Capacitors
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
capacitance definition
It is the ability of a body to hold electric charge
It may also be described as the amount of electric charge for a given voltage
Capacitance equation
C - Capacitance - Farads (F)
Q - Charge - Coulombs (C)
V - Pd - Volts (V)
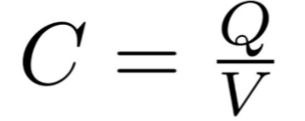
What is a capacitor
It is a device designed to store change
Made by two parallel plates with an insulator between
one plate gains electros from the battery and the other looses electrons to the battery, to make the charges equal and opposite
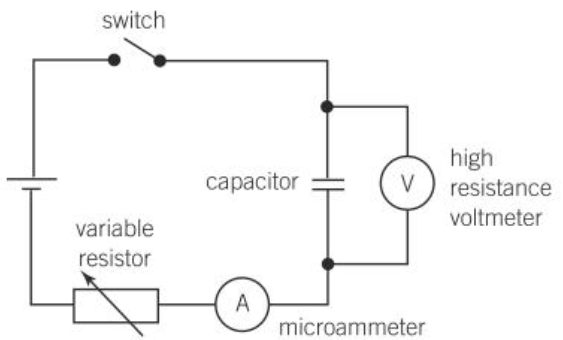
pd can be measured by putting a voltmeter in parallel with a capacitor
what happens when capacitor is charged
energy gets stored in it
as electrons are forced onto one plate and taken off the other energy gets stored as electric potential energy
when discharged across a bulb it will release its energy into a short flash
pd increases as charge stored increases
Energy stored in capacitator equation
E - Energy - Joules (J)
Q - Charge - Coulombs (C)
V - pd - volts (V)
only max 50% of energy supplied can be stored as 50% is wasted from resistance of circuit
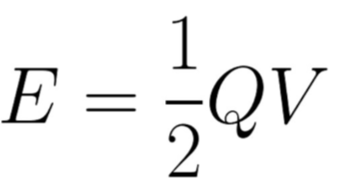
How do the ground and clouds produce lightning
when a thunder cloud is charged, with the ground they will act as parallel plates where air between is the insulator
this produces an electric field, which the charge jumps through to even out the charge
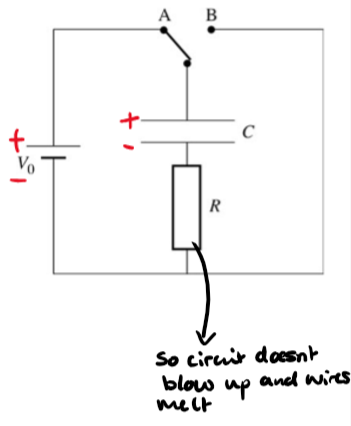
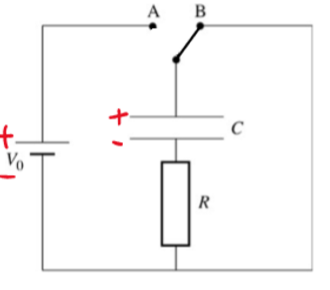
capacitor discharging through fixed resistor
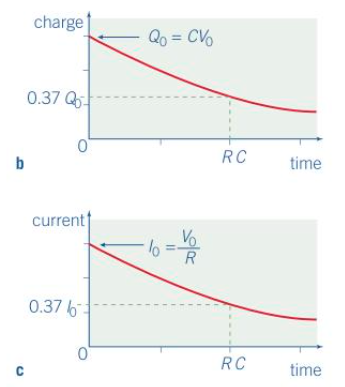
The current will reduce to zero more gradually as the pd decreases
The rate of reduction is exponential, giving a curved graph
When 37% of charge or current is equal to RC = time constant
Capacitance of plates with diff properties equation
C - Capacitance - Farads (F)
A - Area of plate - m2
ε0 - Permittivity of free space - Farads per metre (Fm-1)
εr - relative permittivity - unitless
d - distance between plate - m
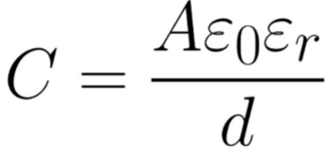
permittivity definition
