Yearling Bull Care and Breeding Soundness Exam in Bulls (not done)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is required to complete a breeding soundness exam in a bull?
Sufficient sex drive to seek out females
Ample amounts of viable semen
Structural soundness
Physical fitness
What do you need to palpate on a BSE?
Internal repro glands
Testicles
Prepuce
Penis
When should you palpate the accessory sex glands?
Prior to electroejaculation
What is the most common abnormality found on transrectal palpation?
Vesiculitis
What does a small testicle indicate?
Fibrosis
What does a large testicle indicate?
Inflammation
What causes a corkscrew penis?
The fibrous band on dorsum of penis tears
When do penile firbopapillomas appear?
Puberty
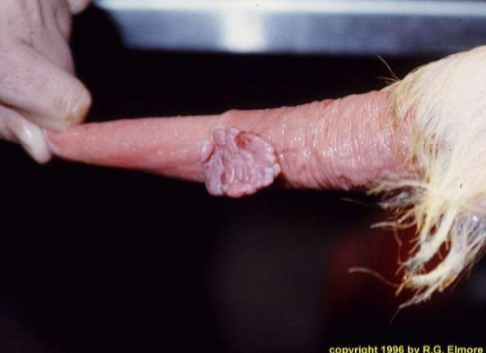
Penile fibropapilloma
How do you tx penile fibropapilloma?
Cut them off
What does a broken penis cause?
Prolapse of the prepuce and a hematoma
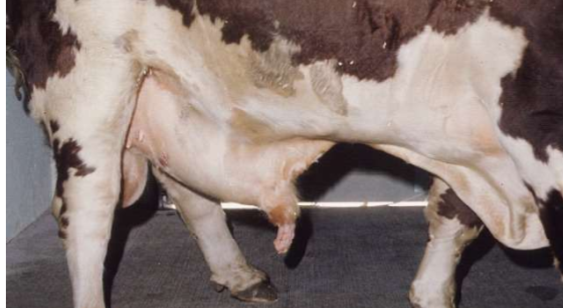
Hematoma of the penis (broken)
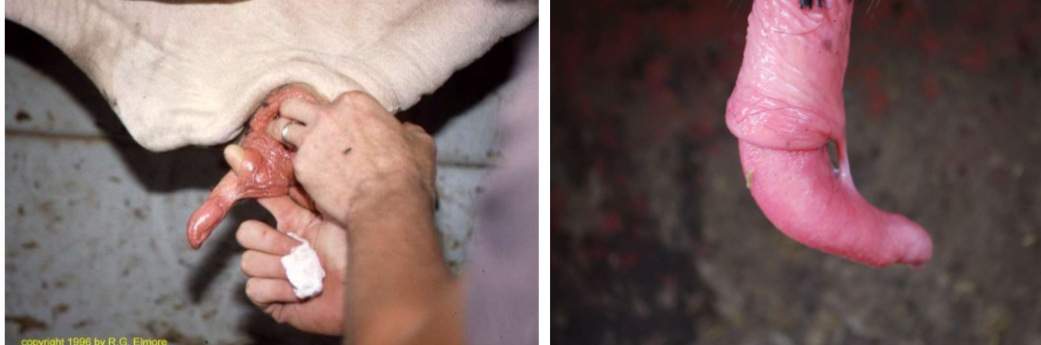
Persistent penile frenulum
When should the frenulum go away by?
Puberty
How do you tx a persistent penile frenulum?
Cut it off
How do bulls get hair ring?
From mounting other bulls and when the penis retracts it can cause a hair ring
What is the sequelae to hair ring?
