Cranial Nerve VIII: Auditory
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the first thing to ask if a child comes in with delayed speech?
have they had a hearing test?
What is the auditory stimulus?
created by compression of air molecules - sound creates waves in the air molecules that have these characteristics
What are the parameters of the auditory stimulus?
pitch (frequency)
loudness (intensity)
timbre
location (orientation)
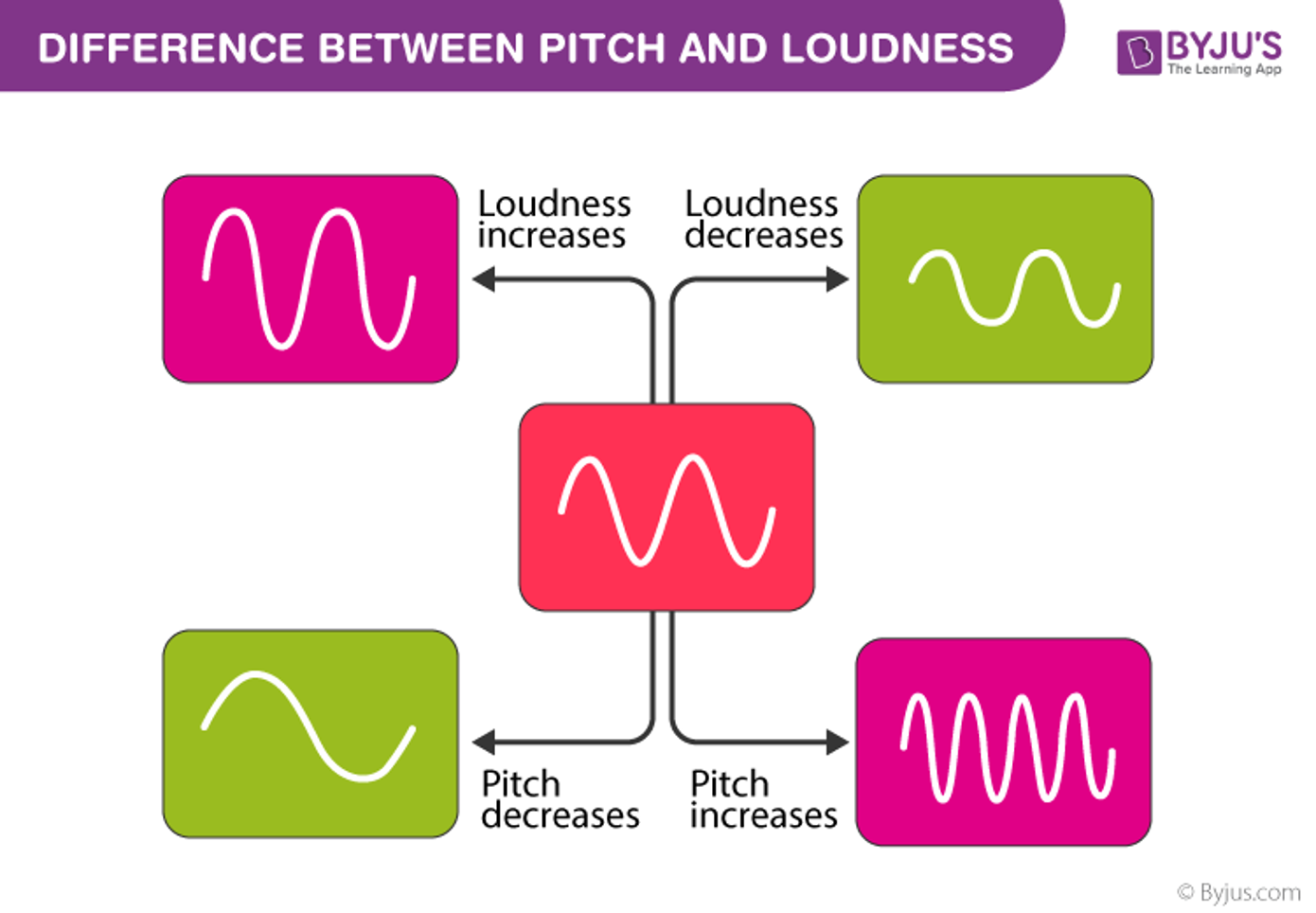
Characteristics of Pitch
measured in Hz
normal range is 20-20,000 Hz
less than 20 Hz called “infrasound” - elephants can hear
above 20,000 Hz called “ultrasound”
Characteristics of Loudness
measured in decibels
normal range is 0-130
prolonged exposure over 85-90 is damaging
Characteristics of Timbre
overtones
distinguish one sound from another at same frequency
a piano and hap both playing middle “c”
Characteristics of Location
want to know where the sound comes from
if an emergency vehicle is coming, you want to know where it is to pull over
As amplitude gets smaller…
the loudness decreases and vice versa
What makes hearing challenging?