the resistance of the material to an electric field passing through it
the permittivity of an insulator is measured relative to the permittivity of free space
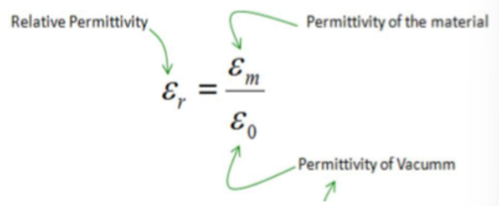
polar molecules
when there is no field molecules orientate randomly
when an electric field is applied the negative ends are attracted to the opposite and vice versa, so they rotate and align themselves
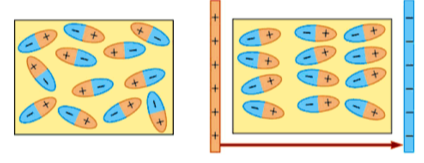
Discharging a capacitor equation
Q - Charge - Coulombs (C)
Q0 - initial charge
e - exponential function
-t - time taken - s
RC - time constant - s
Q can be replaced by either V or I - but for I the eq is the charging one
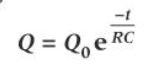
Charging capacitor equation
Q - Charge - Coulombs (C)
Q0 - initial charge
e - exponential function
-t - time taken - s
RC - time constant - s
Q can be replaced by either V or I - but for I the eq is the discharging one
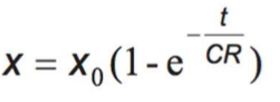
Charging qualities
current flows easily at the start but becomes more difficult to add charge to plates due to repulsion from too much positive build up on one plate
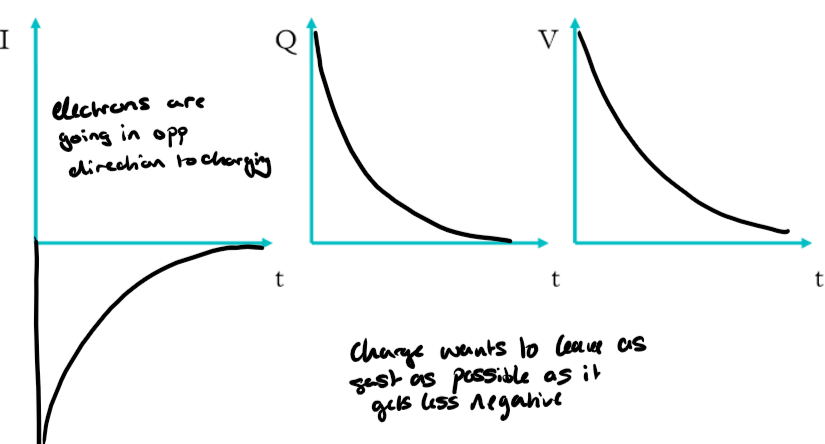
Discharging properties
current flows in opposite direction, starts fast then slows
gradient of a Q/t graph will be negative
Charging on graphs
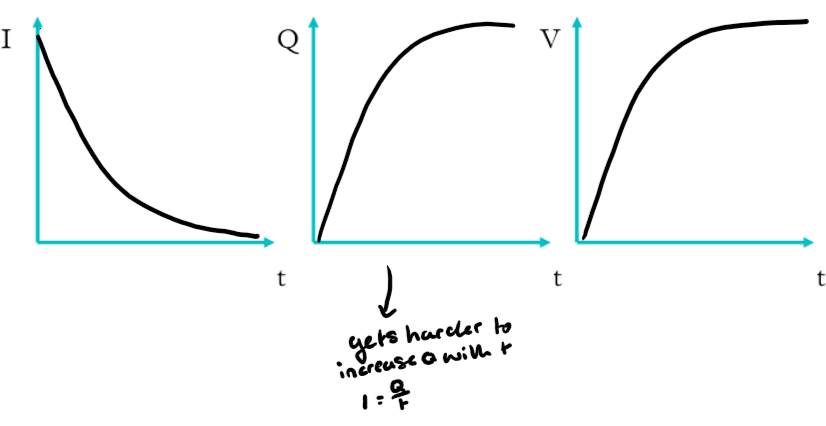
Discharging on graphs
What is the time constant
τ = RC
when charging - 37% of I and 63% of V and Q
When discharging - 37% of I,V,Q
grad of ln(I) graph = -1/RC
what are dielectrics and how do they work
they are electrically insulating materials placed between plates
they help increase ability to store charge
each molecule in the diametric becomes polarised, so the electrons are pulled towards the positive plate, gaining a negative charge so they other side loses negative charge and positive charge is left on the materials surface
how is a large capacitance achieved
by making the area of the plates as large as possible
by making the distance between plates as small as possible
by filling the space between the plates with a dielectric which has a large relative permittivity