Unit 6: Cities and Urban Land-Use Patterns and Processes Jackie’s version!!!!!!!!!
1/72
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
central place theory
all market areas are focused on a central settlement that is a place of exchange and service provision
threshold
the minimum number of people required to support a business
range
the maximum distance that people are willing to travel to gain access to a service
agglomeration
exists when similar business activities are found in a local cluster
resource nodes
towns and cities that were founded due to access to natural resources
land invasion
squatters that generally settle a new area overnight with a large number of families to avoid retributions from landowners and local police
land tenure
the legal right or title to the land upon which they build their homes
micro districts
zones of uniform housing that provide worker housing near job sites
suburbanization
the growth and spatial reorganization of contemporary city
suburban sprawl
the expansion of housing, transportation, and commercial development to undeveloped land on the urban periphery
counterurbanization
the movement of inner-city or suburban residents to rural areas to escape the congestion, crime, pollution, and other negative aspects of the urban landscape
colonial cities
cities with origins as centers of colonial trade or administration are classified together
fall-line cities
the ports that lay upstream on coastal rivers at the point where navigation was no longer possible by ocean-going ships
fall-line
where a river’s tidal estuary transitions to an upland stream at the first set of river falls
medieval cities
urban centers that predate the European Renaissance, roughly 1400 C.E.
gateway cities
places where immigrants make their way into a country
entrepôt
a port city in which goods are shipped in at one price and shipped out to other port locations at a higher price, resulting in profitable trade
megacity
a metropolitan area with more than 10 million people
megalopolis
the merging of the urbanized areas of two or more cities, generally through suburban growth and expansion
world city
signifies a metropolitan area as a global center for finance, trade, and commerce
primate city
when the largest city in a country has at least twice the population of the country’s next largest city
rank-size rule
a country’s second largest city is half the size of its largest city; the third-largest city is one-third the size of the largest city; and so on, such that the eighth largest city is one-eighth the size of the largest city
de facto segregation
where no law requiring ethnic or racial segregation exists, yet they nonetheless remain zones of separation
redlining
designating neighborhoods on company maps where home mortgage and insurance applications would be automatically denied
restrictive covenants
means of racial discrimination through the real estate system
gentrification
the economic reinvestment in existing real estate by high income residents or professional developers by building in abandoned, blighted and or industrial areas for a low cost and renovate and restore property to flip for a higher price than that they paid for it.
bond levies
raise money by increasing property taxes
brownfield remediation
a process in which hazardous contaminants are removed or sealed off from former industrial s
Metacities
Metropolitan areas with populations of more than 20 million people
Site
Climate, landforms, availability of water, soil fertility, and other physical factors. ex;Cincinnati is on the north bank of the Ohio River and is a valley surrounded by hills with a temperate climate and fertile soil.
Situation
Connections between sites, the relative location often dictates the function of the city. Example: Cincinnati emerged as a river port after 1811. River commerce reached its height in 1852, stimulating steamboat building and industry, specifically pork.
suburbanization
The process of people moving, usually from cities, to residential areas on the outskirts of cities. They form communities that are connected to the city for jobs and services but are decentralized. Less densely populated and less ethnically diverse than cities and develop due to advancements in transportation
Gravity model
Model that illustrates the spatial relationship/amount of interaction between locations of different sizes, flows of people, trade, traffic, communication, etc. Considering the distance between two locations and their relative sizes, larger cities interact more often with other large cities, rather than small cities, small cities are drawn to the influence and impact of large cities.
central place model
Model that illustrates the hierarchical spatial patterns/order of cities and settlements. Based on economic functions/consumer behavior, the “central place” is the large city that provides the most goods and services for the surrounding areas. Smaller settlements (towns, villages, hamlets) are organized around the “central place.”
urban sprawl
the expansion of cities and urban areas into surrounding rural or undeveloped land. It is characterized by low-density development, with a proliferation of single-family homes, strip malls, and other automobile-oriented development.
edge city
Community located on the outskirts of a larger city with commercial centers, office space, retail complexes, and amenities typically found in an urban center. Not usually residential, mostly economic activities and are newly developed in the past 30 years.
