ne202 exam 3
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
3 components of emotions
behavior
physiology
feeling
all interact to create EMOTION and have different neural substrates
Facial Expressions & Emotion, including 7 cross-cultural common facial expressions
Facial expressions are thought to have evolved as non-vocal communication
Adaptive advantage
Infant/Caregiver interaction
Long-term cooperative interaction
Speech
Competitive interaction
7 “universal“ facial expressions
anger
contempt
disgust
enjoyment
fear
sadness
surprise
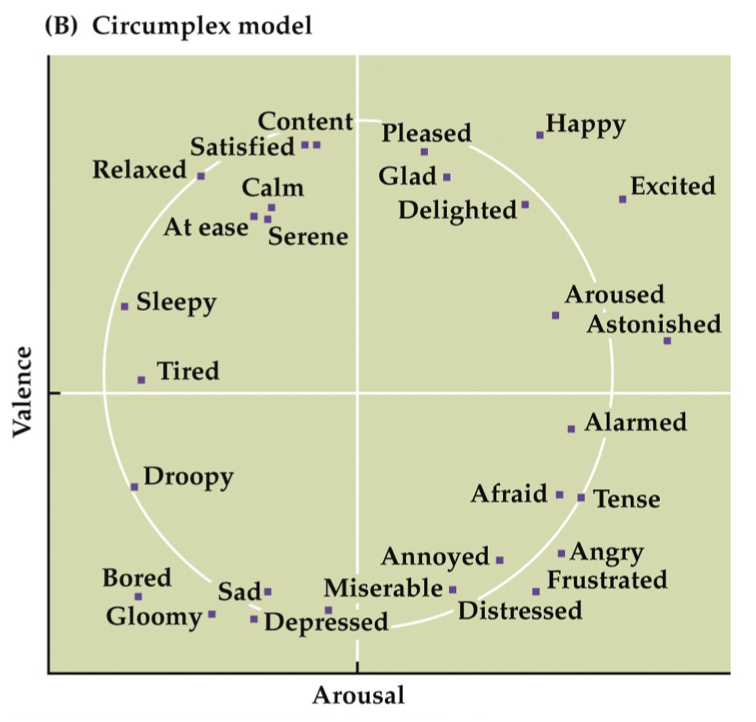
2 dimensional theories of emotion: Vector & Circumplex Models
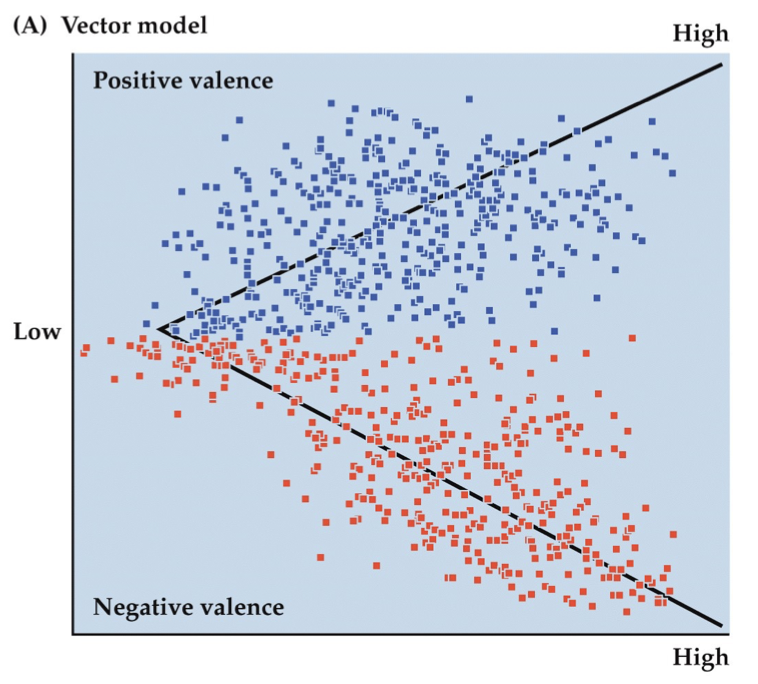
Vector model
describes emotions by 2 components:
Valence
positive or negative emotion
Arousal
strength of an emotion
self-report but also physiology
Circumplex model
also has Valence and Arousal
DIFFERENCE: mapped to a circle, approximately
more suggestive of a continuum of emotional states
think: top left is Pooh bear, top right is Tigger, bottom left is Eeyore, bottom right is i forgot the name but stressed-out yellow rabbit
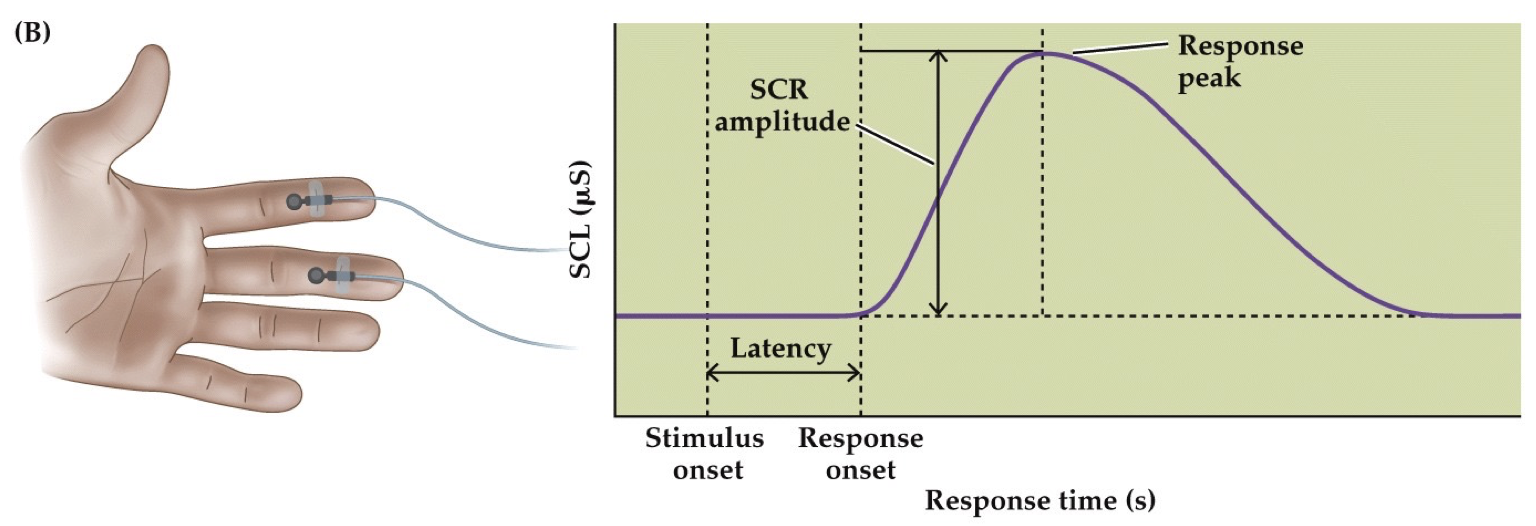
Skin Conductance Response (psychophysiology)
Activity of sweat glands during emotional arousal
Increases electrical conduction of skin surface
Widely used in Polygraph Tests
has SLOW signal; better for measuring Arousal than Valence
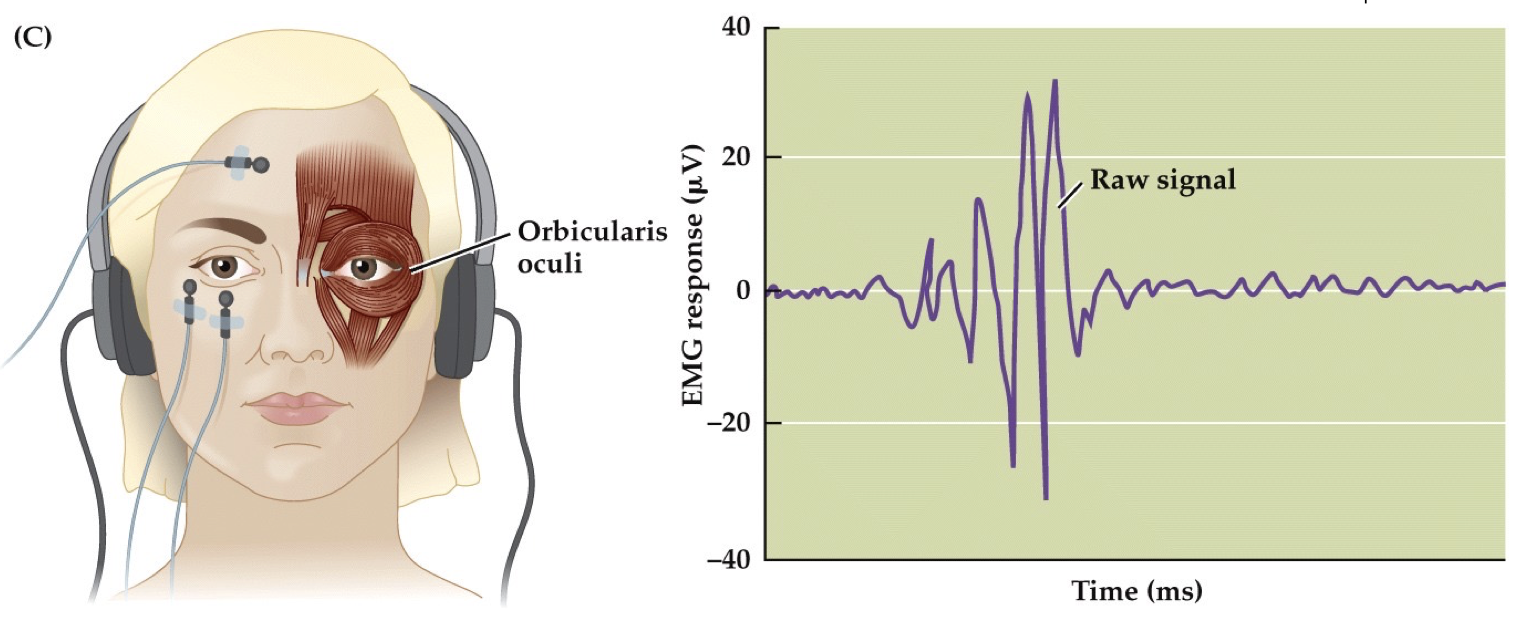
Startle Response (psychophysiology)
