Kinesiology Notes and Vocab - The Respiratory System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Deliver oxygenated blood
Remove carbon dioxide
Acid-base balance
What are the three goals of the respiratory system?
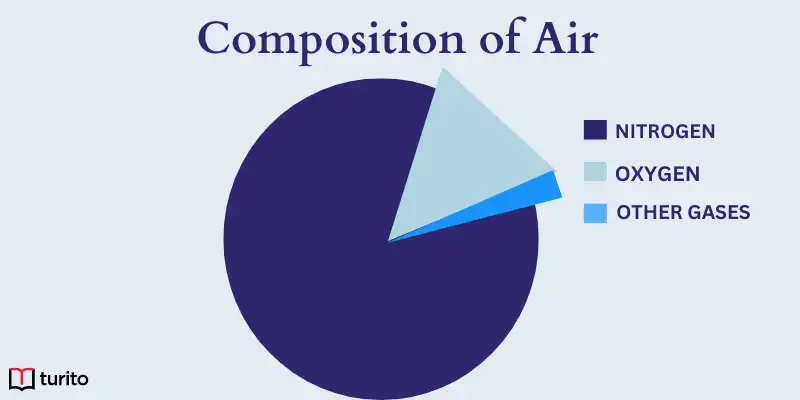
Co2 and other gas (1%)
Oxygen (21%)
78% nitrogen
What is air composed of?
Pleura
The layer that covers the lungs and also lines the thoracic cavity
Visceral Pleura
Lines the outer lungs
Parietal Pleura
Lines the thoracic cavity
Nose
Nasal cavity
Pharynx (throat)
Larynx (voicebox)
Epiglottis
What is the upper respiratory tract composed of?
Trachea (windpipe)
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Lungs
Diaphragm
What is the lower respiratory tract composed of?
Left: 2 lobes
Right: 3 lobes
How are the lungs divided?
Alveoli
Where does gas exchange occur?
exchange occurs between:
air and blood in the lungs
blood and the tissues
Diaphragm
Intercostals
Abdominal muscles
What are the major muscles used in breathing?
Diaphragm (contracts)
External intercostals
sternocleidnomastoid
Scalenes
What muscles are used for Inhalation?
diaphragm (relaxes)
Internal intercostals
Internal obliques
external obliques
Rectus abdomonis
What muscles are used in exhalation?
Nose, mouth
trachea
right and left bronchi
bronchioles, terminal bronchioles
What is the the conduction zone?
Alveoli
What is in the respiratory zone?
Ventilation
Gas exchange
Oxygen utilization
What are the phases in respiration?
Acid-base balance
When you have too much CO2 build up, it triggers your brain to send a signal that we need to breathe
Affected by altitude and temperature
Men: 13 cups
Women: 9 cups
How many cups of water should a man/woman have a day?
8oz/1 cup
Gas Diffusion
The movement of molecules from a higher concentration to a lower concentration
Asthma
Condition in which airings are inflamed, narrowed, and have increased mucus production
Symptoms are wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, increased mucus, chest tightness
Treated with maintenance meds, rescue meds, and steroids
Tested with SP02 (peripheral oxygen saturation) and Peak Flow
Pneumonia
A lung infection that causes the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs to fill with fluid or pus, making it difficult to breathe
Symptoms are cough, fever/chills, shortness of breath, chest pain
Treatment depends on type of pneumonia: Bacterial (ATBs), Viral (Leave alone), and Fungal (Anti-fungal meds)
Tested through x-rays and blood tests
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
A common lung disease that narrows the airways and damages the lungs, making it difficult to breathe
Combination of chronic bronchitis and emphysema
Tested by spirometry pulmonary function tests (PFT), x-rays, and clinical diagnosis
Symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, fatigue, blue lips/fingernails, losing weight without trying, swelling in feet, ankles, and legs
Treated through medications, inhalers, oxygen (not high levels), and respiratory therapy
Double Pneumonia
Affects both lungs
Aspiration Pneumonia
Caused by something that went into the lungs (fluid, food, etc.) through the trachea
Walking Pneumonia
Milder, low fever, and dry cough
through communities, hospitals, or ventilators
How can pneumonia be acquired?