bomburbs
Suburb that has grown rapidly into a large and sprawling city with more than 100,000 residents. Typically made up of planned communities that have begun to merge together. “Feels” suburban, but more closely resembles an urban city in population
exurbs
Community on the outside edge of traditional suburbs, “exurban.” Function like a suburb, but more rural and less connected to the central city core. Low-density residential communities, may include wealthy estates or small rural towns, and have little diversity
globalization
The expansion of economic, political, and cultural processes to the point that they become global in scale and impact.
squatter settlements/shantytowns
A household that cannot provide one of the following basic living characteristics. The people living in those areas do not have legal rights to the land upon which they are built; therefore, they are living there illegally.
redevelopment
New construction on a site that has pre-existing uses.
zoning
A regulation about what type of development or land use can occur in a specific location.
high density housing
Ex:High-rise apartments
metropolitan area
City and surrounding areas
infilling
Redevelopment of vacant land to improve the surrounding area.
ecological footprint
Uses land as currency to measure how fast we consume resources and generate waste compared to how fast nature can absorb our waste and generate new resources.
walkability
Measure of how safe and easy it is to walk in a city.
new urbanism
Seeks to encourage local community development and sustainable growth in an urban area, argue for greater accessibility for pedestrians in cities and a reduced dependency on cars and highways. Tries to create sustainable areas by designing to be more efficient and environmentally friendly.
transportation-oriented development
means integrated urban places designed to bring people, activities, buildings, and public space together, with easy walking and cycling connection between them and near-excellent transit service to the rest of the city.
greenbelts
Ring of parks or agricultural land to prevent sprawl
mixed-use development
cities/plained areas with a use of residential, commercial, office spaces ,retail, educational or industrial uses
brownfields
abandoned and polluted industrial site, a property that is potentially contaminated by hazardous substances , pollutants, or contaminants located in central cities and suburbs.
redlining
Housing discrimination maintained by banks - starting in the 1930s, refusal to grant home loans in certain areas because of the ethnic or racial composition.
disamenity zone
Locations that are typically steep, mountainous, and dangerous terrain that are not connected to city services.
slow-growth cities
places that try to decrease the speed at which outward growth occurs.
smart-growth policies
is an overall approach of development and conservation strategies that can help protect our health and natural environment and make our communities more attractive, economically stronger, sustainable, socially diverse, and resilient to climate change, promotes limiting urban sprawl and saving natural areas and usable farmland.
blockbusting
Housing discrimination maintained by the real estate industry , white families were encouraged to rapidly sell when African-American families moved into neighborhoods.
urban growth boundaries
Separates urban land from rural land by limiting how far a city can grow, simplest form, mandating that the area inside the boundary be used for urban development and the area outside be preserved in its natural state or used for agriculture.
environmental injustice
Communities of color and the poor are more likely to be exposed to environmental burdens such as air and water pollution.
apartheid
the physical separation of different races into separate geographic areas
urban renewal
Programing funded by federal government grants after ww2 intended to redevelop and modernize blighted, abandoned, and or industrial urban areas.
World Cities
Large cities that exert global economic, cultural, and political influence and make up a network of economic, social, and information flows.ex:London, New York, Tokyo, Paris, Singapore, Amsterdam, Berlin, Seoul, Hong Kong, Shanghai.
Food Deserts
Location where residents’ access to affordable, healthy food options (especially fresh fruits and vegetables) is restricted or nonexistent due to the absence of grocery stores within convenient traveling distance.