EMG measurements of eye muscles
Measures Musculo-Skeletal Reflex
has FAST, brief signal; better for measuring Valence than Arousal
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) → Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic divisions
ANS
Hypothalamus = key controlling structure of ANS
Influences functioning of internal organs
Largely unconscious
Sympathetic = fight or flight
Parasympathetic = rest and digest
Periaqueductal gray (PAG)
located in tegmentum of midbrain
plays key role in autonomic function and responses to threats
coordinates emotions in animals; also pain modulation
Key brain structures for Emotion, Motivation, and Cognition
amygdala = learning and fear, involved in recognition of facial expressions esp. fear
cingulate cortex = rationale
cortical areas like OFC = rationale too
vmPFC
hippocampus, subiculum and entorhinal cortex = learning and memory
hypothalamus = homeostasis and drive
thalamic nuclei = sensory relay
nucleus accumbens = reward and drive
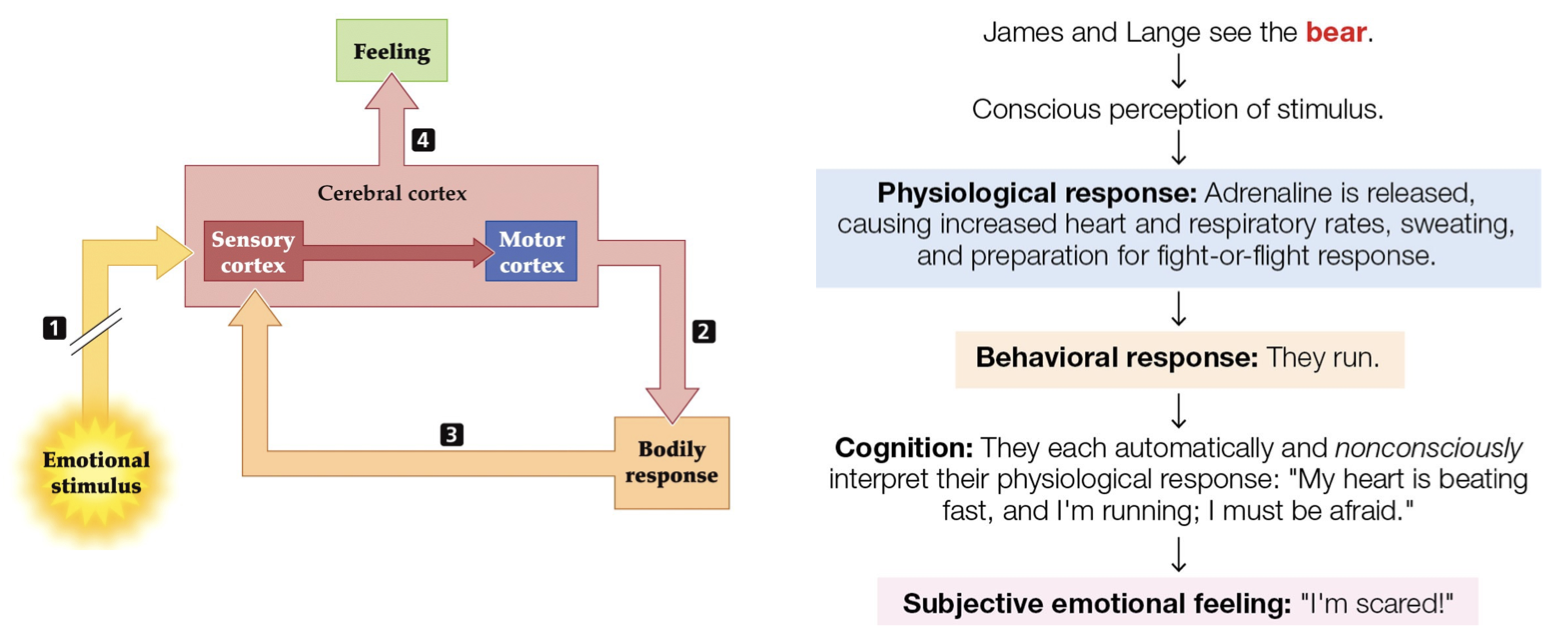
James-Lange Theory of Emotion
feedback loop
states physiological response drives emotional response
William James and Carl Lange (19th century) argued that the autonomic response = emotion itself
BUT, “Somatic theories” lost favor because…
Perceive fear before the symptoms occur
Generating response does not generate emotion
Cognitive appraisal of the situation is key to emotion
External response can be the same for different emotions
