Neo and Post-Impressionism
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Neo-Impressionism (Pointillism)
Impressionists neglected too many traditional elements - fundamental skills in the mastery of form were ignored, chaotic and disorderly
broken and free brushstrokes were hard to follow
Impressionism - random, spontaneous, ephemeral and casual
Neo-Impressionism - analytical, rational, eternal and formal
restoring order and applying rules → use of contour for perfect forms, careful balanced classical composition and regular brushstrokes
liveliness, vivacity, reality and spontaneity lost
Georges Seurat (1859-1891)
trained in the French Academy
turned to Impressionism when he met Monet and Degas
applied his knowledge of science an optics to his painting and founded Pointillism
Paul Signac (1863-1935)
follower of Seurat, mostly painted landscapes
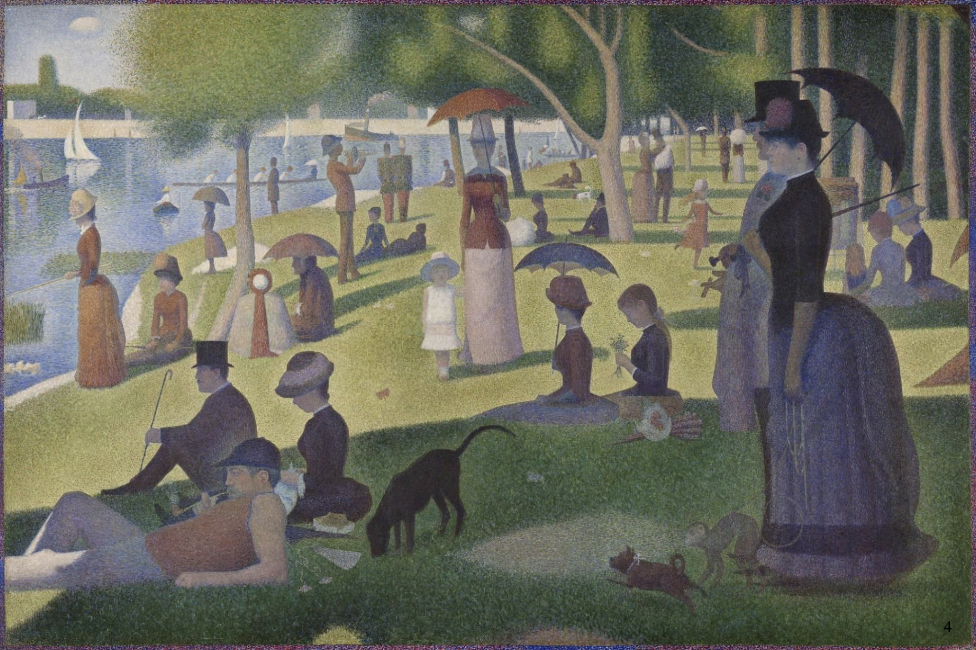
A Sunday on La Grande Jatte, Georges Seurat 1884-86
studio art completely - spent 2 years on this piece
figures are all either frontal, in ¾ profile, full profile, ¾ back or full back
figures are reduced to essential forms - harmonics composition achieved by schematic arrangements of lines and colours
creates the effect of a timeless and serene scene
optical mixture → allows human eye to do the mixing
Seurat juxtaposed dots and dashes of col9urs systematically and restored order to the disorderly brushstrokes of Impressionism
reminiscent of mosaics
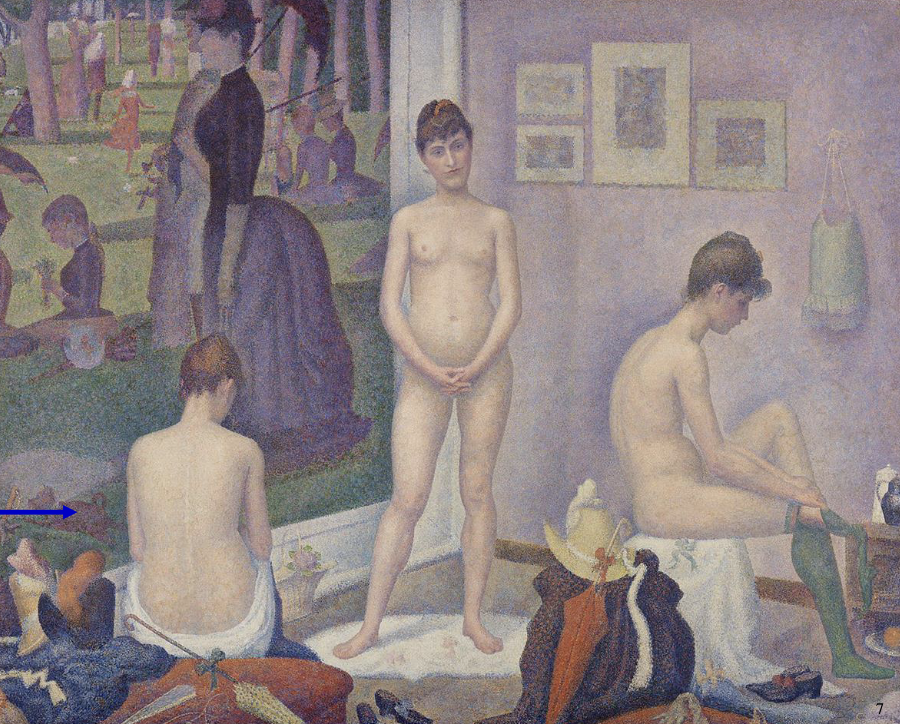

