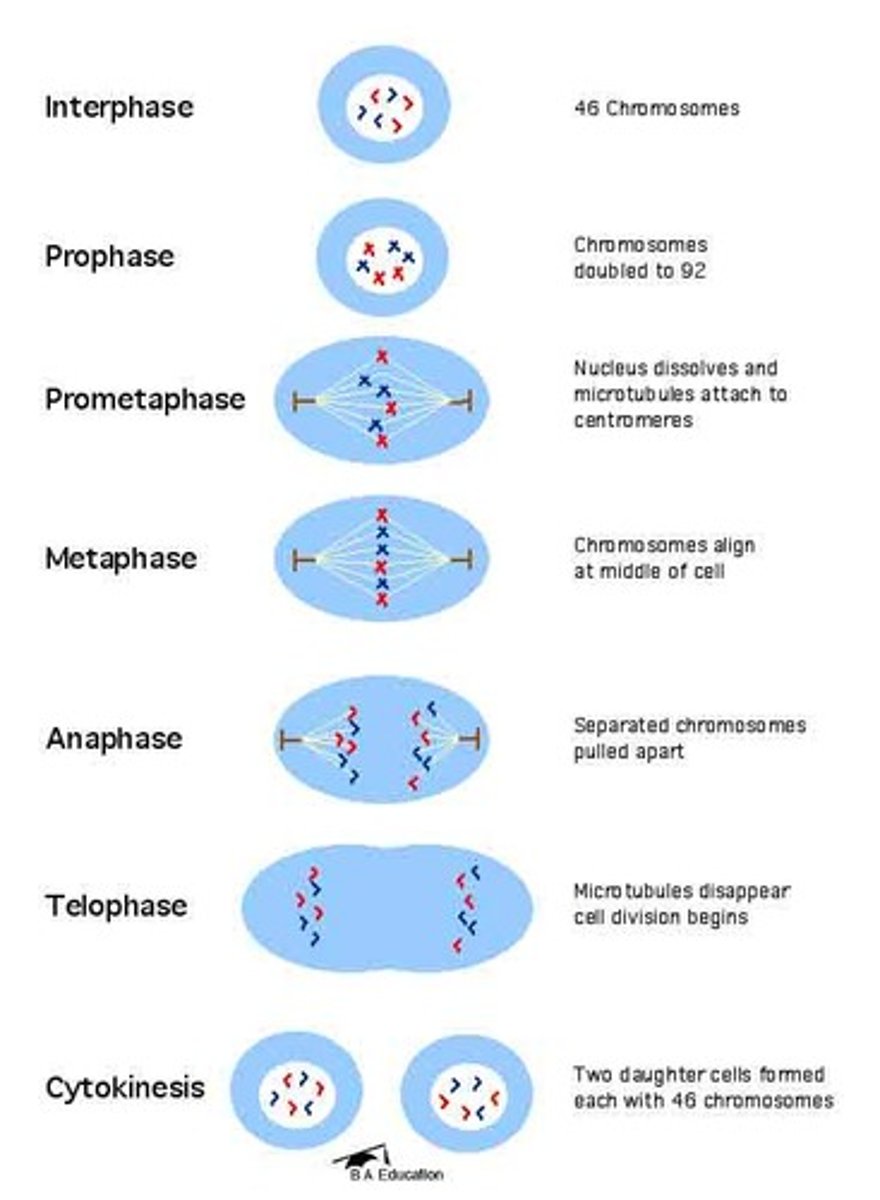
What happens to the chromosomes in late interphase?
They have been duplicated but are not yet condensed.
What occurs during prophase?
Chromosomes coil tightly, nucleoli disappear, and the mitotic spindle begins to form.

What is the role of the kinetochore?
A specialized protein structure at the centromere that attaches to microtubules during prometaphase.
What defines metaphase in the cell cycle?
Sister chromatids are arranged at the metaphase plate, an imaginary plane equidistant from the poles.
What occurs during anaphase?
Centromeres divide, separating sister chromatids, which are pulled toward opposite poles.
