histamine related pharmacology
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
where is histamine naturally found?
within mast cells
histamine is naturally found within ________ cells. it is released due to _______
mast cells; internal and external stimuli
when histamine is released in a high amount, it induces ________
an allergic reaction
itching, urticaria, flushing, hypotension, tachycardia, bronchospasm, angioedema, etc.
what are the histamine receptors called?
H1, H2, H3
where are the histamine receptors located in the body?
they are widely distributed throughout the body, with the highest concentrations in the GI tract, lungs, and skin.
histamine related drugs work on which receptors?
H1 and/or H2
(they cannot act on H3)
histamine receptors (H1, H2, H3) are widely distributed throughout the body, but are in high concentrations where?
GI tract, lungs, skin
if H1 receptors are activated, what happens?
Calcium channels are opened. This induces:
-smooth muscle contraction
-increased capillary permeability
-vasodilation
-sensory nerve endings- pain and itching
if H2 receptors are activated, what happens?
release of cAMP. This induces:
-increased gastric acid secretion
-vasodilation
-increased capillary permeability
H2 receptors are located mainly in the ________
stomach
activation of which histamine related receptor induces an increase in gastric acid secretion?
H2
where are H2 receptors located?
mostly the stomach
what is betahistine?
a histamine analogue (structurally the same as histamine).
it affects both H1 and H2, but mainly H1 in the CNS. it is a powerful vasodilator with cerebral action, increasing the blood flow in the inner ear, so is useful for treating acute peripheral vestibular syndrome.
what drug is used to treat acute peripheral vestibular syndrome in veterinary medicine?
betahistine
because it is a powerful vasodilator with cerebral action, acting on H1 receptors in the CNS. it increases the blood flow to the inner ear.
what is the mechanism of action of betahistine?
H1 receptor agonist in the CNS. it induces vasodilation, increasing bloodflow in the inner ear.
which drug is an analogue of histamine and mostly affects H1 in the CNS?
betahistine
what are the side effects of betahistine?
nausea, vomiting, headache, pruritus
we avoid the use of betahistine in patients with.....
peptic ulcers or asthma.
because it causes bronchospasms and gastric acid secretion
what do H1 receptor antagonists do?
block H1 receptors and the effect of histamine.
what type of antagonism do antihistamines exert?