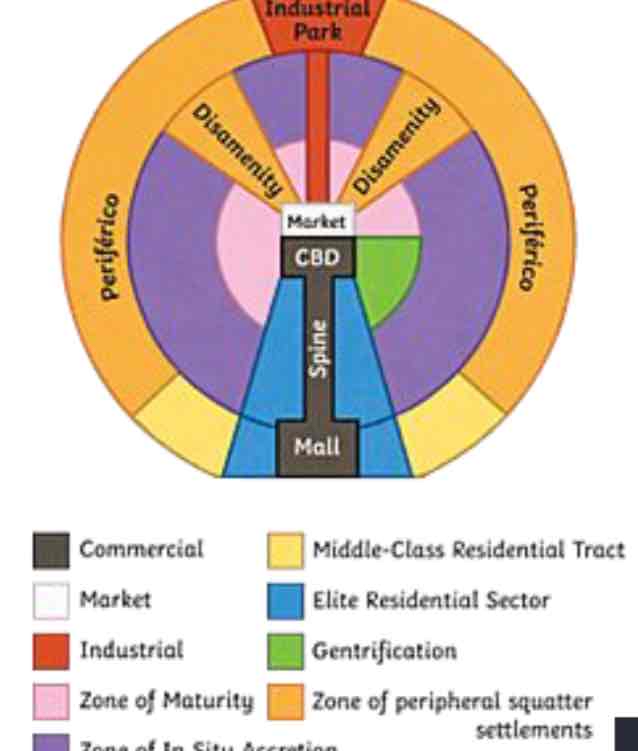
latin american model
Characteristized by the “spine” that runs from the modernized CBD in the center, through wealthy housing and connects to a secondary urban center called the mall. Spine: High-end commercial sector. Market: Traditional market. As distance from the CBD increases, housing becomes less expensive due to a lack of critical infrastructure available in those areas.
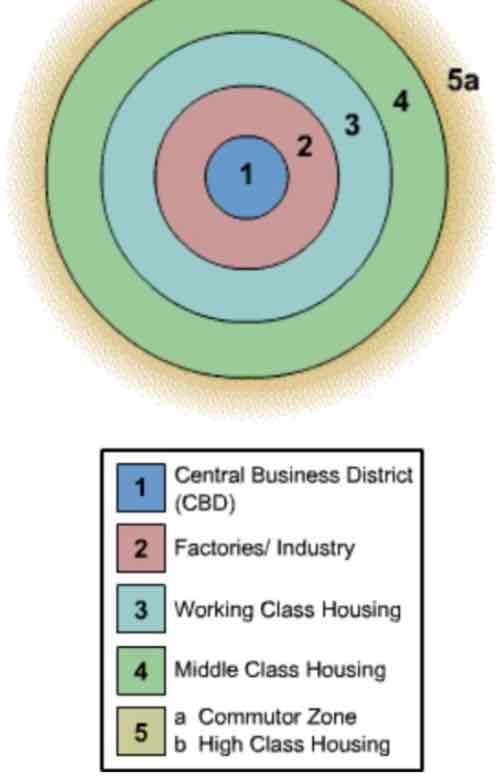
burgess concentric zone
Ring #1. Bid-Rent Theory -> The CBD is the location of major economic activity and the most expensive land.
Ring #2: Zone of Transition. Factories and industry with a mix of low income apartments.
Ring #3. Another ring of low income housing. High population density, poor living conditions.
Rings #4 & 5.As distance from the CBD increases, the cost of land is less expensive -> Larger plots of land -> low population density -> single family homes.
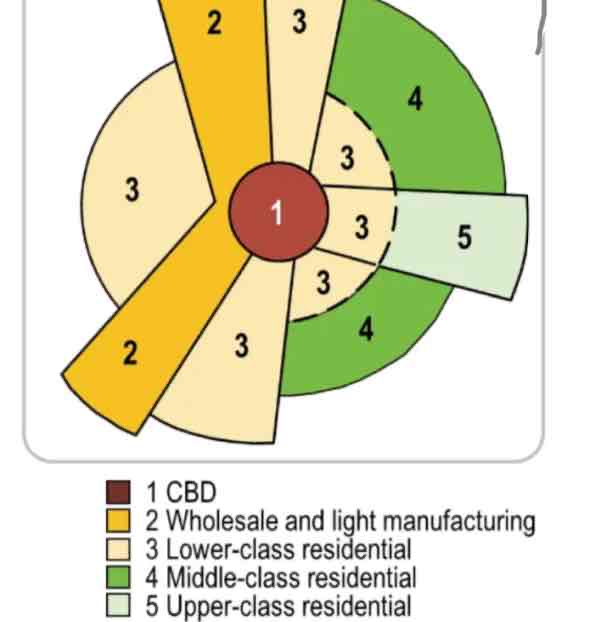
hoyt sector
Use of sectors/wedges to classify each type of land use pattern.Sectors develop along transportation routes. Low income housing develops surrounding industry and major transportation routes. Middle and high-income housing develops further from the city center and manufacturing so as not to experience heavy traffic, pollution, etc.
