OPT 114 EOMs
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What EOMs have an origin at the annulus of zinn?
-superior rectus
-inferior rectus
-lateral rectus
-medial rectus
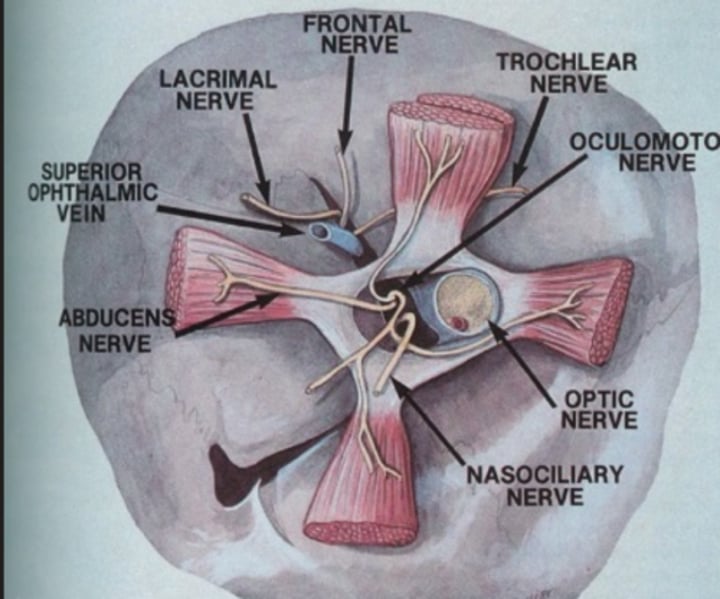
Where is the annulus of zinn located?
orbital apex, nasal and posterior to the orbit
Where in the CTR does the superior rectus attach to?
upper limb of the ring, also attaches to dural sheath of ON
Where in the CTR does the medial rectus attach to?
upper and lower limb of the ring , dural sheath of ON
Where in the CTR does the lateral rectus attach to?
upper and lower limb of the ring, spina recti lateralis of the greater wing of sphenoid
Where in the CTR does the inferior rectus attach to?
lower limb of the ring
Describe the course of the medial rectus
medial orbital wall, follows curve of globe
What does the sheath of the medial rectus form?
medial check ligaments which hold the globe into place
Describe the course of the lateral rectus.
lateral orbital wall
What does the sheath of the lateral rectus form?
lateral check ligament which holds the globe into place
Describe the course of the superior rectus
forward beneath the levator muscle (so UL elevates on upgaze)
Describe the course of the inferior rectus.
above the inferior oblique, the sheaths for the capsulopalpebral fascia (LL lowers downgaze and elevates on upgaze)
What happens to the recti muscles before insertion?
they become tendons and penetrate tenon's capsule
What do the recti muscle insertions form?
