Levels of Organisation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the levels of organisation?
Chemical or molecular
Cellular
Tissue
Organ
Organ System
What is chemical or molecular level?
Atoms such as hydrogen, carbon, oxygen and nitrogen and molecules such as water, sugars, fatty acids, amino acids and nucleotides
What is the cellular level?
Cells are the smallest unit of life, cellular differentiation can take place so cells are specialised for different function in higher life forms
What is tissue level?
Cells that secrete and regulate extracellular material and fluids combine to form tissues with special functions
What is organ level?
A discrete collection of two or more tissues cooperatively performing a function. Tissues combine to form organs with multiple functions
What is organ system level?
Organs interact in organ systems
What are some examples of cells?
Cells lining intestinal tract
Smooth muscle cell
Neuron in brain
What do epithelia do?
Tissues that cover exposed surfaces, line internal passageways and chambers, and produce glandular secretions
What do connective tissues do?
They fill internal spaces, provide structural support, and store energy
What are some examples of organs?
Heart
Femur
Biceps brachii muscle
What are the 11 body system?
Integumentary
Skeletal
Muscular
Nervous
Endocrine
Cardiovascular
Lymphatic
Respiratory
Digestive
Urinary
Reproductive
What are the key functions of the integumentary system?
Protection, thermoregulation, sensation
What is the key function of the skeletal system?
Protection
What is the key function of the muscular system?
Allows movement
What is the key function of the nervous system?
Communication
What is the key function of the endocrine system?
Allows communication and coordination through hormones
What is the key function of the cardiovascular system?
Transport gases and nutrients as well as waste
What is the key function of the lymphatic system?
Defence against pathogens (involved in the immune response)
What is the key function of the respiratory system?
Ventilation
What is the key function of the digestive system?
Takes nutrients into the body
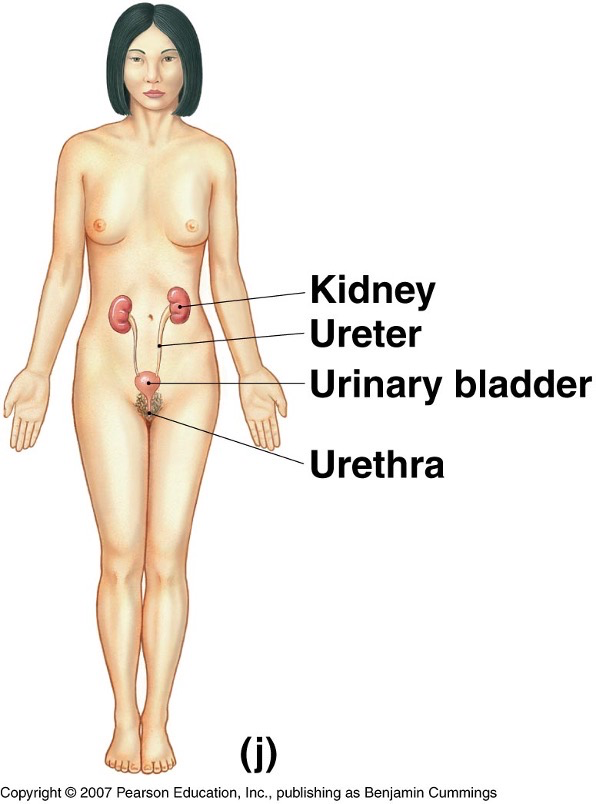
What is the key function of the urinary system?