competitive antagonism
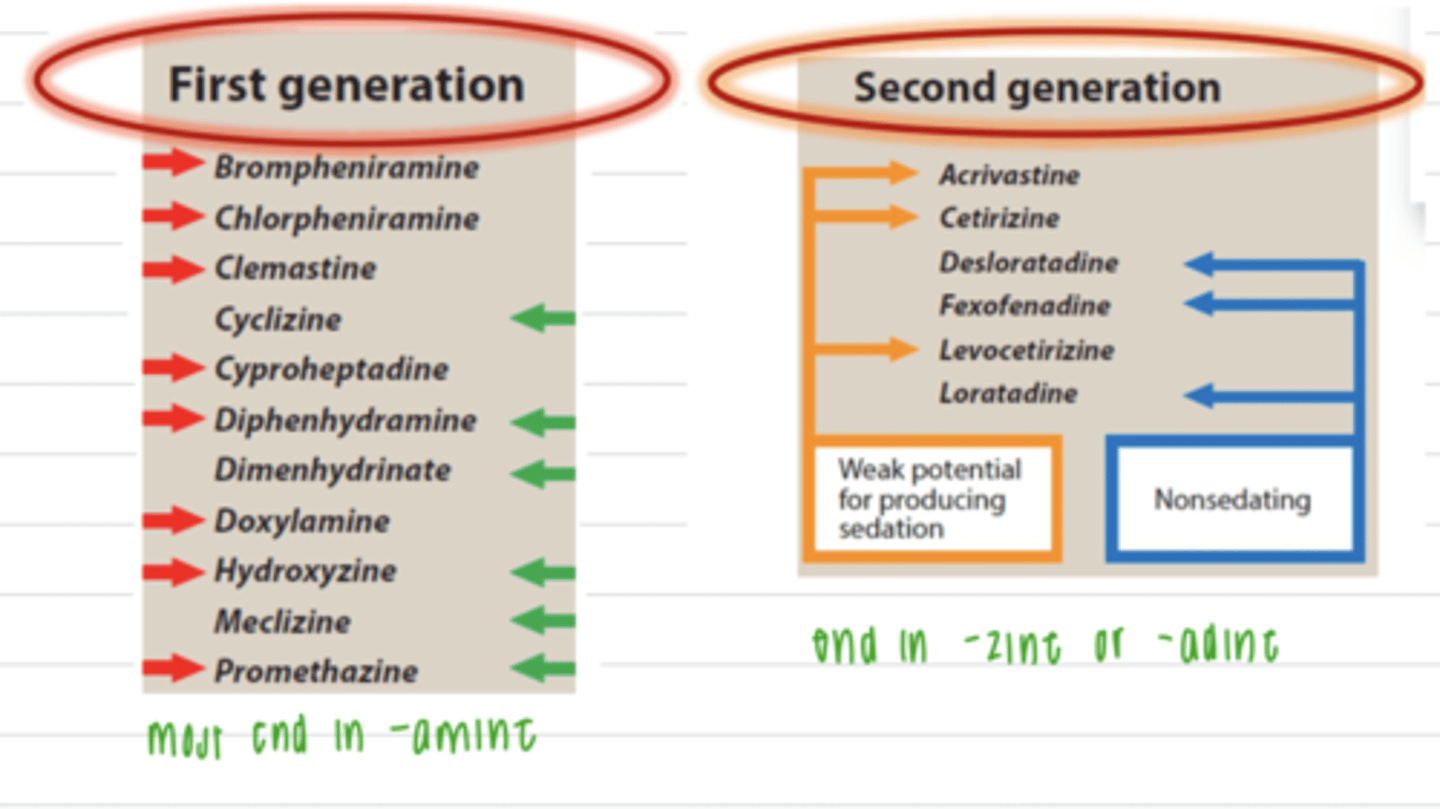
what are the 2 groups of antihistamines (H1 receptor antagonists)?
first generation:
brompeniramine
chlopheniramine
clemastine
cylizine
cyrroheptadine
diphenhydramine
himenhydrinate
doxylamine
hydroxyzine
meclizine
cyproheptadine
promethazine
second generation:
acrivastine
cetirizine
desloratadine
fexofenadine
levocetirizine
loratadine
what do first generation H1 blockers do?
block H1, muscarinic, cholinergic, alpha-adrenergic, and serotonin
H1 block:
decrease allergic inflammation, itching, sneezing, rhinorrhea, CNS neurotransmission, cognitive and psychomotor performance; increase appetite and sedation
serotonin block:
increase appetite
alpha-adrenergic block:
increase hypotension, dizziness, and reflex tachycardia
cholinergic block:
increase dry mouth, urinary retention, and sinus tachycardia
what are the main clinical uses of first generation H1 blockers?
treat and prevent allergies (Hydroxyzine and chlorpheniramine)
sedation induction (promethazine and diphenhydramine)
prevention of motion sickness and nausea/vomiting (diphenhydramine)
appetite stimulant for cats (cyproheptadine)
what receptors do first generation H1 blockers act against?
H1
serotonin receptors
cholinergic receptors
alpha-adrenergic receptors
muscarinic receptors
are first generation H1 blockers specific for H1 receptors?
NO, they also antagonize serotonin receptors, cholinergic receptors, serotonin receptors, alpha-adrenergic receptors, and muscarinic receptors
what is the effect of first generation H1 blockers when they block H1 receptors?
decreases:
allergic inflammation
itching
sneezing
rhinorrhea
CNS neurotransmission
cognitive and psychomotor performance
increases:
appetite
sedation
what is the effect of first generation H1 blockers when they block serotonin receptors?
increased appetite
what is the effect of first generation H1 blockers when they block alpha-adrenergic receptors?
increased hypotension, dizziness, reflex tachycardia
what is the effect of first generation H1 blockers when they block cholinergic receptors?
increased:
dry mouth
urinary retention
sinus tachycardia
can first generation H1 blockers cross the blood-brain-barrier?
yes, because they are unionized at physiological pH. this is why they are very sedative
in what types of animals can first generation H1 blockers be used?
large and small animals
what first generation H1 blockers are used in veterinary medicine for treating and preventing allergies (heaves, feline asthma, insect bites, etc.)?