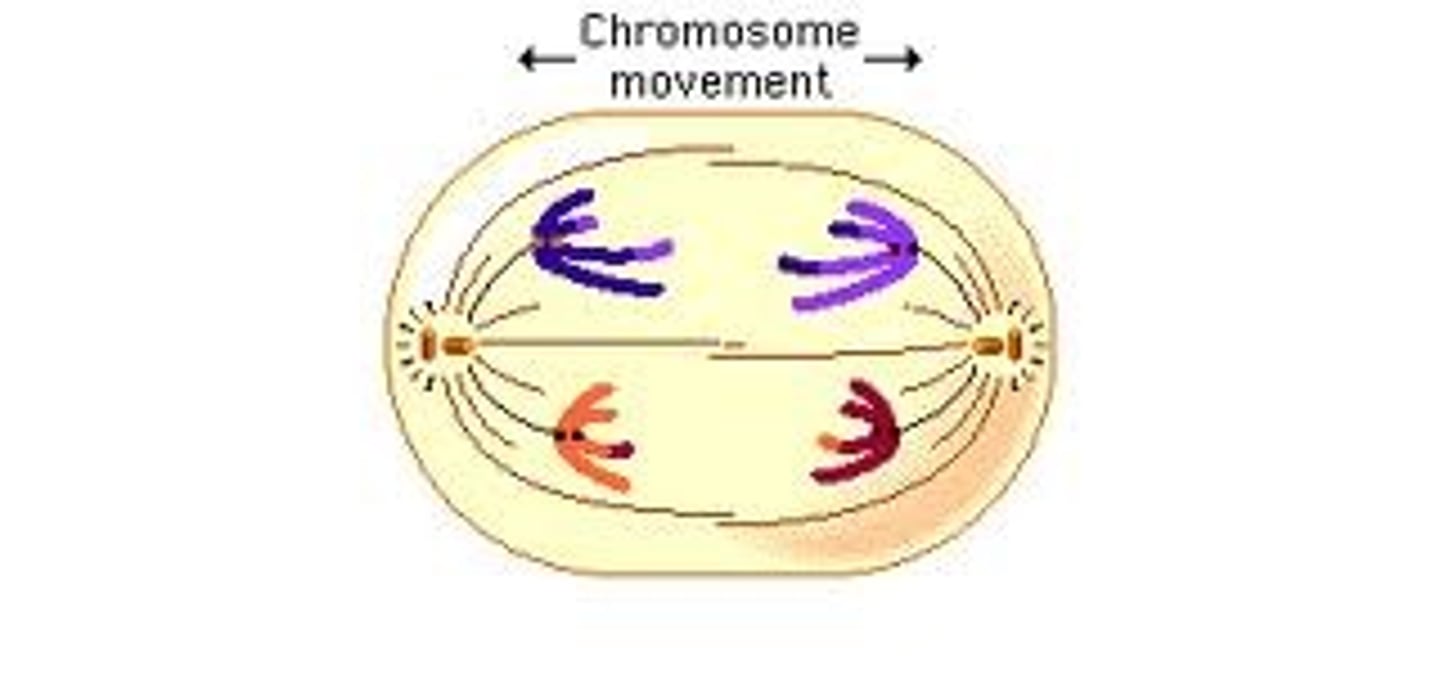
What are asters in the context of mitosis?
Radial arrays of shorter microtubules that extend from the centrosomes.
What happens to the nuclear envelope during prometaphase?
It fragments, allowing microtubules to interact with condensed chromosomes.
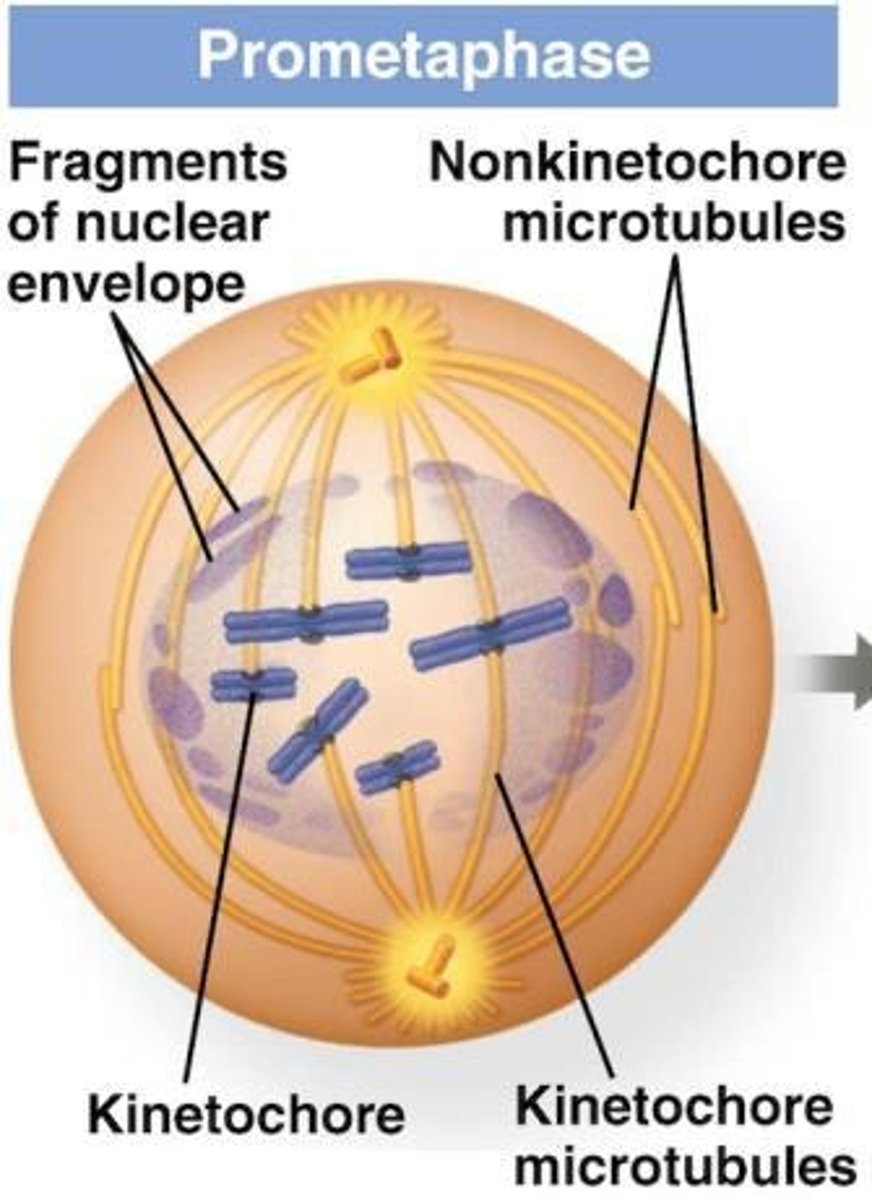
