M1 | Introduction to Software Engineering, Project Organization and Management
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
An engineering discipline whose focus is the cost-effective development of high-quality software systems.
Software Engineering
It answers the questions:
1. What does it mean to be cost-effective?
2. What doese it mean to be high quality?
Software Engineering
He further explains that software is “abstracts and intangible”
Ian Sommerville
He defines software engineering as “an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software production from the early stages of system specification to maintaining the system after it has gone into use
Ian Sommerville
These are the TCQ Triad:
Time, Cost, Quality
This is also called the triple constraint model of product management.
TCQ
True or False:
You can have something FAST and CHEAP, but it won’t be good QUALITY
True — If a product is fast and cheap, quality usually suffers because there’s not enough time or resources to do it well.
Is a valuable intellectual property
Software
It is moving towards a more disciplined profession.
Software Enineering
True or False:
Software plays a key role in all dimensions of our lives.
True — Software impacts communication, transportation, healthcare, business, education, and more.
True or False:
As professionals, software engineers must conduct their practices at some level of professionalism to minimally ensure that their work results in no harm to society
True — Engineers must follow professional standards.
True or False:
It is one of the principles for ethics and professional practices in software engineering. Software engineers shall act in a manner that is in the best interests of their client and employer, consistent with the public interest
True — Because professional ethics in software engineering require balancing loyalty to clients and employers with responsibility to society, ensuring that work benefits stakeholders while avoiding harm to the public.
True or False:
It is one of the principles for ethics and professional practices in software engineering. Software engineers shall ensure that their products and related modifications meet the highest professional standards possible
True — Software Engineers must ensure products and modifications meet the highest professional standards possible.
True or False:
It is one of the principles for ethics and professional practices in software engineering. Software engineers are not required to maintain integrity and independence in their professional judgment.
False — Engineers must maintain integrity and independence in all professional judgments.
True or False:
It is one of the principles for ethics and professional practices in software engineering. Software engineering managers and leaders shall subscribe to and promote an ethical approach to the management of software development and maintenance
True — Managers and leaders must promote an ethical approach in software development and maintenance.
True or False:
It is one of the principles for ethics and professional practices in software engineering. Software engineers are not expected to advance the integrity and reputation of the profession consistent with the public interest.
False — Engineers must work to advance integrity and reputation while serving the public interest.
True or False:
It is one of the principles for ethics and professional practices in software engineering. Software engineers shall be fair to and supportive of their colleagues
True — Engineers must be fair and supportive to colleagues to foster a healthy, ethical professional environment.
True or False:
It is one of the principles for ethics and professional practices in software engineering. Software engineers are not expected to engage in lifelong learning or promote an ethical approach.
False — Engineers must engage in lifelong learning and promote ethics.
List five areas where software engineers are expected to exhibit professional behavior.
Handling of information privacy
Handling of quality issues and problem resolutions
Handling of project estimation and project coordination
Handling of reuse and intellectual property
Handling of security
He is one of the earlier authorities to bring forward a set of principles that underlie software engineering.
Alan Davis
True or False:
Alan Davis article on the 15 principles of software engineering actually includes 30 principles
True - it actually includes 30 principles
According to Alan Davis, the most important principles of software engineering are:
Make quality number one
High-quality software is possible
Give products to customers early
Determine the problem before writing the requirements
Evaluate design alternatives
Use an appropriate process model
Use different languages for different phases
Minimize intellectual distance
Put technique before tools
Get it right before you make it faster
Inspect code
Good management is more important than good tech
People are the key to success
Follow with care
Take responsibility
He suggested that there are eight software engineering concepts that have remained relatively constant even though the software industry has been changing.
Anthony Wasserman
He proposed a more modern set of the most important principles of software engineering. Such of these as an example is establish an iterative process that addresses risks early.
Walker Royce
Wasserman’s fundamental software engineering concepts
Abstraction
Analysis and design methods and notation
User interface prototyping
Modularity and architecture
Reuse
Life cycle and process
Metrics
Tools and integrated environment
Is an undertaking, limited in time, with a clear goal and a specific budget, requiring a concerted effort.
