Egypt
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Middle Kingdom
Dynasties XI-XII —> 2040-1640

title, date, material, findspot
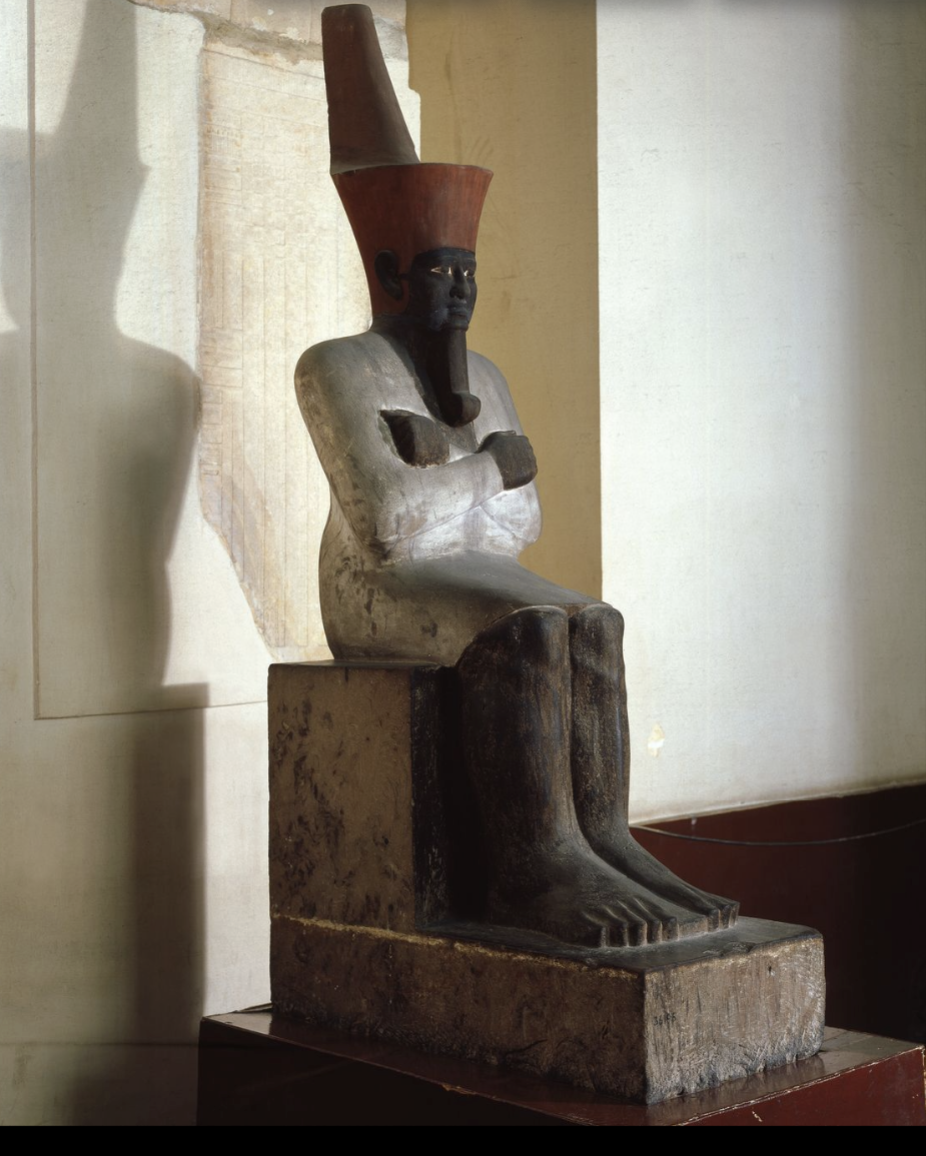
Mentuhotep II (Nebhepetra)
Dynasty XI, 2035-1991 BC
Limestone and paint
Deir el-Bahari
Menutuhotep II (Nebhepetra)
Looking at portrait of the king (Theben monarch) who reunified Egypt from the Thebe infaction
Mentuhotep II
Ended a revolt just north of Thebes at Abydos
Able to reunify Egypt
Militaristic ruler
With this new unification, there are some new king iconography:
Red crown of lower egypt, instead of white crown of upper egypt
Arms are crossed → pose after the god Osirus (Osiride pose)
Revert back to the stalky built (portrayed in face/neck) → cubic
Wearing the Heb Sed cloak
False bear has a curl on the end of it
Skin color changed
Kings began to be portrayed with black skin
Maybe a realistic portrayal?
May be reference to god Osirus (linked to mud of the Nile)?
Death and rebirth
What else is new: where it was found
New type of tomb: Temple Tomb
Found in his Temple Tomb
Ruler who was able to finally re-unify Egypt
Responsible for kicking off the Middle Kingdom (XI and XII)
Mentuhotep II
A new power base arrived in Thebes
New capital, new king iconography
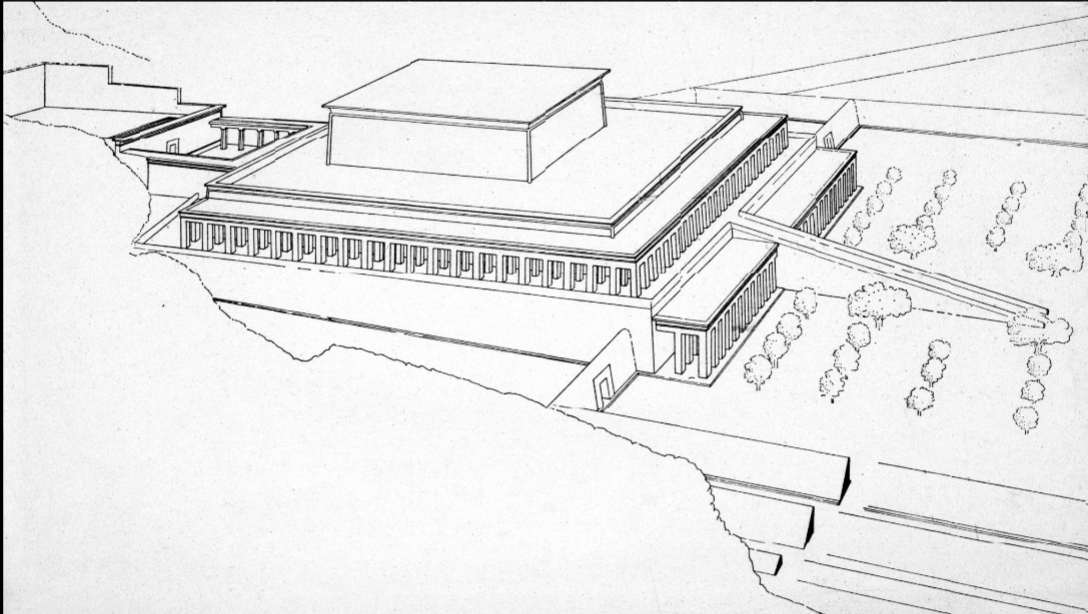
title, date, material, findspot
Funerary Complex, Mentuhotep II
Dynasty XI, 2035-1991 BC
Limestone
Deir el-Bahari
Funerary Complex, Mentuhotep II
This new king wanted to be buried near hometown of Thebes
Built complex in a circle of cliffs
Becomes to locus of burials
Moves from Giza/Saqqara to area of Thebes (very south)
New form:
Focus of the funerary process becomes a central temple (not the burial anymore)
Three-tiered podium
Columns are covered in octagonal … (?)
Approached by a long ramp
Ramp is surrounded by trees
Top is believed to be crowned by a large square or a mini pyramid
The central core of the platform was a funerary temple
Behind temple:
Open court that is called hypostyle hall
Burial was was behind the temple → more in the cliffs
Hypostyle hall: hypo = a lot, style = writing
A lot of round shafted things
Burials were very far from the temple!!!
Major influence on later monuments
New form of burials