transmission of sound waves through air YET they have to transmit accurately through fluid
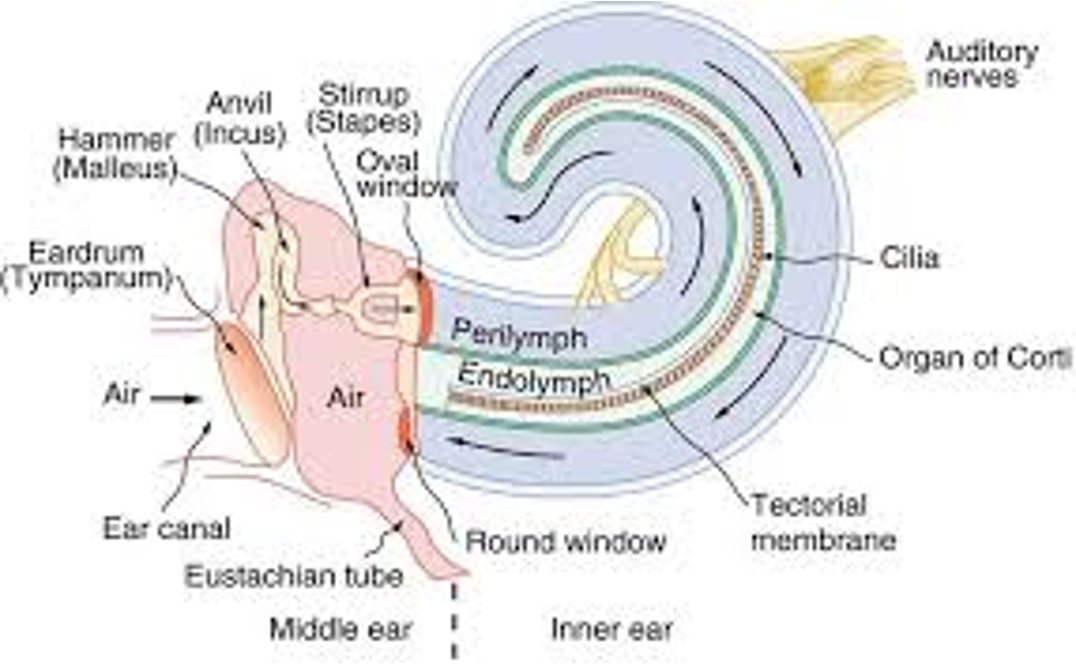
Outer Ear Characteristics
from pinna of ear to outer membrane
main purpose: localization and directing sound to the ear
protected from debris by hair and earwax
What is earwax called?