What pulls each chromatid toward the poles during mitosis?
Spindle fibers.
What happens to the chromosomes by the end of telophase?
They become less tightly coiled.
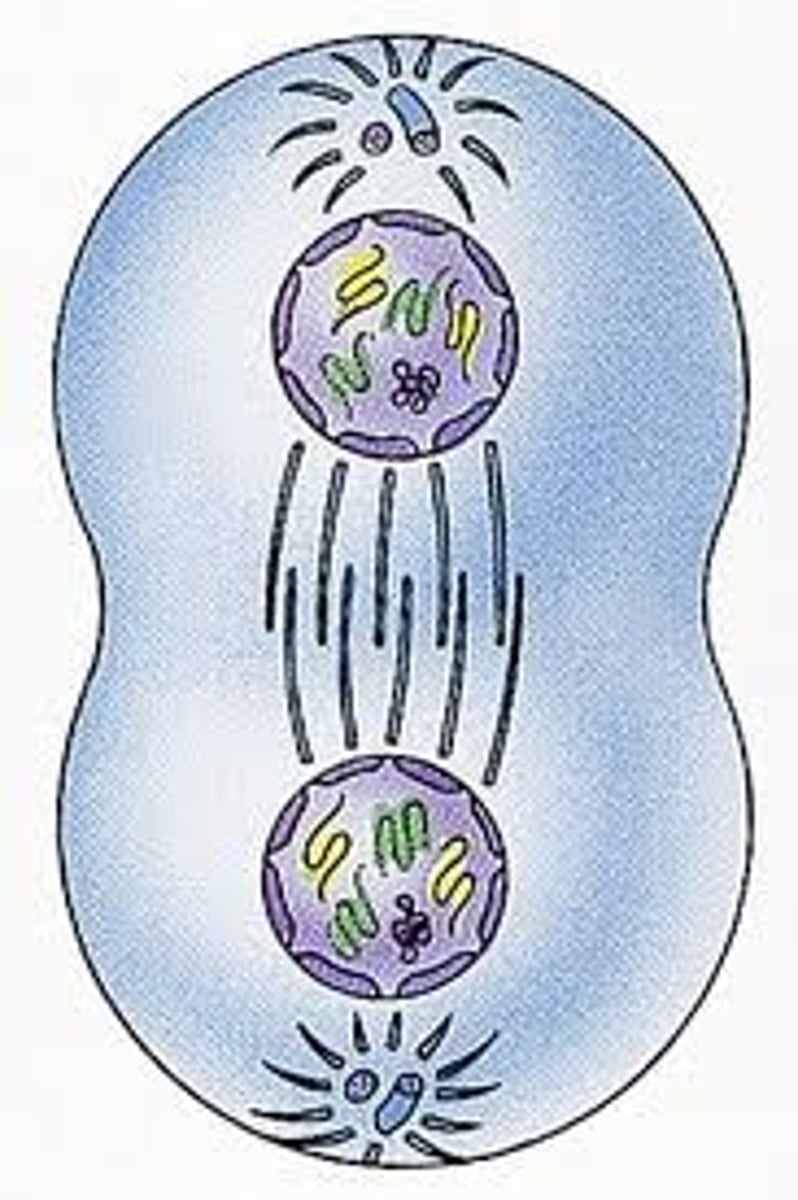
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm, usually well underway by late telophase.