title, date, material, findspot
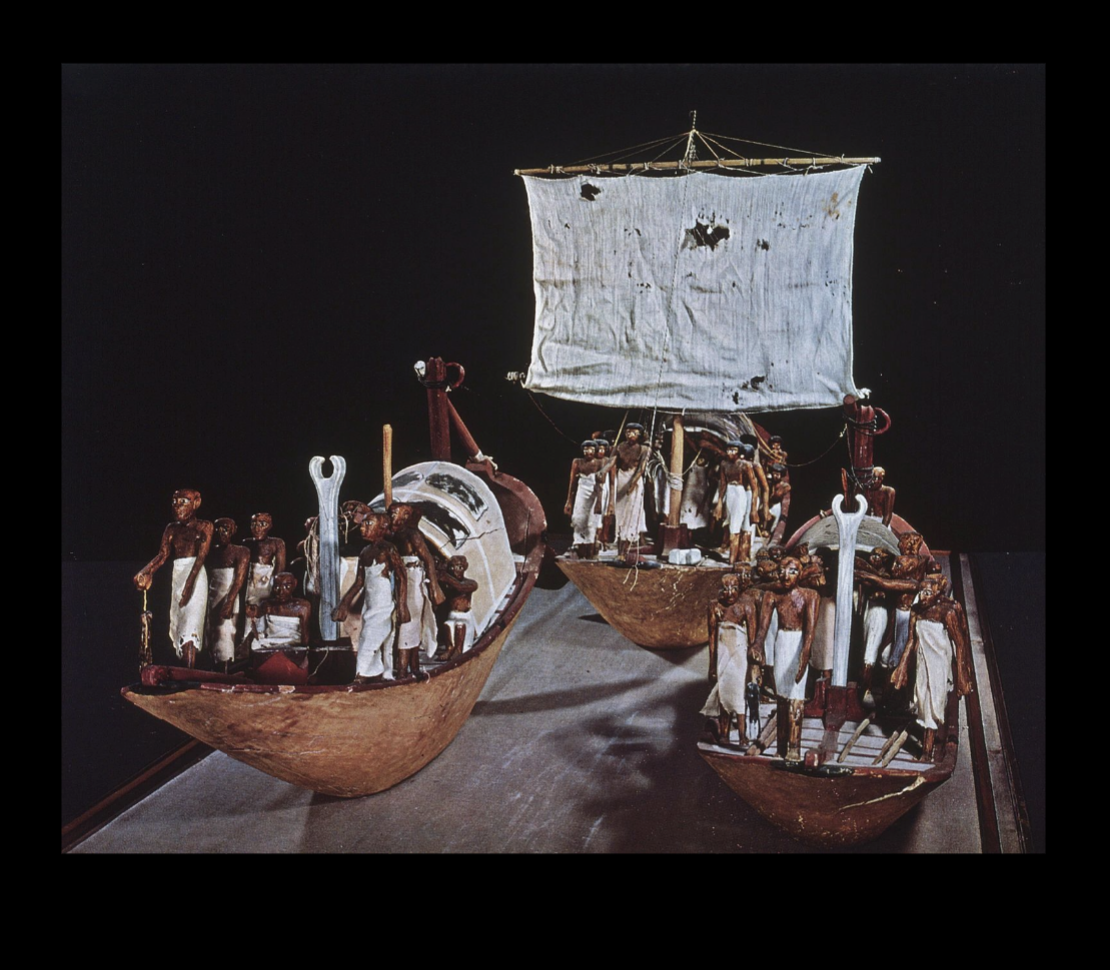
Wooden Tomb Models of Meket-Ra, Woman with Basket, Boats
Dynasty XI, 2035-1991 BC
Wood
Deir el-Bahari
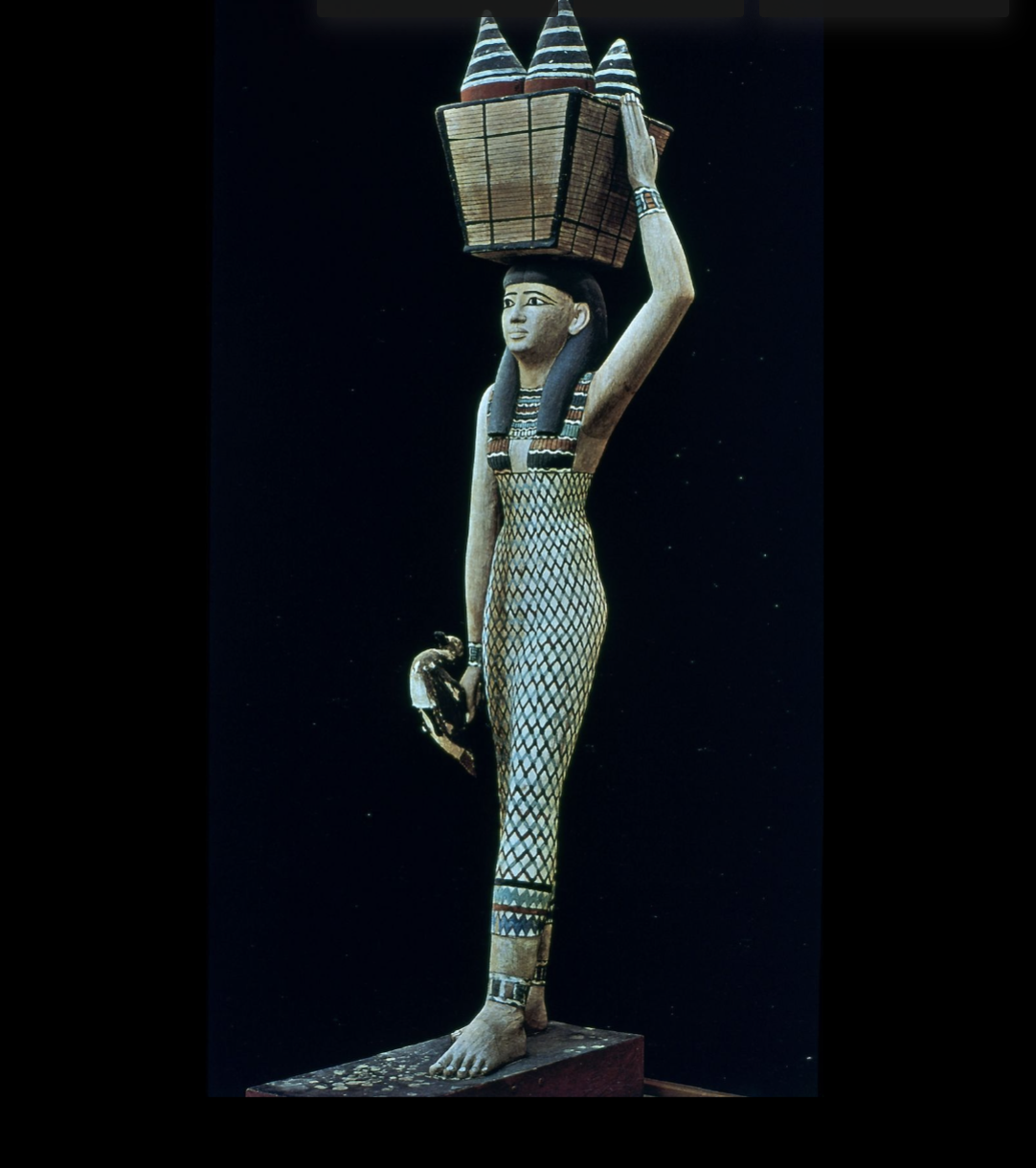