The Models, Georges Seurat 1888
careful and balanced composition - recalls the 3 graces in classical art
art for eternity, not a fleeting moment
woman on the left reminiscent of The Valpincon (Bather) of Ingres
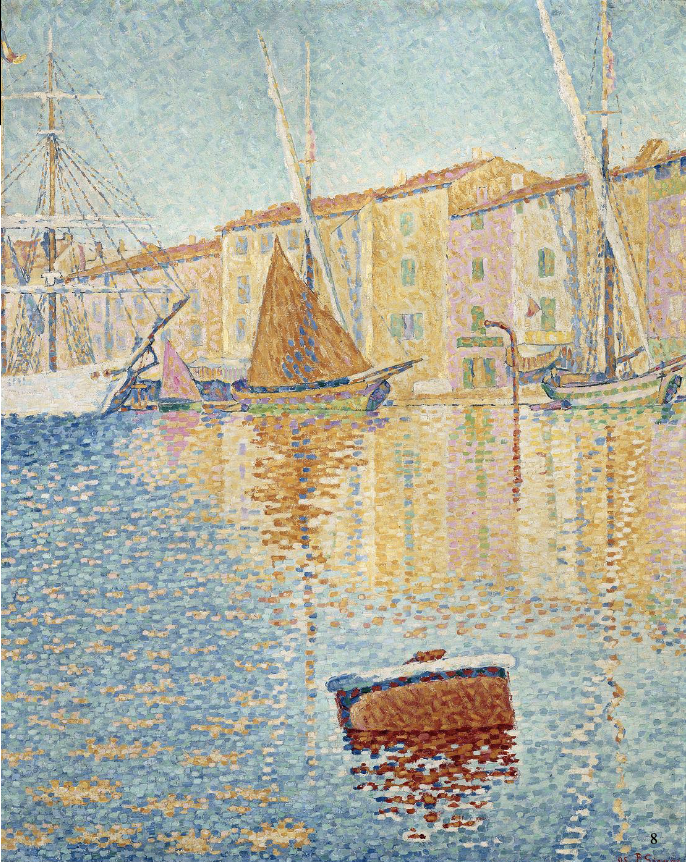

