W13 - Gas exchange/O2
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HR x SV = CO (4-6L) - turn & cought 2-3 times Every 2hrs , 10 deep breaths every
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
pulmonary edema and crackles in lungs are associated with left or right heart?
Left side heart failure / Congestive heart failure
Where is S1 heard the loudedest? how about S2?
Which is the closure of the AV valves? how about Semilunar Valves?
S1 → apex and AV closure
S2 → Base and semilunar closure
What are the main coronary arteries and what areas of the heart does it supply blood to?
Right cornary Artery → right side of the heart
Left cornary Artery
(widow maker) Left anterior descending artery → Left side of heart
Circumflex artery → around the heart
For a patient who recently had a MI, which lab values would be elevated? Which labs is more reliable and why?
Creatine phosphopkinase (CPK)
CK-MB (enzyme in heart tissue)
Troponin would be the better one to look at since it stays in the blood for a longer period of time
What are the 3 treatments for artial Occlusion, please give a short description for each
Thrombolytic (TPA) → breaks down blood clots
Angioplasty → inflates a baloon in the blood vessel
Stent placement → wire mesh to keep the vessel open
What is the major difference between Thrombolytic and anticoags?Why would you not give a thrombolytic to a pt that had recent trauma/ surgery?
Thrombolytic → breaks down present blood clots
Anticoag→ prevents blood clots
You can’t give to pts w/ recent trauma b/c it will cause internal bleeding via dissolving all the blood clots
What is the cardiac conduction pathway? How does it start?
Pacemaker (SA node) → AV node → bundle of His → left and right bundle of his → purkinje fibers
automaticity
When does a wandering pacemaker occur in the heart, and how does it affect electrical impulses?