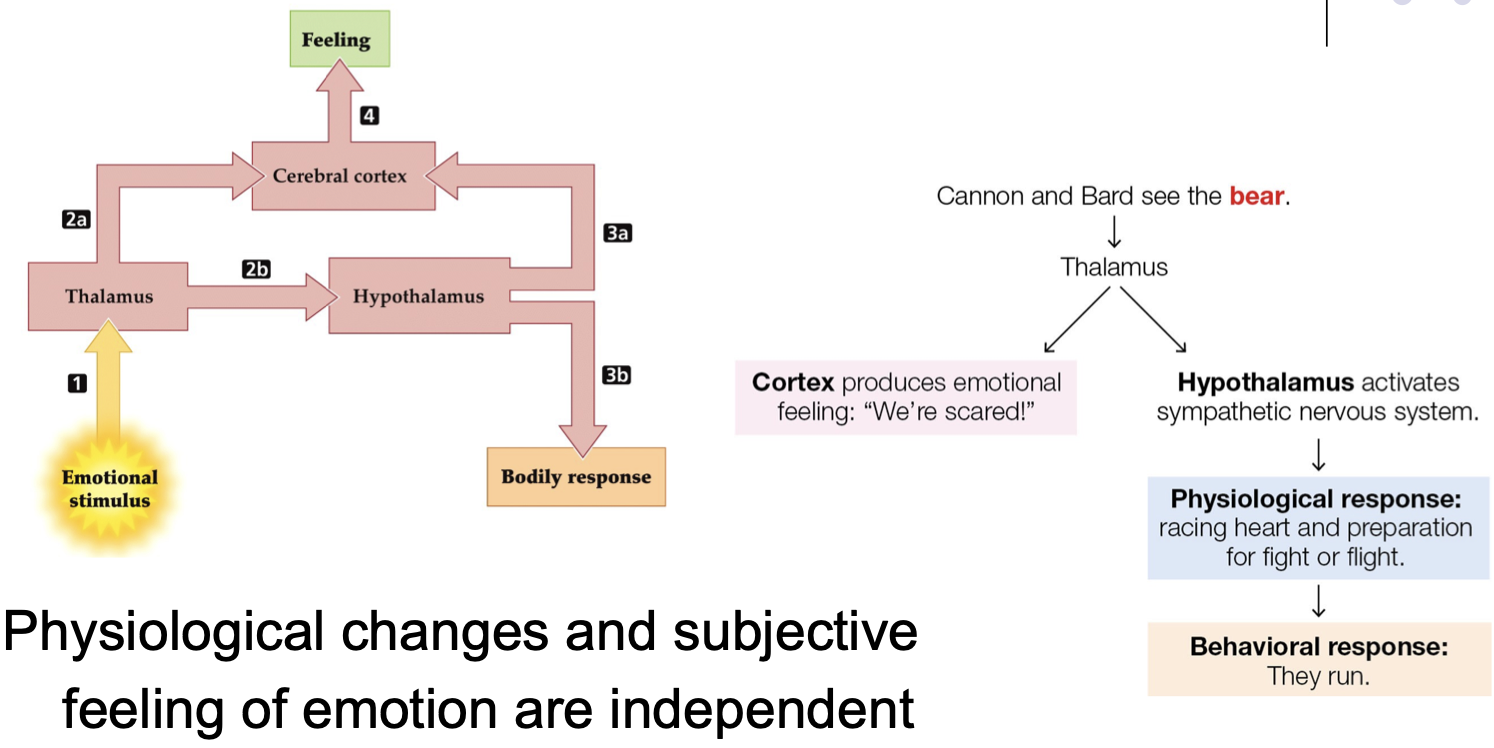
Cannon-Bard Diencephalon theory & sham rage
Cannon-Bard Diencephalon theory
physiological changes and subjective feeling of emotion are INDEPENDENT
emotional expression results from hypothalamus
emotional feeling results from thalamus and cortex
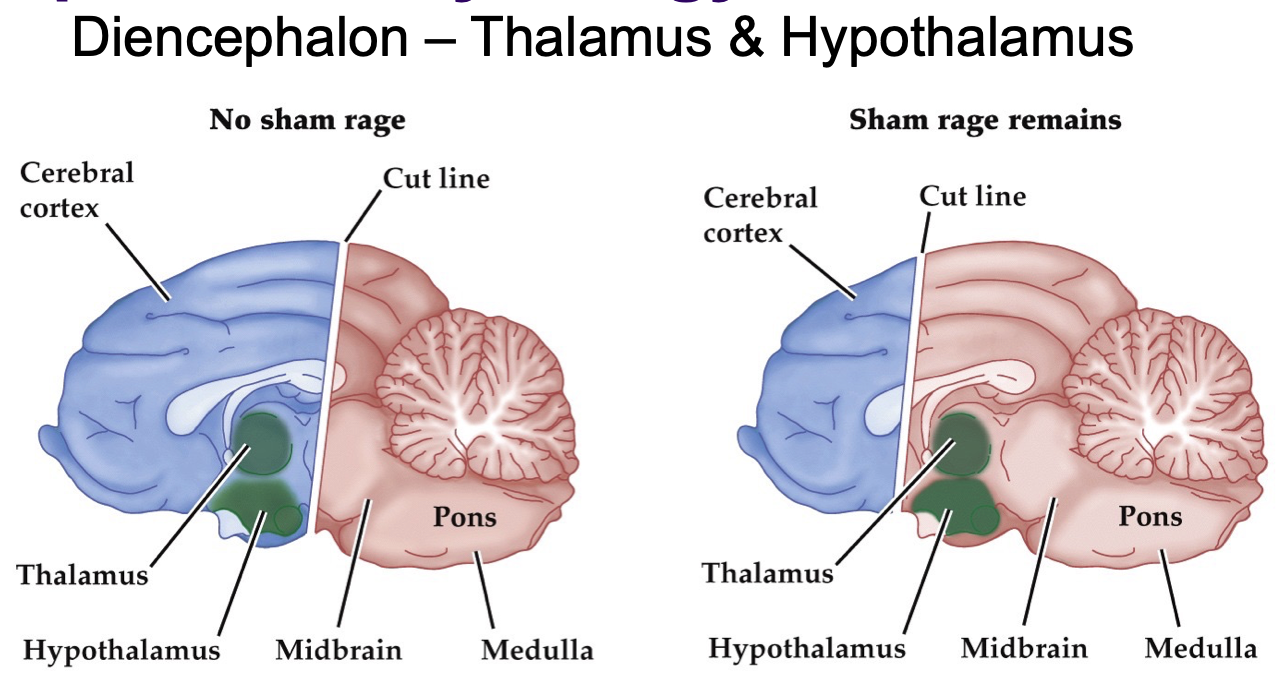
sham rage
= violent movements induced by removal of cerebral cortex; no experience of rage
cutting at level of Diencephalon abolishes fear/anger; stimulating Hypothalamus elicits fear/anger response
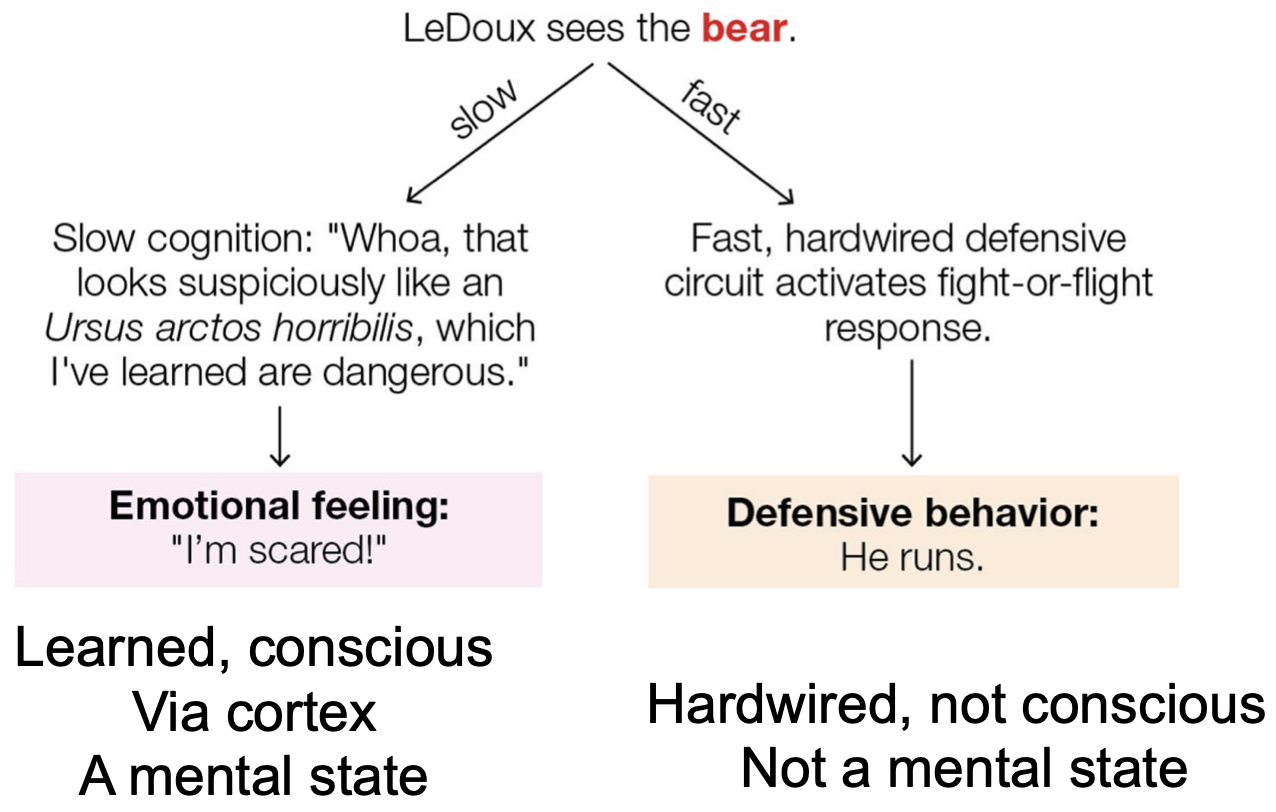
LeDoux Model
high road…
slow cognition → emotional feeling
learned, conscious via cortex
a mental state
…and low road model
fast cognition → activates flight or fight response
hardwired, unconscious, defensive circuit
NOT a mental state
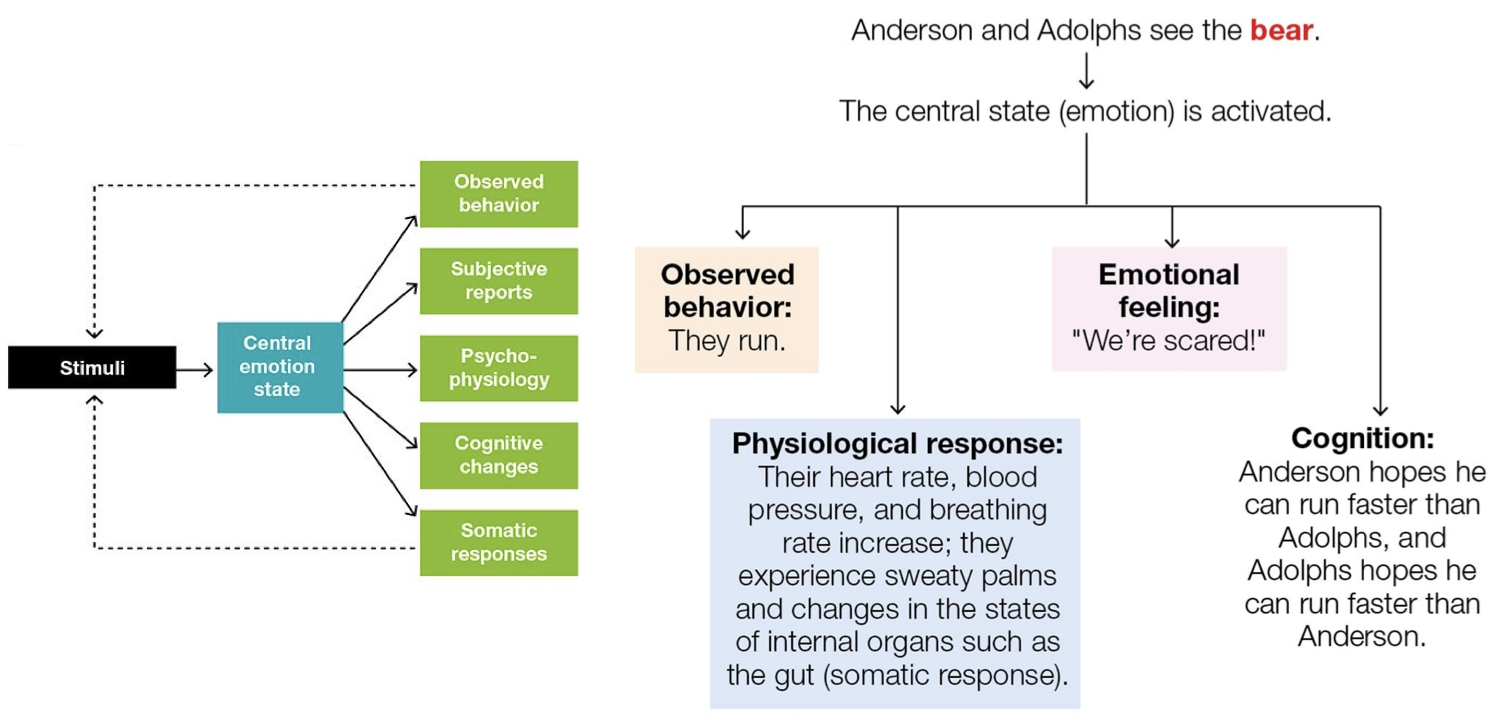
Anderson & Adolphs Model
perceive stimuli → activates Central emotion state → all at once: observed behavior, physiological response, emotional feeling, cognition
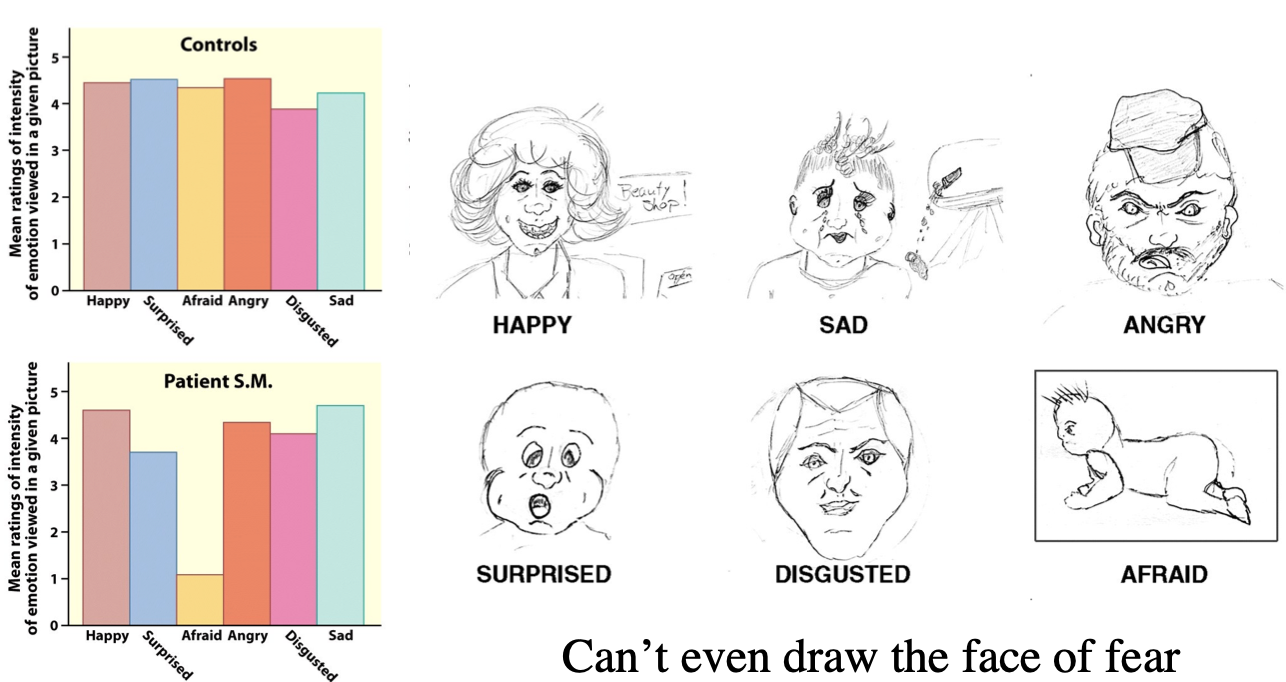
Patient S.M. “The Woman with No Fear“
had rare genetic disorder: Urbach-Wiethe Disease
Bilateral Amygdala destruction
impaired in recognizing negative social cues
couldn’t draw the face of fear
PTSD and Extinction (of conditioning)
PTSD patients are impaired at Extinction
even when stimulus no longer predicts a shock, STILL yields a response…
in skin, amygdala, and vmPFC
People w/ smaller hippocampus have less protection, more vulnerable to PTSD