Wooden Tomb Models of Meket-Ra, Woman with Basket, Boats
Genre of art that was created during the middle kingdom period
Wooden tomb models
King of characteristics that would be placed in tombs to supply the people in the afterlife
made out of wood, then painted
Unlike wall paintings, these things are in 3-D
Daily life
Mostly represent daily activities
Better than the reliefs
Reliefs can be hard to interpret because of the vantage points
Daily life activities:
Women carrying baskets of food on their head
River boats
Crafts or baking bread
Brewery
House of Meket-Ra
Herds of cattle
These figures come in pairs
Dualistic approach (sun rise/sun set, upper/lower egypt, desert/fertile land)
dicomites
Made out of wood
Preservation in Egypt (incredibly dry and hot) are superb
Sail is even more degradable material (linen)
Only preserved because of the dry/hot climate
House
Tomb models
Not all people
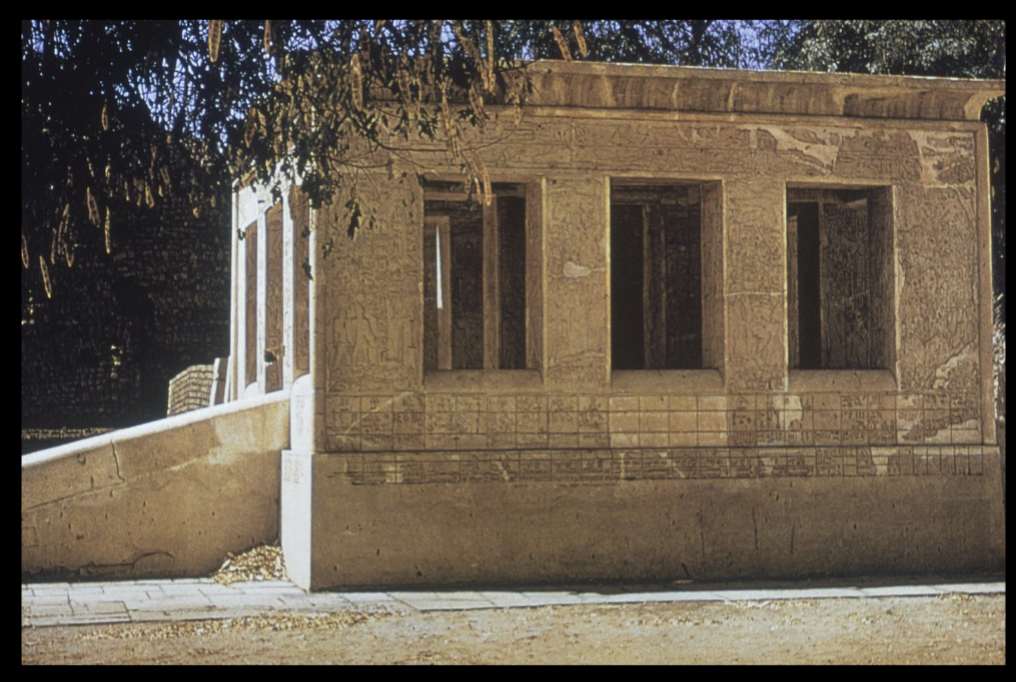

title, date, material, findspot
Chapel of Sesostris I
Dynasty XII, 1991-1784 BC
Limestone
Heb Sed Pavillion/White Chapel, Karnak
Chapel of Sesostris I
Funerary complex has not be explored, but have this monument
Heb sed pavilion!
One of the few monuments from the middle kingdom
Important!
One of the few buildings that survive from middle kingdom
Recovered in pieces from a new kingdom monument in which it got reused
Assemble the building
God Omura at Karnak
Building served as a pavilion or a kiosk as a procession for the gods
Take cult statues out of the temple itself and take them in a ritual procession
Pavilion where they could rest the statue of the god and people can have access to it
Approached by a ramp
Covered in reliefs
Function
Little pavilion gives us a window of a central ritual of Egyptian religion
Deity statues would get stored in the innermost sanctuary of a temple
Only high level priest or pharaohs can see the statues
Statue taken out and recessed in a shrine → people can have access to it and the they can ask yes/no questions
Pavilions like this existed as a way for the cult statues to rest for a bit