Red Buoy, Paul Signac 1895
searched for a balance between scientific law and visual sensation → less rigid in the forms of pigments
bold, decorative use of colour - influenced Fauvism
Post-Impressionism
coined in 1910 by English critic Roger Fry
denotes late 19th century works that are programmatically anti-academic and anti-Impressionist
recuperated what was abandoned in Impressionism → the expressive power of form and colour
Fauvism & Expressionism
Paul Cezanne (1839-1906)
Impressionism lack form and structure
restored solidity and volume to objects, anticipates abstraction in modern art
founding father of modern art
born in Aix-en-Provence, attended the local art school
1861 - moved to Paris, learnt from the collection in the Louvre, made friend with Monet and Pissarro
1872-77 - Impressionistic phase
1880s onwards - looked for solidity of volume in art, began abstraction of form
Paul Gaugin (1848-1903)
freed colour from its deceptive role, explored the expressive role of deep and saturated colour
born in Paris, spent his childhood in Peru
1871 - worked as a stockbroker, started painting
1881 - joined the 6th Impressionist exhibition
1883 - became a full-time painter
1886, 1888 - travelled to Brittany, stayed in Pont-Aven, an artists colony, developed ‘synthesis’ and ‘cloisonnism’
1888 Oct-Dec - joined Van Gogh in Arles
1887-1891 - travelled to Central America, Caribbean, Martinique Islands and Tahiti - where he settled in 1895
Vincent Van Gogh (1853-1890)
Explored the expressive power of colour and brushstrokes.
1853 - 1880 (early life):
born in Barbant Holland, father was a priest
1869-76 - worked in an art dealer company in The Hague, London and Paris
1876 - began preaching
1880-85:
decide to become artist
inspire by Millet, painted peasant life
185 - in Antwerp, learnt fro Flemish Baroque art, began to collect Ukiyo-e prints
1886-88 (Paris period):
lived with his brother Theo in Montmarte
experimental period - exposed to the Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist styles and themes
became friends with Gaugin and Pissarro
1888-1889 (Arles period):
moved to southern France, hoping to establish and artists’ colony
mature period - explored the power of bright, intensively saturated colour
Oct-Dec visited by Gaugin, ended in tragedy
1889-1890 (Saint-Remy period):
entered a psychiatric hospital, painted scenes and objects indoor and outdoor
copied the works of his favourite artists - Rembrandt, Delacroix and Millet
1890 (Auvers-sur-Oise period):
moved back to near Patis, taken care of by Dr. Paul Gachet
painted portraits and local landscapes
worried by the financial stress of Theo, he committed suicide
1880-1890 - produced over 2000 works but only sold one during his lifetime

Self Portrait, Paul Cezanne 1875
called himself a student of Pissaro
reminiscent of Pissarro’s self portrait - broad brushstrokes, same pose
coarser brushstrokes, sculptural form
colour scheme - close to Edouard Manet

Still Life with Apples and Oranges, Paul Cezanne 1899
still life with objects composed with multiple perspectives
represents a painter’s subjective perception
not a logically composed space
solidity of objects is expressed through the intrinsic dynamics of colours
the edge between the horizontal and vertical plane is obscured
geometrical forms - forms if nature
art - a formalistic analysis of objects and of the painted surface #
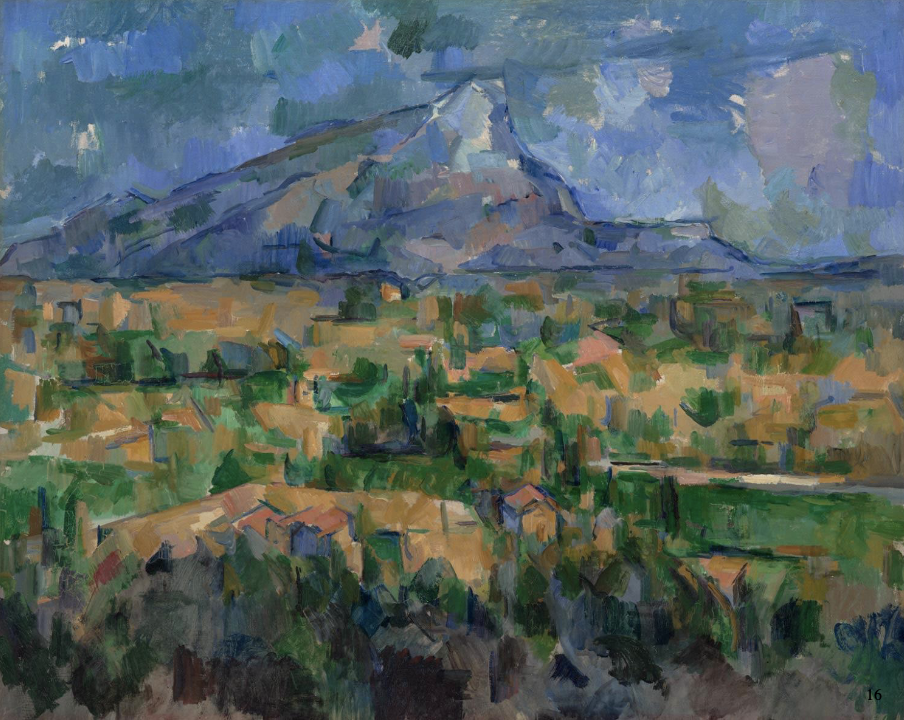