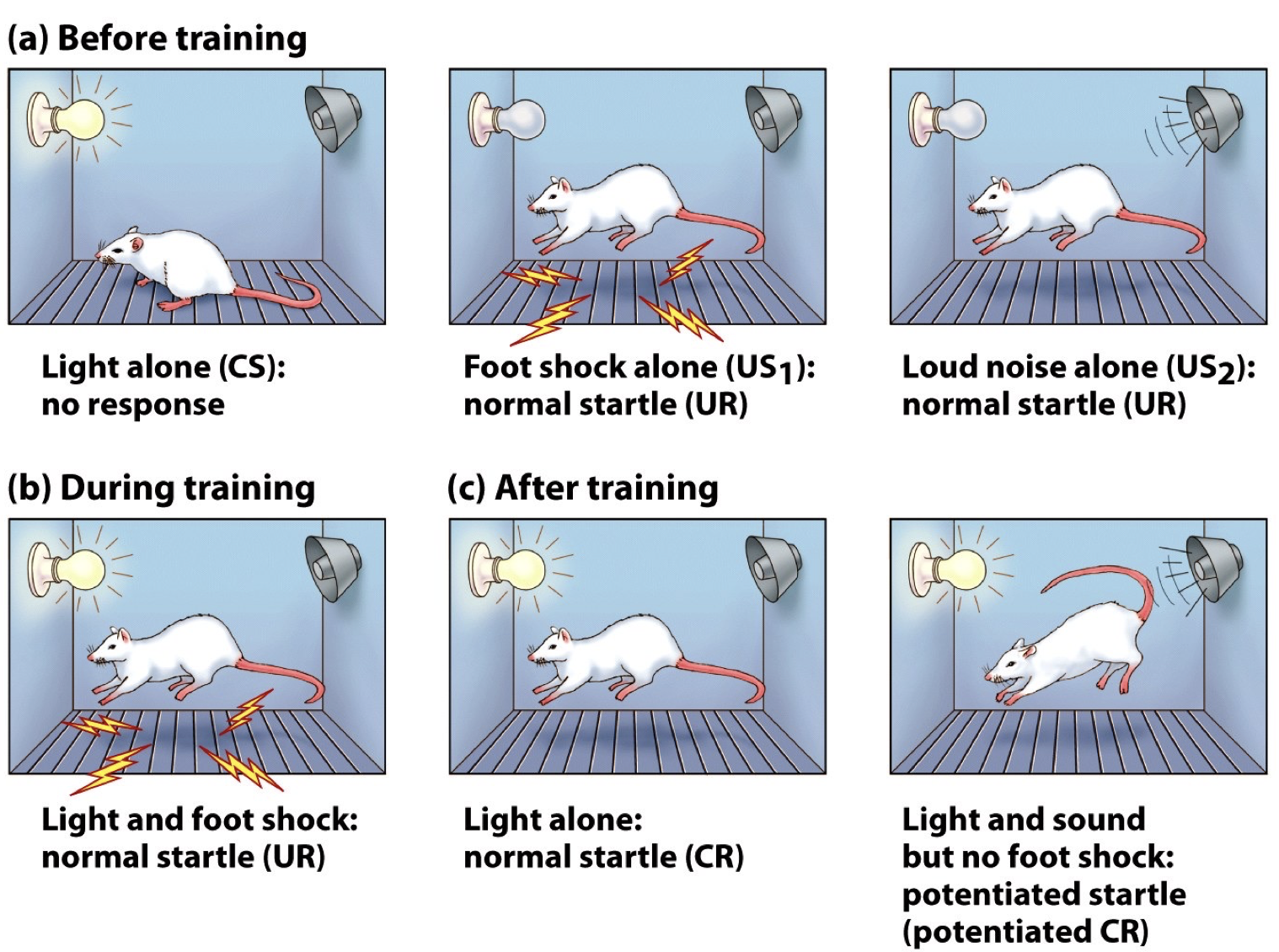
Fear conditioning paradigm
fear conditioning = a primary paradigm used to investigate the amygdala’s role in emotional learning
a form of classical conditioning in which the unconditioned stimulus is aversive
main idea: fear conditioning depends on Amygdala
Extinction (of conditioning)
disappearance of previously learned behavior when the behavior’s NOT reinforced
involves amygdala UNlearning AND ventral medial PFC (vmPFC) learning
but NOT SO SIMPLE because after initial extinction & passage of time, condition responses may return
vmPFC activation level is linked to the expression of conditioned responses (CR) during retention of extinction
damage to vmPFC impairs retention/recall of extinction in rats
Human brain regions related to Extinction
Amygdala is central for fear responses
vmPFC suppresses fear responses
hippocampus
context-dependent recovery of fear conditioning after extinction
Conditioned and unconditioned responses
unconditioned response (UR) = natural/automatic response to stimuli (US)
Conditioned response (CR) = anticipatory response learned from conditioned stimuli (CS)
Amygdala role in fear and emotion
Amygdala is known to mainly control the emotion of fear; important for detecting and avoiding danger
Flashbulb memories
flashbulb memory = very vivid, detailed EPISODIC memory of powerful event, can be an event in the public memory or personal to you (family tragedy, etc.)