title, date, material, findspot
Relief from Chapel of Sesostris I
(Atum giving Life to Sesostris I)
Dynasty XII, 1991-1784 BC
Limestone
Karnak
Relief from Chapel of Sesostris I
Close up of a relief that is displayed and carved into the exterior
See Sesostris I (right side) and god Amun
Amun → with shift of capital (Thebes) that meant the central deity shifted
A local deity rose to importance with this new capital
King being received as king by the local (soon global) deity
God clasping Sesostris’ hand and leads him into the shrine
Amun is holding an ankh to the nostrils of the king (ankh = giving life)
God presenting Ankh to king
Cult center was at Thebes
(Eastern side of nile)
Living stuff on eastern and dead/funerary stuff on the west side of the nile
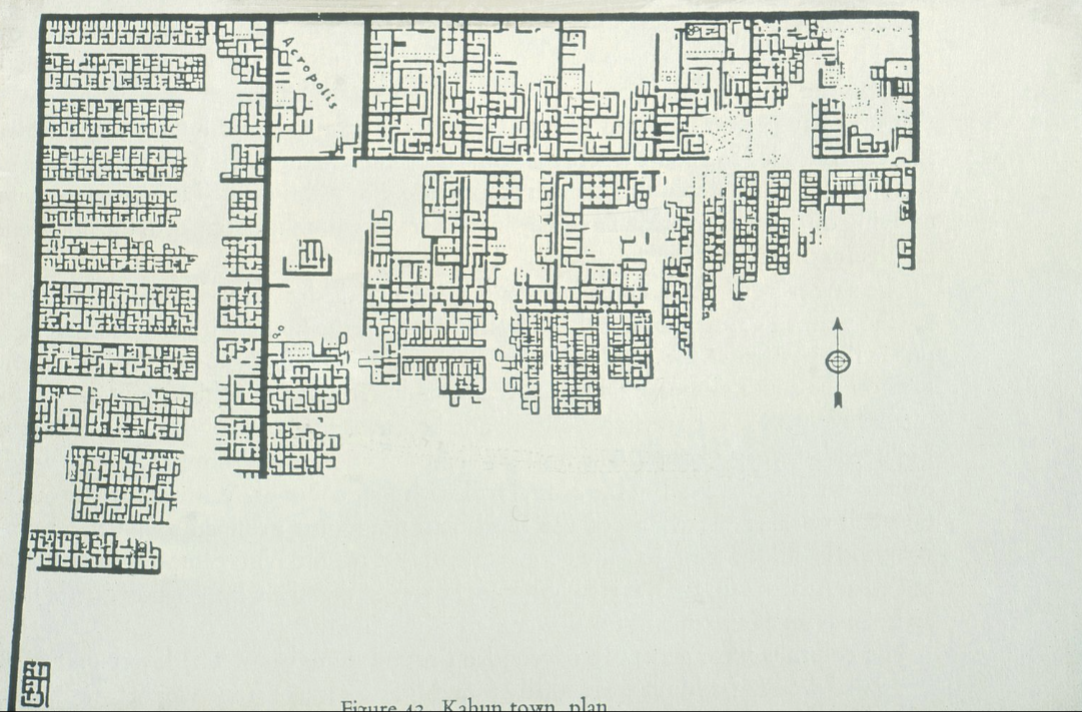
title, date, material, findspot
Pyramid Town of Lahun
Dynasty XII, 1991-1784 BC
Limestone
Kahun
Pyramid Town of Lahun
Grandson of Sesostris I, Sesotris II, built himself a pyramid (like Old Kingdom Pyramids)
Mudbrick core with limestone casing
Now disintegrated
Pyramid doesn’t survive, but a town survives that built the pyramid
Pyramid town → we can take a look at daily life features
Rare examples of domestic architecture
Also neat that there are papyrus records that are left in the town
Hierarchical representation of people who took care of the pyramids
Where it goes blank → area is unexcavated
First thing that is clear is information about how an Egyptian town might have been planned
Very few Egyptian towns that are preserved
Little understanding of urban life
Might have been zoned
Area that is higher than the rest of the town
Acropolis
Idea that this was used for a governor of the town or that the king can see the construction of the town
Larger buildings in the north (Northern Mansions) → belonged to wealthier people
Western Quarter → is blocked off my the rest of the city by a thick wall
This could have housed 5000-9000 people
On individual house → it seems that ruins were arranged around a central court
Found preparations were placed outside the buildings
Separations of men and women quarters
Clear dichotomy or structure that has two levels in it
More than half of the people who were building the pyramid were guest workers from the near east
Women outnumbered men (2 to 1)
New Kingdom
Dynasty XVIII —> 1570-1314 BC

title, date, material, findspot
Seated Statue of Hatshepsut
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1450 BC
Limestone
Deir el Bahari
Seated Statue of Hatshepsut
Queen!! <3
She is actually the daughter of the third king of Dynasty XVIII (daughter of Tuthmosis I)
She got married to her half-brother (Tuthmosis II), when he died, his son (Tuthmosis III) was the heir but way too young
Tuthmosis III’s mother ruled as his regent
Gets depicted as male in art
New style known as Tuthmosis style
Often referred to as the male gender
When looking at her in art, she is in fact depicted as male
In standard king regalia
Often has false beard
In seated pose
Pleated kilt
Broad collar
Depiction of her as a Sphinx (male → has false beard)
Style
Highly idealized style
Almond, flat eyes (almost like hieroglyphic eyes)
“Plastic” eyebrows (plastic → pop out of surface of sculptor – look like appliques)
Small smiling mouth
Slender body
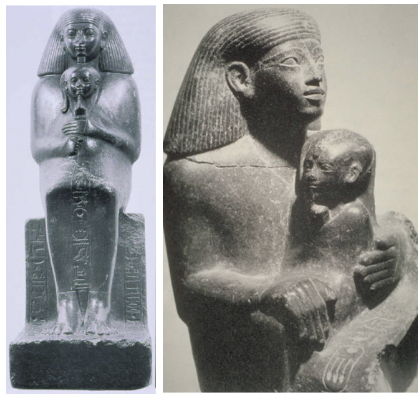

title, date, material, findspot
Senmut and Princess Nefru-Re
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1450 BC
Black granite
Karnak
Senmut and Princess Nefru-Re
Hatshepsut’s closest advisor
Senmut oversaw religion affairs, economic affairs
Also intrusted with Princess Nefru-Re
Ton of surviving statues of Senmut
Statues that get dedicated in temples had to be approved by the Pharaoh
Show firm connection with Hatshepsut, he is often shown as a guardian to the daughter
Daughter is the next in line
Cloak statue → Nefru-Re encircled by Senmut’s cloak
Iconography of children in Egyptian art:
Finger to the mouth and the sidelock
Senmut has idealized Tuthmosis style
Almond shaped eyes
Plastic eyebrows
Mouth is a bit bigger, but still small

title, date, material, findspot
Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut and Reliefs of Expedition to Punt
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1450 BC
Stone
Deir el-Bahari

Funerary Temple of Hatshepsut and Reliefs of Expedition to Punt
Dedicated to the god Amun
Incredible reliefs
Hatshepsut builds herself a funeral complex
complimentary to the three-tiered complex
Super important because she dedicates her temple to the god Amun (importance during the New Kingdom)
middle/second level contains shrine to Hathor
Funerary temple included a series of reliefs
There were a bunch of scenes carved to represent Hatshepsut reign
Record of expedition of Punt
No military conquest
Engaging in diplomatic
Interesting because we get to see the Egyptians
Punt had incense, ivory, leopard skin (?)
Scenes are arranged in characteristic registers
Some depict land and landscape, rivers and some fish in the rivers
Meaning of the Egyptians and the people of Punt
Capture different gestures of people
Exchange of goods and gifts
Mounds of incense and mir
Shown as enormous woman
Good to know how Egyptians depict others
Done in relief and painted

title, date, material, findspot
Great Temple of Amun at Karnak
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1450 BC
Stone
Karnak
Great Temple of Amun at Karnak
Example of Egyptian temple
This is where Amun (Theben version of the Sun God Ra)
This is where Amun’s temple was built starting in the middle kingdom
Expanding to the west and the south
Temples were built up overtime
Best preserved standard plan of Egyptian temple
In Middle Kingdom, this local theben god became prominent
Triad
Amun, Mut, and Khonsu
Central sanctuary, the temple complex became larger, knocked down, rebuilt
Some of the earliest pylons IV and V → pylons get built by a pharaoh of dynasty XVIII by Tuthmosis I
Pylon → giant gateway
Very specific shape
Broader at base and walls become narrower as it gets higher
Gateway – can get through center
Series of pylons and obelisks
Tuthmosis III adds more pylons
Two major pylons that go into major sanctuary
East-west is the original one, and north-south one gets added on later
Product of growth overtime
Standards
Progression of pylons (gateways, giant walls that slant) that create gateways, hypostyle halls,
Obelisk of Sesostris I, 12th Dynasty, 1971-1926 BC (Middle Kingdom), Red Granite. Heliopolis, Egypt (oldest standing obelisk)
Obelisk
From ancient Greek:
Obelos = spit, nail, pointed pillar
Pyramidon
Pointed top of either an obelisk or pyramid
Tall, four sided, tapering monument
Monolithic
Made of a single stone
Egyptian temples were shrines that were based on “Ever increasing levels of Exclusively and Secretsie”
Open courts and halls
For every set of doors, very few people/priests were allowed in
People allowed in are high level priests
Repeating levels
At every stage/succession, the space gets smaller
Space gets smaller in scale, floors would rise and ceilings would go lower
Cult statue of Amun resided in the smallest room
Resting place on Earth of the Ka of Amun
Only the pharaohs and the priests that can go into the cult statue
Attendant deities → Khons, Ptah
Repositories of wealth for the pharaoh
Held golds and treasures
Extensive plots of land
From the land, income!!
Cultivating the land
Similar to Near Eastern temples
Held tools for the land