Removes waste from the body
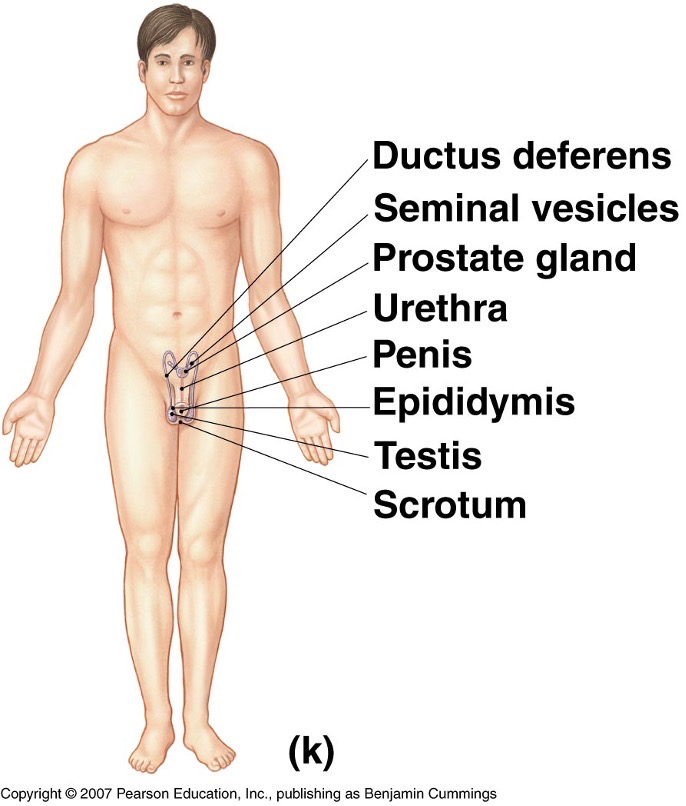
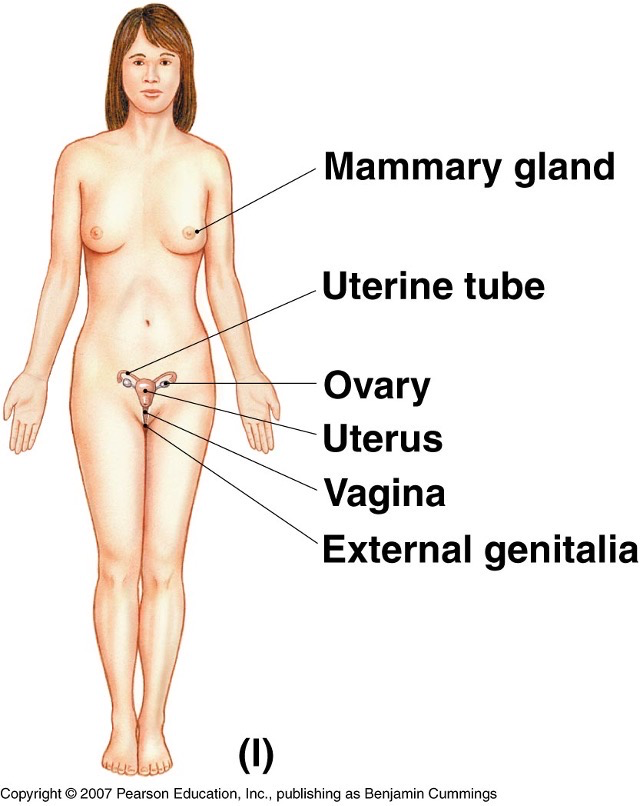
What is the key function of the reproductive system?
Reproduction
What does the integumentary system look like?
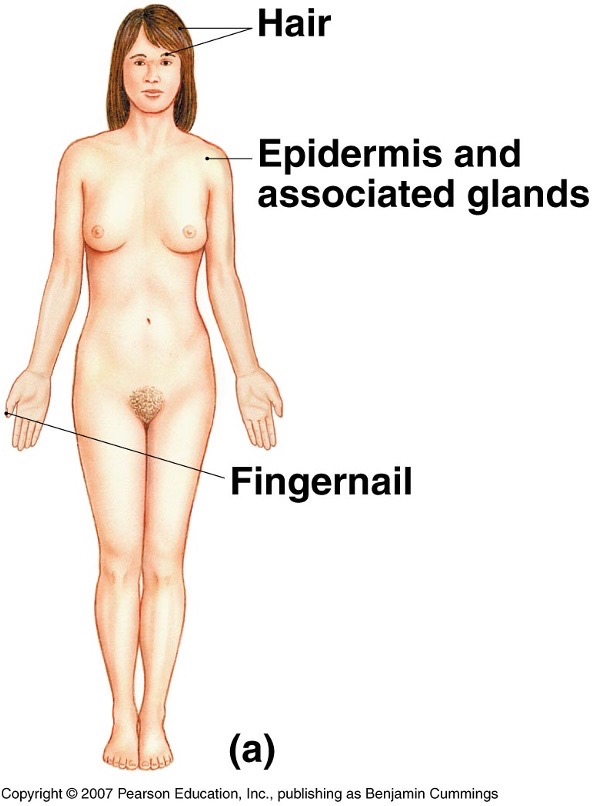
What does the skeletal system look like?
