Pretransfusion Testing and Automation in Bloodbank
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
where does pt identification start
at admission when the armband is generated
how many unqiue identifiers are required for a positive patient identification
two
preferred specimen in blood bank testing
EDTA plasma
how mnay days is a sample good for pretransfusion testing
3 days (expires at midnight)
how mnay days is a sample retained for, incase post transfusion testing is needed
7 days
what temperature are samples stored in
2-8C
what information do we look for in patient history
medical history
transfusion history and reaction
pregnancy history
medication history
what products do not require compatible testing
whole blood (must be identical to patient)
RBCs (must be compatible with recipients plasma)
granulocytes aka WBCs (must be compatible with recipients plasma)
plasma (compatible with recipient’s red cells)
platelets (compatible with recipients red cells)
cryoprecipitate antihemophilic factor (all ABO groups acceptable)
what type of plasma can be given in an emergency conditions
uncrossmatched O negative
red cell transfusion selection for ABO
O-: O-
O+: O+ and O-
A-: O- and A-
A+: O+, O-, A-, and A+
B-: O- and B-
B+: O+, O-, B-, and B+
AB-: O-, A-, B-, and AB-
AB+: O-, O+, A-, A+, B-, B+, AB-, and AB+
plasma transfusion selection for ABO
O: O, A, B, and AB
A: A and AB
B: B and AB
AB: AB
selection of order for unites in blood cell transfusion
O: 1st choice is only O
A: 1st choice is A then O
B: 1st choice is B then O
AB: 1st choice is AB, then A, then B, and then O
what does hold mean
no tests preformed
what does type mean
ABO/Rh
what does type and screen (T&S) mean
ABO/Rh and Absc
what does type and cross (T&C) mean
ABO/Rh, Absc, and crossmatch units
what does typ and cross (T&C) keep ahead mean
ABO/Rh, Absc, crossmatch units
keep ahead means lets say they ask for two units, when you use one you’ll get another
what does a crossmatch entail
patient plasma + cell suspension from donor units (like from a pigtail) read at IS
no agglutination means units are compatible
if a clinically significant antibody has been detected at the antiglobulin stage what is required
crossmatching
when sleecting units for transfusion does the ABO need to be compatible/identical
it needs to be type-specific
what type of blood needs to be chosen for recipients who are D negative at IS
Rh negative
if a person has unexpected antibodies what type of blood should they be given
antigen negative blood
what causes incompatible pretransfusion test results
negative antibody screen and incompatible crossmatch at IS
positive antibody screen and incompatible at antiglobulin (AHG) crossmatch
reasons for a negative antibody screen and incompatible crossmatch at IS
incorrect ABO grouping of recipient or donor unit selected
cold reactive allo- or autoantibody in plasma
abnormalities in recipients plasma (rouleaux, DARA)
possible reasons for positive antibody screen and incompatible at antiglobulin (AHG) crossmatch
donor RBCs have a possible DAT
antibody is only reactive with RBCs having strong expression of particular antigen (dosage) or variation in antigen strength
antibody is low frequency
limitations of pretransfusion testing
hemolytic transfusion reaction if pts antibody was too weak to be detected
hemolytic transfusion reaction due to pt misidentification
transfusion-associated graft vs host disease and transfusion related acute lung injury
hemolytic reaction due to recieving hemolyzed RBCs
allergic, febrile, and bacteriogenic reactions
disease transmission
2 final identification requirements for issuing blood
two-person verification system
automated ID technology (barcoding)
how long can the units of blood be away from the lab if it’s needs to be returned to circulating inventory
30 minutes
how long do you have to complete a blood transfusion
four hours
definition of massive transfusion
the administration of 8-10 units of blood in an adult recipient in <24 hours or acute adminsitration of 4-5 units within 1 hour
what is the ratio of product transfusion according to the ACS (american college of surgeons)
1:1:1
what type of donor units are selected for intrauterine transfusions
group O, Rh negative RBC units that are fresh (< 7 days old), leukocyte-reduced, irradiated, negative for sickling hgb, and antigen negative
what is used to trap red cells in gel technology
dextran acrylamide gel particles
pricniple of gel technology
ultilizes a microtube attached to a card that containd an upper reaction chamber and long, narrow portion
the column contains gel particles which combine with reagents
centrifugation of RBCs occurs through the gel and measured volumes of red cells and plasma/serum are added to allow red cell sensitization to occur
centrifuged again to allow contacts with antisera and gel
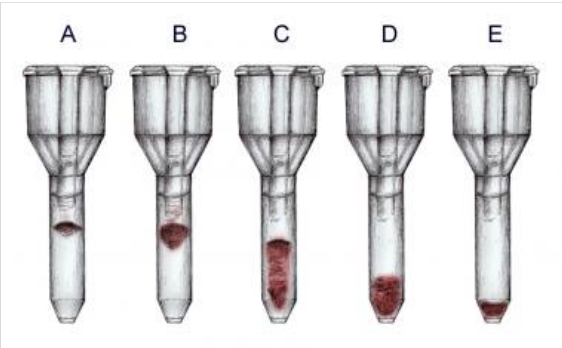
reaction of tube A
4+
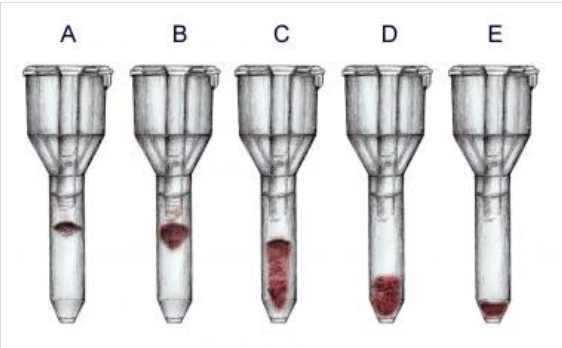
reaction of tube B
3+
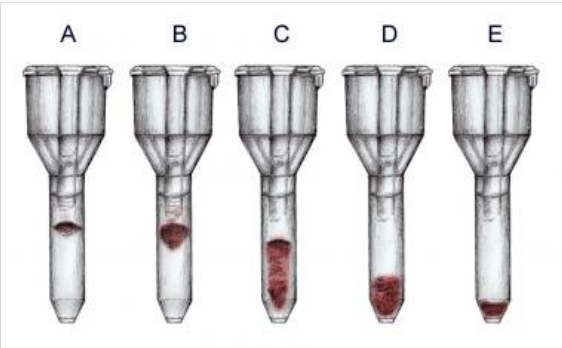
reaction of tube C
2+