cerumen
Middle Ear Characteristics
chamber that is filled with the bones
continuous pathway from middle ear to Eustachian tube into the pharynx to equalize pressure
part that looks like a snail is hearing system
Inner Ear Characteristics
where the neural ear is - sensory receptor and all the action in terms of changing stimulus into electrical signal
sound waves are compressing air and move into outer ear
press on eardrum - tympanic membrane
Cochlea characteristics
about the size of a pea
like a straw wrapped around tip of pencil
pencil tip - modals (bony framework)
straw - membranous apparatus filled with fluid
What is in the modialis?
contains neurons in spiral ganglion (neurons of CN VIII) - around bony framework that contains bipolar sensory cells
What are the layers of the membranous apparatus?
perilymph - outside of membranous apparatus
endolymph - inside
sensory receptor for hearing - organ of corti
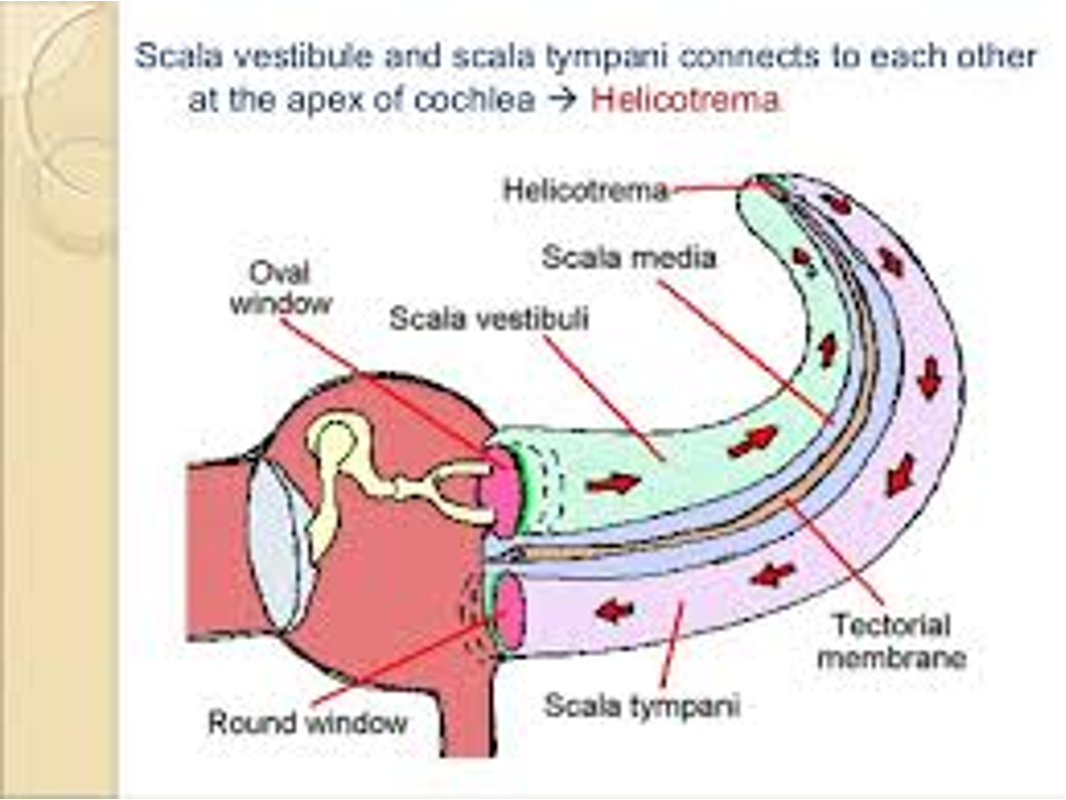
What is helicotrema?
scale vestibule and scala tympani connects to each other at the apex of cochlea
What are the inner hair cells responsible for?
deflecting the stimulus - fires CN VIII and heads into brain for coding
What are the outer hair cells responsible for?