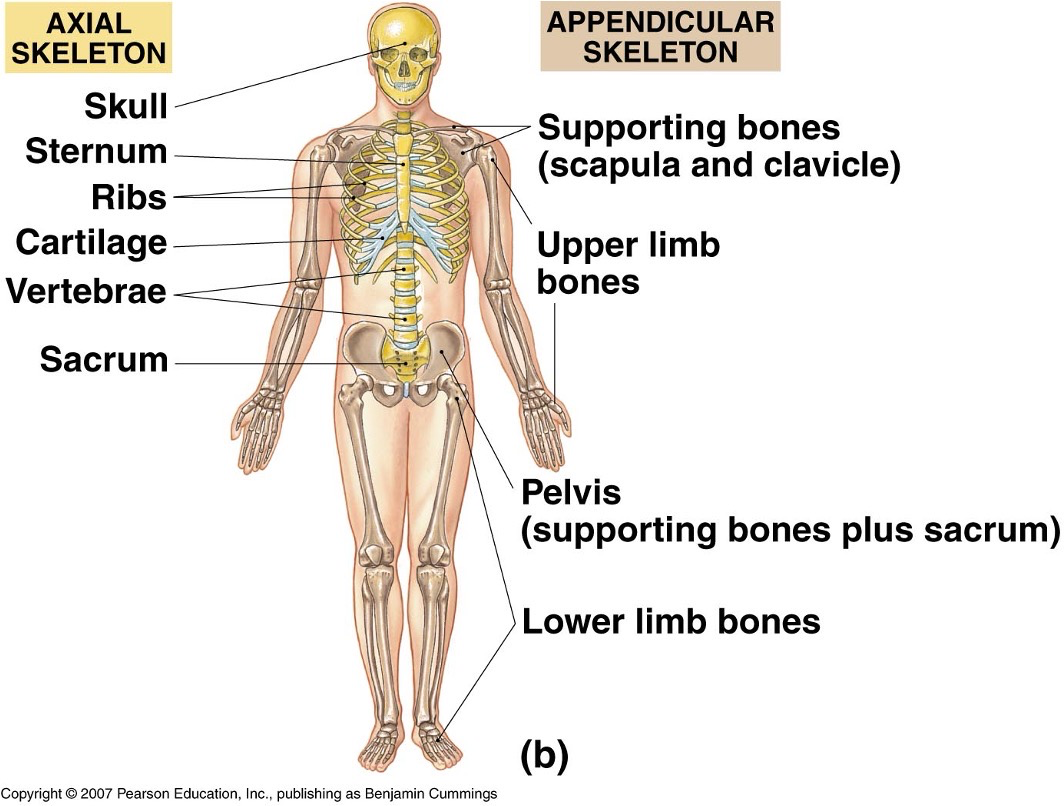
What does the muscular system look like?