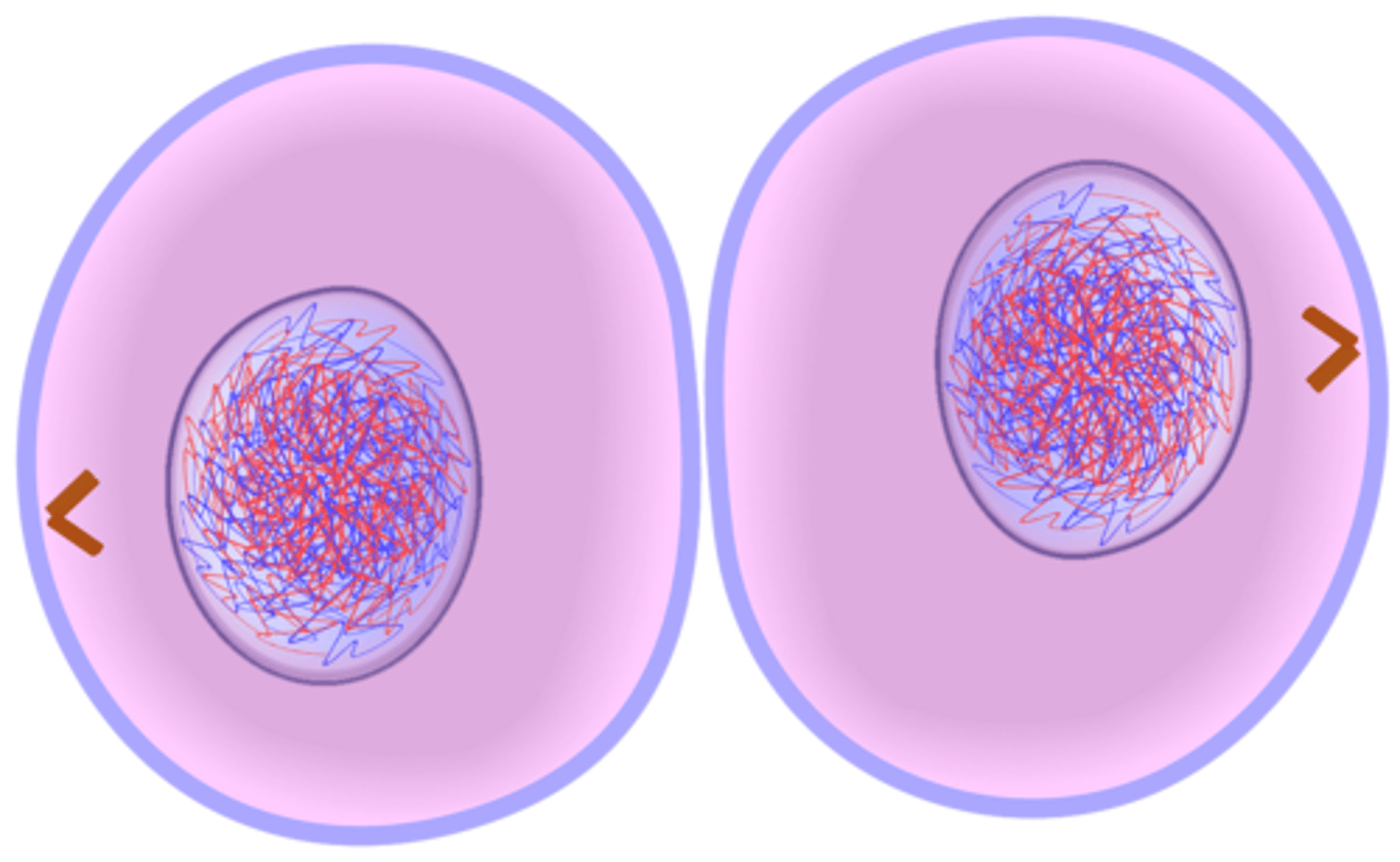
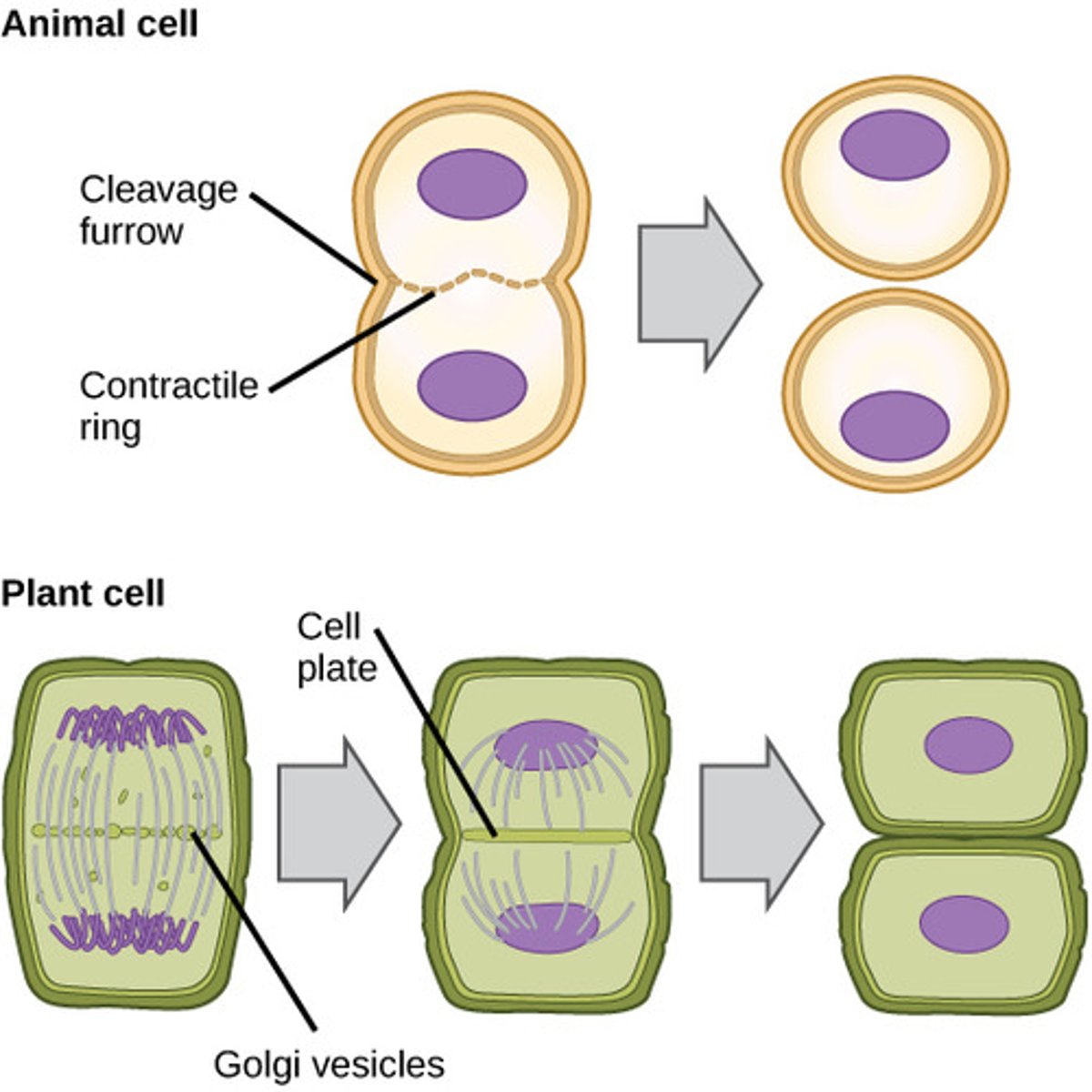
How does cytokinesis differ in animal and plant cells?
In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms; in plant cells, vesicles produce a cell plate.