Monte Sainte-Victoire, Paul Cezanne 1902-04
sought to achieve the effects of distance, depth, structure and solidity in classical art by an optical analysis of nature - lines, planes and colours → motifs that comprise nature
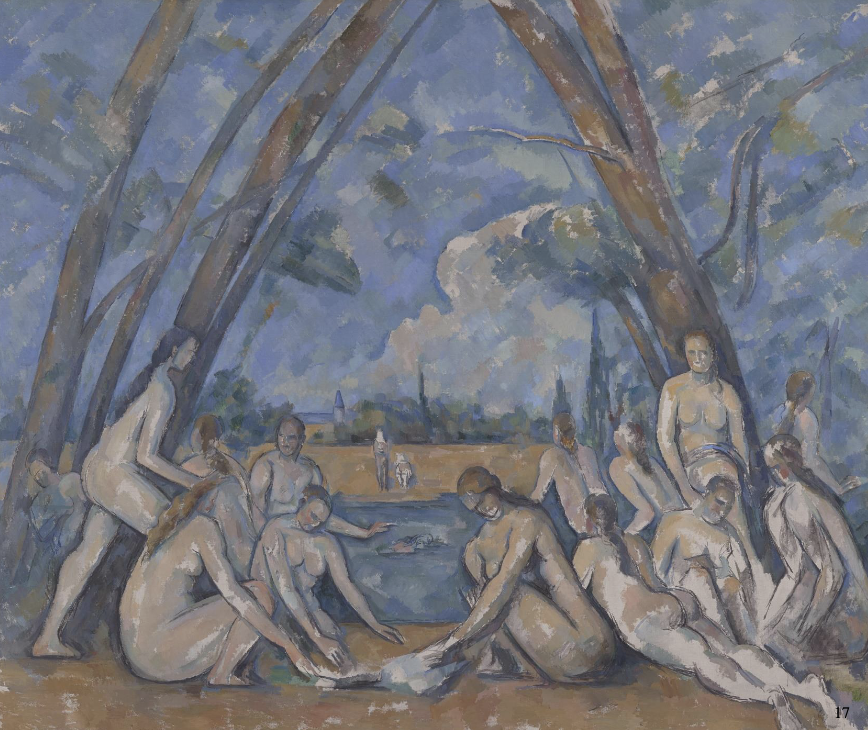

The Large Bathers, Paul Cezanne 1900-1906
favourite theme since the 1870s
figures and trees are drawn in hard contours and given abstract triangular formations
intense blue and brown tones throughout
unfinished

Vision After the Sermon, Paul Gaugin 1888
explored the expressive quality of pure colour
synthesis - conveyed not a realistic world but a synthetic image of deeper invisible meanings and emotions
cloisonnism - like cloisonné enamels, opaque, flat colours are separated by dark lines → figures defined by dark lines before flat colour patches are filled in
Japonisme - tree dissecting the composition diagonally, Jacob wrestling the angel in inspired by Japanese Sumo wrestling art
red- symbolises deep religious faith