title, date, material, findspot
Banquet Scene from Tomb Chapel of Nebamun
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1450 BC
Painted Plaster
Thebes
Banquet Scene from Tomb Chapel of Nebamun
Example of private tomb decoration in Dynasty XVIII
Acropolis of Thebes gets continued
Non royal people are buried in rock-cut tombs
Can bring funerary gifts
Chapels to bring gifts and underneath the chapel were the tombs
Paint on plaster (no carved reliefs)
Subject
Common subjects
Scenes of everyday life
Funeral processions
New scenes: the dead meeting gods and goddesses
Banquet scene
The people who were still alive would cross the nile (East to West) to visit the deads tombs
Eat a meal
Where living and the dead where they can commemorate
Commemorative meal
Hathor = help the living go into the world of the dead
Banquet includes dancers and musicians
Hathor is associated with ritual drunkenness
Plenty of wine on hand
Naked servant girl pouring wine
Style
Registers
Recognizable hieroglyphs
Features that are typical of the new kingdom
Large, almond shaped eyes (set at a slight angle)
Faces are lower and fuller
Fuller neck → meant to indicate that they have a plentiful diet
Further use of frontal poses

title, date, material, findspot
Amenhotep III
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1314 BC
Quartzite
Thebes
Amenhotep III

title, date, material, findspot
Colossi of Memnon
Dynasty XVIII, 1350 BC
Quartzite
Thebes
Colossi of Memnon
Lore surrounding these statues
Original function was to protect
Very little of it remains today
Mudbrick wall
These two statues stood outside
Visible to everyone → location and scale
In addition to represent himself (the king), also the two women of the king (mother and wife)
title, date, material, findspot
Luxor Temple to Amun
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1314 BC
Limetsone
Luxor
Luxor Temple of Amun
Important building
Up the nile (south), at Luxor, he created another temple to Amun
Major building complex of the kingdom
Amenhotep was the first to monumentalize this temple
Processional colonnade
Series of rooms
Rames II builds a courtyard (off axis)
260 meters long (2 and half football fields)
Egyptian Architecture:
Hypostyle hall
Pylon (slanted)
Obelisk
Processional way
Opening court
Rooms getting smaller, smaller, and smaller
Rooms get exclusive
Hold the statues of the gods
And to hold the wealth of the pharaohs
Opet festival
Took place of Luxor
Took image of Amun from Karnak, would be accompanied by the royal family and took a journey to the Luxor
Journey was on land (3 kilometer route)
Monumentalized by two headed sphinxes
To get get, they took a boat
Festival focuses the ka of the king
Helped maintain order (Ma’at – order)
Become a divine king
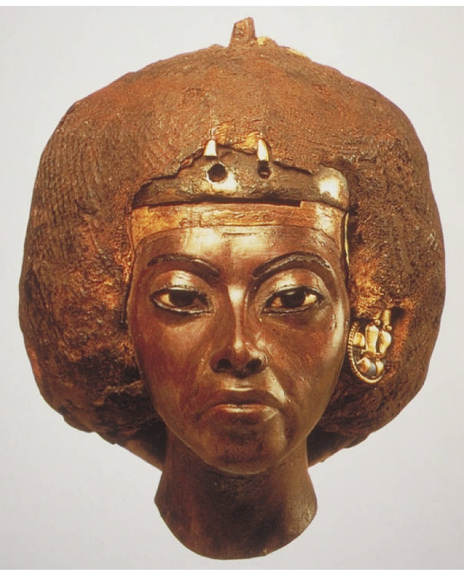

title, date, material, findspot
Queen Tiy
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1314 BC
Ebony
Gurob
Queen Tiy
Gold earrings
Precious jewelry
Headcloth → lapis lazuli (TRADE) and gold
Style:
Naturalistic
Labia lines (lines at the nose to the mouth)
Looks older and individualized
texture

title, date, material, findspot
Statue of Amenhotep Son of Hapu
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1314 BC
Granite
Karnak
Statue of Amenhotep Son of Hapu
Famous vizier of Amenhotep III
One of the few named and celebrated architects of ancient Egypt
Was a commoner
Delta region of nile (fans and dumps into mediterranean)
Constructed on Amenhotep’s funerary complex
Marks and guarded the entrance
Honor of himself having a small funerary complex modeled on royal ones
Built right by the kings
Commoner who become the right hand man to Amenhotep III
Smaller funerary complex is built right by Amenhotep’s
After he dies, his fame rules on and became deified
This statute actually comes from temple at Karnak
He could erect a statue of himself at the temple of Amenhotep
Describe:
Chest area is not very muscular
Less muscle
Not made to look buff
Ink pad on his right side (standard scribe iconography)
Sides are not carved and arms are by his torso
Why create negative space if you don’t have to?
He has wrinkles
Sagging naso-labia lines (lines from nose to mouth)
Sitting down
Sculptor defines someone who is aging
Cheeks fall in/sagging in
Tells us that he lived to be 80 years old
Realistic style
Show the upcoming change of style
Inscription covering his skirt → anyone who offers who reads it can have help in the afterlife if you give him prayers and offerings
Talking statue
A statue that has writing on it that calls out to a passerby and that interacts with the passerby
Statue speaks in first person → “if you do this, i’ll do this for you”
Someone tried to kill this statue
Ancient damage and ancient repair
Nose is flatter
Believe that someone trying to strike/chisel off his nose
We breathe through our nose
If you want to kill a statue, you go for the nose
Carving away the damage part of the nose, and sculpting a new one
More flat than originally planned to be
Object biographies!
Statues have its own life
New Kingdom
Dynasty XVIII — 1570-1314 BC
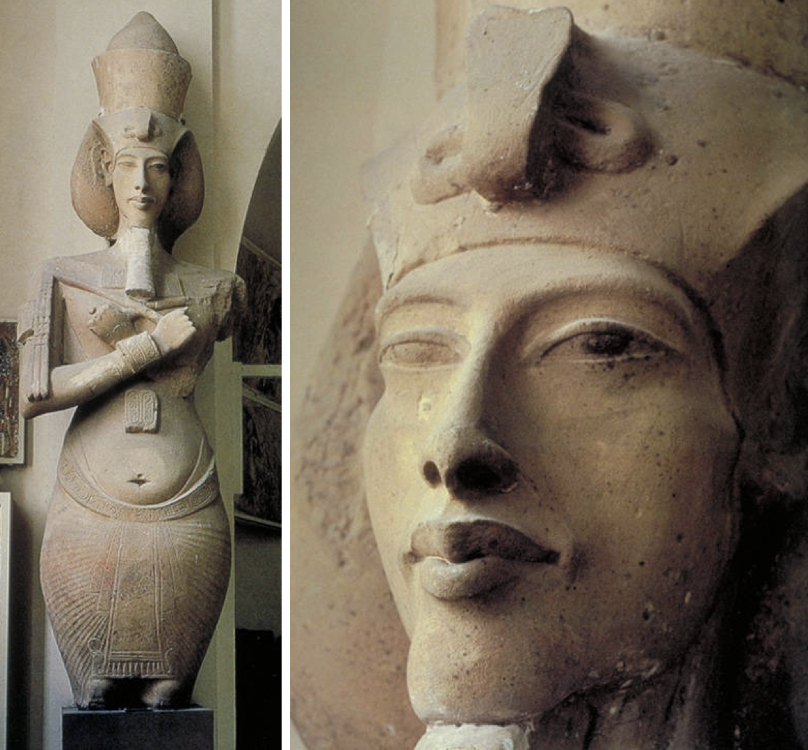

