PCOS
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Short deck because the other one was 18 years to long :p
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
A collection of signs and symptoms in female patients related to menstrual cycles and excess androgens - cysts not required
Impaired glucose tolerance, type II DM, dyslipidemia, CVD, fatty liver disease, obstructive sleep apnea, endometrial hyperplasia/malignancy, depression, anxiety
Patients with PCOS are at an increased risk of developing…
A combination of genetic and environmental
Etiology of PCOS
Ovulatory Dysfunction, polycystic ovaries by U/S, clinical/biochemical hyperandrogenism (required)
Rotterdam Criteria (most common) for PCOS - 2/3
Oligomenorrhea (under 8 cycles per year), Amenorrhea, Irregular menses (result of anovulation, no progesterone)
Menstrual Cycle irregularities is defined as
Anytime under under 1 year post menarche, Under 21 or over 45 days between cycles (1-2 post menarche), under 21 or over 35 days between cycles (3 years post menarche)
When is it normal for having menstrual cycle irregularities?
Thyroid dysfunction (check TSH/T4), Hyperprolactemia (check serum prolactin)
What are some causes for Menstrual Cycle irregularities
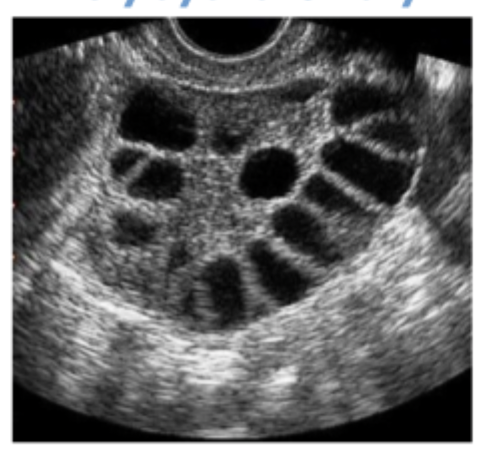
20+ follicles 2-9 mm in diameter in each ovary (TVUS) OR increased ovarian volume (abdominal U/S)
To diagnose PCOS, what do you need to see on U/S - not necessary if menstrual cycle irregularities and hyperandrogenism are present
anti-mullerian hormone (not a sole diagnostic test)
Alternative to U/S
Hirsutism, acne, male pattern hair loss, deepening voice, clitormegaly
Clinical signs of Hyperandrogenism
Free or total serum testosterone/SHBG
Biochemical Diagnosis of Hyperandrogenism
Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (measure morning Serum 17-hydroxyprogesterone, ACTH stimulation test), Androgen secreting tumor (Serum free/total testosterone, DHEAs), Cushing’s Syndrome (Check serum/urine cortisol, dexamethasone suppression test)
Things to exclude before diagnosing PCOS
blood pressure annually, BMI (20% are NOT obese), lipids, sleep apnea, depression/anxiety, 2 hr glucose tolerance test (preferred!), Fasting glucose/Hemoglobin A1c, consider endometrial biopsy (based on excessive thickness)
What do we need to evaluate in a patient with PCOS?
achieve fertility, control of irregular menstruation, treatment of acne/hirsutism
Immediate goal for treatment of PCOS
Coronary heart disease, DM, endometrial cancer
Long term risk of PCOS
weight loss
What is a 1st therapy for PCOS
Androgen levels, hirsutism, menstruation, fertility, reduction of lipid/glucose levels, CVD morbity/mortality
In PCOS, what improves with weight loss?
COMBINED OCPs, Progesterone Based therapies (IUD, nexplanon, etc), insulin sensitizing agents (metformin, spironolactone)
Second line therapies for PCOS
menstrual regulation, endometrial proliferation, antiandrogenic effects
How do OCPs help with PCOS?
Decreased androgen levels, improved glucose tolerance, improved ovulation rate
How do insulin sensitizing agents improve PCOS symptoms?