Self Portrait as Les Miserables, Paul Gaugin 1888
double portrait of himself as Emile Bernard - the poor
inspired by Les Miserables. he painted himself as Jean Valjean. He compared the figure, full of inner power and love with the misunderstood artists of his own time
yellow is used as a tribute to his friendship with Van Gogh - symbol of sun, warmth and love → singed “Les Miserables to my friend Vincent Gaugin”
white flowers - a Japanese motif symbolising the artistic purity of artists
bye green shadow - anguish and ill

la Orana Maria (Ave Maria), Paul Gaugin 1891
during his stay in Tahiti
paid tribute to the universality of religion and myth
Annunciation or Adoration of 3 Magi - traditional theme in Christian art
foreground - exotic fruits, offerings of Tahitians to idols of Maori religion
discovered a paradise on earth
top right - Archangel Gabriel? 3 Magi?
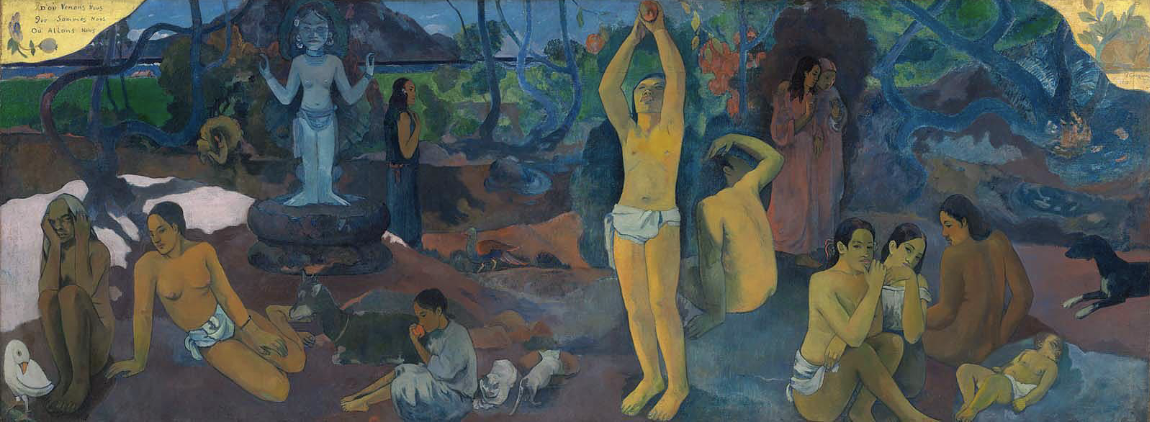

Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?, Paul Gaugin 1897-98
final reflection on life and the deepest questions of human destiny - painted as a testament after the death of his daughter
heavy mood - sense of paradise lost
title in the top left corner
mysterious figures discussion the fall of man kind
4 stages of life on the bottom
Maori god on the left
Even plucking fruit from the tree of wisdom
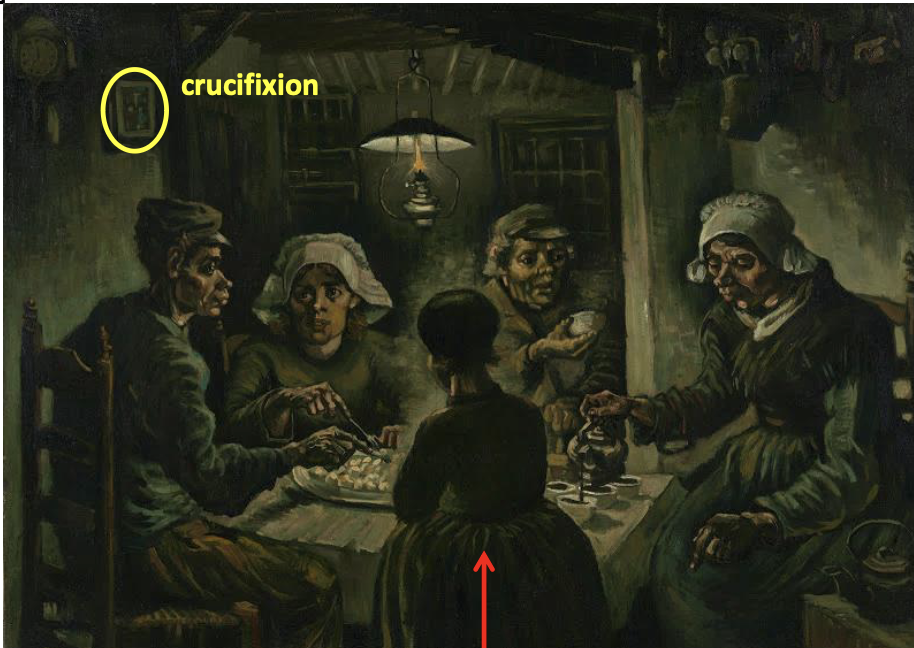