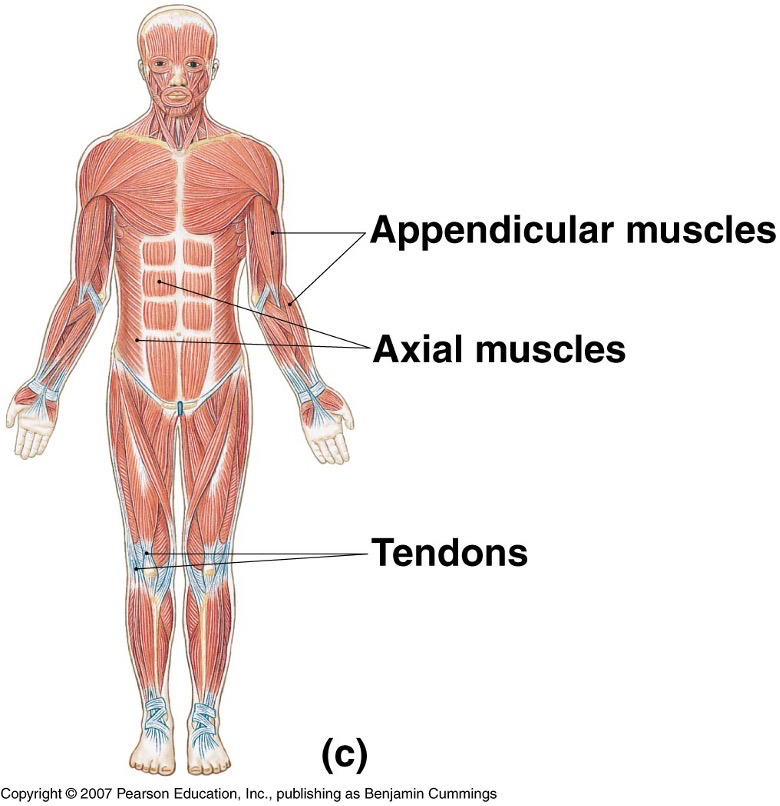
What does the nervous system look like?
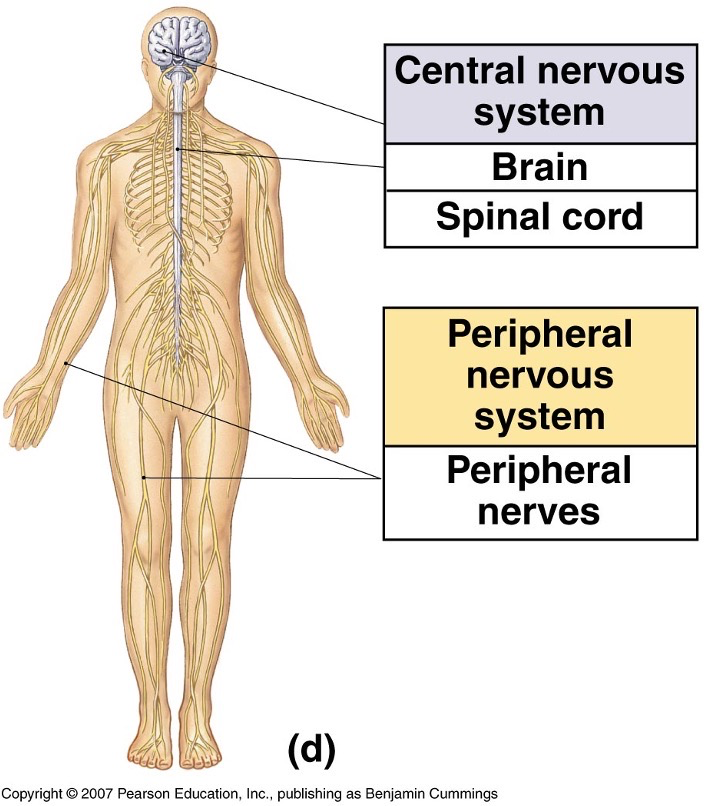
What does the endocrine system look like?