amplifying stimulus by changing flexibility in the system
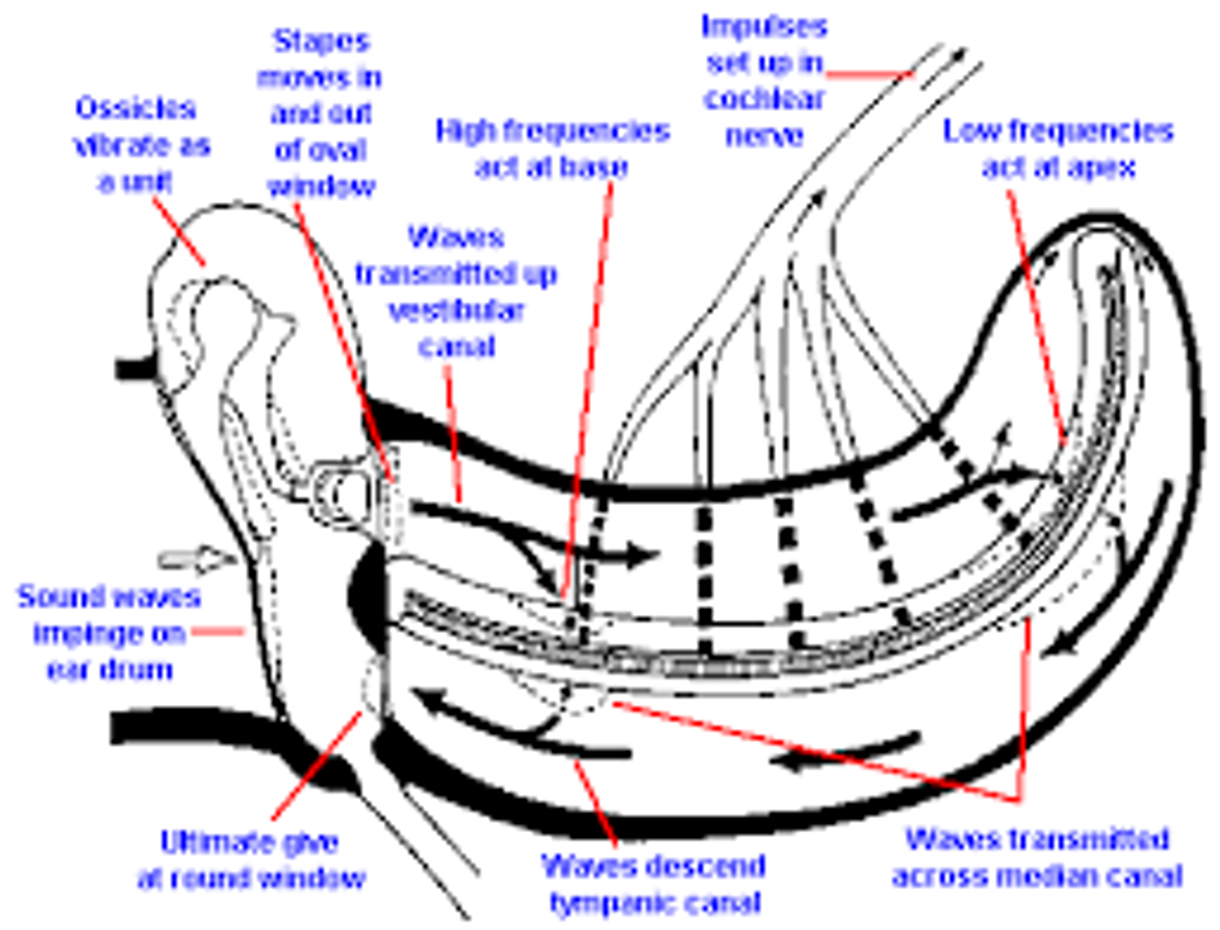
What is tonotopic representation?
regions of the basilar membrane respond differently to different frequencies or tones
high frequencies - at the base
low frequencies - at the apex
What are the ventral and dorsal cochlear nuclei critical to?
SOUND LOCALIZATION - has to do with communication between the two sides
peripheral hearing is…
BILATERALLY REPRESENTED IN THE BRAIN!!!