Potato Eaters, Vincent Van Gogh 1885
harshness of proletarian life rendered with religious meanings
inspired by Millet’s works of poor peasants
dark tones, austere and solemn
dignity of the people - reminiscent of Supper at Emmaus
central person resembles Christ with a halo
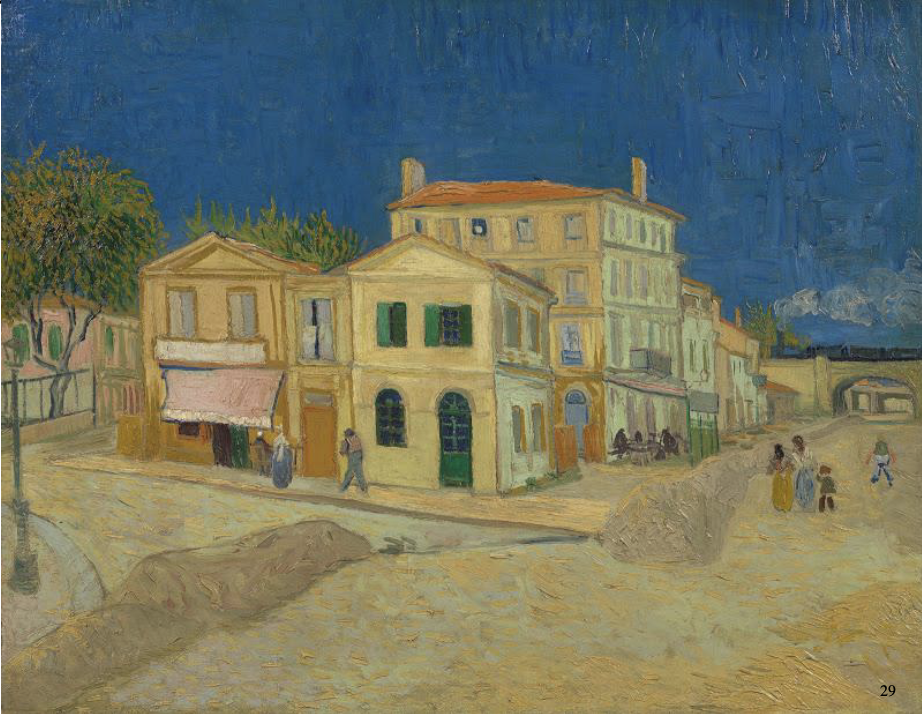

Yellow House, Arles, Vincent Van Gogh Sep 1888
yellow represents his happiness, his optimism and is therapeutic for his bad mental/physical health
intense blue - typical Mediterranean sky, complementary to the intense yellow - strong sunlight of Provence