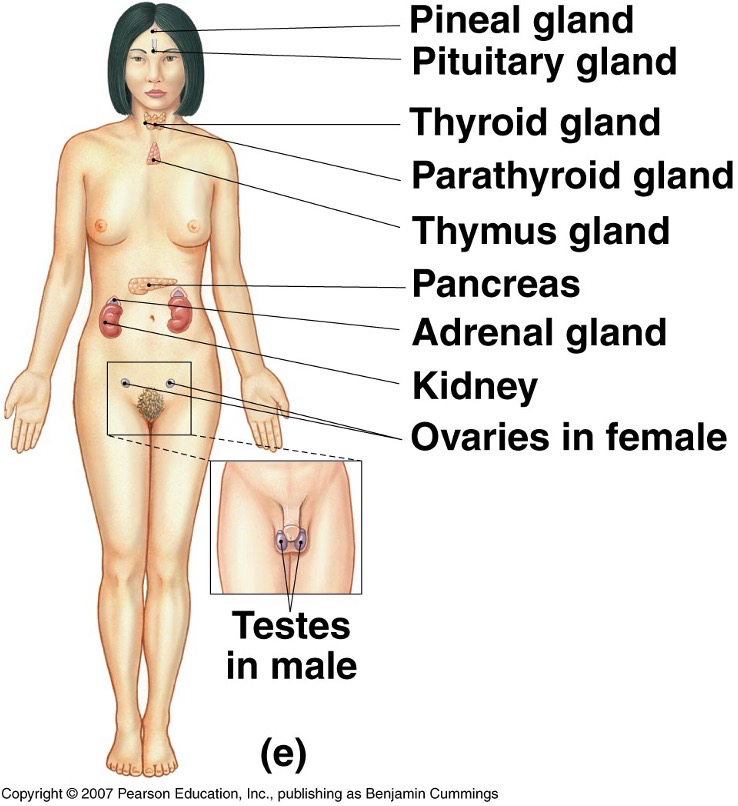
What does the cardiovascular system look like?
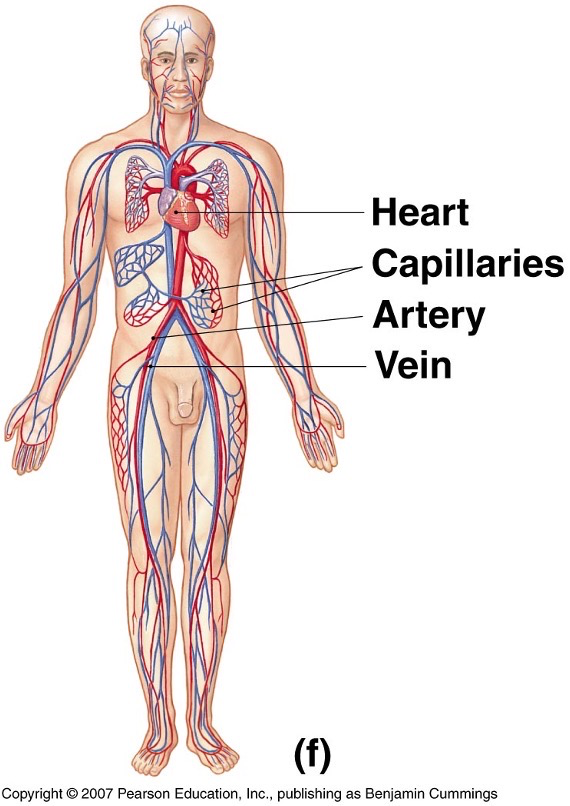
What does the lymphatic system look like?
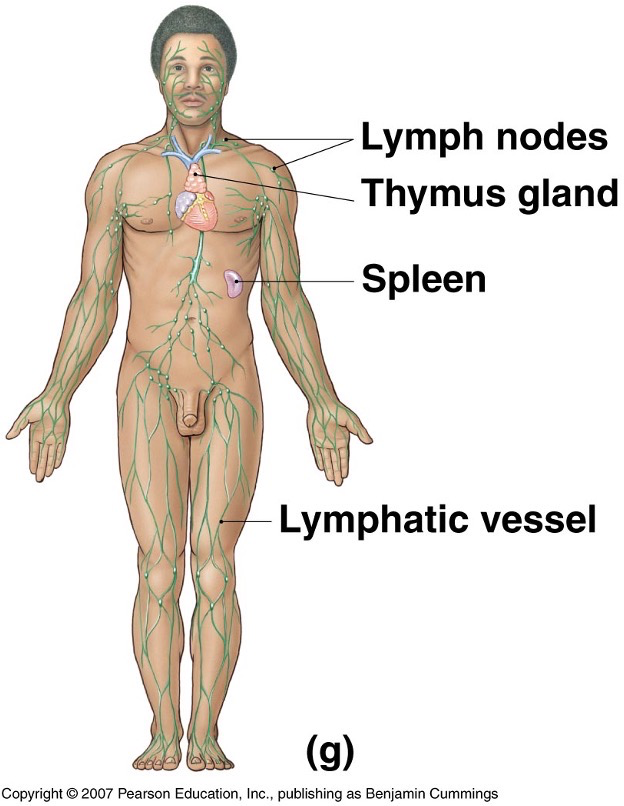
What does the respiratory system look like?