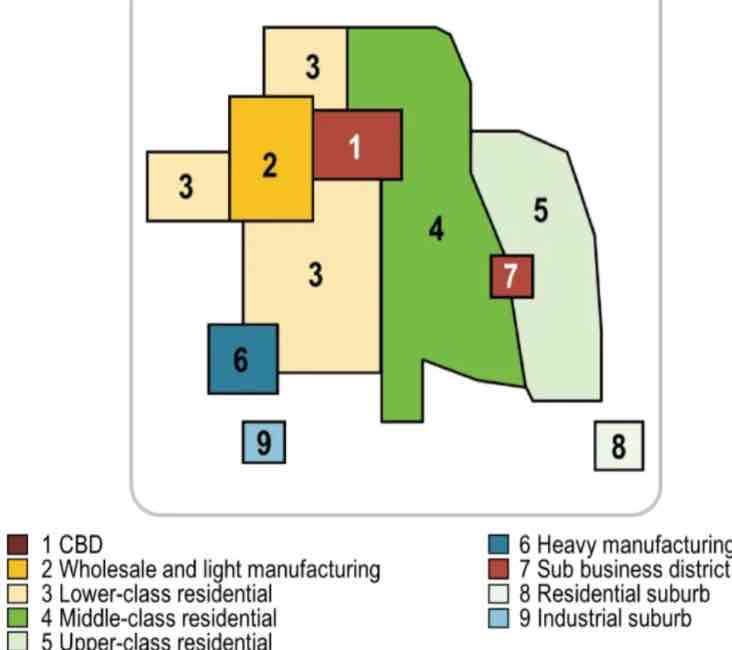
harris and ullman multiple nuclei
Cities develop around multiple focal points and build outwards to create a functional region. Site and situational factors influence land-use patterns. CBD remains an important location, however there are other, smaller business districts in various locations. Manufacturing & Industry are located near transportation routes for easier shipping. Similar businesses locate near each other to take advantage of labor pools, suppliers and communication. Middle and high-income housing develops further from the city center and industry so as not to experience heavy traffic, pollution, etc.
Africa city model
Characteristized by 3 CBDs, and reflects the influence of colonialism throughout the continent. Traditional CBD: Small shops, narrow streets. Colonial CBD: Big streets, straight, often in grid-like patterns, with government buildings with European architectural styles. Sense of place! Market Zone: Traditional open-air markets. Mostly outdated, but the 3 CBDs can still be seen on the cultural landscape today in some African countries.
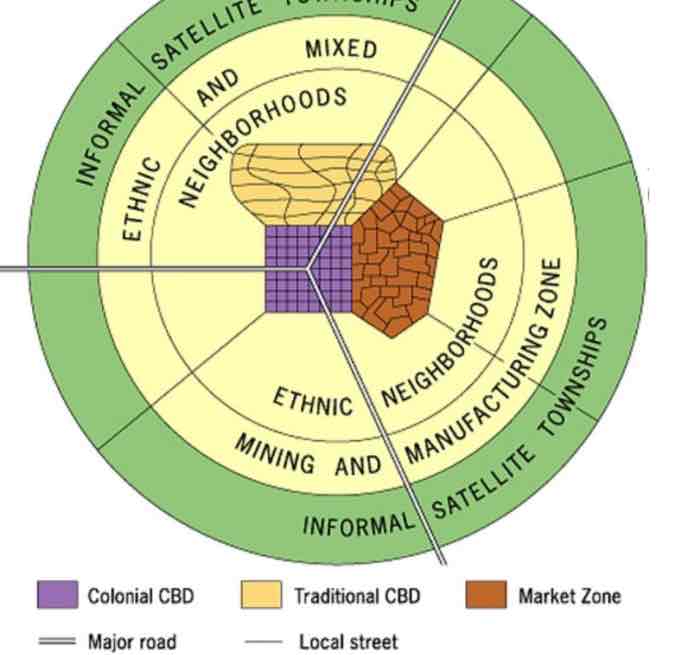
southeast asian
Characteristized by a port zone, which was the center of commerce in colonial SE Asia - export oriented, so no CBD. History of Chinese immigrants throughout SE Asia - on the model, there is a secondary commercial zone for Chinese business called the Alien commercial zone. History of colonialism results in a Western commercial zone in which merchants from European countries are located. Market gardening zone is distinctive due to the climate and agricultural land use in SE Asian locations.