Sunflowers, Vincent Van Gogh Aug 1888
painted 2 for Gaugin’s room
heavy impasto - capture the life cycle of nature, inspired by Dutch vanities paintings
religious sentiment → symbol of sun, warmth and paradise
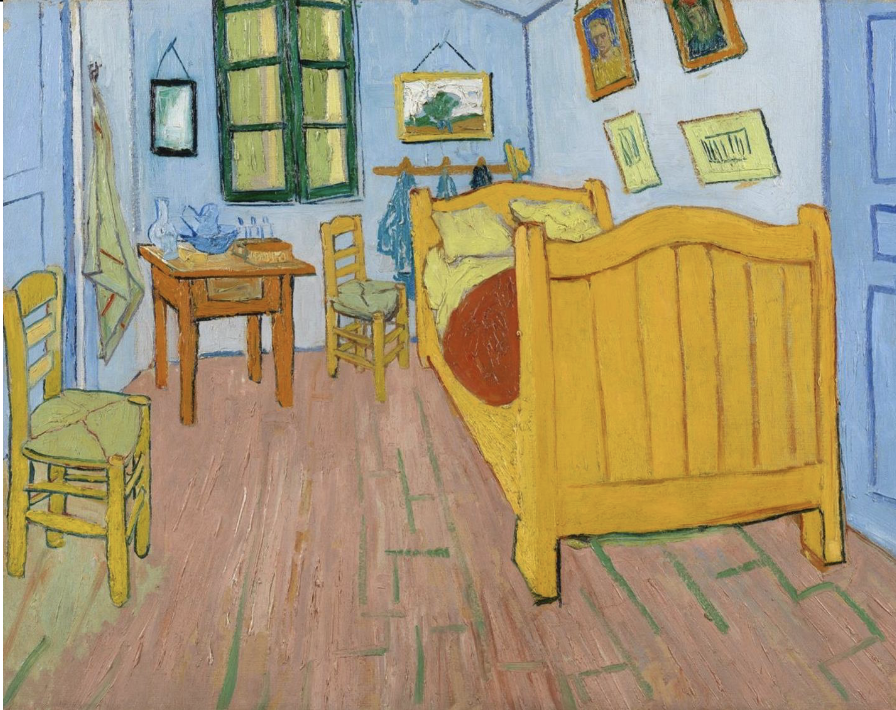

The Bedroom, Vincent Van Gogh Oct 1888
simple furnishings - Japanese household
symbolism of colour - bright colours to express ‘repose’ or ‘sleep’
original painting looked very different - pale violet walls, sheet and pillows bright lemon green, scarlet red bed spread and lilac doors
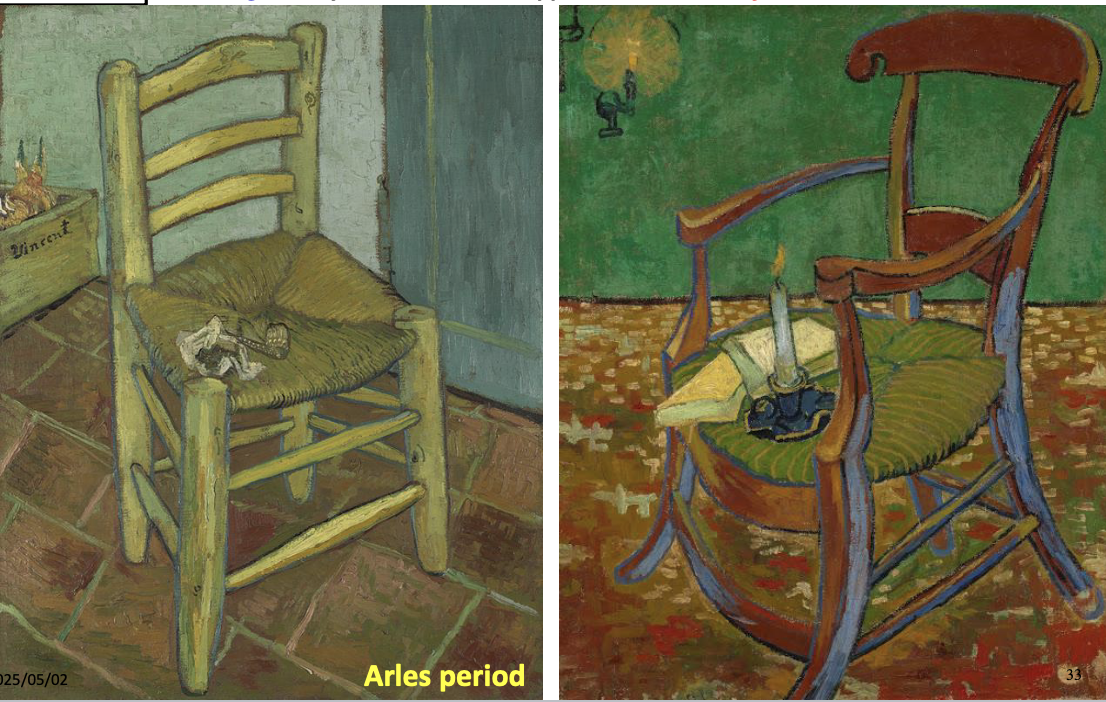