A wandering pacemaker happens when impulses come from different areas of the heart (heart damage) instead of only the SA node, this causes irregular electrical activity
Electrical Impulses
• SA Node: ? BPM
• AV Node: ? BPM
• Bundle of His & Purkinje Fibers: ? BPM
Electrical Impulses
• SA Node: 60-100 BPM
• AV Node: 40-60 BPM
• Bundle of His & Purkinje Fibers: 20-40 BPM
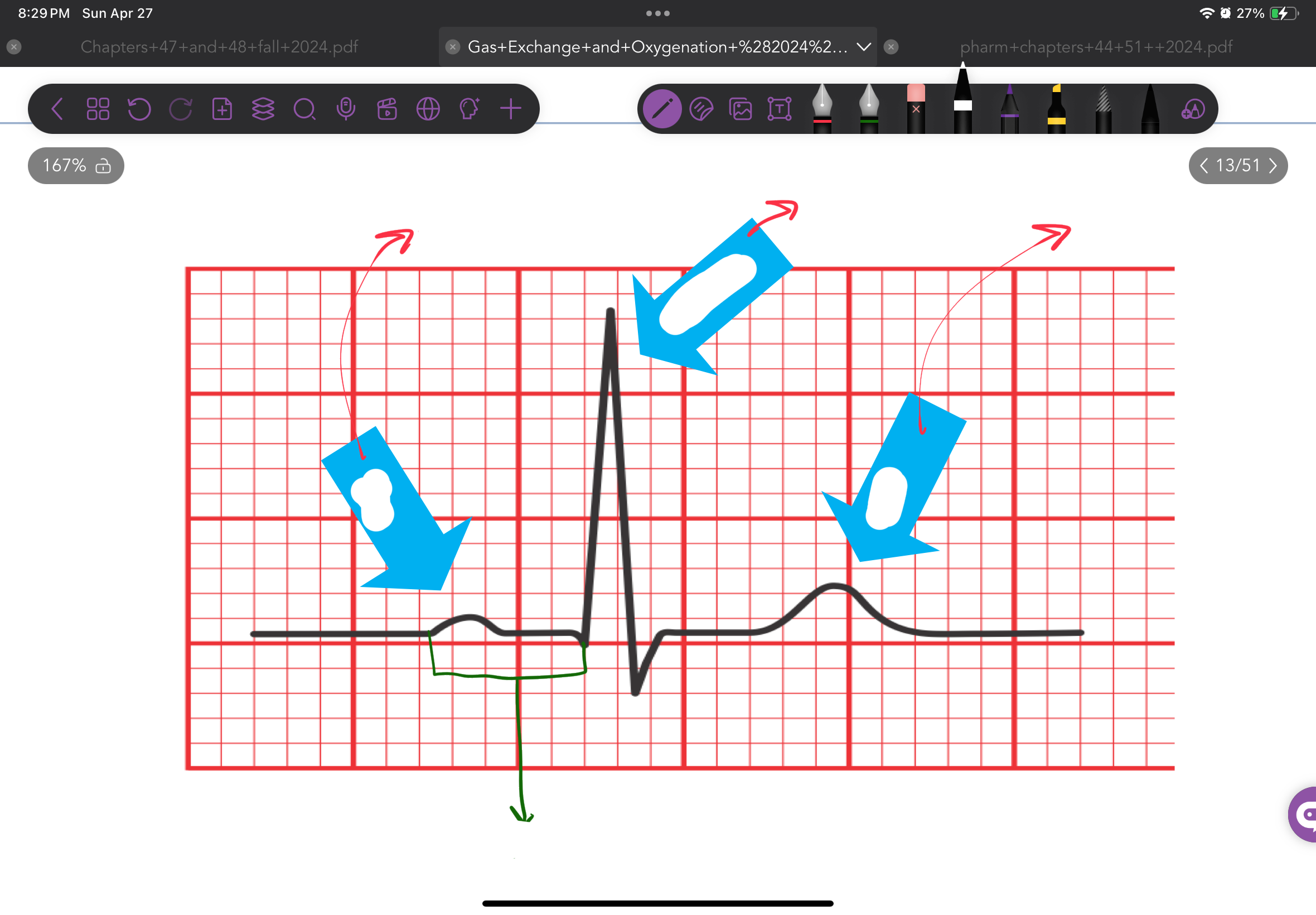
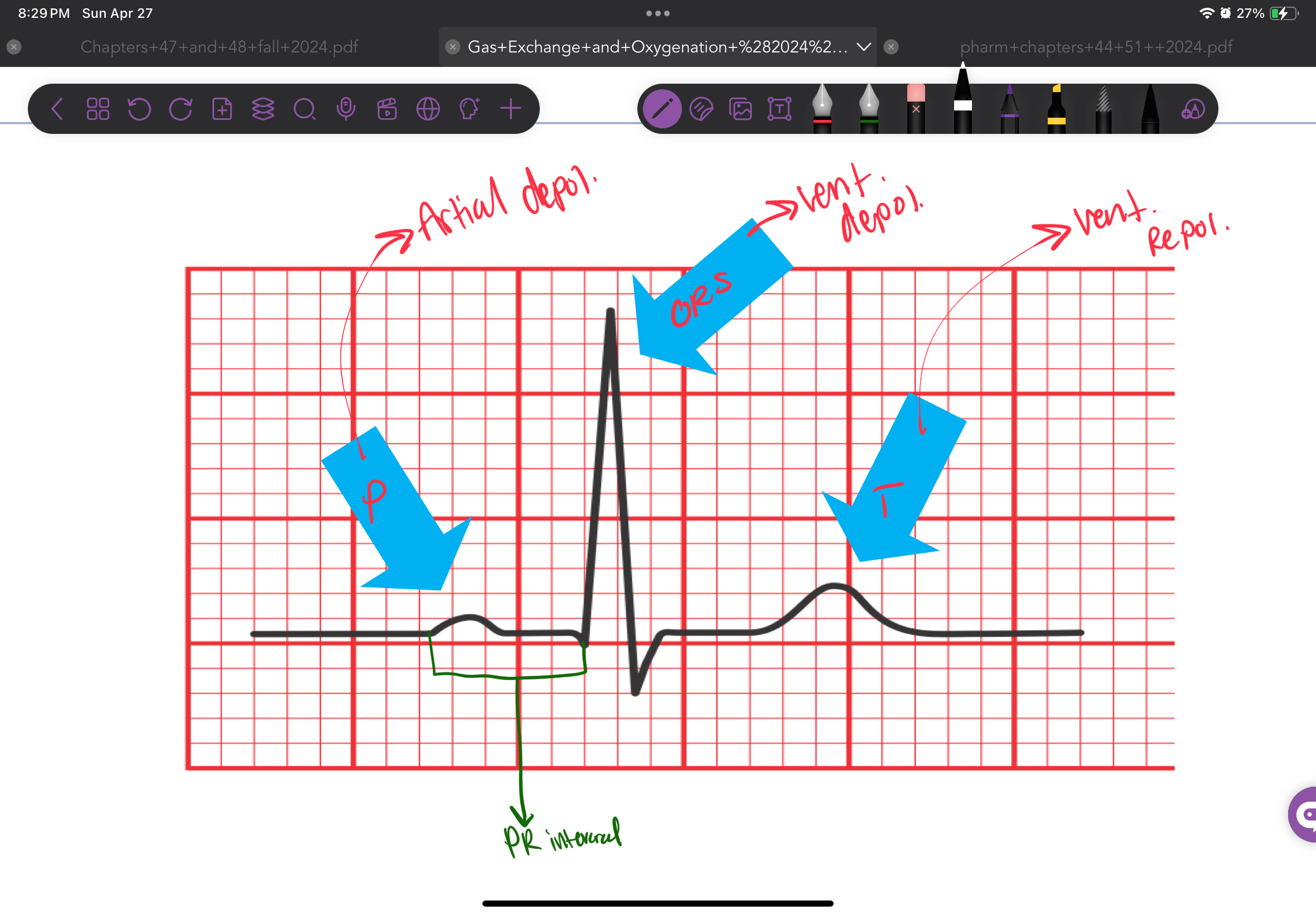
Describe the cardiac cycle 3 phases
Polarization
K+ leak out of cell
Makes inside of cell (-)
Depolarization
Inflow of Na+ and Ca+
makes inside of cell (+)
Triggers contraction of heart muscle
Repolarization
Return of cell to resting state
Makes inside of cell (-)
What 3 things affects contractility, please provide a description for each
Venous return (Starling Law)
Inotropic Effect
Ejection Fraction
Venous return (Starling Law)
Inc volume of blood in the chamber, Inc stretch, Inc recoil = Inc contracility
Inotropic Effect
Positive inotropes (SNS) = inc contractions
Ejection Fraction (55%-75% normal)
% of blood out of ventricle w/each beat
Define
Ventilation
Diffusion
Perfusion
Ventilation → Moving air into lungs
Diffusion → The exchange of respiratory gases from alveoli and capillaries via alveolocapillary membran (high to low concentration)
Perfusion → pumping oxygenated blood into the tissues and returning de-oxygenate
What is the resipatory drive for COPD and NON - COPD?
COPD → O2
NON - COPD → CO2
Goal of ventilation is maintaining:
– CO2 between ? mmHg
– Arterial O2 between ? mm Hg
Goal of ventilation is maintaining:
– CO2 between 35-45 mmHg
– Arterial O2 between 95-100 mm Hg
How does the does the brain regulates respiration? For the automoatic control what is the receptor and what does it detect?
Medulla oblongata (chemorecptor check pH(H+), O2, Co2)
Automatic control
Senstive to narcotics
Cerebral Cortex
Voluntary Control
What is normal blood pH?
7.35 - 7.45
Define…
What are the causes…
What are the effects…
Hyperventilation
Define → Exhaling excessive CO2
