unit 2 anatomy
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Last updated 8:50 PM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
histology
the study of microscopic body tissue
2
New cards
compact bone tissue
ring shaped
3
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
looks multilayered
4
New cards
adipose tissue
no visible nucleus
5
New cards
cardiac muscle
striated, darkened intercalated discs
6
New cards
nervous tissue
long projections
7
New cards
connective blood tissue
divit in middle of cells
8
New cards
simple cuboidal epithelium
nucleus in middle, cube-shaped cells, cells close together
9
New cards
simple tissue
single layered
10
New cards
stratified
multi layered (like the skin)
11
New cards
functions of epithelial tissue
protection, absorption, filtration and secretion
12
New cards
eipdermis layers
- stratum basale
- stratum spinosum
- stratum granulosum
- stratum lucidum (only in palms and foot soles)
- stratum corneum
- stratum spinosum
- stratum granulosum
- stratum lucidum (only in palms and foot soles)
- stratum corneum
13
New cards
dermis layers
reticular
papillary
papillary
14
New cards
reticular layer
blood vessels, sweat and oil glands
15
New cards
papillary layer
capillaries
16
New cards
skin layers
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
17
New cards
function of a sebaceous gland
produce oil/sebum for skin and hair lubrication; kills bacteria
18
New cards
function of a sudoriferous gland
produces sweat to increase heat loss, excrete waste, and prevent bacteria
19
New cards
melanocyte
skin pigment- produces melanin
20
New cards
melanoma
skin cancer
21
New cards
nail diagram
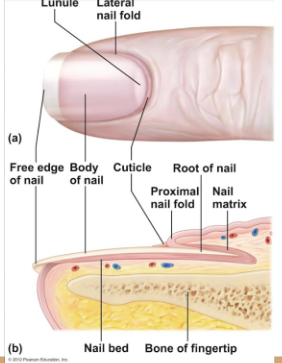
22
New cards
first degree burn
only epidermis
skin red and swolen
skin red and swolen
23
New cards
second degree burn
epitermis and superficial layer of dermis
skin red with blisters
skin red with blisters
24
New cards
third degree burn
destroys entire skin layer; burned area painless
colored grey/white or black
colored grey/white or black
25
New cards
wound healing steps
inflammation
granulation tissue forms
regeneration/ fibrosis
granulation tissue forms
regeneration/ fibrosis
26
New cards
inflammation
capillaries become permiable, clotting proteins migrate to areas from blood stream, clot walls off injured area
27
New cards
granulation tissue forms
growth of new capillaries, rebuild collagen fibers
28
New cards
regeneration
replacement of destroyed tissue by the same type of cells
29
New cards
fibrosis
repaired by dense (fibrous) connective sissue (scar tissue)
30
New cards
the rule of nines
method to determine extent of burns
body divided into 11 areas each representing 9% of body area
critical if:
- over 25% of body has 2nd degree burns
- over 10% of body has 3rd degree burns
- 3rd degree burns on face, hands, or feet
body divided into 11 areas each representing 9% of body area
critical if:
- over 25% of body has 2nd degree burns
- over 10% of body has 3rd degree burns
- 3rd degree burns on face, hands, or feet
31
New cards
ABCDE method
Asymmetry - sides of mole doesnt match
Border irregularity - borders not smooth
Color - different colors in pigmented areas
Diameter - spot larger than 6mm in diameter
Evolving - mark changes over time
Border irregularity - borders not smooth
Color - different colors in pigmented areas
Diameter - spot larger than 6mm in diameter
Evolving - mark changes over time
32
New cards
basale cell carcinoma
least malignant, most common, overlaps deepest layer pf epidermis
33
New cards
squamous cell carcinoma
can metastisize to lymph nodes; sun-induced
34
New cards
malignant carcinoma
most deadly, occurs in melanocytes, metastasizes quickly to lymph nodes and blood vessels
35
New cards
pseudostratified
looks multilayered but is simple
36
New cards
squamous
flattened
37
New cards
cuboidal
cube-like
38
New cards
columnar
column-like
39
New cards
ciliated
material movement (projections)
40
New cards
nonciliated
absorption and secretion
41
New cards
extracellular matrix
nonliving material that surrounds living cells
binds tissues, body support, protection, etc.
binds tissues, body support, protection, etc.
42
New cards
blood
extracellular matrix = plasma
transport gases and nutrients
transport gases and nutrients
43
New cards
bone (osseous tissue)
bone cells (osteocytes) in lacunae (cavities)
protect and support body
protect and support body
44
New cards
cartilage
hyaline - most common, rubbery- nose, trachea, larynx, fetal skeleton
elastic (earlobe)
fibrocartilage (vertabrae discs)
elastic (earlobe)
fibrocartilage (vertabrae discs)
45
New cards
Dense CT
tendons, ligaments, dermis
46
New cards
loose CT
adipose tissue provides protection ,insulation, and energy storage
47
New cards
skeletal muscle
straiated, multinucleated, long, cylindrical
voluntary, pulls on bone and skin
voluntary, pulls on bone and skin
48
New cards
cardiac muscle
straited, single nuclei, cells connected by intercalated discs
involuntary - heart
involuntary - heart
49
New cards
smooth muscle
no visible straitions, single nucleus, spindle shaped cells
involuntary, organ and blood vessel walls
involuntary, organ and blood vessel walls
50
New cards
nervous tissue
neurons and nerves support cells
large matrix with well-shaped bodies
send impulses to other areas of body
large matrix with well-shaped bodies
send impulses to other areas of body
51
New cards
hypodermis
not technically skin, anchors to underlying organs
mostly adiopse loose CT tissue
mostly adiopse loose CT tissue
52
New cards
hair
hair produced by follicle; hard, keratinized epithelial cells
arrector pili muscle pulls hair up when cold
arrector pili muscle pulls hair up when cold
53
New cards
erythrocytes
red blood cells, carry oxygen from lungs and CO2 to lungs
54
New cards
benign
doesnt spread
55
New cards
malignant
metastisized, spreads