Hydroxyzine and Chlorpheniramine
what type of drug is hydroxyzine? what is it used for in veterinary medicine?
first generation H1 blocker
used to treat and prevent allergies (heaves in horses, bronchospasmolysis in pneumonia, feline asthma, insect bites, chronic urticaria, atopic dermatitis)
what type of drug is chlorpheniramine? what is it used for in veterinary medicine?
first generation H1 blocker
used to treat and prevent allergies (heaves in horses, bronchospasmolysis in pneumonia, feline asthma, insect bites, chronic urticaria, atopic dermatitis)
what type of drug is promethazine? what is its clinical use in veterinary medicine?
first generation H1 blocker
sedation induction
what type of drug is diphenhidramine (Benadryl)? what is its clinical use in veterinary medicine?
first generation H1 blocker
sedation induction and prevention of motion sickness and nausea/vomiting in dogs and cats.
what are promethazine and diphenhidramine (Benadryl) used for in veterinary medicine?
both are used for sedation induction, because they have a high affinity for H1 receptors in the brain
diphenhydramine is also used for prevention of motion sickness and nausea/vomiting in dogs and cats.
how does diphenhydramine (Benadryl) prevent nausea/vomiting?
because it is a first generation H1 blocker, so blocks muscarinic receptors- which inhibits cholinergic transmission from the vestibular nuclei to the vomiting center
which drug is the most used in veterinary medicine for prevention of motion sickness?
diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
what type of drug is cyproheptadine? what is its clinical use in veterinary medicine?
first generation H1 blocker
it is used as an appetite stimulant in cats
what drug is commonly used as an appetite stimulant in cats?
Cyproheptadine (first generation H1 blocker)
are antihistamines very effective for controlling pruritus?
no. in veterinary medicine, they are not as effective as they are in human medicine.
to control allergic priuritus (and other reactions), it is more effective to administer them BEFORE the onset of the reaction, because they cannot displace histamine from the receptors (competitive antagonism)
first generation antihistamines are continuously given orally for what clinical use?
they provide a small relief to dogs with mild atopic dermatitis, especially before an allergic reaction. however, they cannot displace histamine from the receptors, so if histamine is already present, they won't have an effect.
are first generation antihistamines useful for an animal with an active allergic reaction?
no, because they cannot displace histamine from the receptors- so if histamine is already present, they won't have an effect.
what are the adverse effects of first generation antihistamines?
-CNS depression/sedation
-anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, urinary retention, mydriasis, blurred vision, tachycardia
-intestinal problems: anorexia, nausea/vomiting, constipation, diarrhea
-cardiovascular problems: tachycardia, arrhythmias
do first generation antihistamines have GI adverse effects?
yes- anorexia, nausea/vomiting, constipation, diarrhea
do first generation antihistamines have cardiac adverse effects?
yes- tachycardia, arrhythmias
because they block cholinergic and alpha adrenergic receptors
what are the adverse effects of first generation antihistamines regarding their anticholinergic effects?
dry mouth, urinary retention, mydriasis, blurred vision, tachycardia
Cryptoheptadine is mainly used in veterinary medicine for __________. but it has these adverse effects: __________
appetite stimulation in cats;
excessive hunger, sedation, and vomiting
what neurological adverse effect can first generation antihistamines cause?
sedation. however, this is usually considered an advantage rather than a disadvantage
is Advil safe for use in animals?
no, it is dangerous because it is formulated with other ingredients with a low TI
are first generation antihistamines considered safe to use in animals?
no, because they are often formulated in combination with other drugs that may not be safe.
they also have antagonist effects on alpha adrenergic receptors, muscarinic receptors, and serotonin receptors.
what receptors do second generation H1 blockers act against?
only H1 (they are highly specific)
no anticholinergic, antiemetic, or neurological effects
can second generation H1 blockers cross the blood-brain-barrier?
NO, so they have little to no sedative effect
first generation H1 blockers CAN cross the BBB, which is why some are used for sedation induction
can second generation H1 blockers be used as antiemetics?
no, because they are highly selective for H1
which generation of antihistamines are sometimes used for their antiemetic effect?
first generation
what are the main therapeutic uses of second generation H1 blockers?
treating allergic disorders:
rhinitis
dermatitis
conjunctivitis
urticaria
eczema
drug and food allergies
which generation of antihistamines is better for treating allergic disorders?
second generation antihistamines (H1 blockers), because they ONLY affects H1 receptors- while first generation has lots of other adverse effects due to their unspecificity.
however, first generation H1 blockers are more commonly chosen, because they are much cheaper
which generation of antihistamines is most commonly chosen for treating allergies in animals?
first generation.
second generation are better because they have less side effects, BUT first generation are cheaper.
which, first or second generation antihistamines are safer in animals?
second generation
first generation are not considered safe due to their unspecificity. however, second generation antihistamines are highly specific for H1 receptors, so are even sold over the counter because of how safe they are.
can you buy antihistamines over the counter for veterinary usage?