examples: 9/11 terrorist attack, Boston Marathon bombing
more likely to occur when
important, surprising, and has EMOTIONAL impact
evidence that emotional content is important for memory
COULD BE INACCURATE from repeated retrieval and re-encoding
Medial Temporal Lobe (MTL) role in emotion & memory
MTL crucial to episodic memory
if bilateral damage to the MTL, unable to remember specific past episodes or to learn new ones, but implicit memory may be spared
(MTL) contains several structures related to important cognitive and emotional functions
hippocampus and its adjacent parahippocampal cortex, entorhinal cortex, and perirhinal cortex are primary regions responsible for memory formation and spatial cognition
Chomsky’s views on Language
language is standard equipment for humans
full-blown language is unique to people
Language and mental grammar exists independent of any cultural construct
Language is universal
every tribe of people has complex language, so there’s no grammatically primitive tribes
Mental grammar
brain must contain program that can build an unlimited set of sentences out of a finite list of words
Virtually every sentence that a person utters or understands is a brand new combination of words. Language cannot be a repertoire of responses
innate, universal grammar
Children develop complex grammars rapidly and
without any formal instruction, so they must be innately equipped with a plan common to the grammars of all languages
^ means language is a genetically determined brain module
Language acquisition stages
cooing = all possible phones (distinct speech sound) are produced and discriminated
babbling = distinct phonemes of primary language
1-word utterances
2-word utterances; telegraphic speech
speech during the two-word stage of language acquisition in children, which is laconic and efficient
ex: “ball up,“ “more doll,“ “shoe wet“
basic adult sentence structure
around age 4
similar progression for speech perception
from day 1, infants appear programmed to tune into their linguistic environments with goal of learning language
Wug study
asks: Do children understand the rules of grammar? Or have they just learned associations?
Children know the rule for generating plural nouns
Similar results with verb past tense, etc
involves children 4-7 years old who are shown a new (novel), weird animal
“This is a Wug” (novel word)
then shown two of the animal → “There are two Wugs!”
Critical Periods in Language Acquisition
language is innate, but difficult to learn a 2nd one in adulthood
Critical Periods:
time windows of rapid development
a particular ability must develop within time window or it’ll never be adequately developed
even decades of adult experience usually fails to overcome a missed critical period window
FOXP2 gene - role in language
Missing one copy is linked to developmental
verbal dyspraxia (motor speech disorder, know what you want to say but have problems with articulation)
Identified from KE family
~50% of extended family has severe forms of Specific Language Impairment
Fine motor control deficits for lower half of face
Speech is difficult
Morphology & Verbal/Cognitive Deficits
FOXP2 and Procedural vocal learning
FOXP2 supports Procedural vocal learning
FOXP2 expressed in Striatum of Basal Ganglia
knockdown of this gene in BG of songbirds disrupts song learning
substitution of human FPXP2 in mice increases dendrite length and synaptic plasticity in dl-Striatum AND faster procedural learning
Language-genesis: Pidgin vs. Creole
Pidgin
develops when mixing peoples who don’t share a common language
A makeshift jargon; not a real language
Very little grammar, highly variable in order
Pidgin can be transmuted into a full complex language in one fell swoop. A single generation
IF a group of children is exposed to pidgin at the age when they acquire their mother tongue
Creole
The language that results when children make pidgin their native tongue
in other words, it’s a mother tongue formed from the contact of two languages through an earlier pidgin stage (aka simplifying and mixing into a new form)
ex: Hawaiian Creole (China, Japan, Korea, Portugal, Phillipines, and Puerto Rico), Portuguese-based Creole
Sign language
sign languages like American Sign Language (ASL) and British SL are true languages
complex grammar, abstract symbols
deaf children who aren’t exposed to SL at an early age never master to the degree they would’ve with early exposure
Nicaraguan Sign Language (ISN: Idioma de Señas de Nicaragua) = a form of SL developed by deaf children in many schools in Nicaragua in the 1980s
Fluency vs. comprehension
Fluency = ability to easily speak or write with normal prosody and grammar
lesions: insula, arcuate fasciculus
Comprehension = ability to understand
spoken/written language
lesions: middle temporal gyrus, dorsolateral PFC
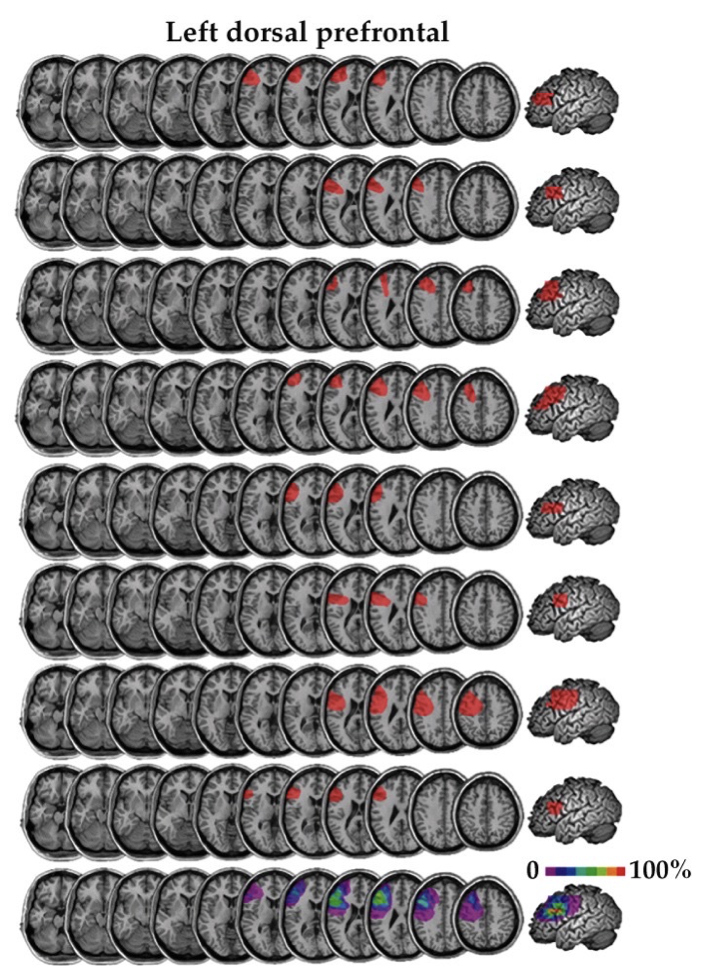
Voxel-based lesion symptom mapping (VLSM)
identifies key brain regions underlying neuropsychological deficit
combines:
structural images of brain lesions
neuropsych tests to categorically diagnose
result: percentage of voxels showing damage in patient group
can be used to show fluency/comprehension deficits and lesions
primary lesions detected are near, but not in Broca’s and Wenicke’s Areas aka VLSM got the location wrong
Structural vs. Metabolic deficits
a lesion in one location might impair processing at other locations