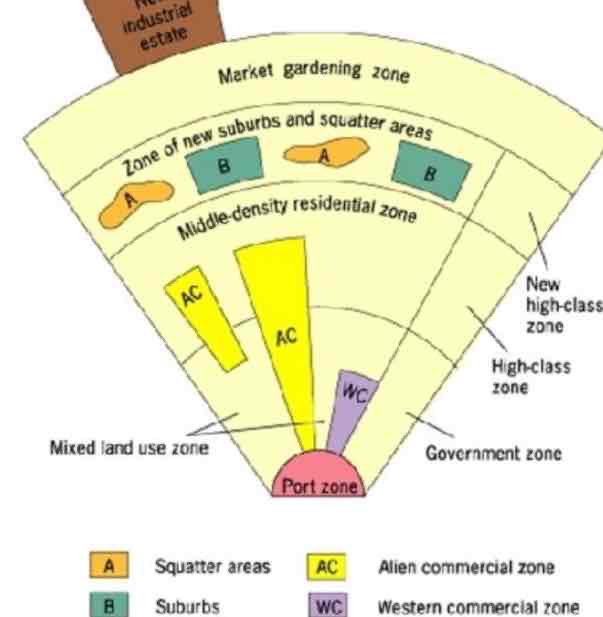
galactic Model
Most modern; developed in the 1980s. Focuses on the decentralization and suburbanization of urban environments. As suburbanization and the ownership of cars increased starting in the 1950s, urban areas developed differently than in the past. Includes edge cities which are like mini-CBDs, which include shopping, entertainment, and offices and are typically located along transportation routes.
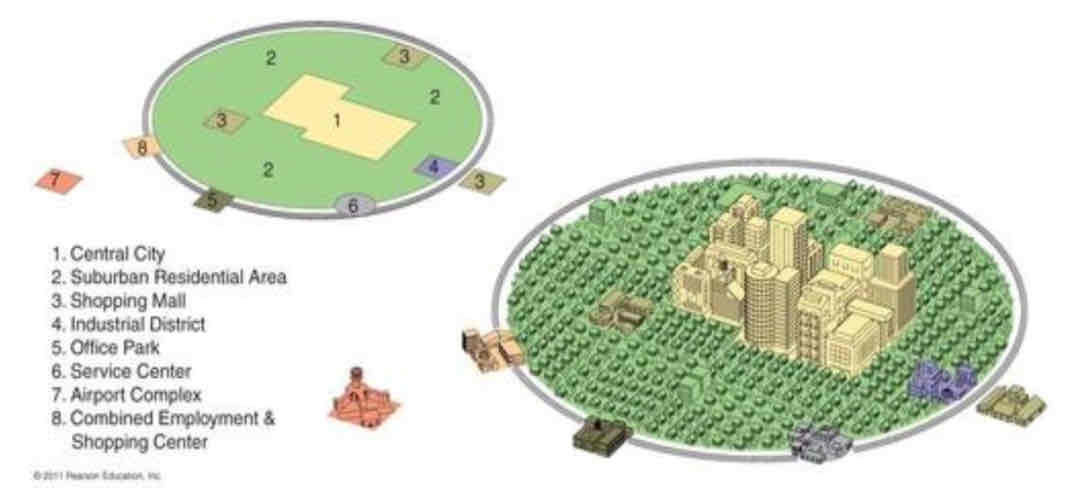
Qualitative
Data that involves descriptive depictions or characteristics of a research topic - often based on people’s perceptions or opinions. EX:case studies
Quantitative
Data that involves numbers and statistics - can be measured.
examples: census data
squatters
people who settle on land that they don’t own