title, date, material, findspot
Colossal Sandstone Statue of Akhenaten
Dynasty XVIII, 1350-1321 BC
Limestone/Sandstone
Aten Temple, Karnak
Colossal Sandstone Statue of Akhenaten
Amenhotep IV → assumes a new name: Akhenaten
Because of his physical makeup and revolutionary reign: he has been referred to as a female, frolic syndrome (deforms limbs), monotheism, mentor to Moses, and even been called the for-runner of Christ
Reigns from 1350-1321 BCE
Because he moves to capital to Amarna, this period is called the Amarna Period (still Dyn XVIII)
Religious revolution
Decided to suppress the worship of the pantheon of egypt gods and only worship one god, the sun
The sun → Aten (the sun disk)
Representation of anthropomorphic → not shaped like a human
Worshiped the new sun god as merely a disk
Deity is not shaped like a human or a mix of creatures
Aten disk (sun disk) looked more like the hieroglyphic of the word sun
Did finish sculpting things at Karnak using his birth name
Referred to himself at Amenhotep III
He made the sun disk as the deity of Egypt
New representation of the god is a disk with radiating rays with at the ends of them have hands and hold the symbol of life (ankh)
Put himself at the center of this cult
Takes on this new name → Akhenaten
One of the series of colossal statues
Knocked down and buried where they fell
Standard iconography and standard egyptian inventions:
False beard
Pleated kilt of skirt
Nemes headcloth with cobra
Eyes are slanted
Arms across his chest → Osiris pose
Eyebrow ridge (plastic eyebrow)
Blue crown
Standing → king pose (only 3 poses)
Akhenaten looks very different^
“Early Karnak style”
Difference:
Rounded, pouched belly, fully bloated abdomen
Thin arms
Curved body (hourglass figure)
Narrow, nipped-in waist
Fuller hips
Is he a female because of the body shape?
Prominent collarbones
Broad shoulders
Face is super thin and very long
Elongated head
Neck is very skinny and elongated
High prominent cheekbones
Prominent lips and chin that sticks out from his face
In higher relief → very modeled and shapely
Radical change in style
Some of these sculptures are signed by the sculptor
Bak
“The king taught me how to do it”
King had clear input in the way that he looked
Scholars → “he had this certain disease, etc”
Nobody can agree!
Known to have 6 daughters and 1 son (King Tut!)
Kodak moment
Kodak company with film
Capture reality → picture is same as reality
Art historians say that you cannot assume that these are kodak moments
Style may have greater meaning
title, date, material, findspot
Standing-striding figure of Nefertiti
Dynasty XVIII, 1350-1321 BC
Limestone
Amarna (now Ägyptisches Museum Berlin)
Standing-striding figure of Nefertiti
Long, thin neck
Art historical context
Early Karnak Style
Does she have these diseases?
Sculpture that is meant to communicate ideas more than a Kodak moment
Sandstone is colossal
And she is just about 1 foot tall
Found in workshop → about to be painted
Similar in style:
Rounded stomach, swollen abdomen
Full hips
Long, elongated neck
Face seem ovular → elongated, but oval face
Long, thin nose
Full lips
Ears are high up and elongated
Hunched over
Unfinished sculpture found at a workshop in the temple
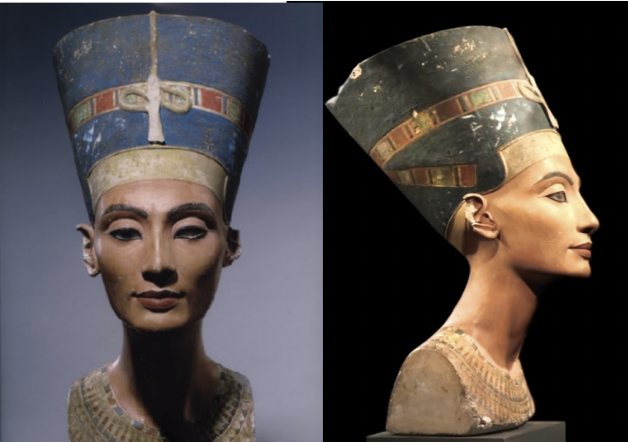

title, date, material, findspot
Sculptor’s Model of Nefertiti
Dynasty XVIII, 1350-1321 BC
Painted limestone
Sculptor’s Workshop, Amarna
Sculptor’s Model of Nefertiti
Long, thin neck
Mystery and beauty to egypt
Same elongated neck, elongated face, elongated nose and ears
Seems that have been a sculptor models
Didn’t make pieces like this
Incomplete piece
Sharply cut off at the neck/shoulders
Scholars have interpreted this as a model
Likeness of the queen
Only one of the eyes get inlaid and leave out the other one
Fully painted!
Gives us an example of a new kingdom, new elaborate taste that we wouldn’t see without the paint
Light red, blue crown, highly ornate decorated collar
Gives window of new kingdom taste of color
Early karnak style → elongated