CT and structural MRI not enough to know extent of processing damage
often function will return in reduced metabolism region without lesion
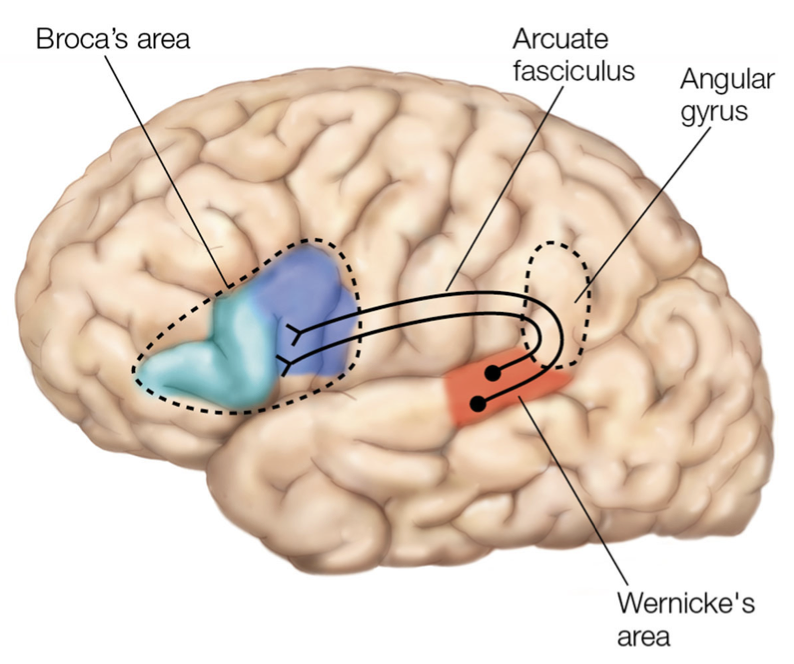
Broca’s, Wernicke’s Aphasias and related brain structures
Broca’s Aphasia
non-fluent aphasia
speech PRODUCTION problem → patients know what they want to say, but can’t articulate it
common symptoms:
word finding difficulties (anomia)
agrammatism (production and perception)
speech apraxia (saying words accurately, smoothly)
related brain structures:
left interior frontal gryus
pars opercularis (BA44), pars triangularis (BA45)
Wernicke’s Aphasia
fluent aphasia
speech COMPREHENSION problem → core deficit comes from not finding the right relationship between words and their meanings (lexical-semantic = study of word meanings)
common symptoms:
related brain structures:
posterior superior temporal gyrus (STG) (generally involves large temporal lobe lesions)
part of BA22
planum temporale
much larger on Left Hemisphere
Broca’s aphasia with recurring utterances
Broca’s most famous patient, Leborgne, called “Patient Tan“ due to his recurring utterance “tan tan“
insula = responsible for speech production → recurring utterances
Signing Aphasias
left hemisphere damage:
frontal - expressive aphasia
temporal - receptive aphasia
Fluency Deficits & Lesions
fluency = production
expressive encoding and production of language output
lesions:
insula
arcuate fasciculus
Comprehension Deficits and Lesions
comprehension = perception
receptive comprehension and decoding of language input
lesions:
middle temporal gyrus
dorsolateral pre-frontal cortex
Hemispheric Dominance in Language
language dominance in Left Hemisphere for about 97% of people
RH can still process language, but mute, little grammar, little awareness
Speech Segmentation Challenges
easily observed for non-native languages
problems:
how to determine where one phoneme ends and the next begins?
silence is not reliable indicator for word breaks
phonemes change depending on:
speaker
context in words
Coarticulation
normal speech uses coarticlation
without this, speech sounds weird/artificial
phoneme differs with context
ex: lip vs. put, ten vs. tenth
phonemes are produced in a way that overlaps in time
speakers shape vocal tracts to produce end of one phoneme and start of the next
auditory spectrum of spoken phonemes depends on context of neighboring phonemes
no coarticulation = explains why computer speech sounds funny
means each phoneme (or morpheme nowadays) presented independently
same issues for speech recognition → must break up words
Neural substrates of speech phonology processing
phonology = sounds of speech
Phonological processing is the use of the sounds of one's language (i.e., phonemes) to process spoken and written language
phonology-specific processing along Superior Temporal Sulcus (RH and LH)
NOT Wernicke’s, which is posterior of STG
words > non-words: LH middle Temporal Gyrus, Angular gyrus, and Temporal Pole
McGurk Effect
Visual signals combine with Auditory Signals to produce speech perception
McGurk & MacDonald ‘76:
dubbed audio onto a video
“bah“ “kah” “gah” “pah”
visual signal (aka different mouth movements) determined speech perception
Visual & Auditory can combine to yield speech percepts that match either one!
“speech perception is an illusion”
3 language ERPs: N400, LAN, P600
none of these ERP signals is specific to language
N400 = ERP signal for semantic anomalies (aka semantic errors)
perception of anomalous (deviating from expected/normal) words yields a negative response 400ms after words beings
central, parietal sites
semantic rather than grammar effect
observed for both spoken and written words
Left Anterior Negativity (LAN) = ERP response to syntactic violations (aka syntax errors = wrong part of speech)
LAN also can occur rapidly (100-300ms)
for phase structure violations (like “the cat is the in bag“)
Synaptic Positive Shift (P600) = ERP response for syntactic anomalies (syntactic agreement or garden-path sentence errors)
detected at parietal recording sites
possibly posterior temporal lobe (posterior to Wernicke’s areas)
agreement errors = number of subject and verb: he swim; she eat
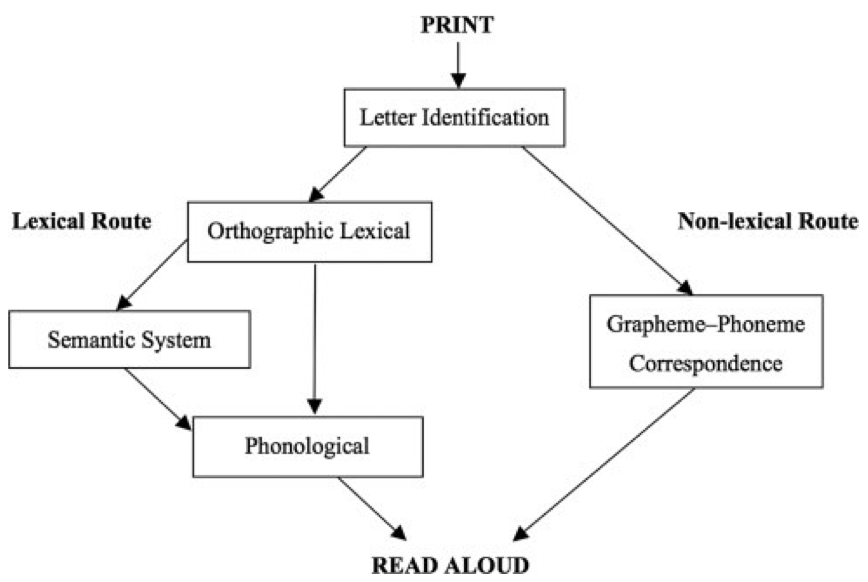
Dual Route Model of Reading
according to this model, reading can be achieved by either the lexical route or the sublexical route
orthographic or lexical or direct route
written word is recognized as visual word form
non-lexical or indirect route
graphemes (letters) converted to phonemes
recognized as auditory word form
2 Forms of Dyslexia (acquired)
surface dyslexia
over-regularize pronunciation
ex: “heed“ for head; pretty and bowl (rhyme with jetty and howl)
rely exclusively on non-lexical or indirect route
visual processing problem
deep or phonological dyslexia
unable to read pseudowords, no problem with complex words
rely exclusively on orthographic or direct route
Anomia
difficulty finding words
Alexia without Agraphia
can write, CAN’T READ
Visual word form area
located in LH
superior and posterior to Fusiform Face Area (FFA)
Great Ape language abilities and limitations
Apes lack complex grammar capabilities
Chimps, gorillas lack the vocal cords to produce human speech, but they can learn Sign Language
Washoe, Nim Chimpsky (chimp)
132 ASL signs
grammar: 2-word utterance level
Kanzi the Bonobo
used computer keyboard and lexigrams to communicate, also knew some ASL