What is the clinical implication of peripheral hearing being bilaterally represented?
unilateral brain CNS lesion does NOT cause hearing loss
If someone has hearing loss, where is the problem likely?
middle or inner ear, NOT brain
do NOT hear person had a stroke and lost hearing in contralateral ear
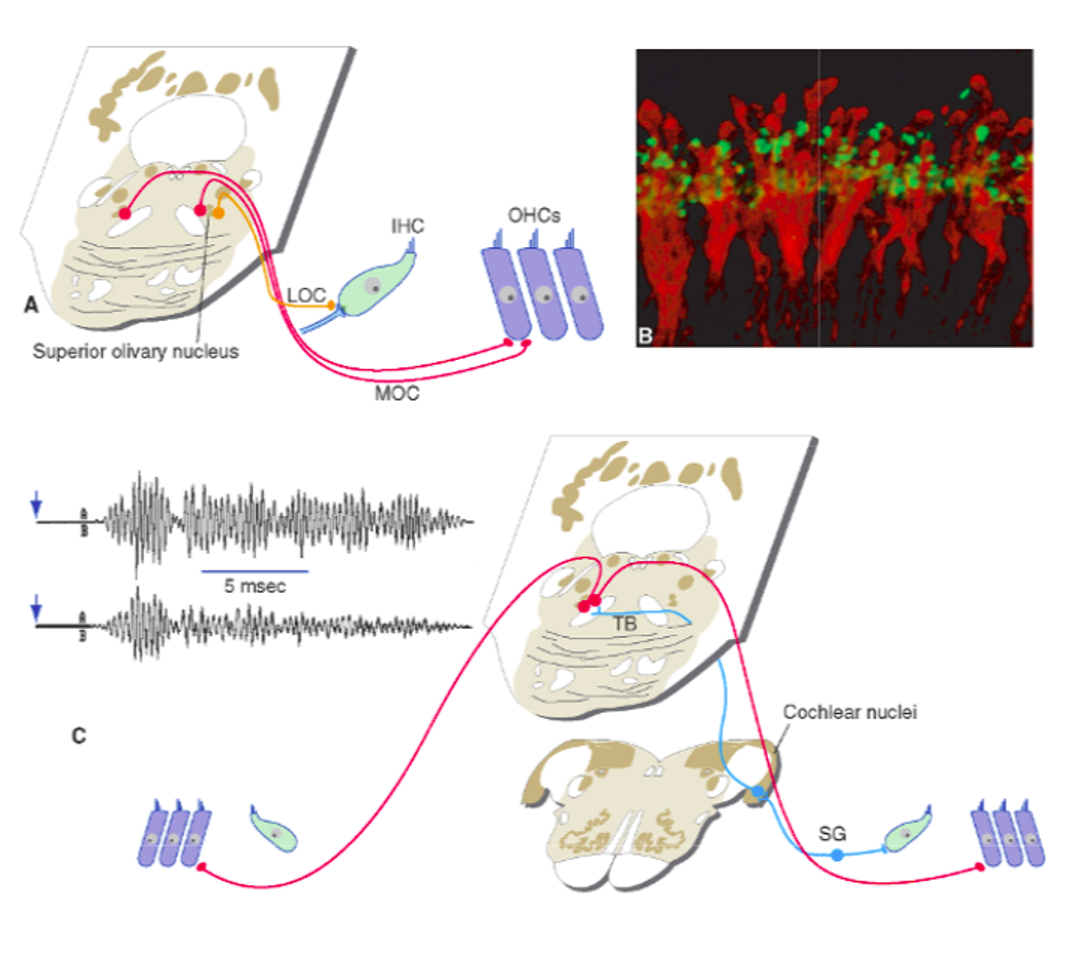
Where does everything eventually join?
in an ascending fiber bundle - lateral lemniscus
What is the primary termination site?