Project
A project consists of:
○ Start date and duration
○ Deliverables
○ Schedule
○ Technical and managerial activities
○ Resources
This is a collection of techniques, methodologies, tools and heuristics that support the development of:
○ A high-quality software system
○ Within a given budget
○ Before a given deadline
○ While change occurs
Project Management
They are the person who manages the project.
Project Manager (PM)
This person administers the resources and team members.
Project Manager (PM)
This person makes sure the project goals are met.
Project Manager (PM)
What are some key responsibilities of a Project Manager (PM) in a project?
Creating a project implementation plan from start to finish
Monitoring the entire project progress
Coordinating and connecting people
Providing leadership, motivation, and team management
Change management or dealing with changes fast and with the best results
Risk management or combating risks proactively and reactively
Stakeholder and customer satisfaction
Final product presentation and approval
Post-delivery paperwork or writing reports and logging all data
True or False:
Responsibilities or specific tasks are assigned to roles; roles are assigned to people; and people are assigned to teams.
True — Tasks go to roles, roles go to people, and people form teams.
It is a major unit of work and culminates in a project milestone.
Activity
These are Project Tasks and Activities:
Planning
Requirements elicitation
Analysis
System design
Software configuration management
Detailed design (object design)
Implementation
Testing
Delivery
Maintenance
These are people that grouped into departments, each of which addresses an activity or function.
Functional organization
These are people that are assigned to a
project, each of which has a problem to be solved in a
certain time within a given budget
Project-based organization
These are people from different departments of a functional organization are assigned to work on one or more projects
Matrix organization
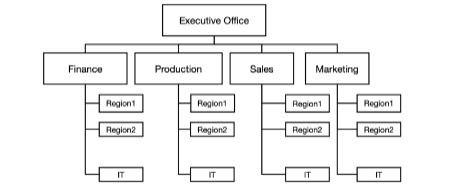
This is an example of what form of organization?
Functional organization
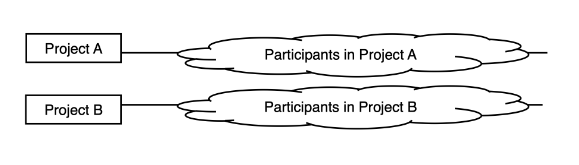
This is an example of what form of organization?
Project-based organization
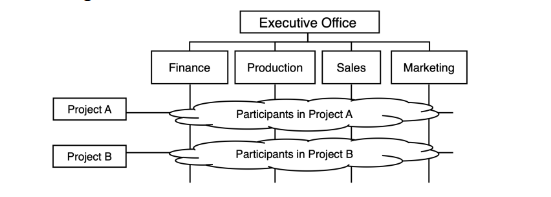
This is an example of what form of organization?
Matrix organization
This is defined as “imparting or exchanging
information by speaking, writing, or using some other
medium”
Communication
It plays a key role in project management
Communication
True or False:
In large system development efforts, developers often
spend more time communicating than coding
True
True or False:
Clear and accurate communication is critical for the
success of a software development project
True
The software PM and software engineers need to acquire
several skills, including:
Collaboration – negotiate requirements
Presentation – present the system during a review
Technical writing – write proposals and project
documentation
Management – facilitate a team meeting, find
compromises, negotiate between conflicting demands
It is a tool or procedure that can be used to deal with a communication event
Communication mechanism
What is a communication event in project management?
An information exchange with defined objectives and scope, including:
Scheduled events (planned communication, e.g., formal meetings)
Unscheduled events (event-driven communication, e.g., informal meetings, coffee breaks)
It requires communication partners to be available at the same time e.g. a phone call
Synchronous mechanism
It does not require communication partners to communicate at the same time e.g. group chat
Asynchronous mechanism
These are when teams come together for discussion
Meetings
True or False:
Meetings often fail to reach the desired outcome because people may get bored if the meeting is too long.
True
True or False:
Important points are always remembered and discussed during meetings.
False
True or False:
Decisions from meetings are never forgotten, even if they are not written down.
False
True or False:
Shy participants might struggle to share their opinions when others dominate the discussion.
True
These are some guidelines to follow during meetings:
Active listening and participation
No one-on-one or side meetings
Respect the agenda and keep time
Willingness to reach consensus
Freedom to check process and ground rules
Share responsibility for the team's progress