reaction of tube D
1+
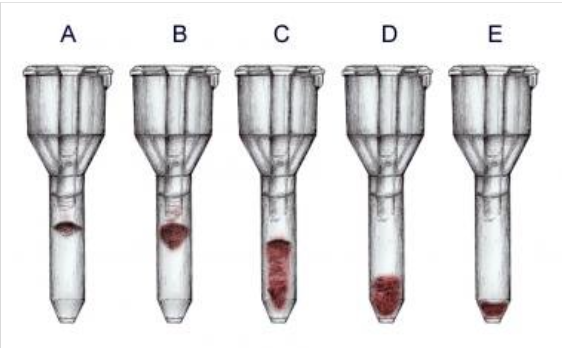
reaction of tube E
0
advantages of gel technology
standardization
stable, well-defined endpoints
simple procedures (very fast)
objective, reproduceable, and consistant
decreased sample volume needed (don’t need full blood tube to preform)
enhanced sensitivity and specificity (picks up a lot of insignificant stuff though)
disadvantages of gel technology
sample restrictions
special equiptment needed
calibrated pipette must be used
immucor principle of solid technology test
test plasma and LISS added to microwells already coated with antigen
incubate microplate so antibodies can bind to antigen
wash with buffered saline
add IgG-coated indicator cells and centrifuge to force the indicator RBCs into close contact with antibodies
how does the use of LISS affect agglutination
if ab-ag complex occurs, it adheres to the walls of the test well
what color does the solid technology indicator change to
purple to blue

circle one grade
4+

circle 2 grade
3+

circle 3 grade
2+

circle 4 grade
1+

circle five grade
0
advanatges of solid phase
standardized
stable, well defined endpoints
no predilution of reagents
can test hemolyzed, lipemic, and icteric samples
enhanced sensitivity
long shelf life of microplates (120 days)
disadvanatges of solid phase
need specialized equiptment
technique can affect the results of a manual test
may detect weak autoantibodies