transverse temporal gyri of temporal lobe
What does a typanogram do?
give information about prescence of fluid in the middle ear, mobility of middle ear system - fluid built up when there is infection
What is the most common hearing testing done?
otoacoustic emission testing/newborn screening
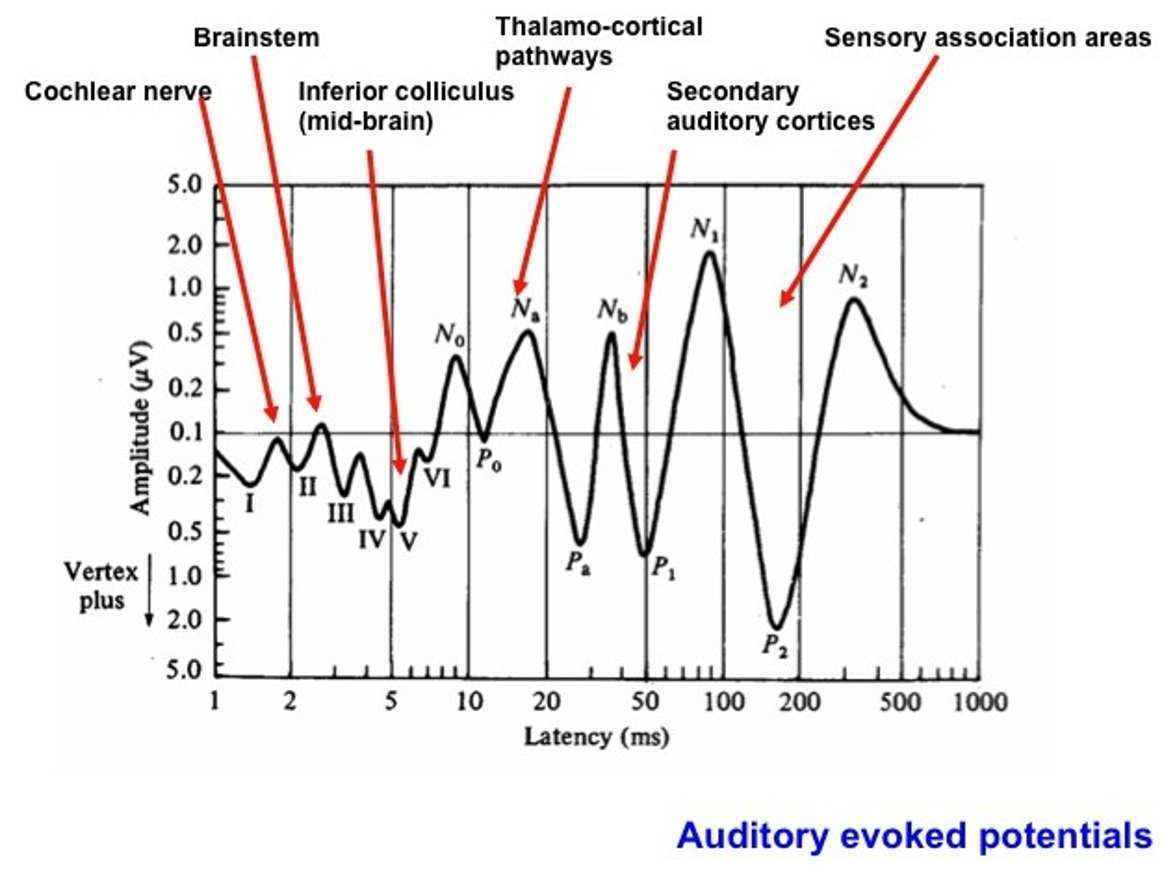
What is the gold standard for hearing testing?
auditory evoked response testing
What is conductive hearing loss?
hearing problem in EXTERNAL or MIDDLE ear
if BONE conduction is impaired
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
hearing problem in INNER ear
if AIR conduction is impaired