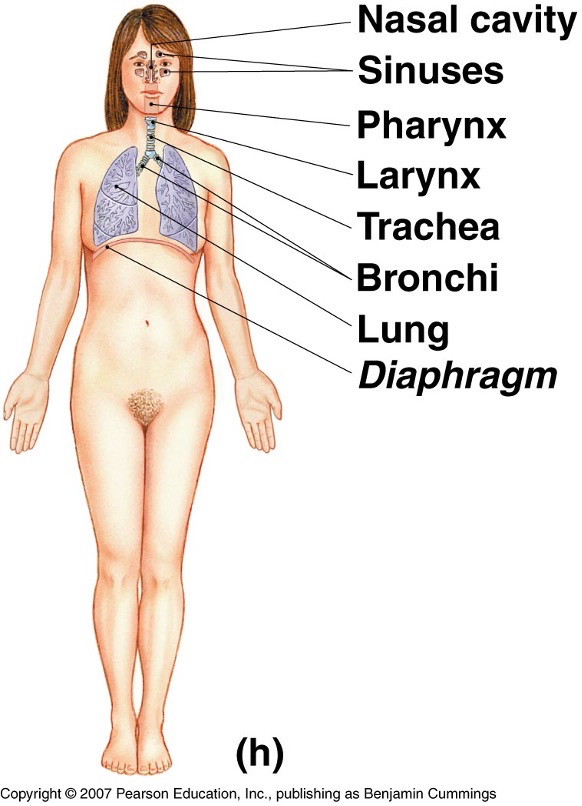
What does the digestive system look like?
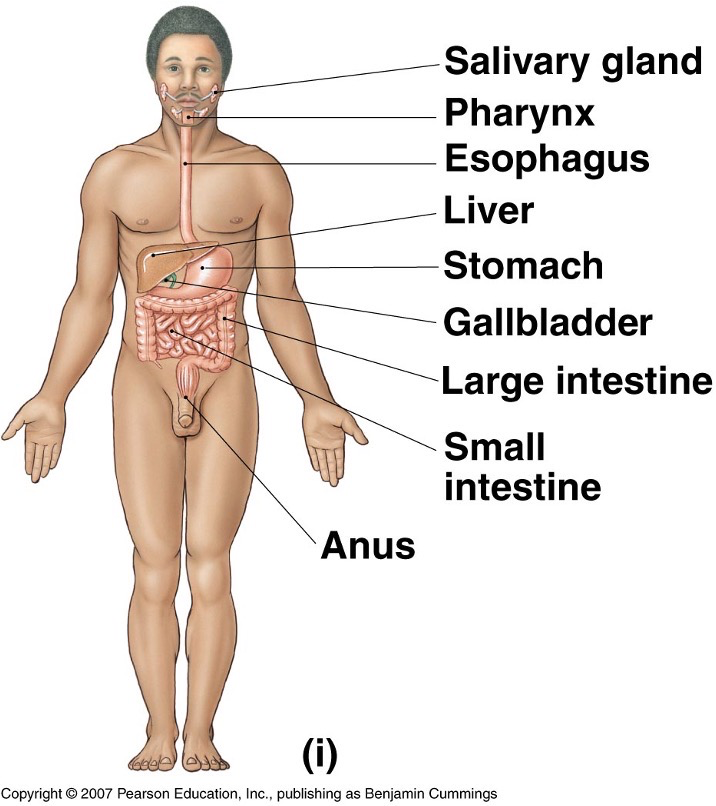
What does the urinary system look like?
What do the reproductive systems look like?
What is homeostasis?
The maintenance of a constant internal environment
What is negative feedback?
Opposes variations from normal. For example, thermoregulation (stimulus → receptor → control centre → effector → response)
What is positive feedback?
Exaggerates variations. For example, blood clotting