title, date, material, findspot
Stele Showing Akhenaten and Family
Dynasty XVIII, 1350-1321 BC
Limestone
Amarna
Stele Showing Akhenaten and Family
Example of functional art
Religious revolution
Series of reliefs of the Amarna period
Limestone – easy to carve
Typical scene of the royal family worshiping Aten
Outside, open courtyard
Columns on each side → meant to show the outside at a pavilion
Behind Akhenaten → stack of offerings
This is the king and queen and the royal family only
Daughters climbing around
Also shows representation of Aten → sun disk
Rays of sun that have hands on the side of them → holding Ankhs (symbol of life)
Function:
Royal family was meant to worship Aten
And everyone else was supposed to worship the royal family
In houses → this is how the worship of Aten worked
Royal family worshiped Aten and everyone else worships Akhenaten
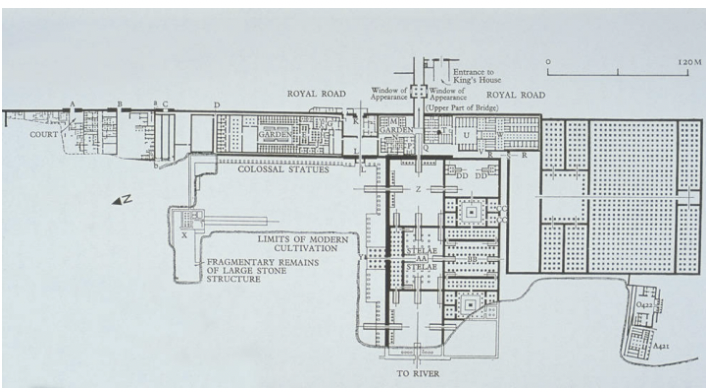
title, date, material, findspot
Palace at Amarna
Dynasty XVIII, 1350-1321 BC
Limestone
Amarna
Palace at Amarna
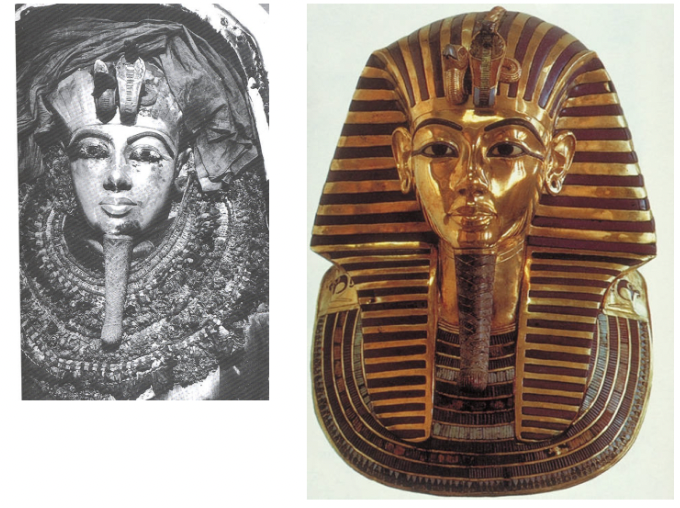

title, date, material, findspot
Gold Mask of Tutankhamun
Dynasty XVIII, 1333-1323 BC
Gold
Thebes
Gold Mask of Tutankhamun
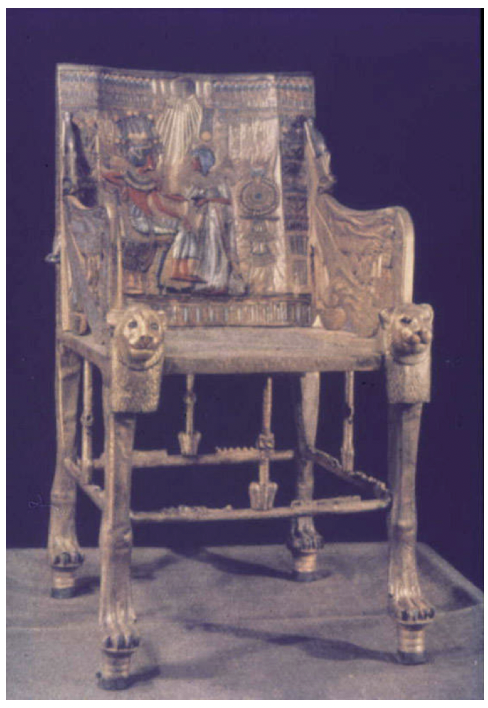

title, date, material, findspot
Inlaid Chair of Tutankhamun
Dynasty XVIII, 1333-1323 BC
Wood, gold, precious stone, and glass inlay
Thebes
Inlaid Chair of Tutankhamun
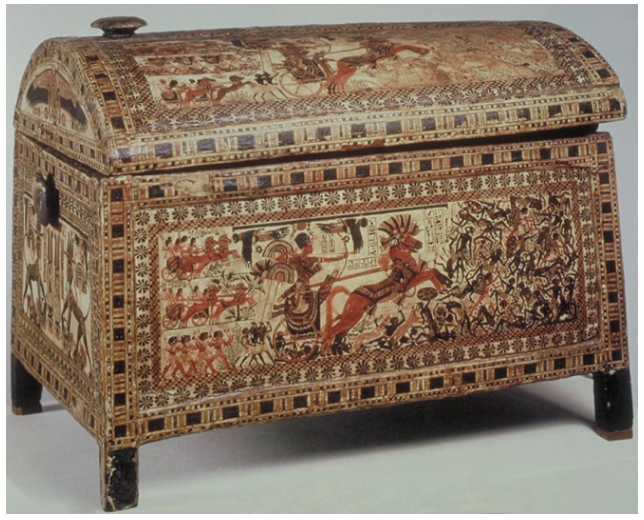

title, date, material, findspot
Painted Chest
Dynasty XVIII, 1333-1323 BC
Wood, gold, precious stone, and glass inlay
Thebes
Painted Chest

title, date, material, findspot
Paintings from Tomb of Huy
Dynasty XVIII, 1333-1323 BC
Painted limestone
Thebes
Paintings from Tomb of Huy
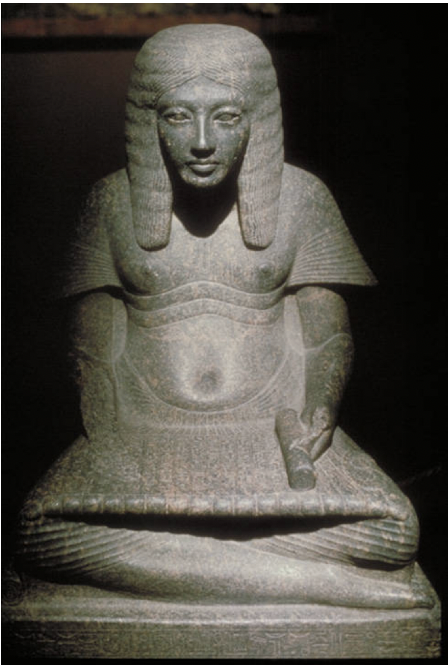

title, date, material, findspot
Horemheb as Scribe
Dynasty XVIII, 1319-1307 BC
Granite
Memphis
Horemheb as Scribe
New Kingdom/Ramesside Period
Dynasty XIX — 1307-1196 BC
Dynasty XX — 1196-1070 BC

title, date, material, findspot
Ka Statue of Ramses II Det. w/Relief on Pedastal
Dynasty XIX, 1290-1224 BC
Sandstone
Entrance to colonnade, Temple at Luxor
Ka Statue of Ramses II Det. w/Relief on Pedastal
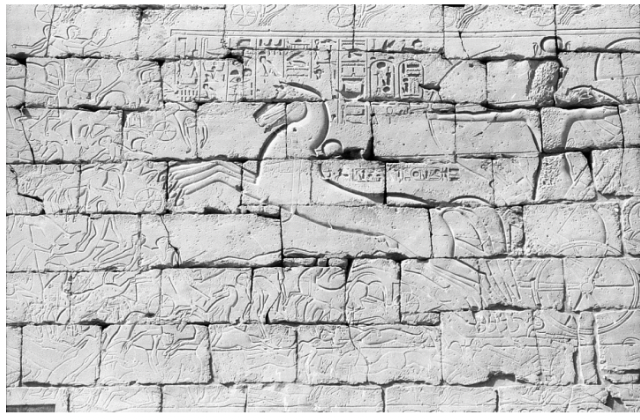