What are the causes:
Anxiety
Infections
Hypoxia
Compesation for metabolic Acidosis
What are the effects
Agitaiton
inc rate/depth of Respirtation
Alkalosis state, which cause vasoconstriction
paresthesia
Define…
What are the causes…
What are the effects…
Hypoventilation
Define → Dec amount of air entering alveoli
What are the causes:
Obstuction
Atelectasis (collaps aveoli)
Inappropriate administeration of O2 in COPD pts
What are the effects
Mental status change
Dysrythmias
Define…
What are the causes…
What are the effects…
Hypoxia
Define → Inadequate tissue oxygenation at cell lvl
What are the causes:
Obstuction
Atelectasis (collaps aveoli)
Inappropriate administeration of O2 in COPD pts
What are the effects
Mental status changes (early signs)
Cyanosis (late sign)
What do these Cardiopulmonary diagonstic test do?
EKG/ECG
Holter Monitor/Event Monitor
Stress Test (exercise/chemical)
Echocardiography
Cardiac Catheterization
ABG
Pulse Oximetry
Spirometry/Peak Flow Meter
Blood Studies (Cardiac Enzymes, Serum Electrolytes)
EKG/ECG
Holter Monitor/Event Monitor
Stress Test (exercise/chemical)
Echocardiography
Cardiac Catheterization
ABG
Pulse Oximetry
Spirometry/Peak Flow Meter
Blood Studies (Cardiac Enzymes, Serum Electrolytes)
What diet improve heart functions?
Low fat high fiber diets
What is a low-Flow system and what are some examples?
The amount of O2 delivered is variable since it depends on the paient breathing pattern
Nasal Cannula
Simple mask
Nonrebreather
What is a high-Flow system and what are some examples?
The amount of O2 delivered is set and the pt is getting that O2 %
Venturi Mask
2L is what % of O2
28%
What us the O2 % for NC and what’s the min-max Liters of O2 that can be adminstered?
22-44%
1/2- 6L/min
What us the O2 % for Simple mask and what’s the max Liters of O2 that can be adminstered?
40%-60%
5-8L/min
What us the O2 % for Nonrebreather and what’s the max Liters of O2 that can be adminstered?