spiral of tillaux; medial rectus sits the most anterior and then clockwise movement each rectus muscle inserts further back
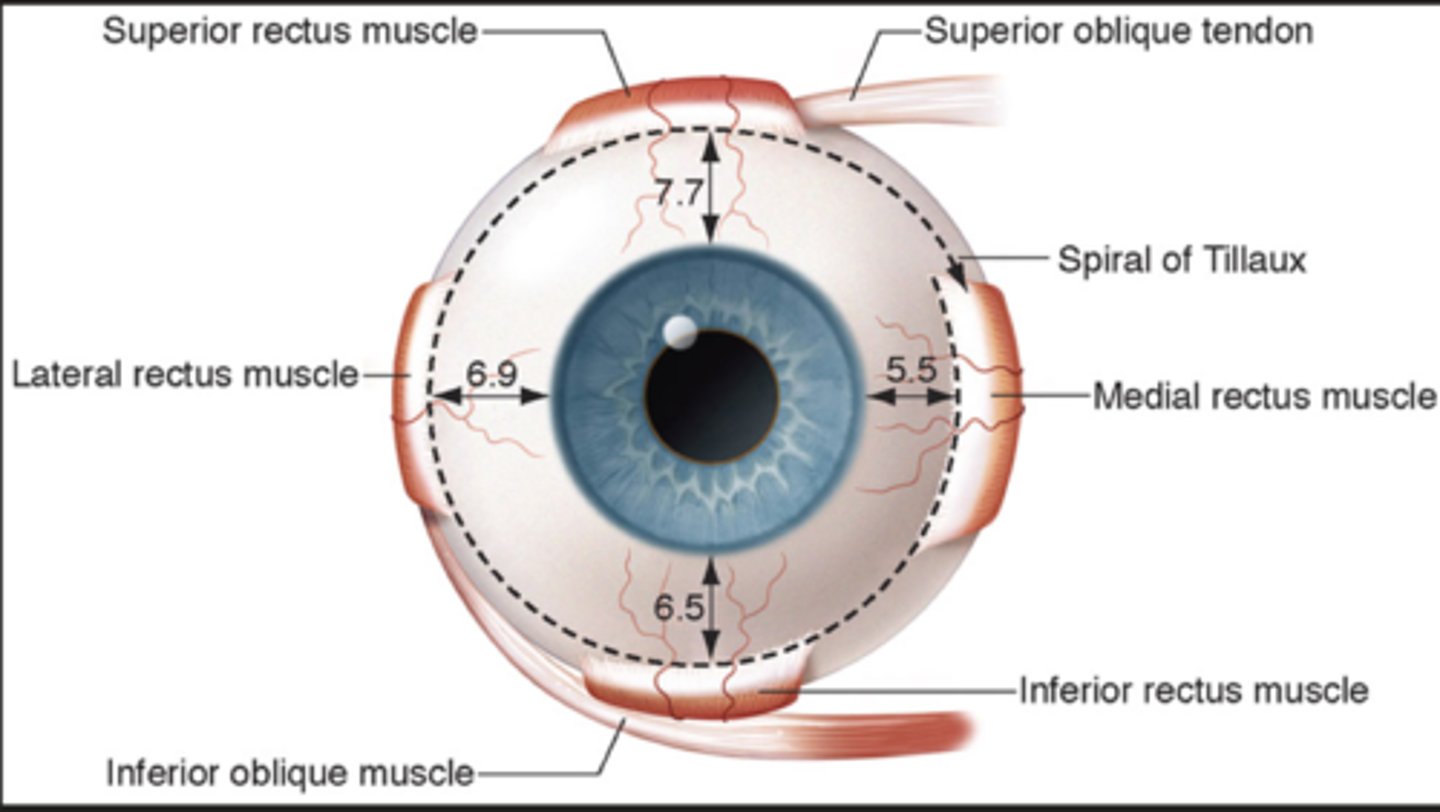
Where does the superior oblique originate from?
Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone and above optic canal orbital apex
Where does the inferior oblique originate from?
maxillary bone (only EOM with muscle in the anterior orbit)
What is the longest EOM?
superior oblique
What does the superior oblique pass through?
trochlea (this is the functional origin)
What muscle forms a 55 degree angle with the visual axis?
superior oblique
What is a duction?
Movement of one eye
What types of ductions are along the x axis?