title, date, material, findspot
Scene from Battle of Qadesh: Remses II vs Hittites
Dynasty XIX, 1290-1224 BC
Sandstone
Pylon of the Temple at Luxor
Scene from Battle of Qadesh: Ramses II vs Hittites
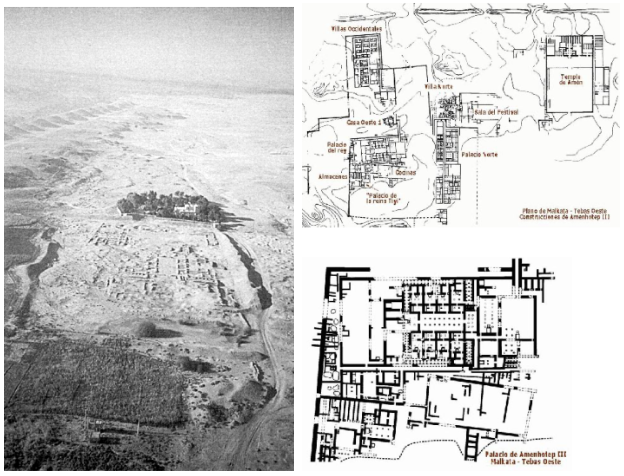
title, date, material, findspot
Malkata Palace of Amenhotep III
Dynasty XVIII, 1570-1314 BC
Mud-brick, stone, plaster
Thebes
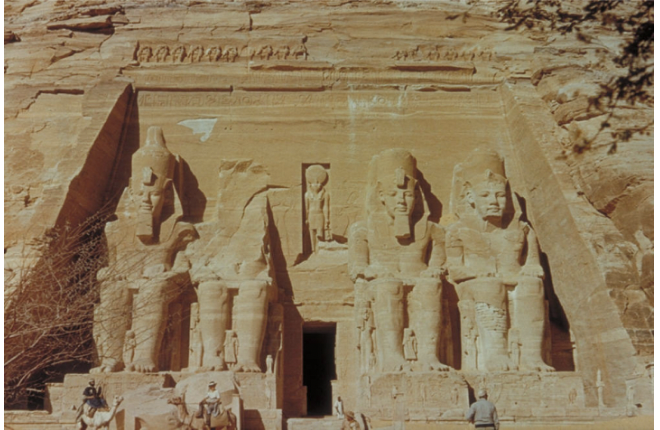

title, date, material, findspot
Great Temple at Abu Simbel
Dynasty XIX, 1290-1224 BC
Sandstone
Abu Simbel, Nubia
Great Temple at Abu Simbel
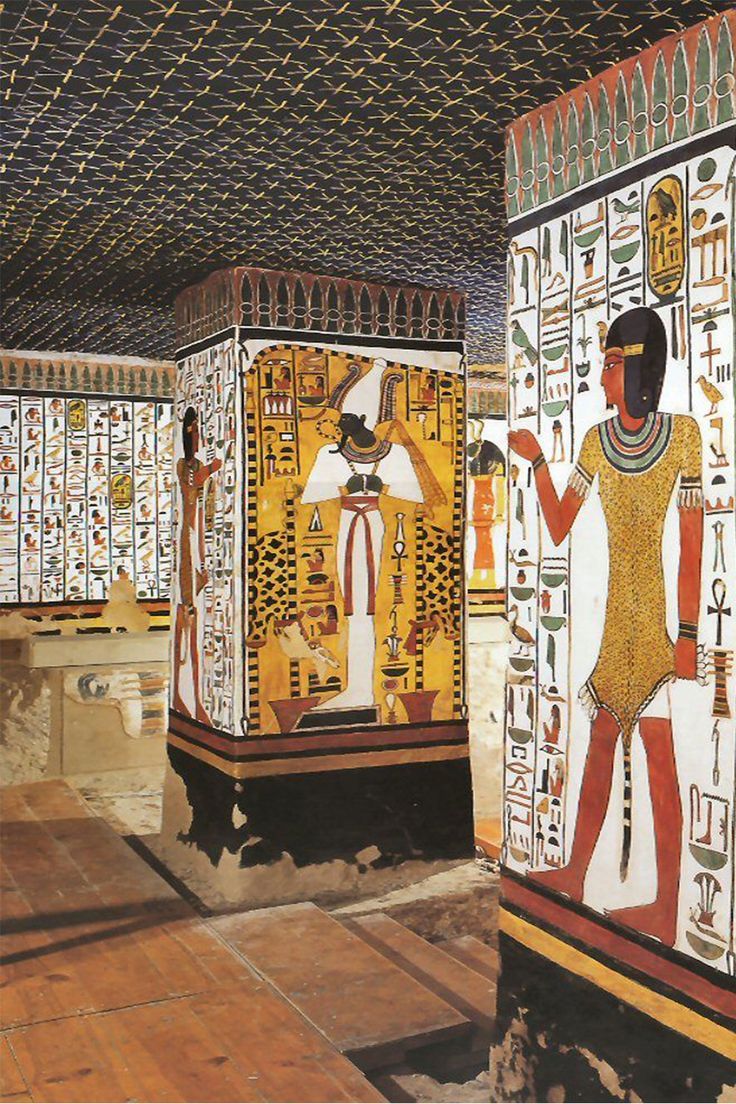

title, date, material, findspot
Paintings from Tomb of Queen Nefertari (wife of Ramses II)
Dynasty XIX, 1290-1224 BC
Painted, relief-cut plaster
Valley of the Queens
Deir el-Bahari
Paintings from Tomb of Queen Nefertari (wife of Ramses II)
title, date, material, findspot
Funerary Temple of Ramses III
Dynasty XX, 1194-1163 BC
Limestone
Medinet Habu, Thebes
Malkata Palace of Amenhotep III
New kingdom → two preserved palaces
This palace is situated in the southern portion of Thebes
One mile south of Amenhotep III funerary complex
Connected through a roadway
Domestic architecture
Sprawls out for a mile
Numerous buildings surrounded by parade areas/open courts
The main buildings include the palace of the king
Main feature of the southern portion
Temple to Amun to the North
Huge audience pavilion in the center of the complex
Far nw corner → smaller houses grouped around a large home
Village area that has tiny living spaces for workmen
Construction:
Mudbrick
Some stone → columns bases, etc
The walls and the ceilings were decorated with painted plaster
Most column shafts are wooden
Ceiling beams are wooden
Living quarters were seen as temporary
Tombs on the other hand had to be built of stone so they are there for eternity
Decoration of the palace
Plastered walls and plastered ceilings
Most of the designed were of animals, plants, birds → naturalistic scenes
Some of the motifs (leaping bulls) are echoing common motifs that we know from Aegean Bronze Age palaces (Knossos)
Bulls head on ceiling
International contact!!
Importing some decorative designs
Funerary Temple of Ramses III