80% - 95%
10-15L
What us the O2 % for Venturi mask and what’s the max Liters of O2 that can be adminstered?
24-50%
4-12 L/min
When suctioning the trachea, how long should the pt breath between each suction session? Why can’t a nurse continuously suction the trachea?
3 seconds
The pt can sufficated cuz ur suctioing out air
What does COCA stand for and when is it used?
C → Color
O → Oder
C → Consistencty
A → Amount
For assessing sputum
What is Splininting ?
Cushioning the blow of coughing , such as a hugging a pillow and coughing
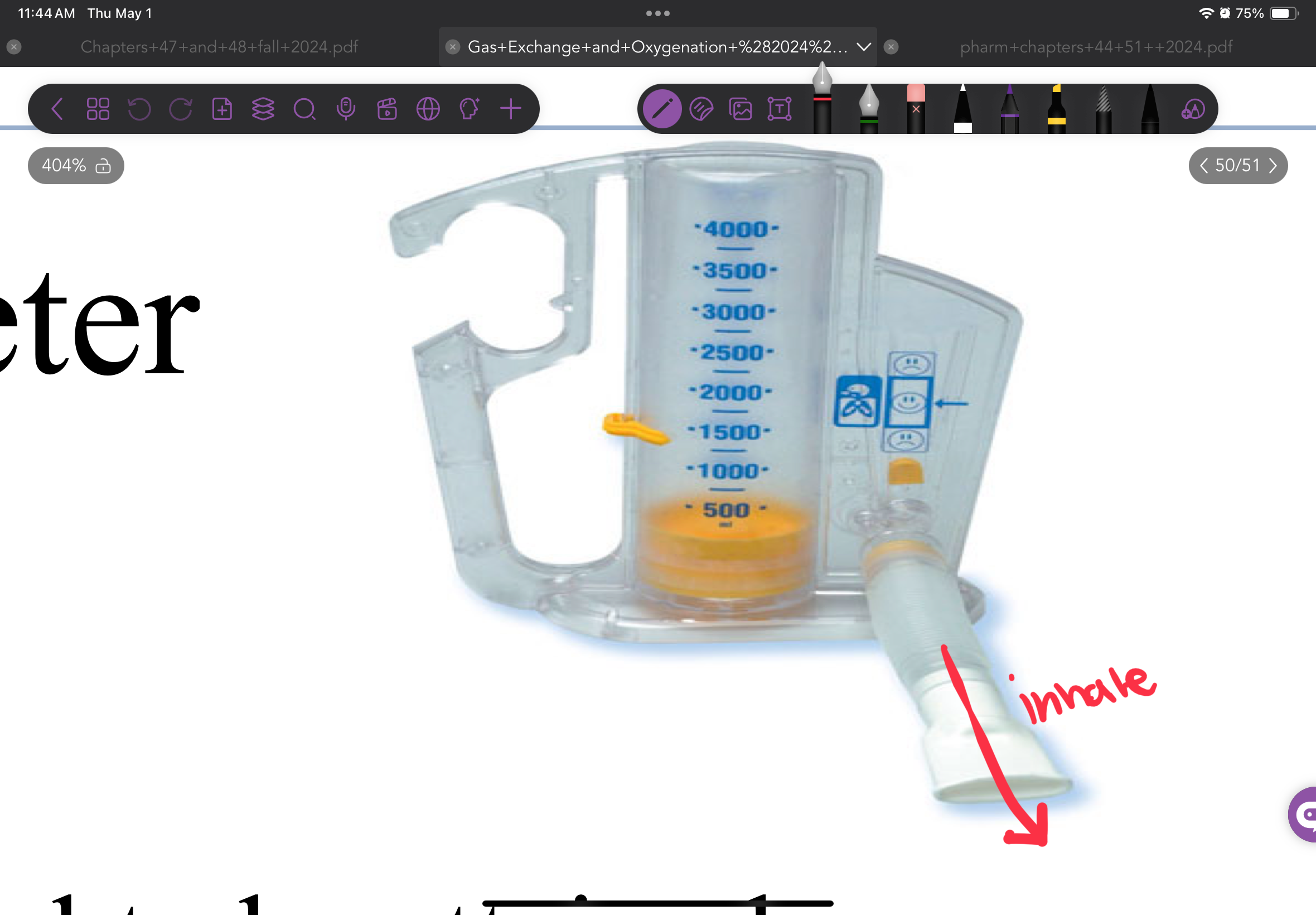
What is a Incentive Spirometer? and does it treat?
It a device that the pts sucks in and it treats Atelectasis