supraduction and infraduction
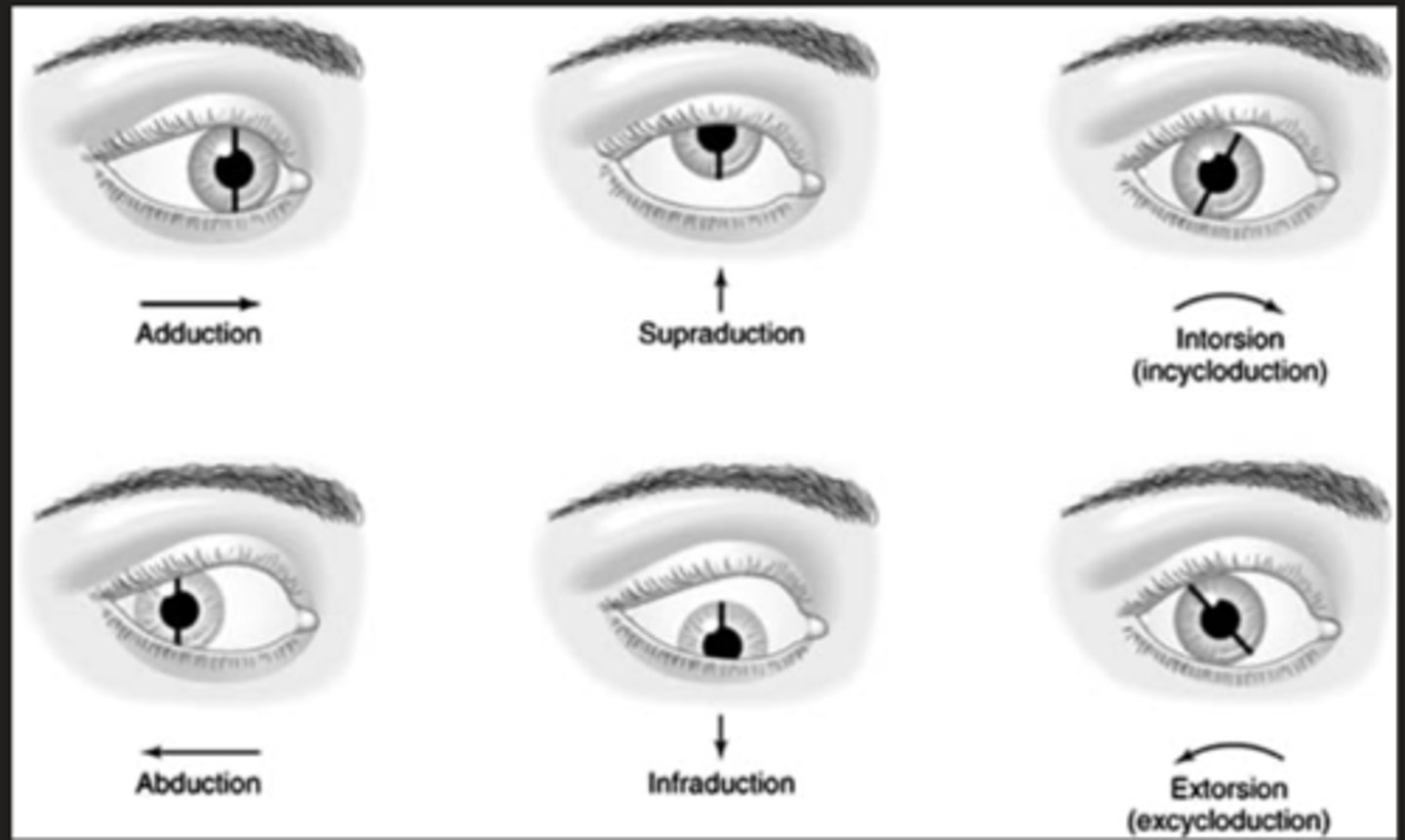
What types of ductions are along the y axis?
introsion and extrosion
What types of ductions are along the z axis? -- this is the vertical axis
adduction (towards midline) and abduction (away from midline)
What is the primary action of the medial rectus?
adduction
What is the primary action of the lateral rectus?
abduction
What is the primary action of the superior rectus?
supraduction
What is the primary action of the inferior rectus?
infraduction
What is the primary action of the superior oblique ?
intorsion
What is the primary action of the inferior oblique ?
extrosion
What muscles does CN III innervate?
superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique
What does CN VI innervate?
lateral rectus muscle
What does CN IV control?
superior oblique