200 productive, 500 perceptive words
communication between 2, but pidgeons trained to do the same task
had 2.5 year old level language abilities
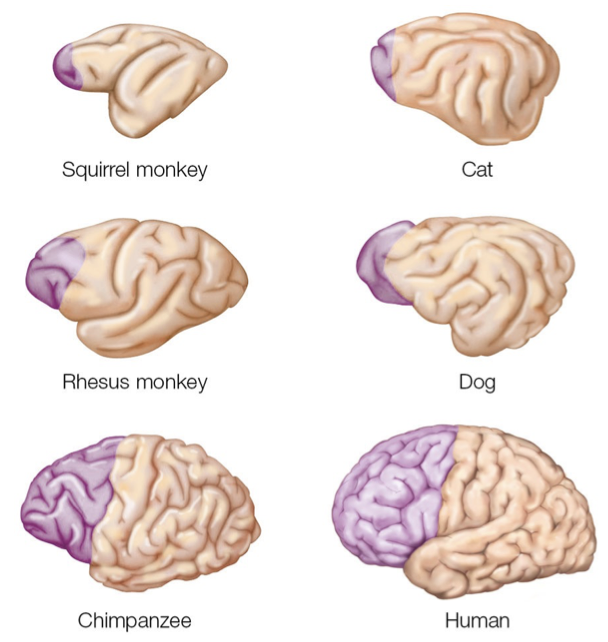
Expansion of Pre-frontal Cortex
figure 12.1: comparison of PFC in different species
purple region indicates the PFC in six mammalian species. Although the brains are not drawn to scale, the figure makes clear that the PFC spans a much larger percentage of the overall cortex in the chimpanzee and human
expansion of PFC in human brain is more pronounced in the white matter (axonal tracts) than in gray matter (cell bodies) → suggests that the cognitive capabilities that are uniquely human may be due to how our brains are connected rather than an increase in the number of neurons
Because the development of functional capabilities parallels phylogenetic trends, the frontal lobe’s expansion is related to the emergence of the complex cognitive capabilities that are especially pronounced in humans
Dual system model of cognition
system 1: “hot“
fast, parallel, automatic and context-dependent
linked to emotionally guided decisions
e.g. immediately available reward
“limbic“ circuitry
ventral striatum, OFC, vmPFC
OFC and vmPFC reflects value
system 2: “cool”
slow, serial, controlled and evidence-based
linked to more rational and deliberate decision processes
“executive function” circuitry [latPFC, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC), posterior parietal
cortex (PPC)]
LPFC reflects self-control
see Dan Kahneman’s “Thinking fast and slow“
2011 popular science book by psychologist Daniel Kahneman. The book's main thesis is a differentiation between two modes of thought: "System 1" is fast, instinctive and emotional; "System 2" is slower, more deliberative, and more logical
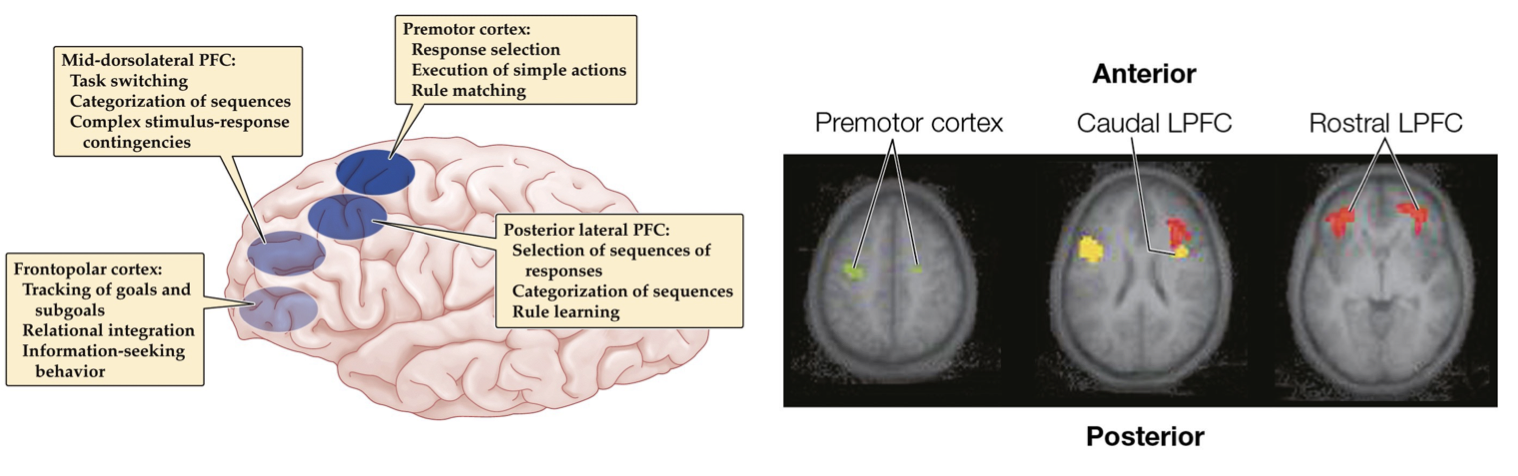
Cognitive neuro evidence for hierarchical cognitive control
increasing complexity from posterior to anterior in lateral PFC
green (ventral pre-motor): stimulus-response mapping
yellow (latPFC): stimulus context; manipulation
red (frontal pole): cognitive context; rules
Environmental dependency syndrome
failure to inhibit behaviors that are contextually inappropriate
utilization behavior: grabbing objects in view and starting an appropriate behavior at an inappropriate time
Task switching***
Wisconsin card sorting task = test of rule learning and task switching
Match cards based on one of 3 rules (Color, Shape, Number), but not explicitly told which rule applies, only feedback is “correct” or “incorrect,” and the rule is changed without any warning
“cognitive set“ = rules and key information held in working memory that support performance of a particular task
observes how fast can subject switch rules and REVEALS dysexecutive symptoms
latPFC patients perseverate (get stuck on a topic or idea)
rule switching in WCST involves inferior frontal sulcus
Frontal lobe patient deficits
Patients with frontal lobe lesions have difficulty executing a plan and may exhibit stimulus-driven behavior
Deficits in cognitive control are found in numerous psychiatric disorders, as well as when mental health is compromised by situational factors such as stress or loneliness
Dysexecutive syndrome
results from Frontal Lobe damage
lateral PFC damage
deficits in planning, project completion, attention span
Disinhibition syndrome
results from Frontal Lobe damage
medial PFC damage
constant movements
socially inappropriate aka “no filter“
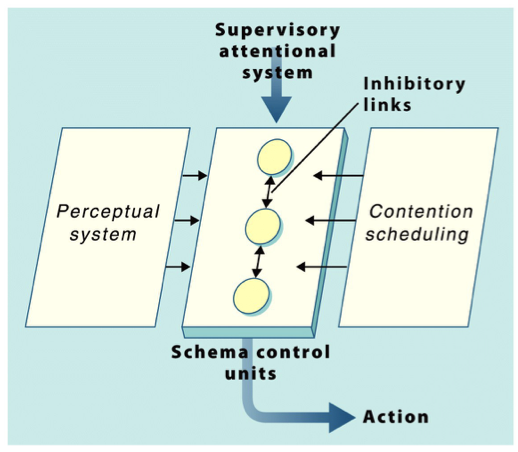
Supervisory Attentional System
aka Norman & Shallice Model of Response Selection
a psychological model of cognitive control, outlining the conditions under which the selection of an action might require the operation of a high-level control system
situation examples: planning/decision-making is required; responses are novel/not well-learned; situation is difficult or dangerous
Perceptual system is able to directly activate Action Schema
2 types of inhibitory control
contention scheduling
inhibition between competing Action Schema to focus on one at a time
involves the allocation of cognitive resources to competing processes or goals. When multiple tasks or goals demand attention simultaneously, contention scheduling determines which processes receive priority
ex: driving and get to a red light - slam on break (priority)
supervisory attentional system
provide flexible top-down control of goals
override perceptual and schema biases
higher-level cognitive control mechanism responsible for monitoring, coordinating, and regulating routine processes. The SAS is engaged in situations that are novel, complex, or require conscious decision-making
ex: using your GPS in a car, choosing the route, paying attention to the road, not missing turns
Error-related Negativity (ERN)
hypothesized to originate in anterior cingulate
anterior cingulate responds with errors, but also activated with other forms of monitoring
When people make an incorrect response, a large evoked response sweeps over the prefrontal cortex just after the movement is initiated. This signal, referred to as the error-related negativity (ERN) when time locked to the response, and the feedback related negativity (FRN) when time-locked to feedback, has been localized to the anterior cingulate
Rule switching and pre-frontal cortex***
Rule switching in WCST involves inferior frontal sulcus
*add more?