YES, some first generation antihistamines and all second generation antihistamines
second generation antihistamines are commonly used in combination with......
NSAIDs, acetaminophen, decongestants, and cough suppressants
H2 receptor blockers are more commonly known as.......
antiulcer medications
(ranitidine, famotidine, cimetidine, nizatidine)
which drugs competitively inhibit the action of histamine on H2 receptors?
antiulcer medications (H2 receptor blockers)
Famotidine
Ranitidine
Cimetidine
Nizatidine
what is the mechanism of action of H2 receptor blockers?
competitive inhibition of H2 receptors- blocking gastric acid secretion
what drugs are H2 receptor blockers?
Ranitidine
Famotidine
Cimetidine
Nizatidine
which drug is the preferred antiulcer medication in veterinary medicine?
Famotidine, because it is less likely to cause adverse affects (it has no prokinetic action).
what is Famotidine used for in veterinary medicine?
antiulcer
are H2 receptor blockers sold over the counter?
yes
what are H2 receptor blockers used for in veterinary medicine?
antiulcer: treatment/prevention of gastric, abomasal, or duodenal ulcers.
treating hypersecretory conditions of the stomach
treating esophageal and gastric reflux
frequently administered to any vomiting patient
which drug is frequently administered parenterally to a patient that is vomiting?
H2 receptor blockers-
Famotidine
Ranitidine
Cimetidine
Nizatidine
what are the side effects of H2 receptor blockers (antiulcers)?
side effects are rare in animals, because they have a high TI.
Cimetidine- inhibits microsomal enzymes in the liver, affecting the rate of metabolism of other drugs
why was Ranitidine preferred to Cimetidine as an antiulcer medication?
because Cimetidine inhibits microsomal enzymes in the liver, which decreases metabolism. Ranitidine does not have these effects on hepatic enzymes, and have prokinetic activity, which increases gastric emptying and prevents vomiting.
however, nowadays Ranitidine is not used because it releases carcinogenics.
why is Ranitidine no longer in use?
because it is proven to release carcinogenics
Ranitidine has prokinetic activity. what does this mean?
this means that it increases gastric emptying and prevents vomiting.
this is positive for some patients, but bad for patients with a GI obstruction
which H2 receptor blocker is known for having prokinetic activity?
Ranitidine
which- H1 or H2 receptor blockers produce more side effects in animals?
H1 antagonists- the first generation especially produces many side effects (neurological, GI, respiratory, cardiovascular, etc.).
H2 antagonists rarely produce side effects- they have a very high TI.
what is Cromolyn?
a drug that inhibits the degranulation of mast cells and histamine release.
it is not technically an antihistaminic because it does not act on a histamine receptor.
it also has vasoconstrictor and antiinflammatory activity, and is used to treat allergic conjunctivitis and seasonal allergies.
what drug is commonly used in veterinary medicine as a treatment for allergies affecting the eyes?
Cromolyn (sodium cromoglycate)
administered as an ophthalmic solution
what are the pharmacological effects and clinical use of Cromolyn?
-inhibit degranulation of mast cells, and therefore release of histamine
-vasoconstriction
-anti-inflammatory
clinical use: treats allergic conjunctivitis, alleviate seasonally allergies affecting the eyes (applied in the eyes as an ophthalmic solution)
what is the dosage form of Cromolyn?
ophthalmic solution
which drugs are used in veterinary medicine for the treatment or prevention of gastric, abomasal, or duodenal ulcers?
H2 receptor blockers:
Ranitidine (now banned)
Famotidine (preferred)
Cimetidine
Nizatidine
what is Famotidine used for?
antiulcer medication.
treatment or prevention of GI ulcers, hypersecretory disorders, reflux, or vomiting
what receptor does Cromolyn act on?
it does not act on a receptor, but instead prevents mast cells from degranulating and releasing histamine.
which drug inhibits the degranulation of mast cells?
Cromolyn
can you buy Famotidine over the counter?
yes, it is very safe
which are the second generation H1 blockers?
Acrivastine
Cetirizine
Desloratadine
Fexofenadine
Levocetirizine
Loratadine
which- first or second generation H1 blockers can cross the blood-brain-barrier so are more able to cause CNS depression?
first generation
(second generation H1 blockers cannot cross the blood-brain-barrier)
other than allergic reactions, what are second generation H1 blockers used for?
nothing, they are only used for treating allergic reactions