Chair with Pipe and Tobacco (left), Gaugin’s Arm chair (right), Vincent Van Gogh Nov-Dec 1888
two symbolic portraits of the relationship between Van Gogh and Gaugin; Gaugin worshipped as the leader of the brotherhood

Self-Portrait with Pixie, Vincent Van Gogh Jan 1889
23/12/88 → after a heated row with Gaugin, Van Gogh had a nervous breakdown and cut his own ear off
recovering and able to paint
done in complementary colours and systematic brushstrokes
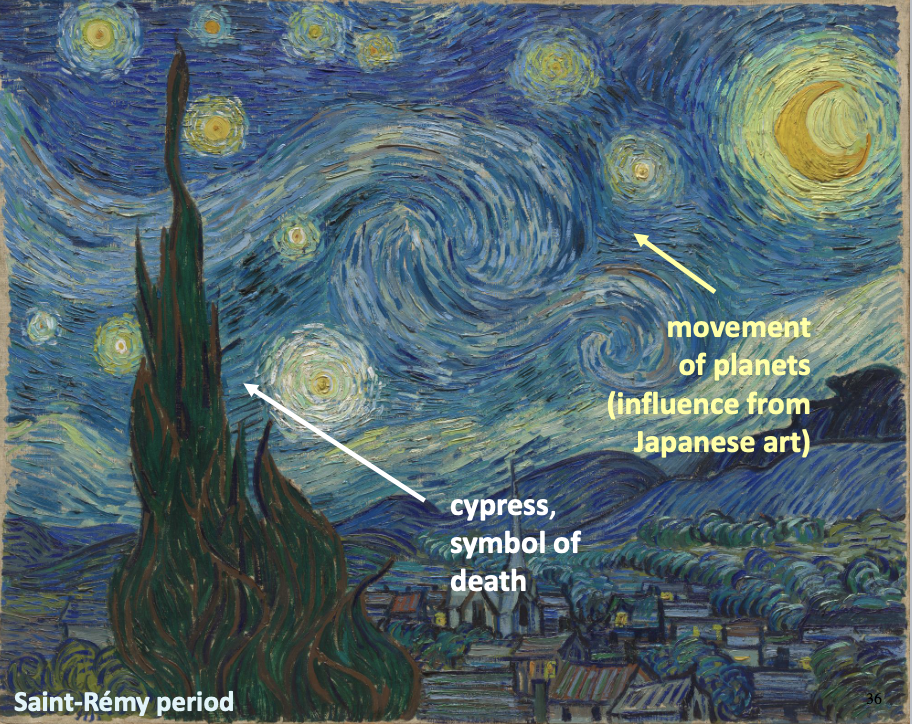
Starry Night, Vincent Van Gogh Jun 1889
“we take a train to reach _ and we take death to reach a star”
fully developed the expressive power of brushstrokes and colour
influence of pointillism - systematic pigments in short dashes, jutaxposed with complementary colours
connected in wavy geometric forms, suggest movement

Portrait of Dr. Gachet, Vincent Van Gogh Jun 1890
an amateur painter and friend of many impressionists
took care of Van Gogh at Auvers
represents the heart-broken expression of our time - melancholy
holding foxglove

Wheatfield with Crows, Vincent Van Gogh July 1890
meandering road in the middle of wheat fields - documentation of where he’s going to kill himself?
black strokes on the sky and crows - overwhelming mood of death