Inhibitory control of action
ACC next to region with similar functions: Pre-supplementary Motor Area
more motor-decision process than cognitive decision
suggests stop signal (our inhibitory control) in “Go/No Go“ task strongly activated by Right Inferior Prefrontal Cortex
DTI tract-tracing: Inferior frontal cortex connects with Subthalamic nucleus of Basal Ganglia and Pre-supplementary Motor Area
Stroop effect
task is to say the color of the word asap, hard and slower to complete because the letters spell out out the name of a different color - incongruent condition
main idea: word reading is “automatic“ and can interfere (or aid) the color-naming task, which is more novel/less practiced
interactions between medial and lateral PFC
Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) function
major brain region that supports executive attention and control
apart of Medial Frontal lobe
holds contents of working memory → word meanings and visual orienting and visual features
ACC-LPFC interactions
Stroop effects shows interactions between medial and lateral PFC
LPFC doesn’t show diff between congruent and incongruent conditions, but ACC does show Stroop Effect
ACC activity on one trial for Stroop effect predicts LPFC activity on next trial
Wisconsin card sorting task
Wisconsin card sorting task = test of rule learning and task switching
Match cards based on one of 3 rules (Color, Shape, Number), but not explicitly told which rule applies, only feedback is “correct” or “incorrect,” and the rule is changed without any warning
“cognitive set“ = rules and key information held in working memory that support performance of a particular task
observes how fast can subject switch rules and REVEALS dysexecutive symptoms
latPFC patients perseverate (get stuck on a topic or idea)
rule switching in WCST involves inferior frontal sulcus
dopamine system
provides a means for coding value
VTA/DA signals changes in info, not reward → signal to support learning
in reward circuitry and dopaminergic pathways, dopamine (DA)…:
serves as reward signal
is key to how we value things
DA neurons found in Substantia Nigra (SN), Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA)
Key structures:
VTA, Nucleus Accumbens (NAc) (aka Ventral Striatum)
role of dopamine in valuation/reward
DA serves as reward signal and is key to how we value things
VTA
VTA plays key role in reward evaluation
projects to NAc, medial PFC (mPFC), amygdala, and hippocampus
subjective biases in value***
factors that contribute to subjective value representation
payoff
probability
effort or cost
context
preference
because of such variation, people are inconsistent in their decision-making behavior
temporal discounting
the observation that people tend to value immediate outcomes more highly than delayed outcomes, and that the subjective value of a reward decreases as the time to its receipt increases
increased valuation for immediately available rewards
reflected in activation of ventral striatum, posterior cingulate cortex and mPFC
tracks subjective value of rewards
getting same reward sooner has greater subjective value (and greater real value)
OFC damage impairs temporal discounting
so their "value over time" decays exponentially quicker than a person with a normally functioning OFC
Expected value
describes the average reward of a probabilistic process
= probability * utility = sum of probability-utility pairings for each possible outcome
utility can be positive or negative
Ventral striatum/Nucleus accumbens
one of the key structures + VTA for reward circuitry and Dopaminergic pathways
Ventral medial pre-frontal cortex and value representations
vmPFC brain activity tracks the subjective value we individually apply on items
Marshmallow experiment - original and 40 year follow-up neuroimaging
delayed gratification experiment
original premise:
kids were handed a marshmallow, told to wait for 10-15 min and they would get a bigger marshmallow
little kids generally showed less control and munched on the small marshmallow, older kids usually waited
40 year follow-up
neuroimaging of these children as adults
realized kids who delayed and won bigger marshmallow generally scored better life outcomes (better SAT scores, higher academic success)
^not so simple, other factors could impact their self-control
ex., kids could’ve been distrustful of adult figures
low delayers (hot circuitry): more activity in Ventral Striatum
high delayers (cool circuitry): more activitiy in RH inferior Frontal Cortex
Reward prediction error
midbrain dopaminergic neurons in response to expected and omitted rewards
DA release increases when unexpected reward occurs
no change in DA when reward matches expectations (aka baseline DA remains)
decrease in DA when reward is omitted
DA neurons don’t code reward, but rather code changes in information/value supporting learning of the changes
DA neurons in VTA and substantia nigra (SNc) appear to mimic error function (RPE)
Frontal lobe damage and value assessments***
2 types of frontal lobe damage
dysexecutive syndrome (lateral PFC)
disinhibition syndrome (medial PFC)
value-based decisions
ventral striatum codes motivation/value
vmPFC/OFC codes SUBJECTIVE value
Default Brain Network vs. Default mode network
Default Brain Network
when directing attention outward, higher brain activity
areas activated by social cognition overlap with many regions of Default Mode Network
activated under different social cognition tasks
suggests competition of neural resources between directing attention to social factors vs. external stimuli without social components
Default mode network
decreased activation when concentrated on a task
increased activity when daydreaming
Theory of Mind
the cognitive abilities to represent information in minds of others, distinguishing them from what we know
in other words, our cognitive capacity to understand mental states of others
term that describes psychological property, NOT A THEORY OF THE MIND
Mentalization
broader term that encompasses Theory of Mind and includes thinking about one’s self
thinking about minds of others and one’s own mind
ability to perceive and interpret human behavior in terms of intentional mental states
like goals, desires, feelings, beliefs
can be seen as form of imaginative mental activity
Autism can be seen as failure to develop mentalization abilities
Mindblindness
inability to understand social goals, intents, beliefs of others
Ethical decision making
famous moral dilemma
runaway train
flip a switch to save 5, but one dies as a consequence
OR push one to death in order to save 5 other lives
False belief task
famous example is Sally-Anne task
Sally places her marble in the basket → Sally exits and Anne transfers Sally’s marble to a drawer → Sally re-enters → where does Sally look for the marble?
around age 4, normal kids develop this ability to understand that other minds might have different info/beliefs of their own
Social cognition and Default Network
social cognitive functions like Theory of Mind and Ethical Decision Making activate core regions of the Brain default network
medial prefrontal cortex
posterior cingulate cortex
retrosplenial cortex
temporo-parietal junction (TPJ)/angular gyrus
anterior superior temporal sulcus
this closely mirrors “default“ network that shows high activation at rest
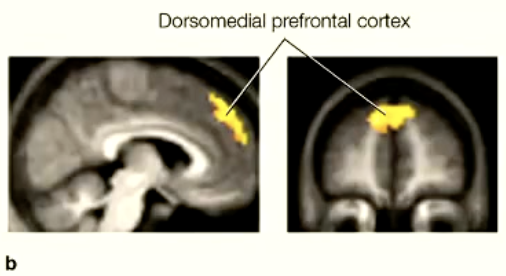
Personality assessments
dorsomedial PFC activates when assessing a person’s personality/forming an impression
Phineas gage - damage, deficits
damage to left OFC and medial PFC
“Gage is no longer Gage“
stopped observing social conventions
behaves unethically
made poor personal decisions
deficits result from specific brain lesion, not general reaction to accident
Role of right Temporal Parietal Junction (TPJ)
involved in self-processing and integrating multi-sensory body-related information, which plays a key role in the feeling of embodiment
Orbitofrontal damage and social cognition
self-perception is diminished in real-time, but not in video playback
social rules are understood, but not applied to filter own behavior
Self-referential processing
thinking about things in relation to ourselves
when we process info related to ourselves, we obtain a depth of processing advantage → stronger memories
Implicit bias
unconscious attribution of particular qualities (stereotypes) to members of certain social groups
implicit association test
caucasian vs. African American faces
positive or negative words/traits
logic is similar to Stroop test (Reaction Time differences)
more explicit tests exist, but most people won’t explicitly give biased answer
Implicit Association test and brain activation
race association: African Americans vs. European Americans
reaction time measures reveal implicit bias among Caucasians toward African Americans
results generalize to other in-group/out-group
multiple variants of these tests
race, gender-career, age, religion, etc
Amygdala activity correlates with IAT bias
fast, automatic, emotional response to out-group
dorsolateral PFC
people with greater implicit bias tend to employ cognitive control over responses, engaging DLPFC
those who well-regulate implicit bias exhibit larger ERN
Dorsomedial PFC and social cognition
Activity in the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) increases during tasks that involve self-referential mental activity or self-focused attention and decreases during tasks that involve externally focused attention
Amygdala and social cognition
uses the face to make social judgments
another region involved in person perception
signaled when value expectation is violated and to form new associative perceptions that may flexibly change behavior
Mirror neurons
activated when observing another’s action and when one is performing it oneself
Mirror neuron network
every linked brain region that responds when mirror neurons are invoked
premotor cortex and inferior parietal cortex
also includes:
rostral inferior parietal lobule (rIPL), dorsal premotor cortex (dPMC), medial fr ontal cortex (MFC), ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (vlPFC), and anterior cingulate gyrus (ACG)
Empathy and emotion sharing
empathy = feeling others pain
mirror neurons in premotor cortex, insula cortex, ad anterior cingulate cortex (ACG) activate for our pain
Disgust processing
insula activates from perception of disgust
Emotion sharing
brain regions that mediate emotion sharing (pain)
anterior insula
secondary somatosensory cortex
STS (biological perception)
TPJ, MFC (theory of mind/simulations)
ACG
conflict monitoring
Neural substrates associated with: face processing, biological motion
Superior temporal sulcus (STS) = perception of biological motion
face processing
core system (visual analysis) →
STS = changeable aspects of faces: perception of eye gaze, expression, lip movement
inferior occipital gyri = early perception of facial features
lateral fusiform gyrus/inferotemporal cortex = invariant aspects of faces: perception of unique identity
→ extended system (further processing in concert with other neural systems)
intraparietal sulcus = spatially directed attention
auditory complex = prelexical speech perception
amygdala, insula, limbic system = emotion
anterior temporal lobe = personal identity, name and biographical information