Pressure necrosis and urethral fistula
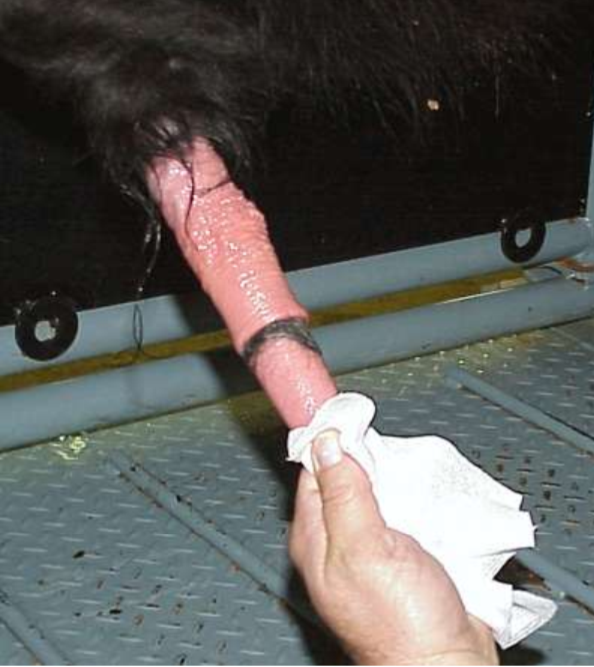
Hair ring
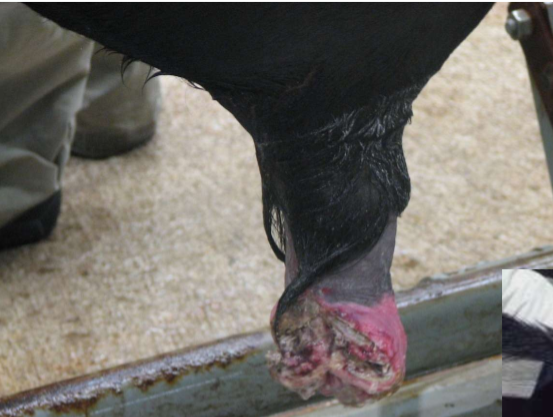
Scrotal frostbite
How do you measure scrotal circumference?
Measure around widest part of scrotum
T/F all testicles produce the same number of sperm per gram?
True
How can you determine what bull makes more sperm?
Bigger testicles
What is the benefit of an increased scrotal circumference?
Earlier puberty in daughters
What are the major abnormalities?
Correlated to impaired fertility
What are minor abnormalities?
Do not impair fertility
What are transitory abnormalities?
Defects caused by temporary insults to sertoli, leydig, and/or epididymal cells
What can cause transitory abnormalities?
Heat stress, nutritional stress, environmental stress, recoverable illness
Photoperiod change if seasonally fertil
What morphologic changes are transitory abnormalities?
Proximal droplets
Distal midpiece reflex
Coiled tail
T/F defects on the permanent list may be transient and vice versa?
True
What is the best way to differentiate between transient and non-transient defects?
Repeated evaluation
What can cause abnormal sperm production?
Stress, heat, season, heredity, puberty, toxicity, nutritional
What are some hereditary causes of abnormal sperm production?
Sperm defects, testis size
What does puberty sperm look like?
Disturbed spermatogenesis
What nutritional problems can cause abnormal sperm production?
Protein, vit A, selenium deficiency
What are some toxins that can cause abnormal sperm production?
Plant, bacterial, environmental toxins
What does stress suppress?
LH release and testosterone levels
When are bulls routinely offered for sale?
12-15 months (yearlings)
When do bulls reach puberty?
9-11 months
What peripubertal bull has what in an ejaculate?
50 million sperm and 10% motility
What scrotal circumference will not pass a BSE for yearling bulls?
<30cm
When should you recheck a yearling bull?
up to 3 attempts at one exam
Recheck in 2 weeks especially if there is a wart or frenulum removed, <70% normal morphology, vesiculitis, or failure to extend
Why do you re-check morphology?
To look for improvement
What do you need to communicate with clients for yearling bull considerations?
Check near puberty, time BSE relative to sail
What the BSE results mean
What are the 3 results of a yearling bull BSE?
Pass
Fail
Fail to pass but deferred for a later check
What is the classification of a BSE tell you?
That ON THIS DATE the bull is
Satisfactory
Unsatisfactory
Classification deferred
T/F all bulls pass equal?
True
What happens if a bull fails any part of the BSE?
Fail exam, can defer if desired
What are the common reasons to fail a BSE?
Poor movement, foot/leg flaw
Too thin/fat
Blind
Penis, prepuce or scrotum injury
Small testicles
Abnormal sperm
What problem do older bulls have with a BSE?
Musculoskeletal problems due to age
What happens to most bulls that fail a BSE?
Go to slaughter, need to be sure that they truly fail
What are some common causes of false failure?
Non-typical sample due to young bulls, electroejaculator, certain individuals
What should you do if you think you have a non-typical sample?
Rest and try again
What are the limitations of a BSE?
Only reflects the breeding soundness on day tested
Sperm cells were made weeks ago
Does not predict future ability
Many factors affecting fertility are not measured
Are we better at identifying subfertile or highly fertile bulls?
Subfertile
What are the strengths of the BSE?
Guarantees that known sub-fertile bulls are not tested out at the start of the breeding season
Removes bad genetics
Herd fertility and breed fertility are increased over time
What does a scrotal surface temp that is high or does not decrease from top to bottom means what?
More abnormal sperm
Fewer pregnancy
What is used to evaluate/detect fibrosis, soft areas and psermatoceles?
US
What does the ability of heparin-binding protein in seminal fluid binding to sperm cells tell you?
MAY be related to fertility based on one lab report